Chapter 43: Behavior and Behavioral Ecology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what is behavior
Any action by an organism
Generally, a response to a stimulus (a piece of information gathered about the environment)
Everything an organism does & how it does it
- Muscular activities (e.g., movement, sound production )
- Secretion of scents
- Learning
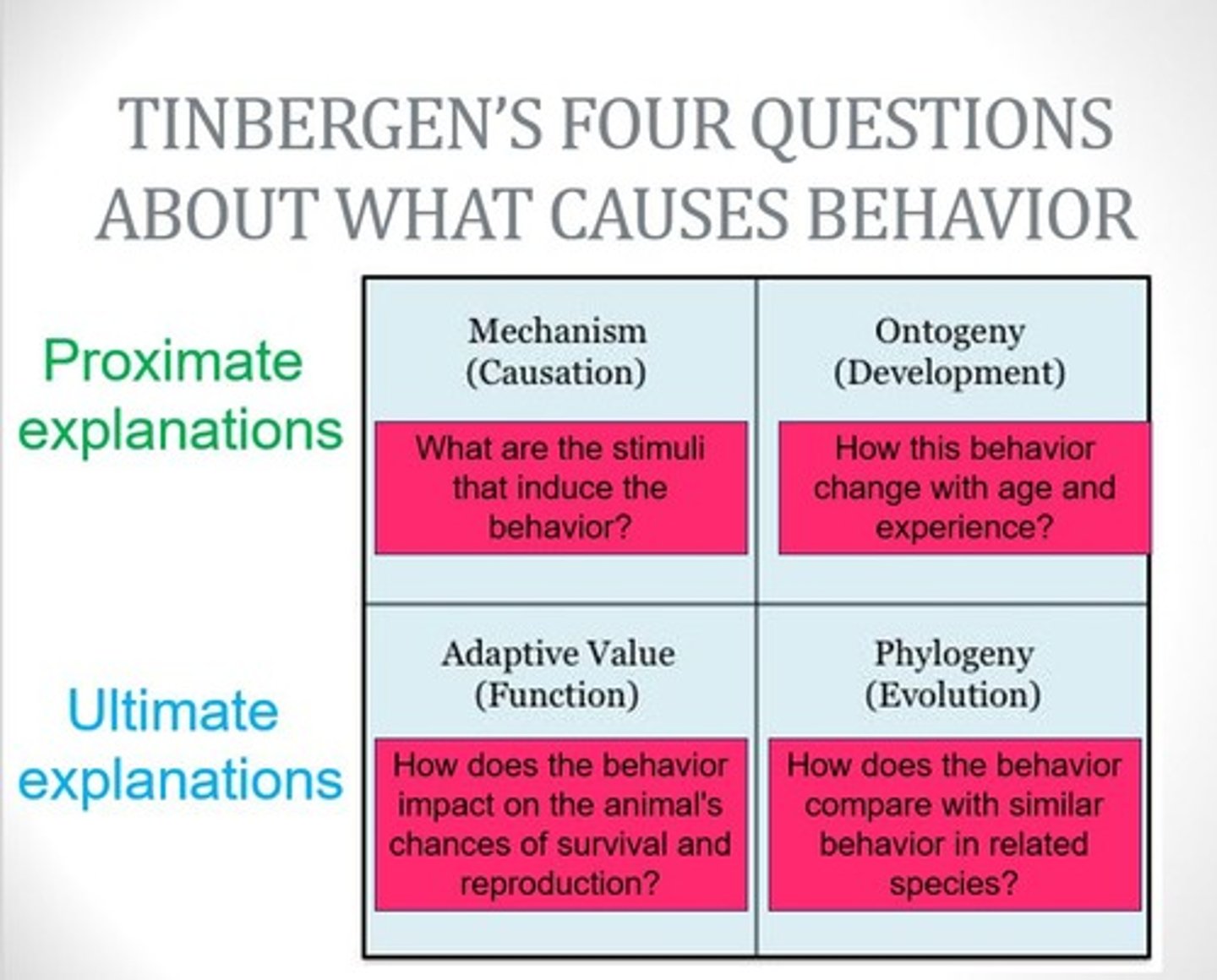
Tinbergen's 4 questions
1. causation
2. development
3. function
4. evolution
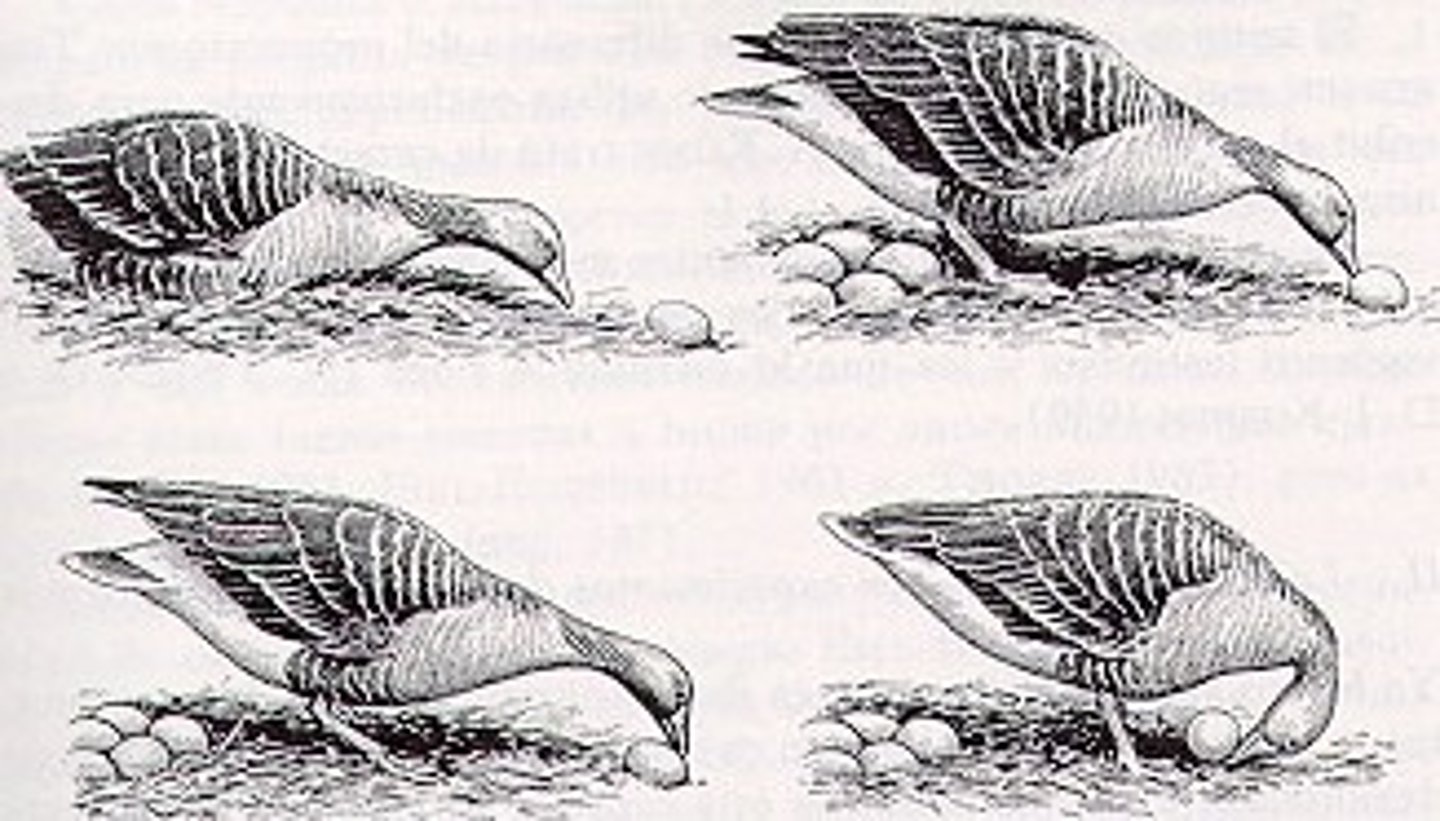
fixed action patterns
• A sequence of unlearned behaviors that is essentially unchangeable and invariant
• An "innate" behavior
• Generally, a behavior that is so important that all genetic variation has been lost
Imprinting
a combo of learning and genes, based on the timing of learning
- the process by which certain animals form attachments during a critical period very early in life
feature detection
The nervous system must process stimuli in order for a response to be carried out.
Stimulus recognition is often carried out by specialized sensory receptors that respond to important signals in the environment.
