RAD 110 - Ch 5 Humerus & Shoulder Girdle Positioning - Positioning
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Humerus Routine
- AP
- Lateral (rotational & horizontal beam)
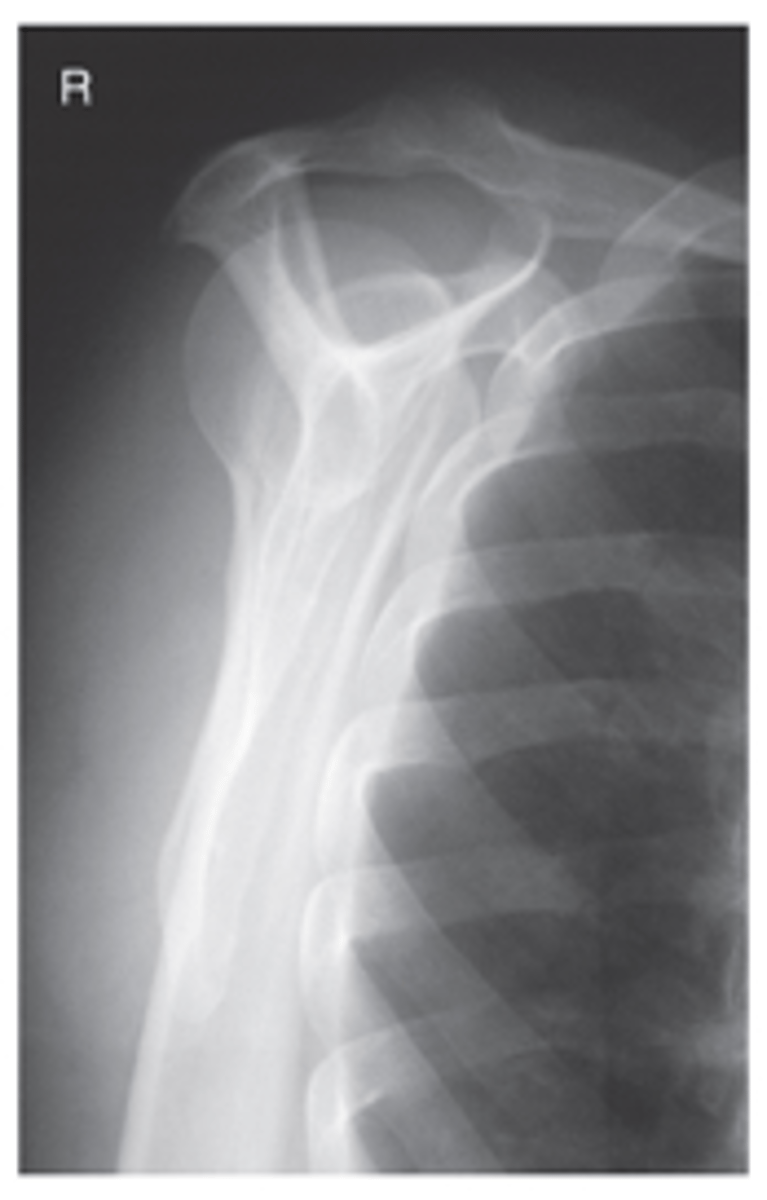
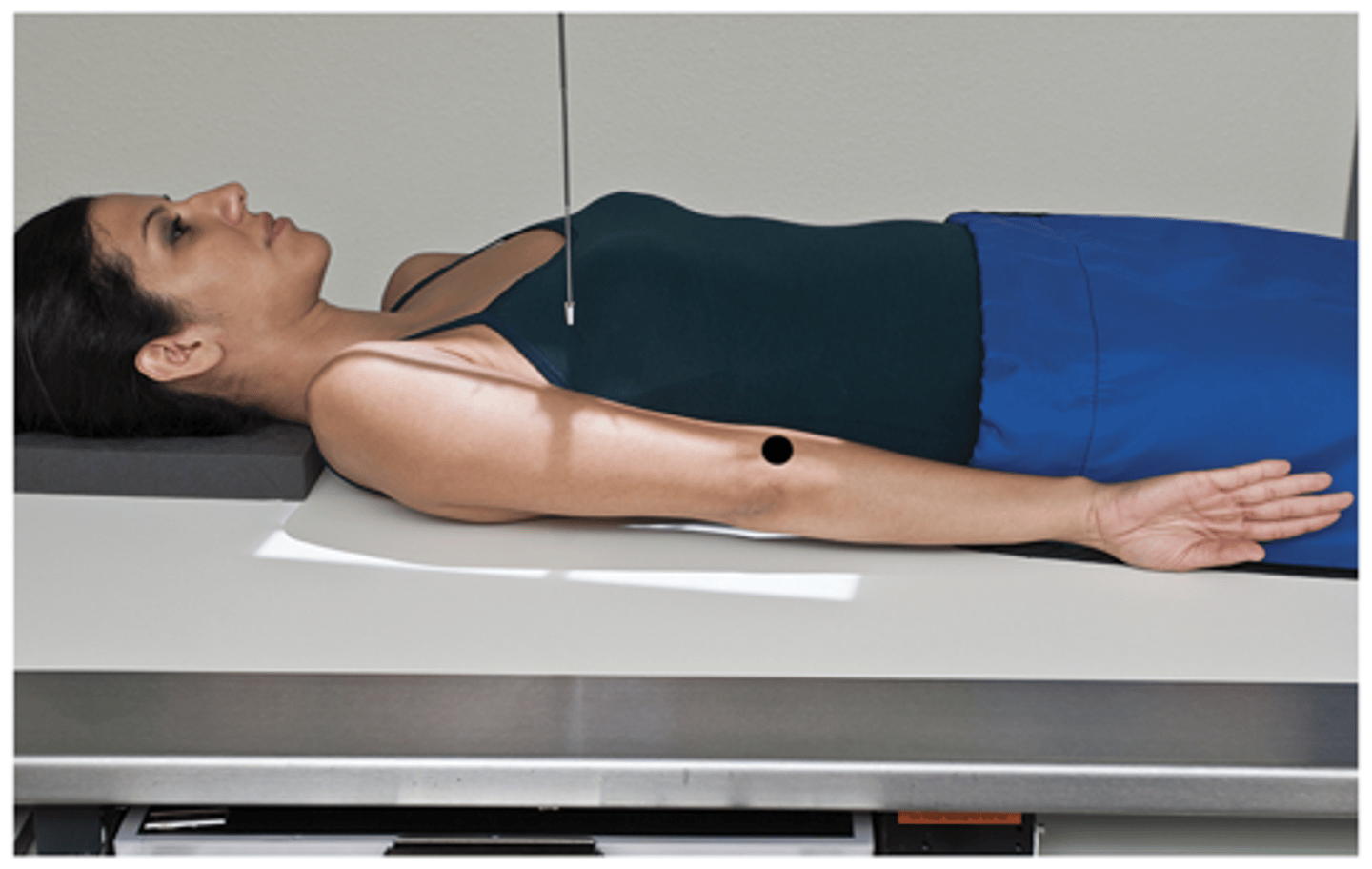
AP Humerus Recumbent
What projection is this?
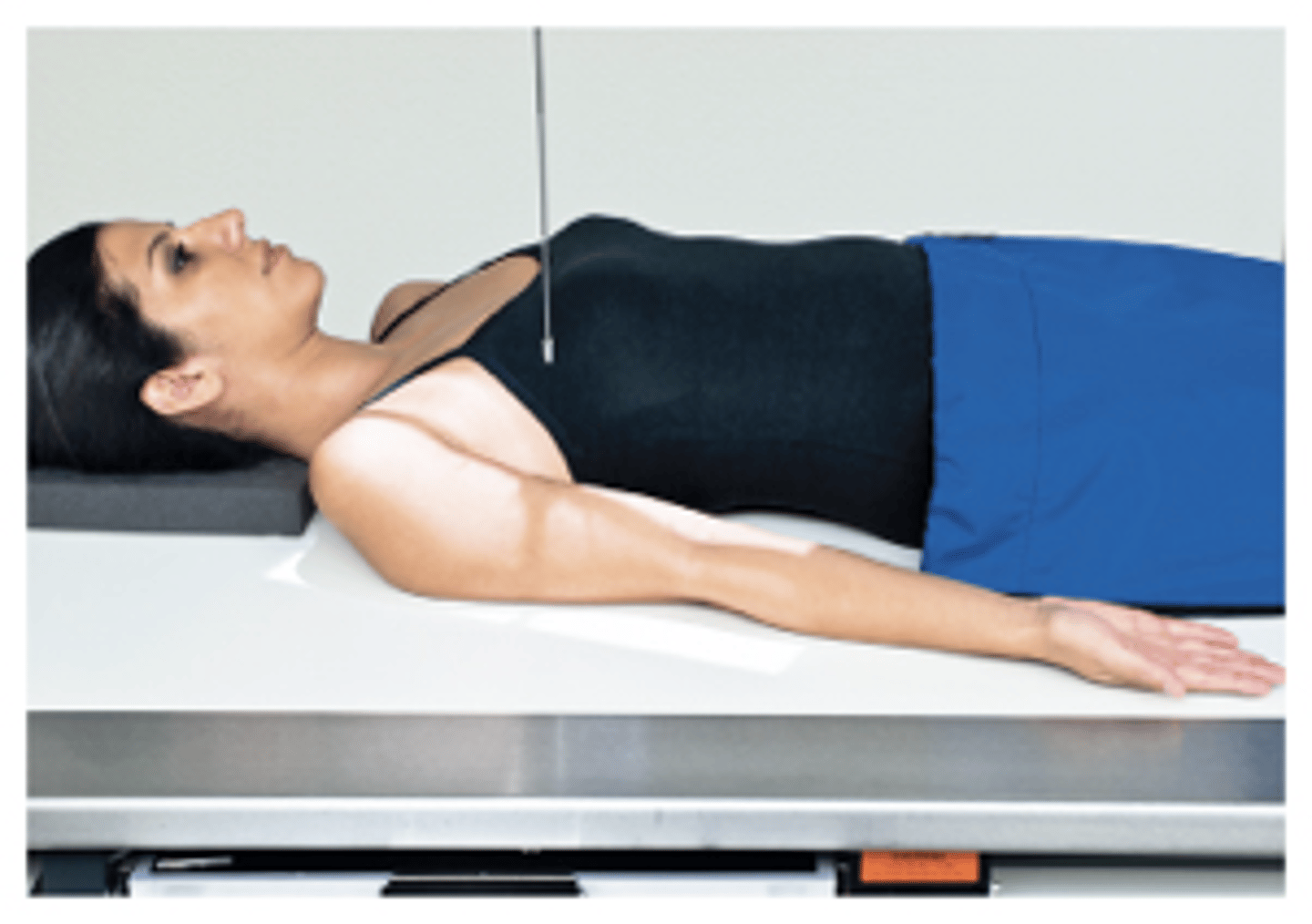
AP Humerus Erect
What projection is this?
