Medication Management of Obstructive Airway Disease
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
per the GINA guidelines, what are goals of asthma therapy?
GINA: global initiative for asthma
1) symptom control: achieve good control of symptoms and maintain normal activity levels. no sleep disturbance due to asthma and unimpaired physical activity
2) risk reduction: minimize the risk of asthma-related death, exacerbations, persistent airflow limitation and side effects. no exacerbations, stable personal best lung function, no systemic corticosteroids, no med side effects
per the GOLD guidelines, what are goals of COPD treatment?
GOLD: global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease
1) reduce symptoms
2) reduce frequency and severity of exacerbations
3) improve exercise tolerance and health status
what are the MOAs for inhaled corticosteroids
suppress production of early phase and late phase inflammatory cytokines
what are the MOAs for short acting beta 2 agonists and long acting beta 2 agonists (SABA, LABA)
activate beta 2 receptors in the airways, causing relaxation and bronchodilation
what are the MOAs for short acting muscarinic antagonists (SAMAs)
block muscarinic-3 (M3) receptors in the airways, causing bronchodilation; may also block neuronal M2 receptors, which normally inhibit acetylcholine-mediated bronchoconstriction
what are the MOAs for long acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMAs)
block M3 receptors in the airways, causing bronchodilation; little effect on M2 receptors
what are common side effects/ADRs of inhaled corticosteroids
oral fungal infection, URTIs (upper respiratory tract infections), voice hoarseness
what are ADRs for SABA/LABAs
excitement (younger children), nervousness, tremor, tachycardia, URTIs
what are ADRs for SAMA/LAMAs
dry mouth, bronchitis, tachycardia
per GINA guidelines, what is first-line therapy for children and for adults with asthma
for children: as needed (prn) SABA + lose dose ICS (inhaled corticosteroid)
for adults: prn low dose ICS-formoterol combination (formoterol is a LABA)
in general, first line therapy for asthma is?
inhaled corticosteroids; anti-inflammatory agents
what would be an inhaled product likely to be used by an adult with moderate asthma
inhaled corticosteroids and LABAs (ICS-formoterol also known as symbicort)
ICS examples: beclomethasome, budesonide, ciclesonide, fluticasone, proprionate, mometasone
LABA examples: arformoterol, formoterol, olodaterol, salmeterol
what medication class and route would most likely be used in an asthma exacerbation
1) repeated doses of SABA
2) early oral corticosteroids
3) controlled flow O2 if necessary to maintain O2 saturation at 93-95%
per GOLD guidelines, what therapies are recommended for mild, moderate, and severe COPD
mild: a bronchodilator (includes inhaled SABA, LABA, SAMA, LAMA)
moderate: LABA and LAMA
severe: LABA and LAMA, but consider adding ICS (anti-inflammatory agent) to tx if blood eosinophil count >/= 300

what medication class and route would most likely be used in a COPD exacerbation
1) initial tx: SABA +/- SAMA until symptom control, then return to baseline long acting therapy
2) systemic corticosteroids (IV is hospitalized, po (by mouth) otherwise) —> can improve lung function, reduce risk of relapse, and decrease duration of hospitalization; max 5-7 days of therapy
3) respiratory abx (macrolides, fluoroquinolones) —> can shorten recovery time and reduce risk of early relapse and tx failure (IV if hospitalized, po otherwise)
4) non-invasive ventilation (face or nasal mask with ventilation pressure support)
which class of agents increase risk of developing an oral fungal infection?
all inhaled corticosteroid products
which products may promote caries development
1) most dry powder inhalers contain lactose as a filler —> deposited on teeth in the process of inhalation, lactose will promote caries
2) tiotropium can cause dry mouth (other LAMAs probably do too)
SABAs are the first line of therapy for ?
mild COPD; mild asthma along with ICS in children
what are example agents of SABAs
albuterol, levalbuterol
LABAs are the first line of therapy for?
COPD; for mild asthma along with ICS in adults/adolescents
SAMAs are the first line of therapy for?
mild COPD
what are example agents of SAMAs
ipratropium, glycopyrrolate
LAMAs are the first line of therapy for?