What else triggers behaviors
-detection of features of a signal
-sound patterns or portions of the pattern
-hormones and their derivatives
-patterns of behavior of a predator or competitor
-patterns of behavior of potential mates
-visual signals such as open mouths of chicks begging for food
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
kinesis
random, undirected movement
taxis
specific directional movement
navigating relies on:
- Sun orientation
- Landmarks
- GPS in the brain
- Olfactory signals
types of biological clocks
- Circadian clock
- Lunar clock
- Annual clock
migration
the long-distance movement of a population associated with the change of seasons/resources
communication
Any process in which a signal from one individual modifies the behavior of another individual
For communication to be completed, the signal must be:
1. sent
2. received
3. acted upon
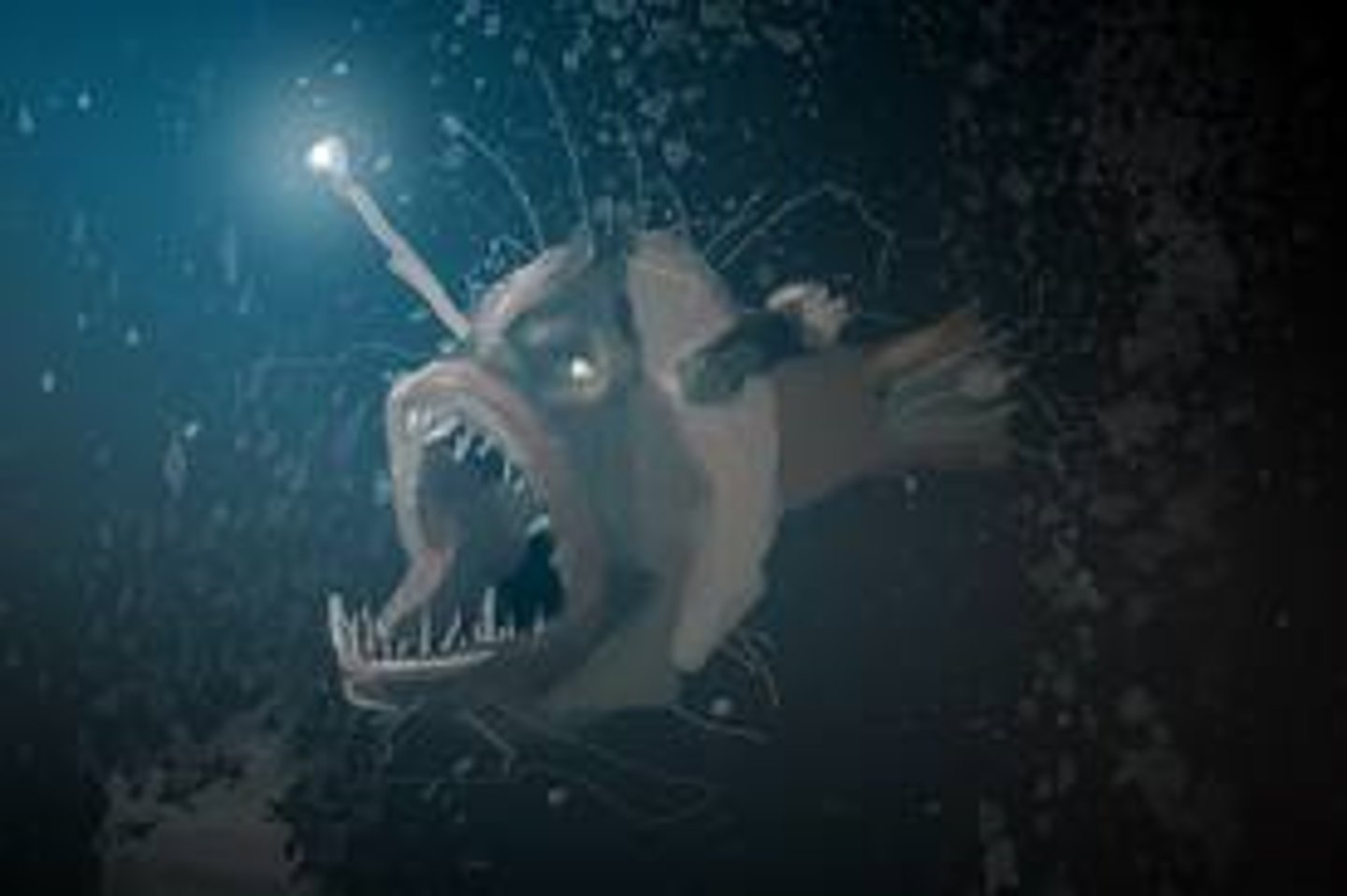
Dishonest Communication
"untrue" signal - lowers the fitness of either sender or receiver
- anglerfish using "lure" to attract prey

Altruistic behaviors
decrease the fitness of the organism exhibiting the behavior and increase the fitness of the recipient
- reciprocal altruism
kin selection
• Natural selection that favors altruistic behaviors directed at close relatives
• Because close relatives share many alleles, reproductive success of a close relative is almost as good as one's own reproductive success
• An organism can pass on its alleles not only by having offspring, but by helping close relatives have offspring
hamilton's rule
when C/B < r
C = cost to the altruistic party
B = fitness benefit to recipient of altuism
r = genetic relatedness
Optimal foraging theory
Views foraging behavior as a compromise between benefits of nutrition and costs of obtaining food.
• For birds that travel far, it is most efficient to catch more insects before returning to the nest
what affects mate choice
Females typically invest more energy in offspring
- Eggs take more energy than sperm to produce
- Females often must invest more time and resources in gestation and/or parenting
Thus, females are often pickier about mates
Females typically choose males who demonstrate that they can contribute good alleles and/or lots of resources to their offspring
intersexual selection
Selection whereby individuals of one sex (usually females) are choosy in selecting their mates from individuals of the other sex; also called mate choice.
intrasexual selection
A direct competition among individuals of one sex (usually the males in vertebrates) for mates of the opposite sex.
sexual dimorphism
Differences in physical characteristics between males and females of the same species.