Evaluation Criteria Humerus
- Include both shoulder and elbow joints
- CR to midhumerus
- Entire humerus demonstrated
- Greater tubercle in profile
- Medial and lateral epicondyles in profile
- Exposure factors
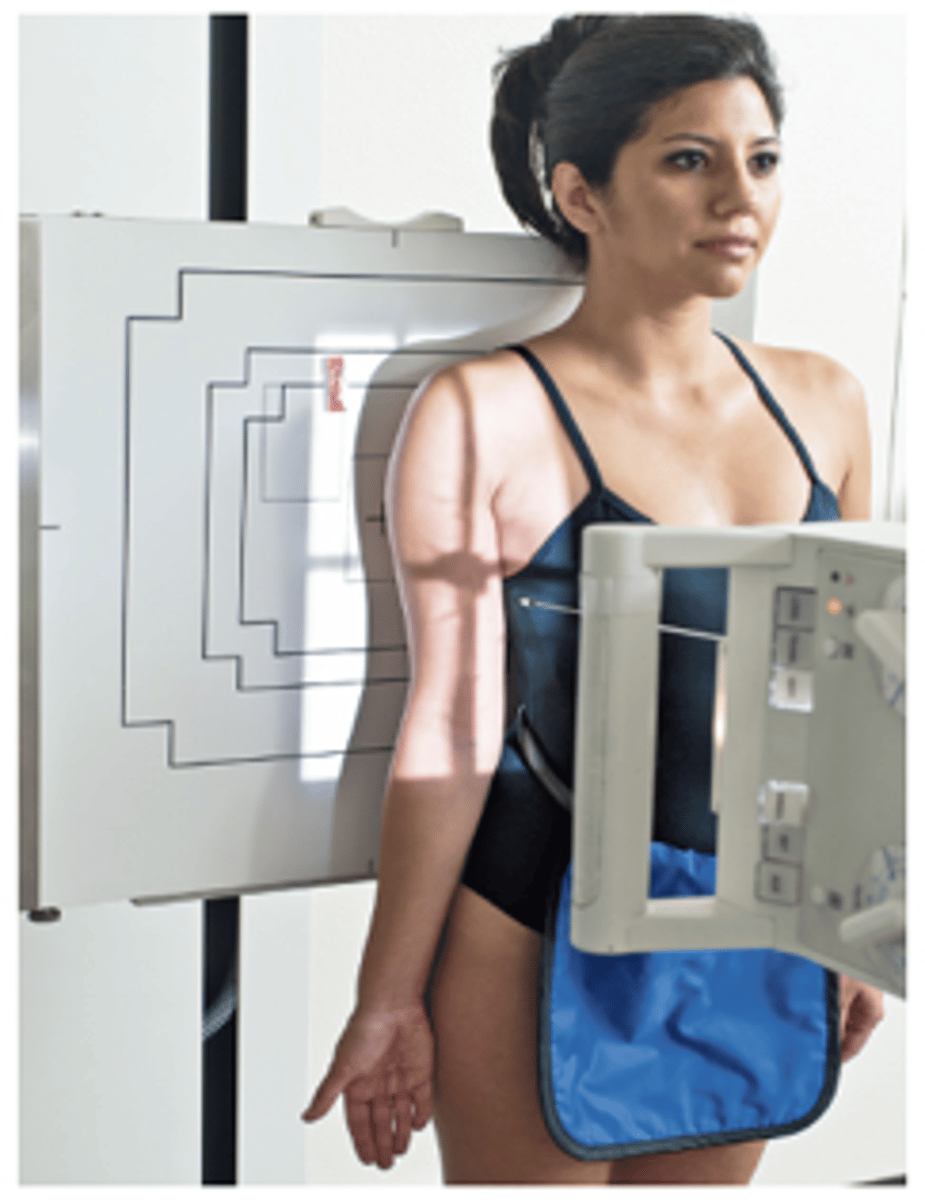
Lateromedial Humerus Erect
What projection is this?
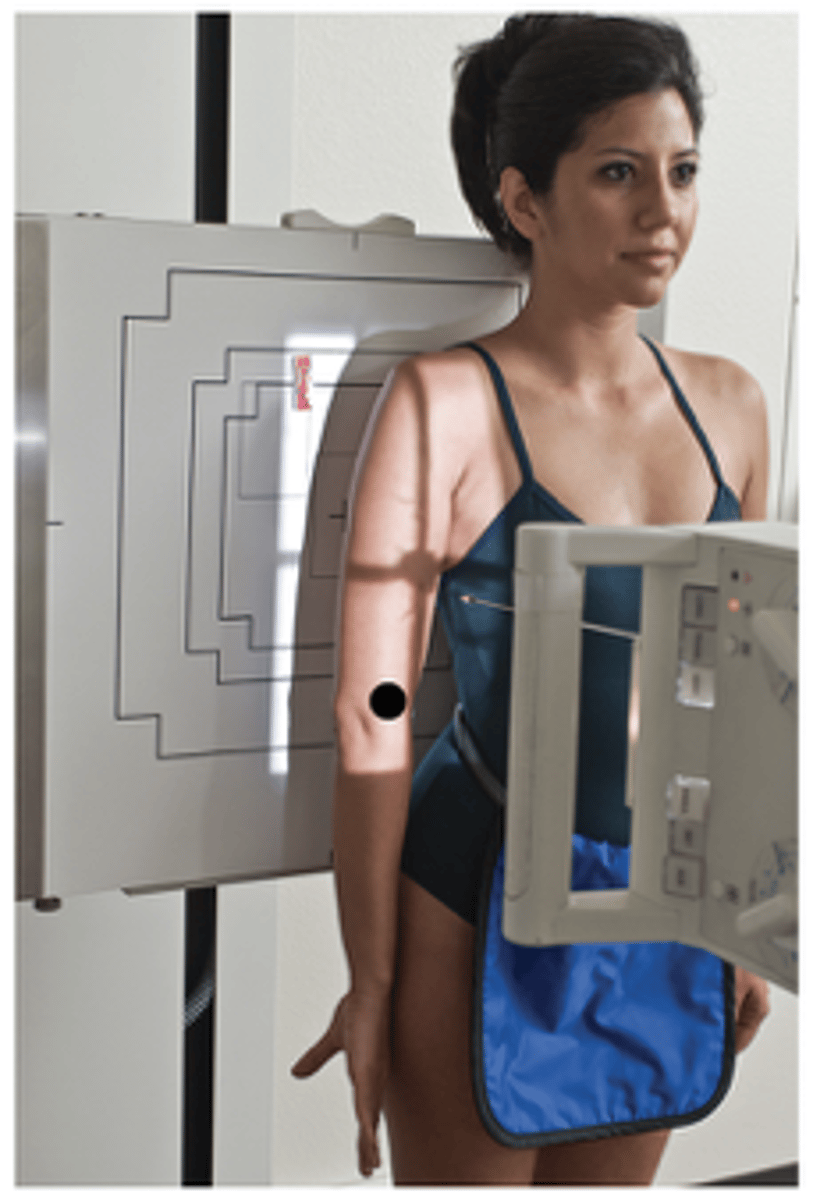
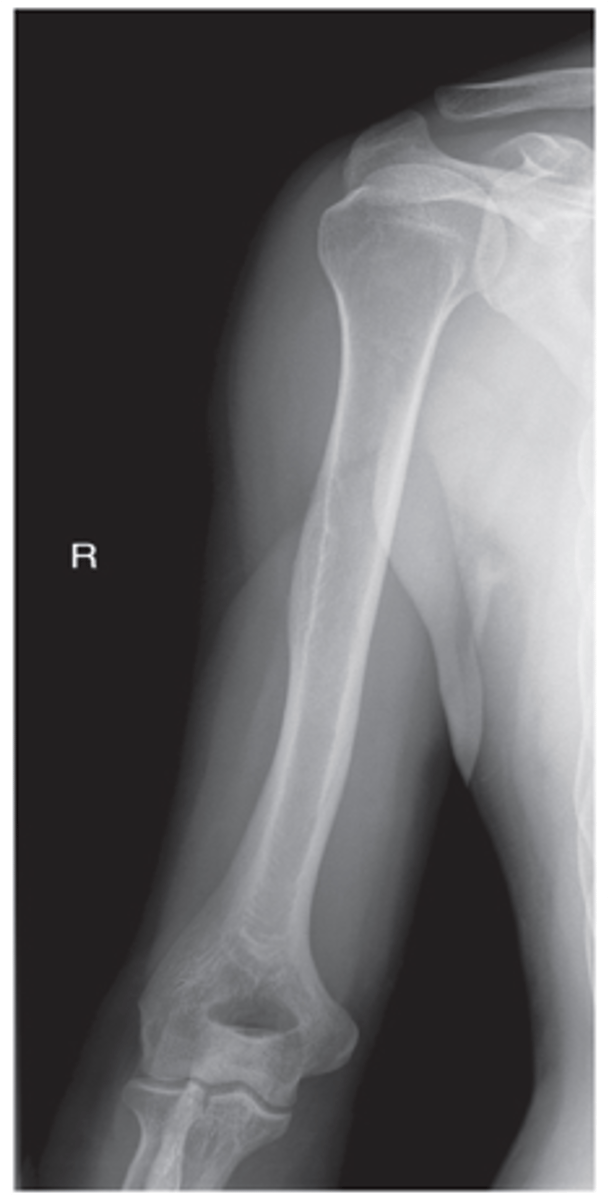
Mediolateral Humerus Erect
What projection is this?
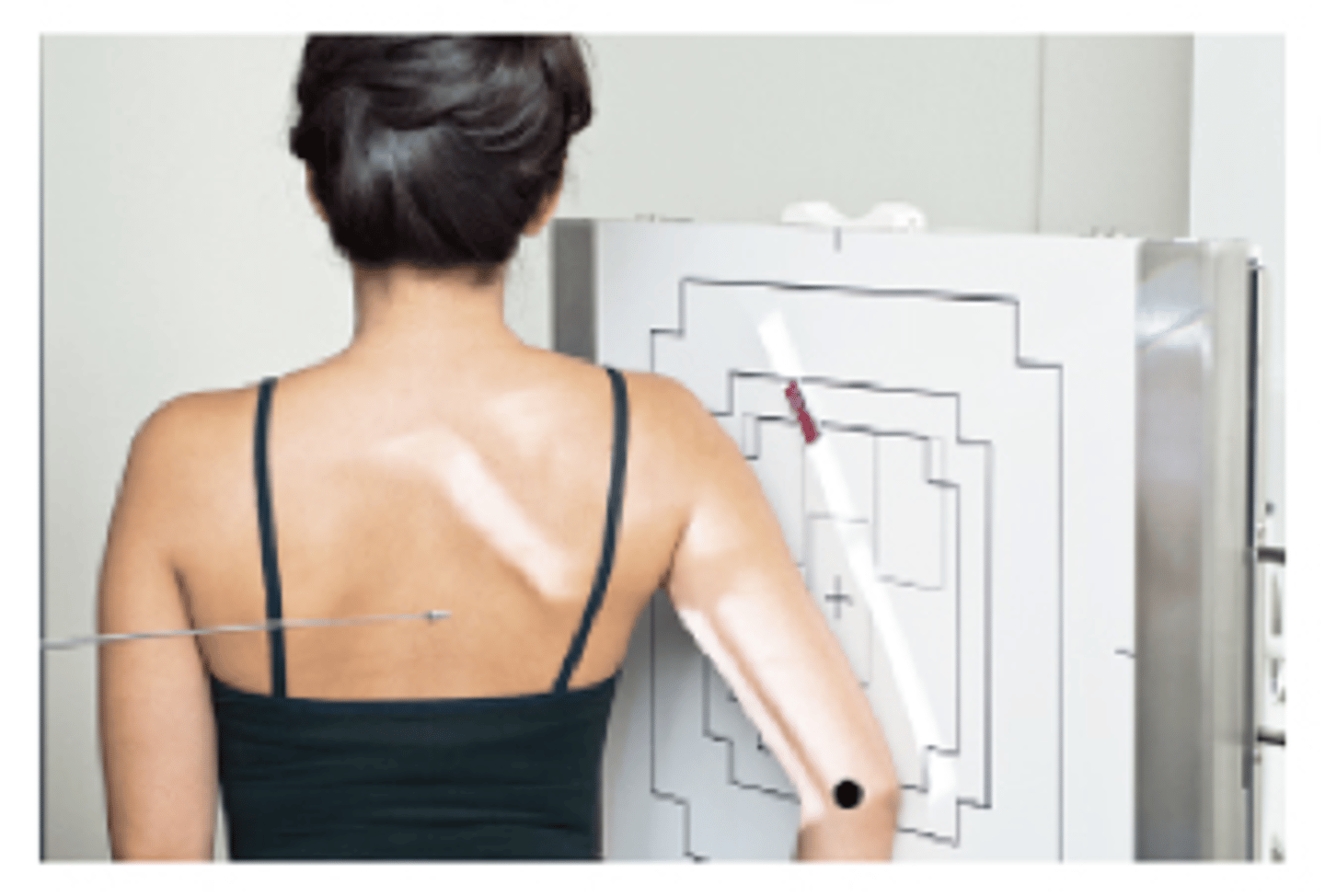
Rotational Lateral Humerus Recumbent
What projection is this?