COPD
what are example agents of LAMAs
aclidinium, revefenacin, tiotropium, umeclidium
describe the GINA asthma tx principles
1) identity and mitigate triggers and aggravators
2) incorporate pt preferences and goals, train in guided self-management
3) use ICS-containing controller medication (children should always use ICS + SABA for prn symptoms —> called anti-inflammatory reliever or AIR-only; low dose ICS provides adequate benefit for most patients —> ICS-formoterol is called maintenance and reliever therapy (MART)
describe the GOLD principles of COPD tx
1) smoking cessation is key
2) pharmacotherapy can reduce symptoms and exacerbations (data is strongest for LABAs and LAMAs; combination of these 2 are more effective than either alone; routine ICS alone does not modify long term outcomes so usually used in combo with bronchodilators)
3) COPD increases severity of respiratory tract infections (immunization lowers risk of morbidity for lower RTIs)
4) pulmonary rehab can improve symptoms and QOL
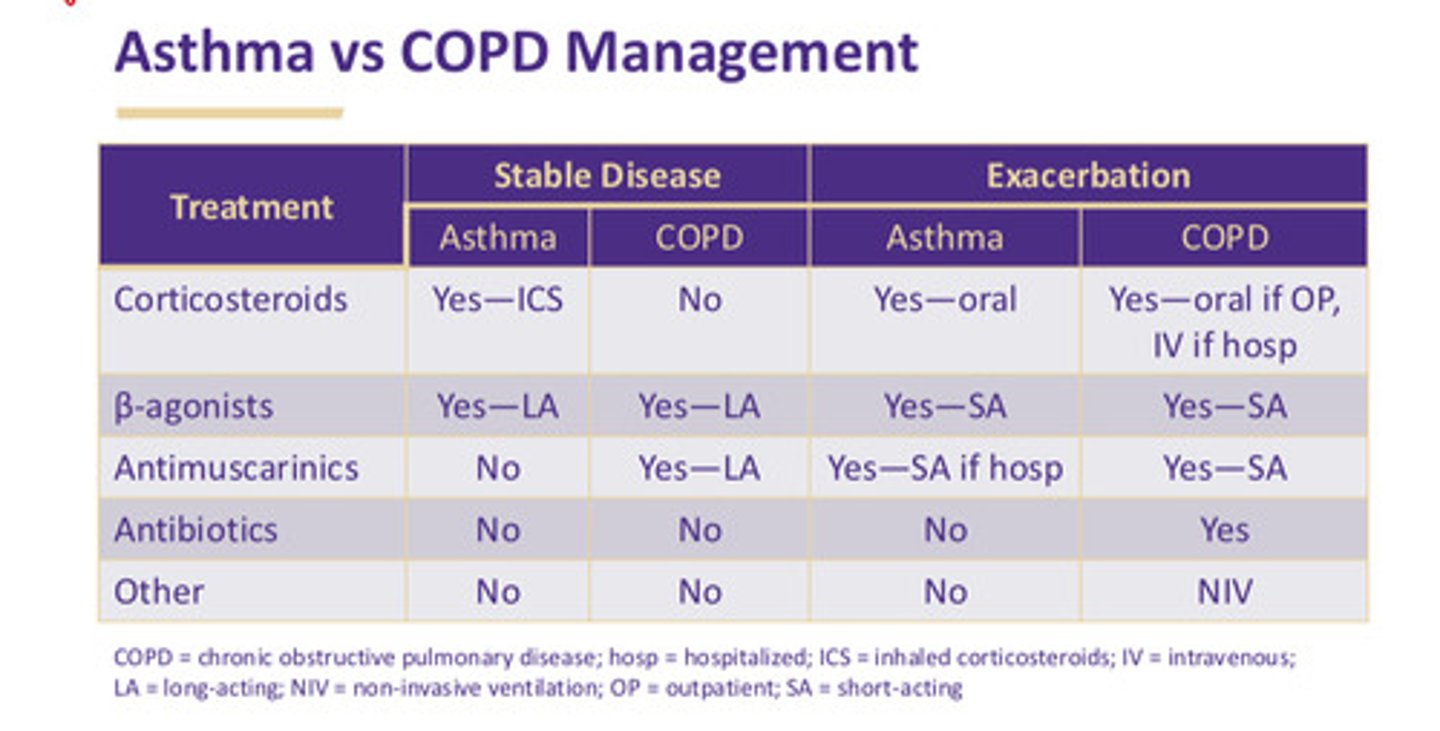
asthma vs COPD management table