Chapter 10 - Reaction Rates + Equilibrium
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
rate of reaction
how fast a reactant is used up
factors that affect reaction rates
-temperature
-concentration
-pressure
-surface area
-catalyst
increasing TEMPERATURE
-the particles gain more kinetic energy so more frequent collisions
-the particles move faster so more frequent collisions
so increases rate
increasing CONCENTRATION
more particles in a given volume so more frequent collisions so increases rate
increasing PRESSURE
less space between particles so molecules are closer together so more frequent collisions so increases rate
catalysts
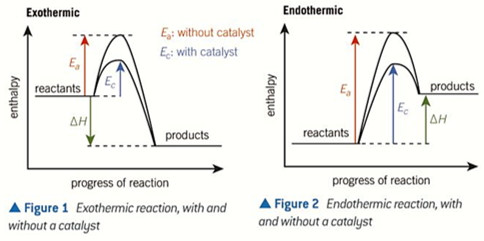
-lower the activation energy needed by providing an alternative reaction pathway
-so more particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more frequent collisions so increases rate
effects of catalyst on BOND ENTHALPY (draw)
.
types of catalyst -homogenous
has the same physical state as the reactants - forms an intermediate
examples:
-esters with sulfuric acid catalyst - all liquids
-ozone depletion with chlorine radical catalyst - all gases
types of catalyst -heterogenous
has a different physical state from reactants
-reactant molecules are adsorbed onto surface of catalyst where reaction takes place, product molecules leave surface of catalyst by desorption
examples:
-the Haber process - making ammonia
-hydrogenation of alkenes
how are catalysts sustainable?
increase sustainability
-lower the temperature needed so less energy is used so has cheaper costs
-less combustion of fossil fuels means less carbon dioxide produced which is a greenhouse gas
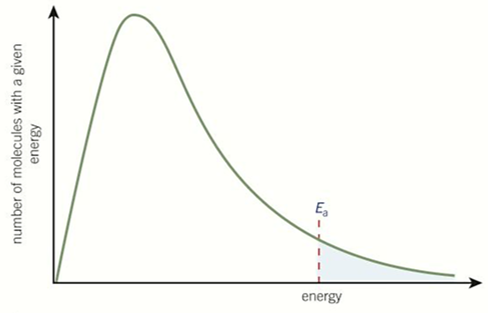
Boltzmann Distribution
-bell-shaped curve
-the area under the curve = the total number of particles
-curve starts at the origin = no molecules have no energy
-curve does not touch x-axis = no maximum energy
-only the molecules with energy greater than Ea can react
-the area under the curve does not change
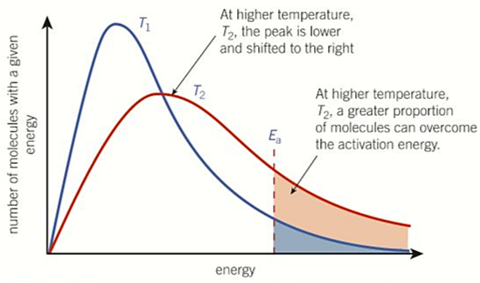
changes to Boltzmann curve if TEMP increases
-shifts to the right and peaks lower
-more molecules have greater energy than activation energy so plateaus above and peaks lower
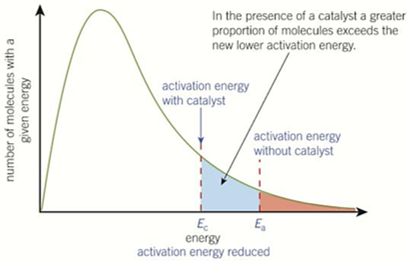
changes to Boltzmann curve if CATALYST added
-curve does not change but activation energy is lower
-catalysts lower the activation energy needed so more molecules have energy greater than activation energy
example of reversible reactions
Haber Process: nitrogen + hydrogen → ammonia
dynamic equilibrium
the rate of forward reaction = the rate of reverse reaction
-the concentration of both reactants and products remains constant - but may still continue to react
-only reached within a closed system
Le Chatelier’s Principle
the position of a dynamic equilibrium shifts to minimise the effect of any change
Le Chatelier’s Principle -temperature
-if temp increases, equilibrium position shifts to endothermic reaction to absorb more heat to reduce the temp
-if temp decreases, equilibrium position shifts to exothermic reaction to release more heat
Le Chatelier’s Principle -pressure
-if pressure increases, equilibrium position shifts to side with fewer molecules of gas to reduce pressure
-if pressure decreases, equilibrium shifts to side with more moles of gas to increase pressure
Le Chatelier’s Principle -concentration
-if conc of reactants increases, equilibrium shifts to the right to use up reactants + form more products
-if conc of products increases, equilibrium shifts to the left to use up products + form more reactants
-decrease = opposite effect
Le Chatelier’s Principle -catalysts
have no effect on the position of equilibrium as they increase the rate of both the forward and reverse reaction by the same amount
equilibrium constant Kc -expression
[products]no. of moles / [reactants]no. of moles
square brackets = concentration
Kc value
-if Kc < 1 means high conc of reactants + equilibrium is towards the left
-if Kc > 1 means high conc of products + equilibrium is towards the right
what affects Kc?
-only temperature
-in endothermic = if temp increases, Kc increases + if temp decreases, Kc decreases
-in exothermic = if temp increases, Kc decreases + if temp decreases, Kc increases