Evaluation Criteria Lateral Humerus
- Epicondyles perpendicular to IR
- CR to midhumerus
- Entire humerus demonstrated
- Lesser tubercle in profile
- Epicondyles superimposed
- Exposure factors
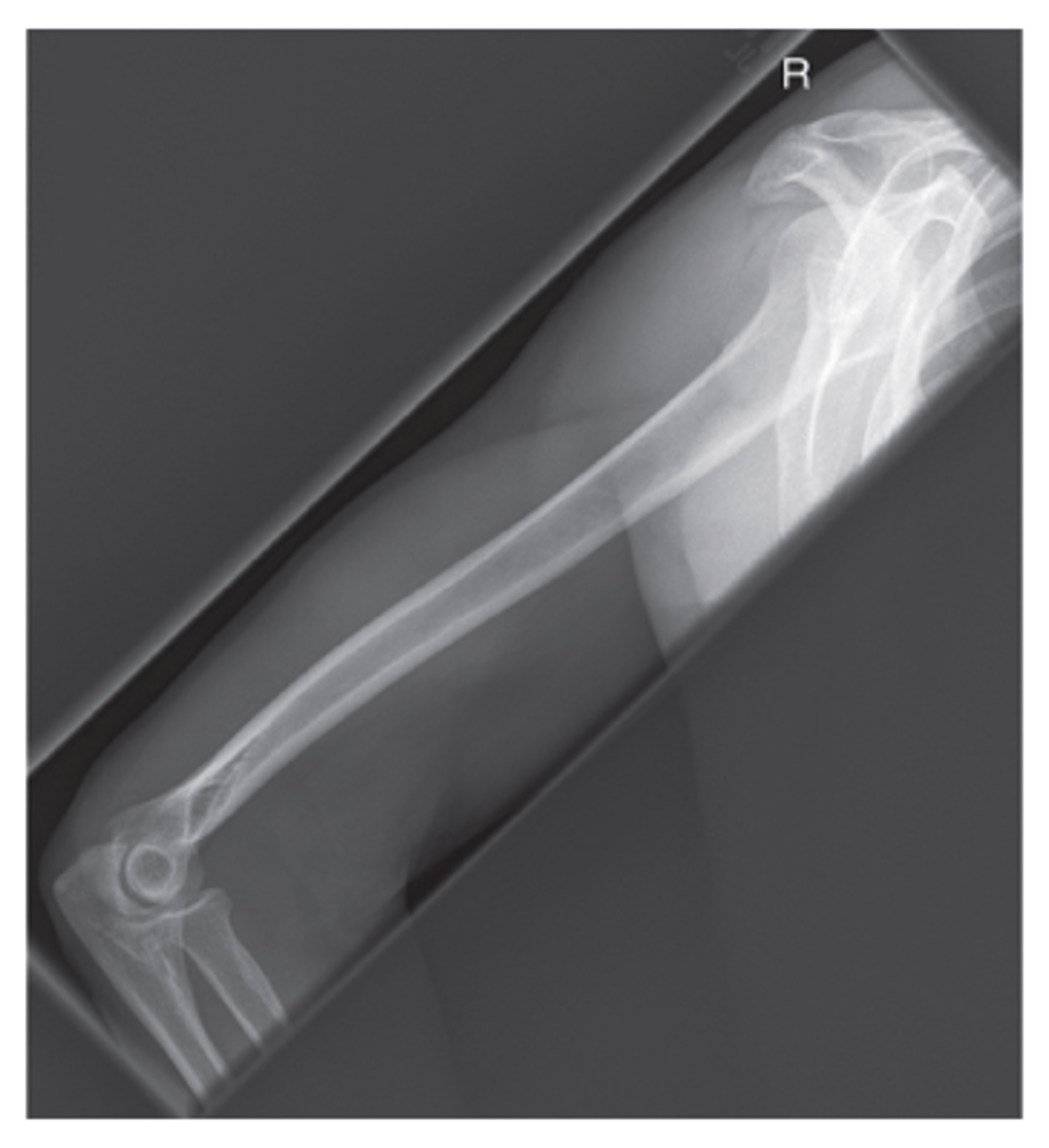
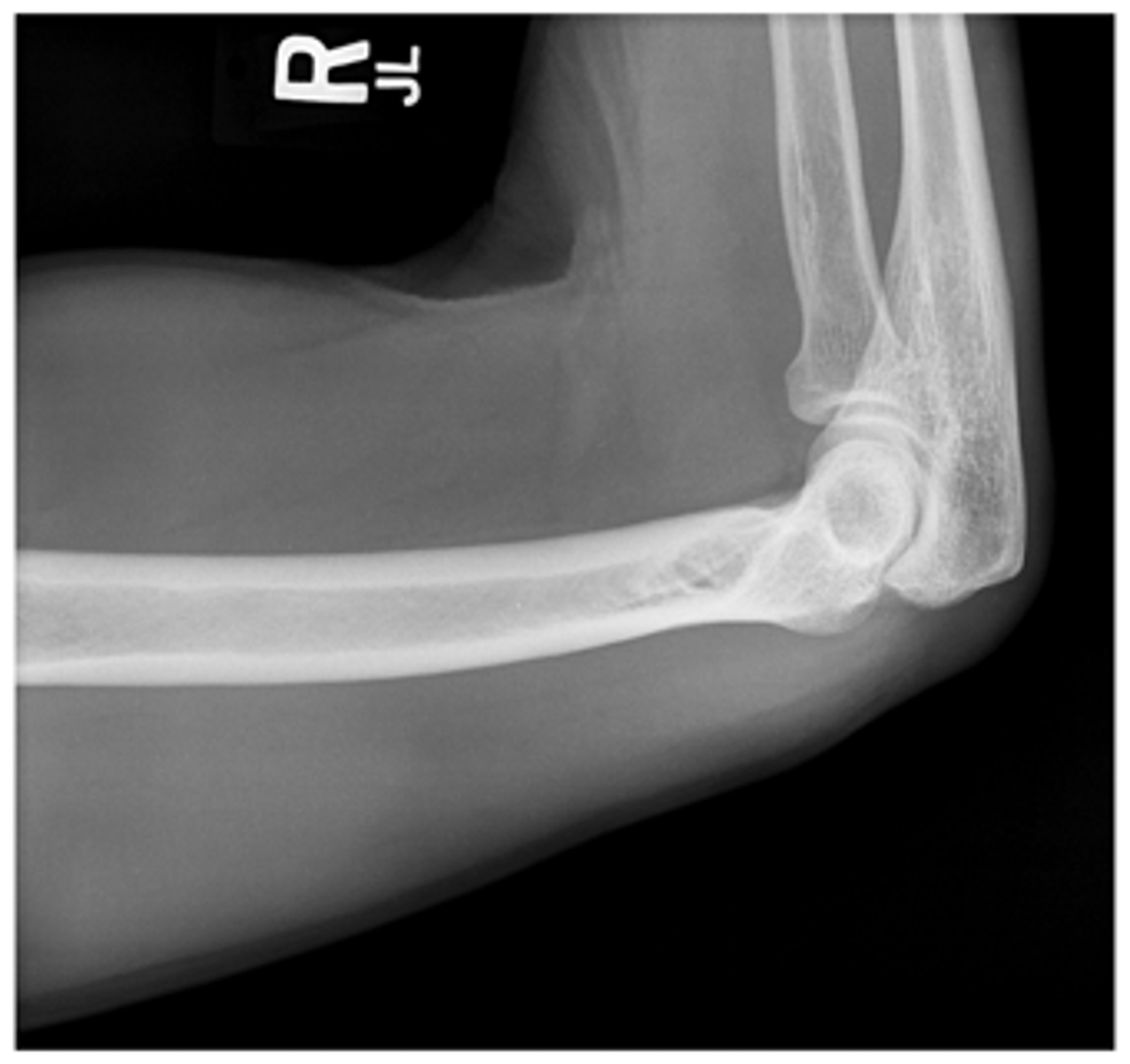
Lateral Mid & Distal Humerus Recumbent Trauma
What projection is this?

Evaluation Criteria Lateral Mid & Distal Humerus Recumbent Trauma
- Mid and distal humerus
- Distal ⅔ humerus demonstrated
- 90° perspective from AP projection
- Epicondyles superimposed
- Exposure factors
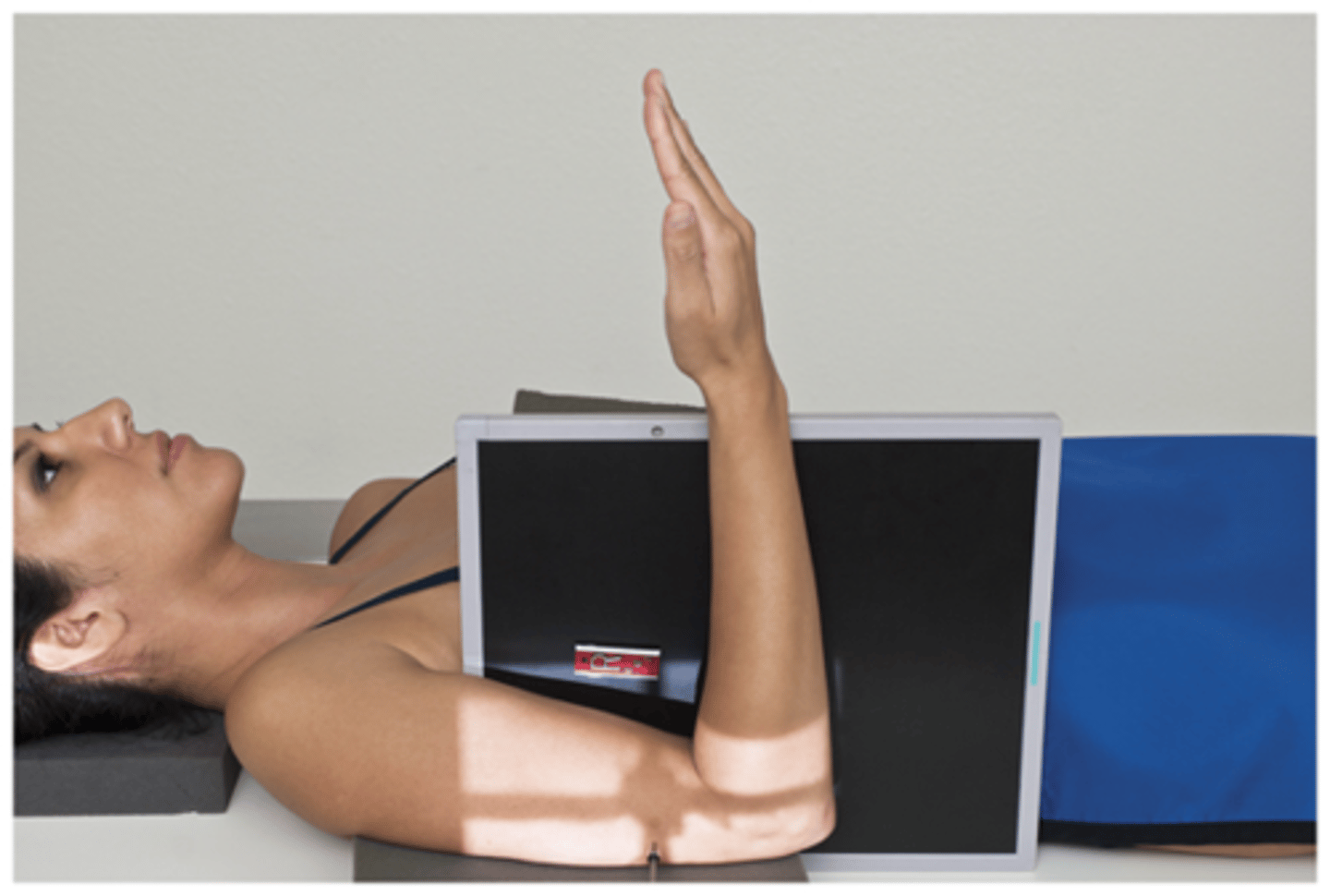
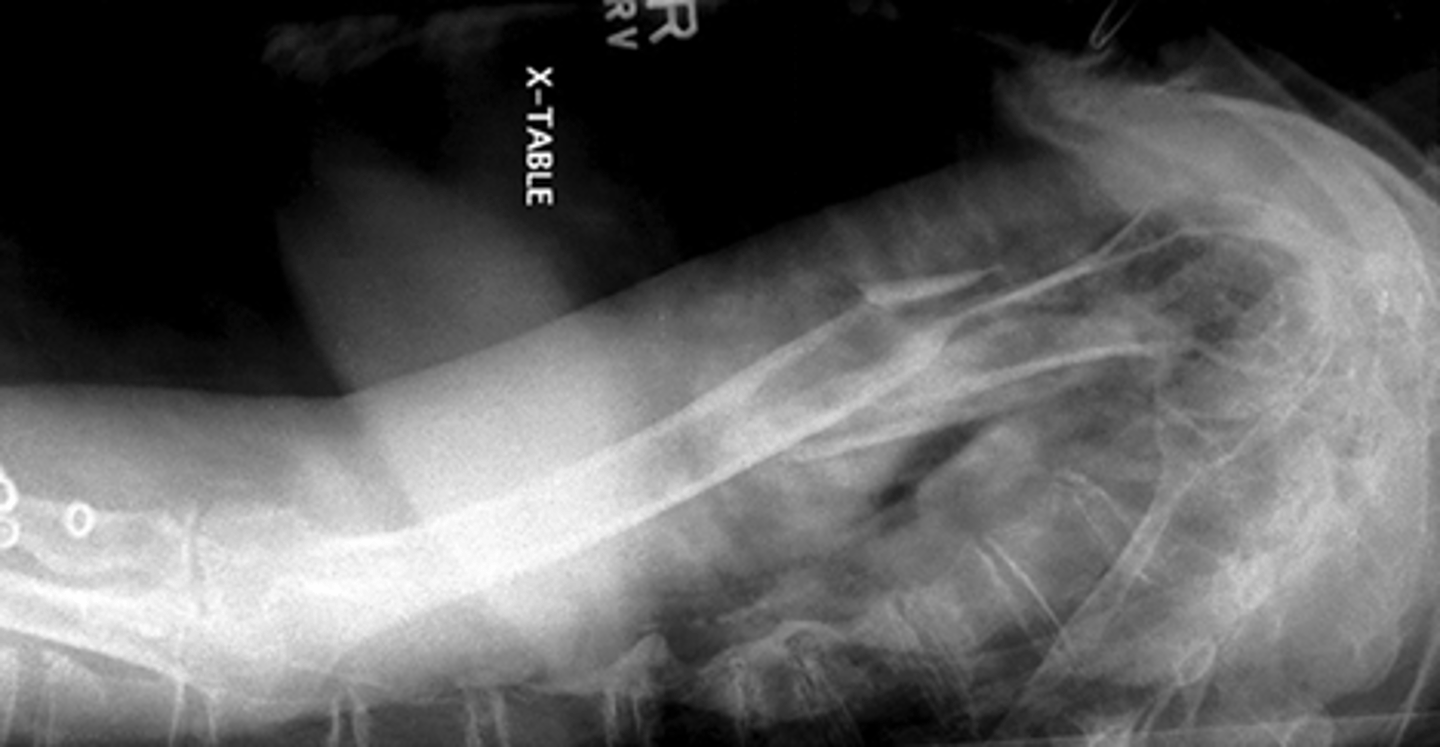
Horizontal Beam Transthoracic Lateral Humerus Trauma
What projection is this?
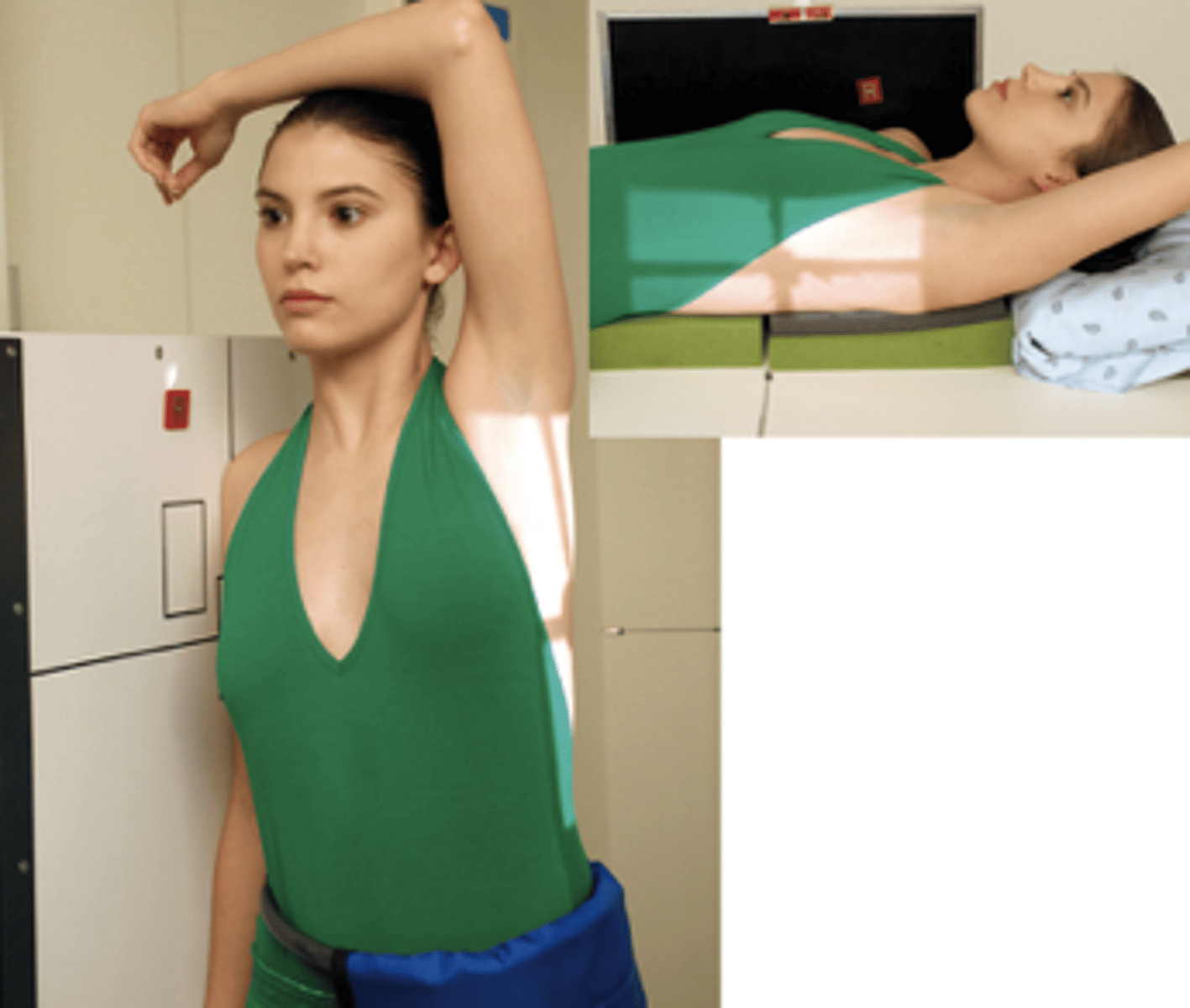
Evaluation Criteria Horizontal Beam Transthoracic Lateral Humerus Trauma
- Demonstrates entire humerus without rotation
- Unaffected limb raised over head
- CR to mid aspect to involved humerus
Shoulder Girdle Technical Factors
- kV range: analog 70 to 75; digital 75 to 85 kV
- Grid (>10 cm)
- High mA (short exposure time)
- Small focal spot
- AEC (center chamber)
- 40 inches (102 cm) SID (except AC joints)
AP Proximal Humerus/Shoulder Routine
- External (AP)
- Internal (Lateral)
External Rotation AP Proximal Humerus/Shoulder
What projection is this?
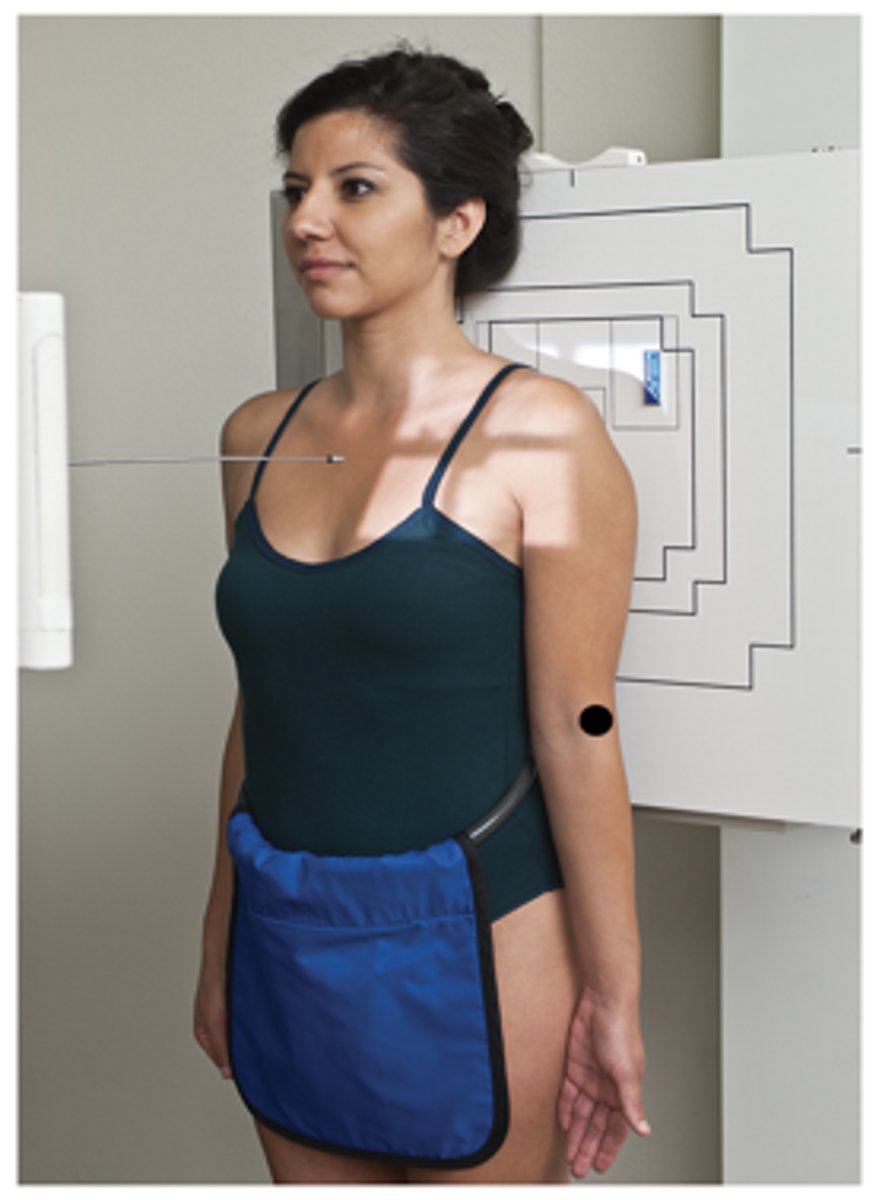
Evaluation Criteria External Rotation AP Proximal Humerus/Shoulder
- Epicondyles parallel
- CR 1 inch (2.5 cm) inferior to coracoid process
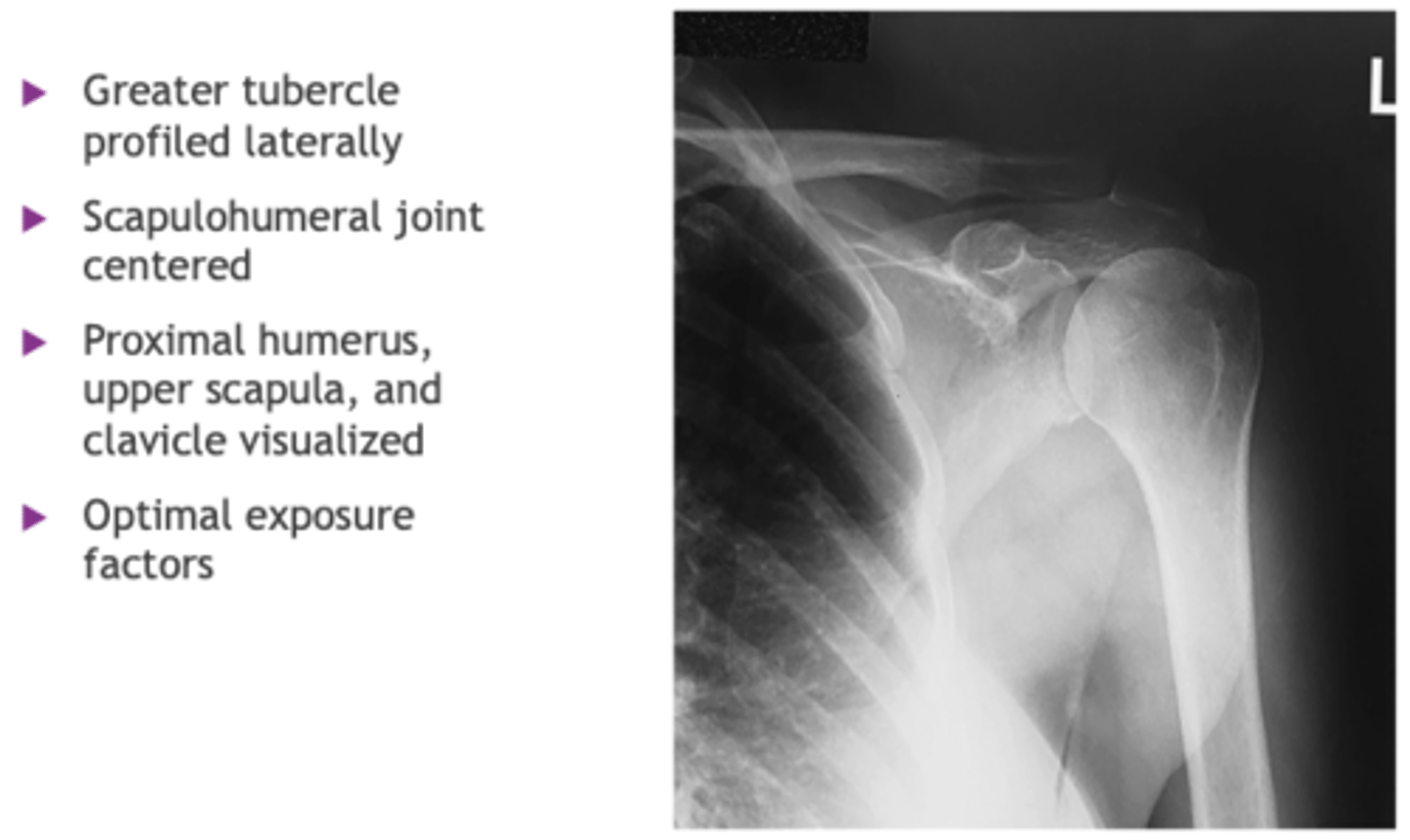
- Greater tubercle profiled laterally
- Scapulohumeral joint centered
- Proximal humerus, upper scapula, and clavicle visualized
- Optimal exposure factors
Internal Rotation Lateral Proximal Humerus/Shoulder
What projection is this?
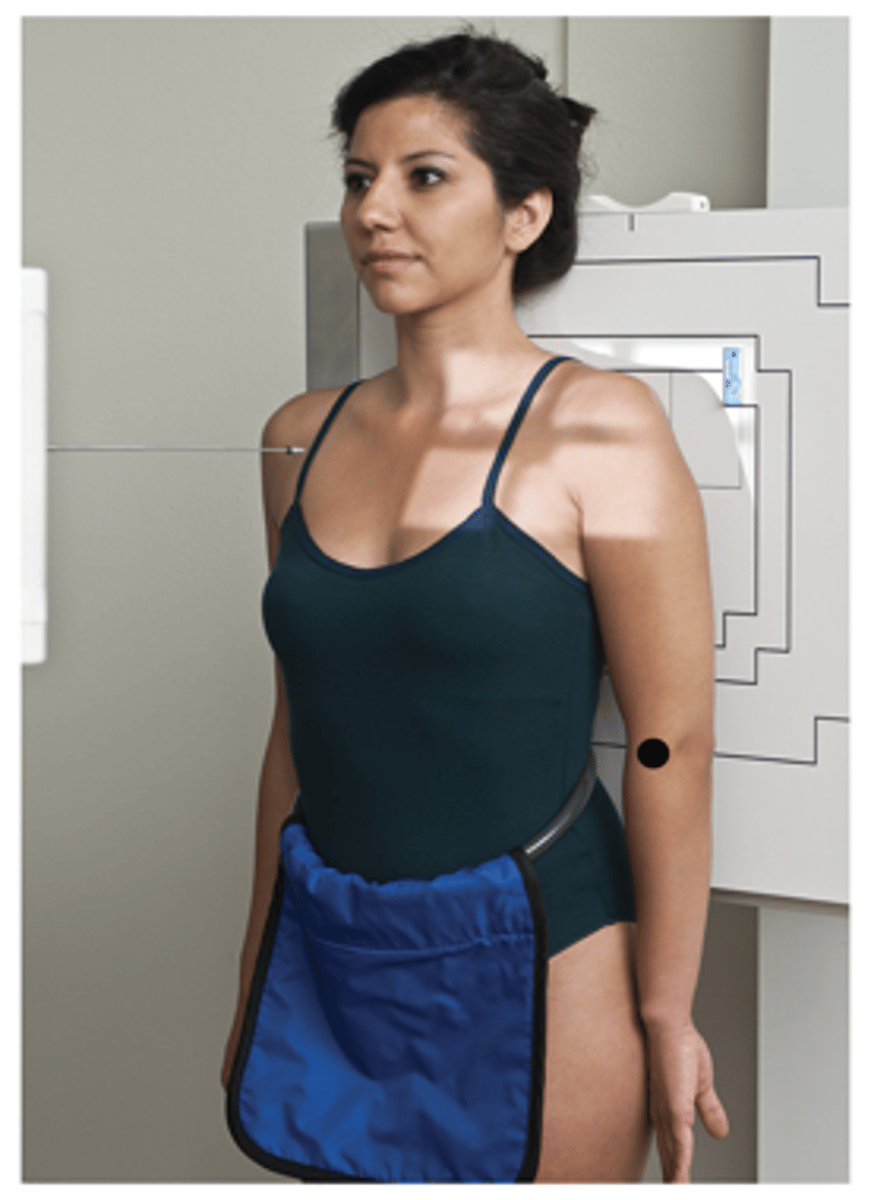
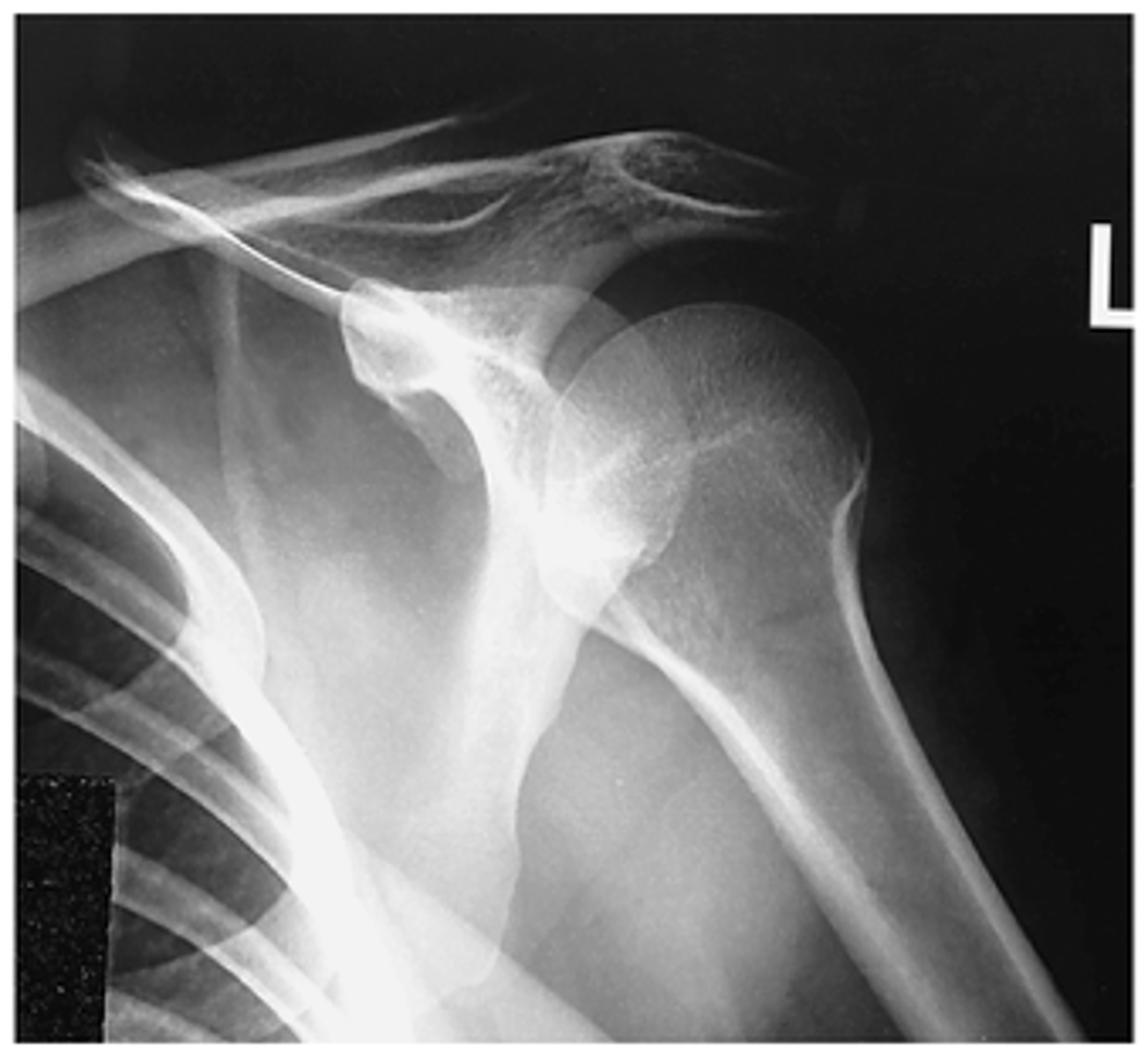
Evaluation Criteria Internal Rotation Lateral Proximal Humerus/Shoulder
- Epicondyles perpendicular
- CR 1 inch (2.5 cm) inferior to coracoid process
- Lesser tubercle profiled medially
- Scapulohumeral joint centered
- Proximal humerus, upper scapula, and clavicle visualized
- Optimal exposure factors
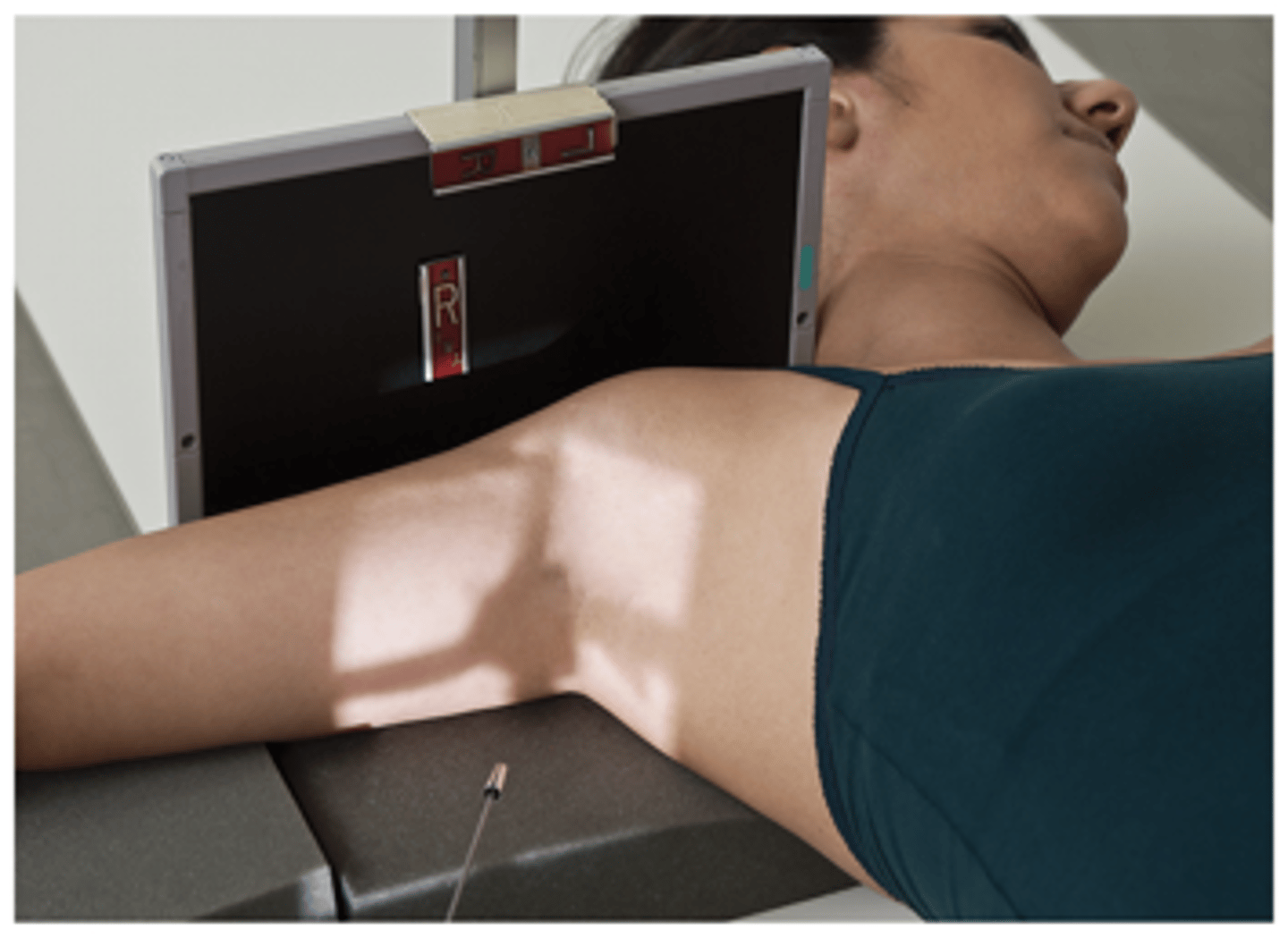
Shoulder - Inferosuperior Axial (Lawrence Method)
What projection is this?
Shoulder - Inferosuperior Axial (Lawrence Method) Alternate Position w/Exaggerated Rotation
- Demonstrate possible Hill-Sachs defect
- When there is an anterior dislocation, sometimes it may result in a wedge shape compression fracture on the humeral head.
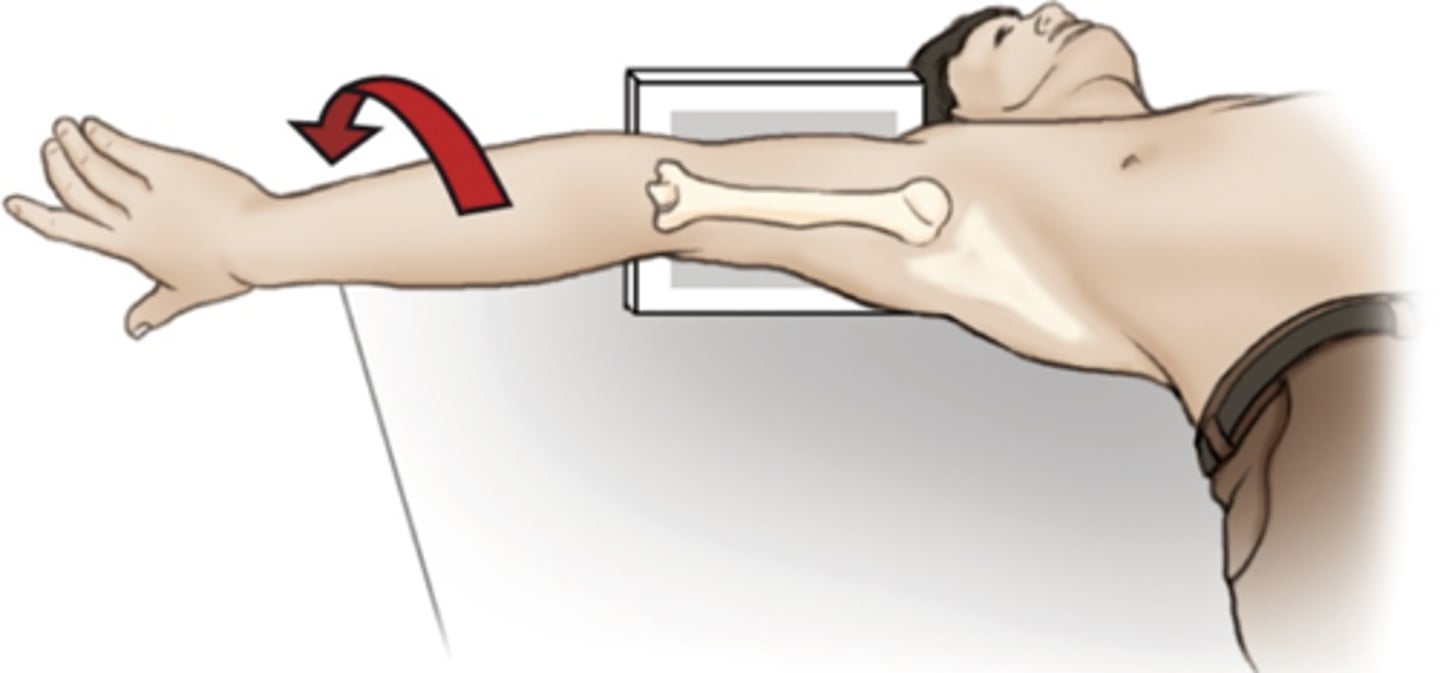
Evaluation Criteria Shoulder - Inferosuperior Axial (Lawrence Method)
- CR 25° to 30° medial to axilla
- Arm supinated, abducted 90° (or as near 90° as possible)
- Supine with shoulder elevated 2" from the TT, sponge
- Lesser tubercle profiled anteriorly
- Humeral head and glenoid fossa profiled
- Optimal exposure factors
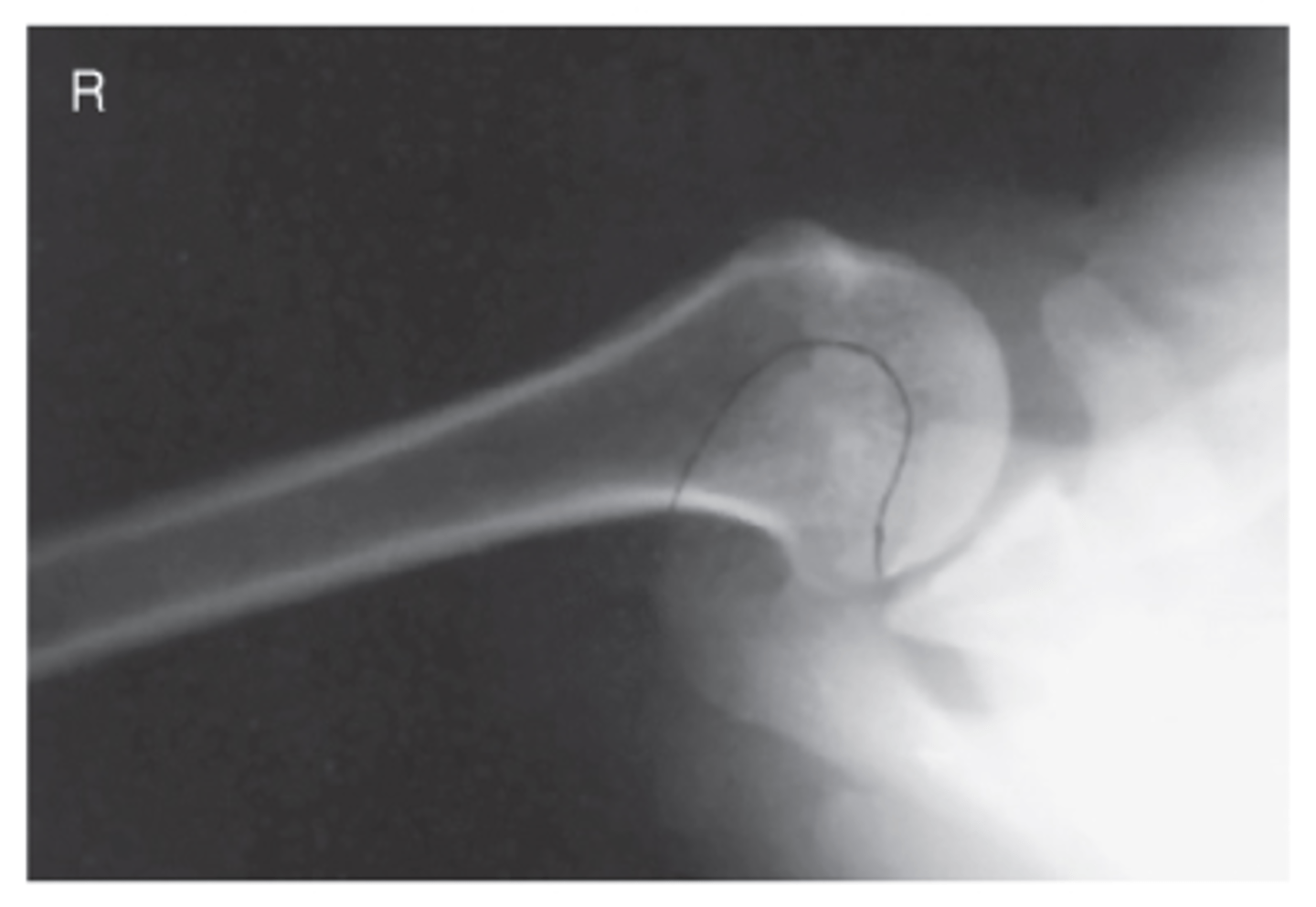
Shoulder - Inferosuperior Axial (Clements Modification)
What projection is this?
Evaluation Criteria Shoulder - Inferosuperior Axial (Clements Modification)
- CR perpendicular to IR
- If patient cannot abduct arm, CR 5° to 15° to axilla
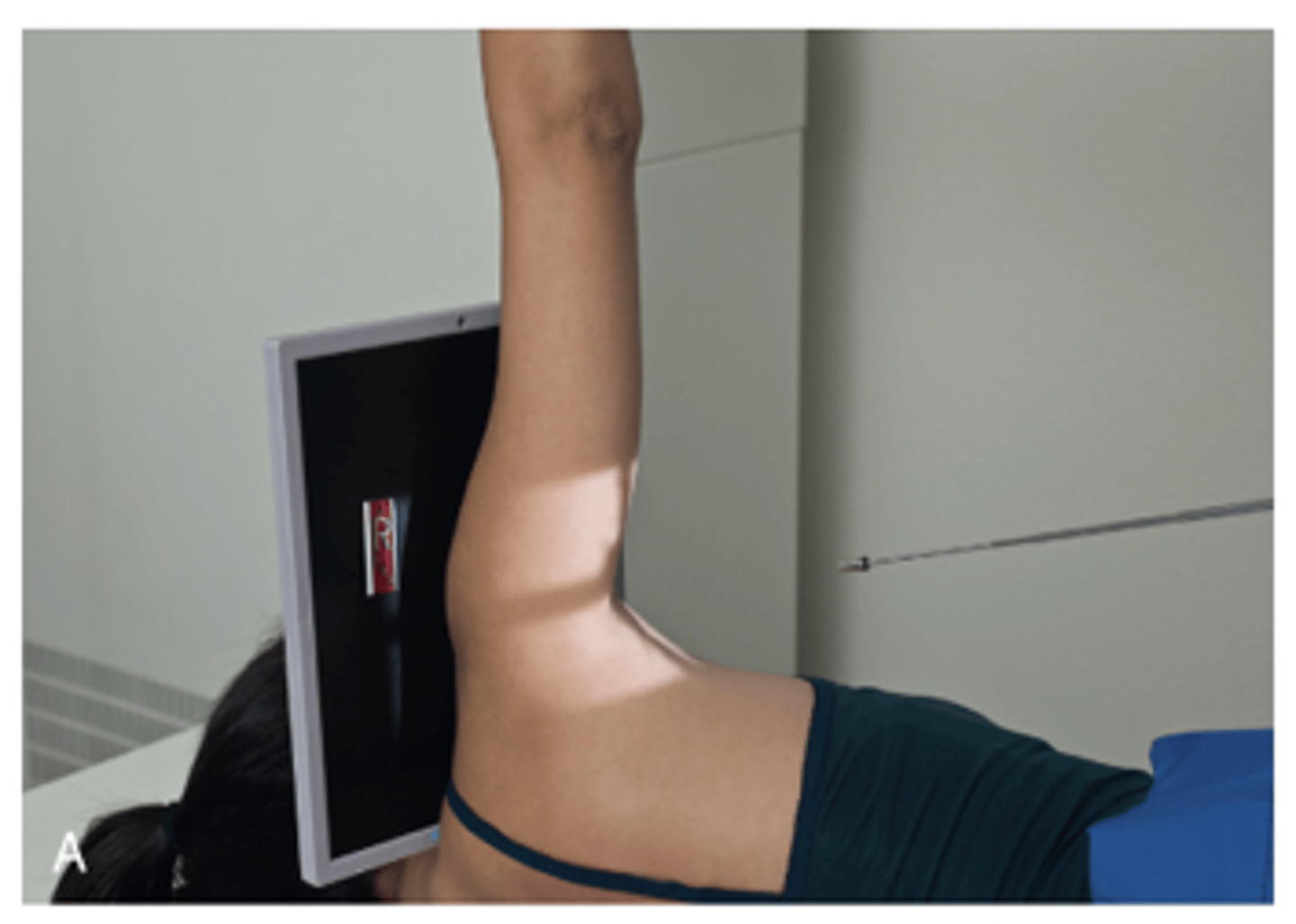
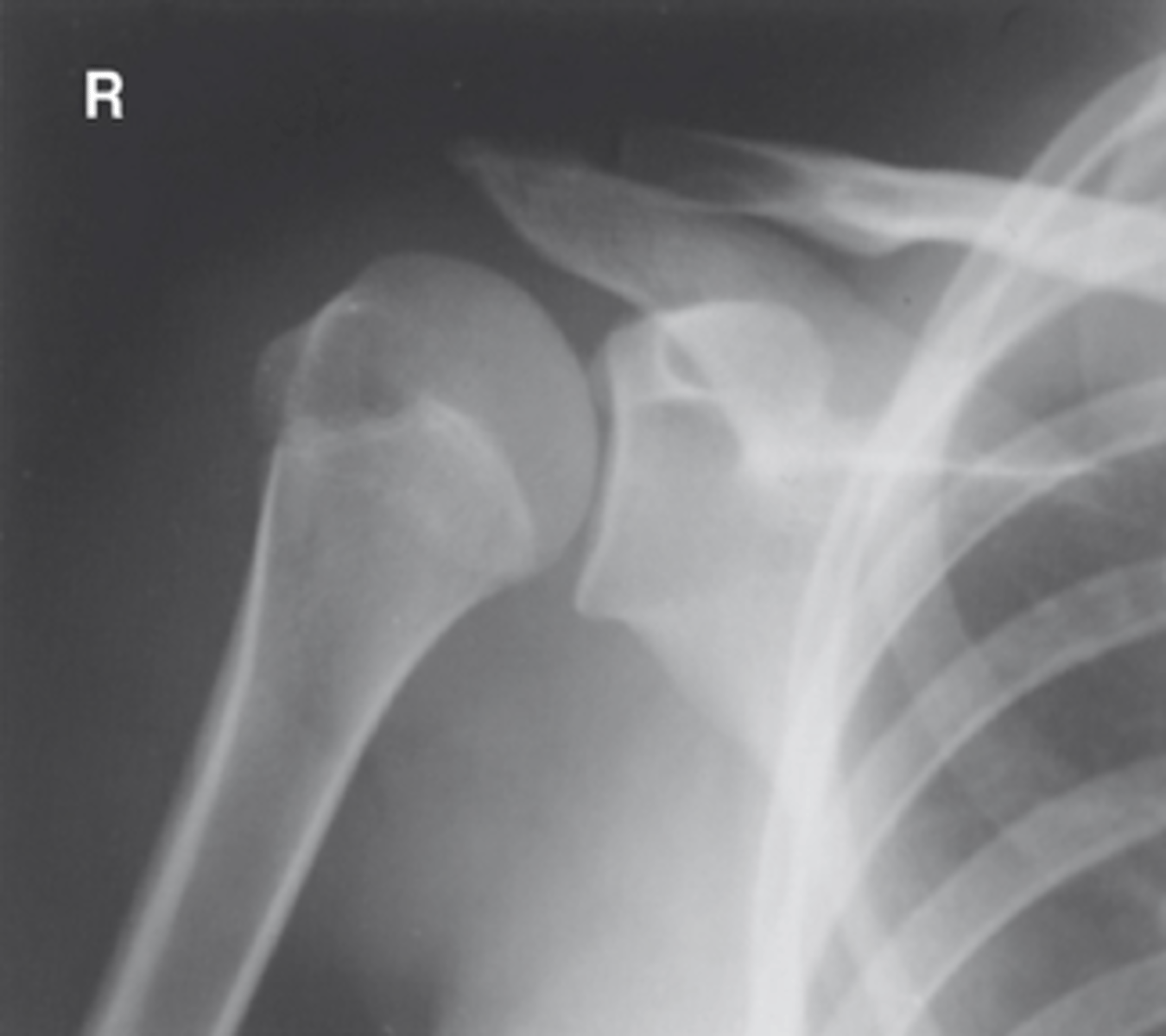
Shoulder - Posterior Oblique Glenoid Cavity (Grashey Method)
What projection is this?
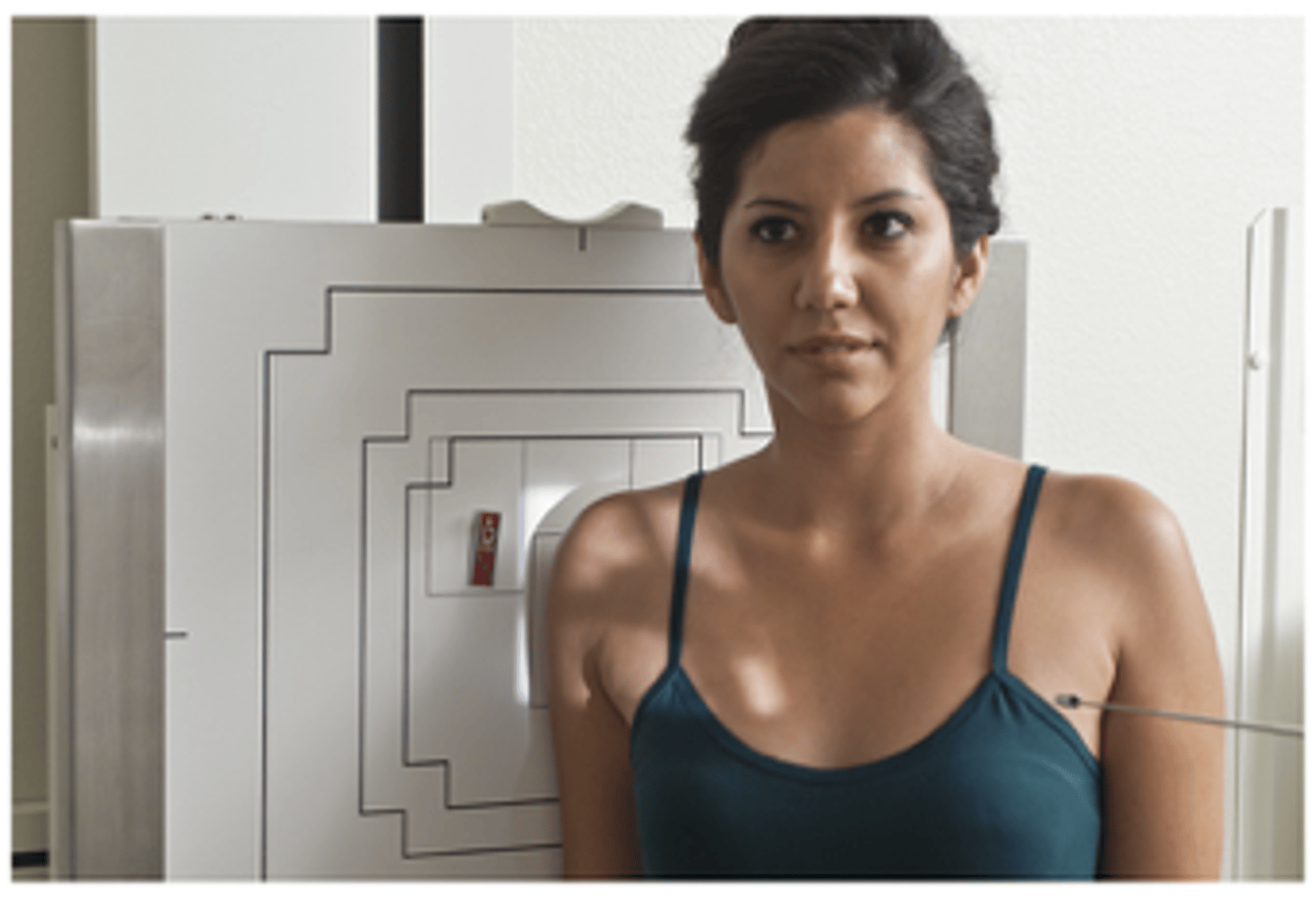
Evaluation Criteria Shoulder - Posterior Oblique Glenoid Cavity (Grashey Method)
- 35° to 45° oblique
- CR perpendicular to IR 2 inches (5 cm) inferior and medial from superolateral border of humerus
- Glenoid cavity profiled
- Scapulohumeral joint centered
- Optimal exposure factors
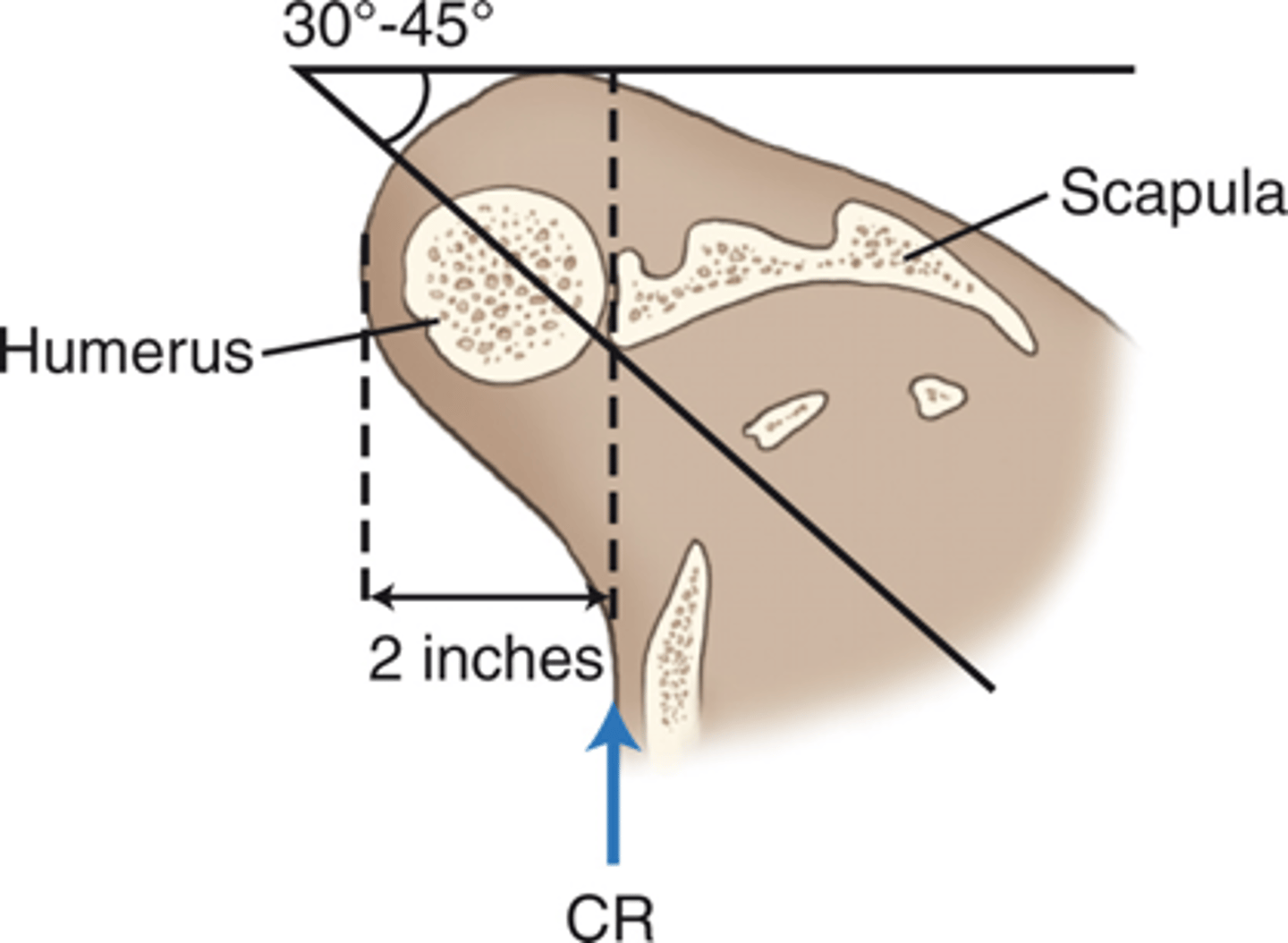
Shoulder - Posterior Oblique Glenoid Cavity (Grashey Method) Graphic
- 35° to 45° oblique
- CR perpendicular to IR 2 inches (5 cm) inferior and medial from superolateral border of humerus
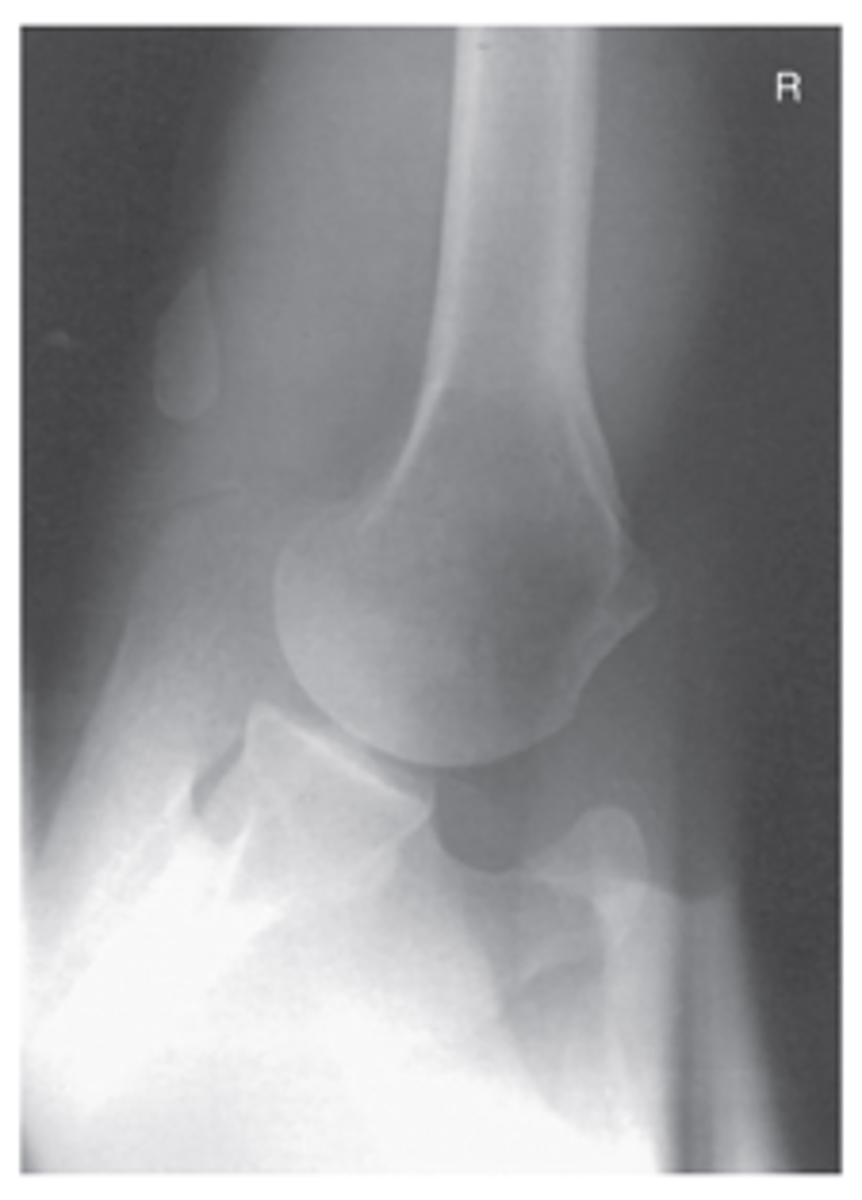
Shoulder - Tangential Projection (Fisk Method) Intertubercular Groove (Erect)
What projection is this?
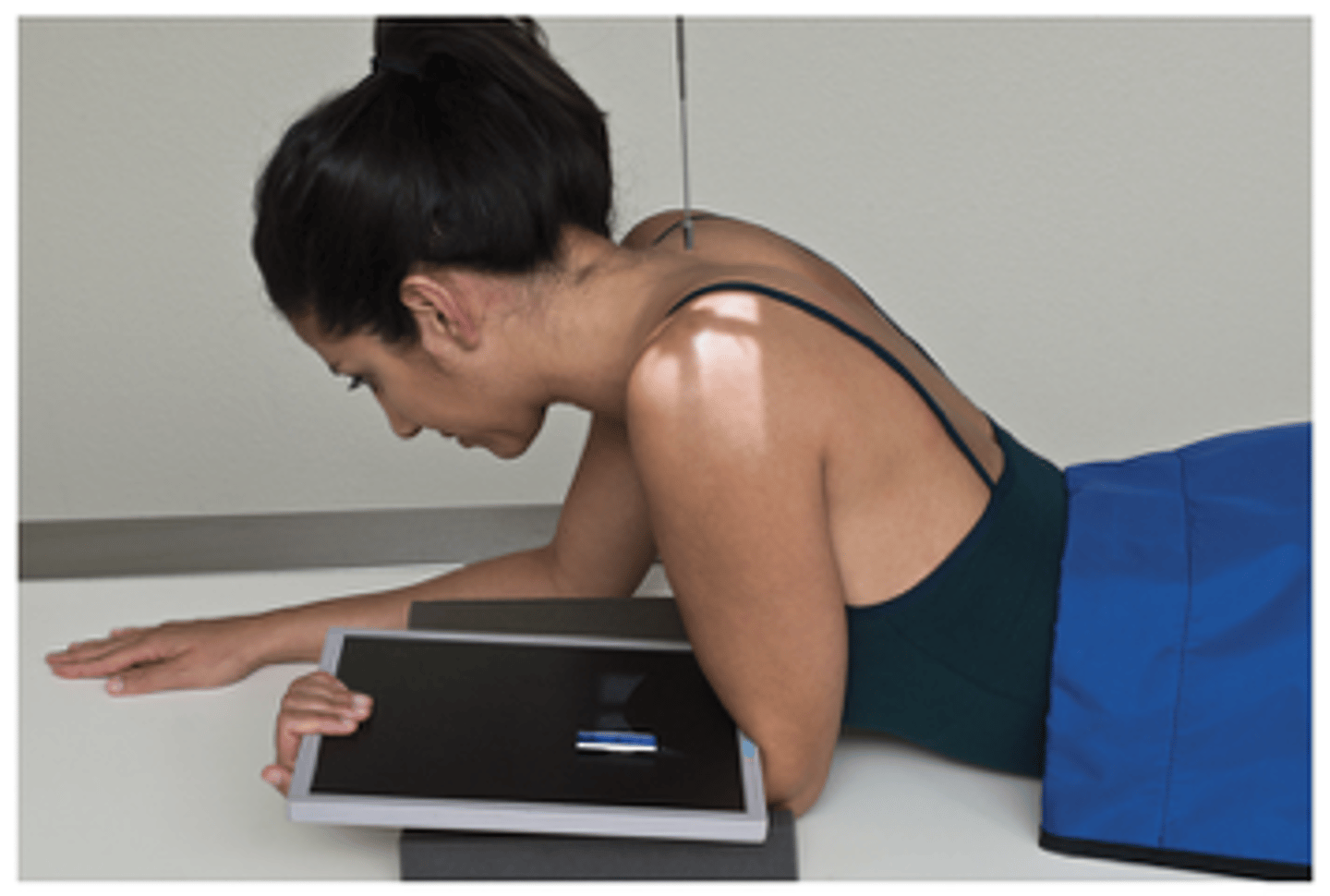
Position & CR Shoulder - Tangential Projection (Fisk Method) Intertubercular Groove (Erect)
- Humerus 15° to 20° to CR, which is perpendicular to IR
- Patient leaning forward slightly to place humerus 10 to 15 from vertical
- Turn head away from affected side
- Midanterior on humerus, carefully palpated
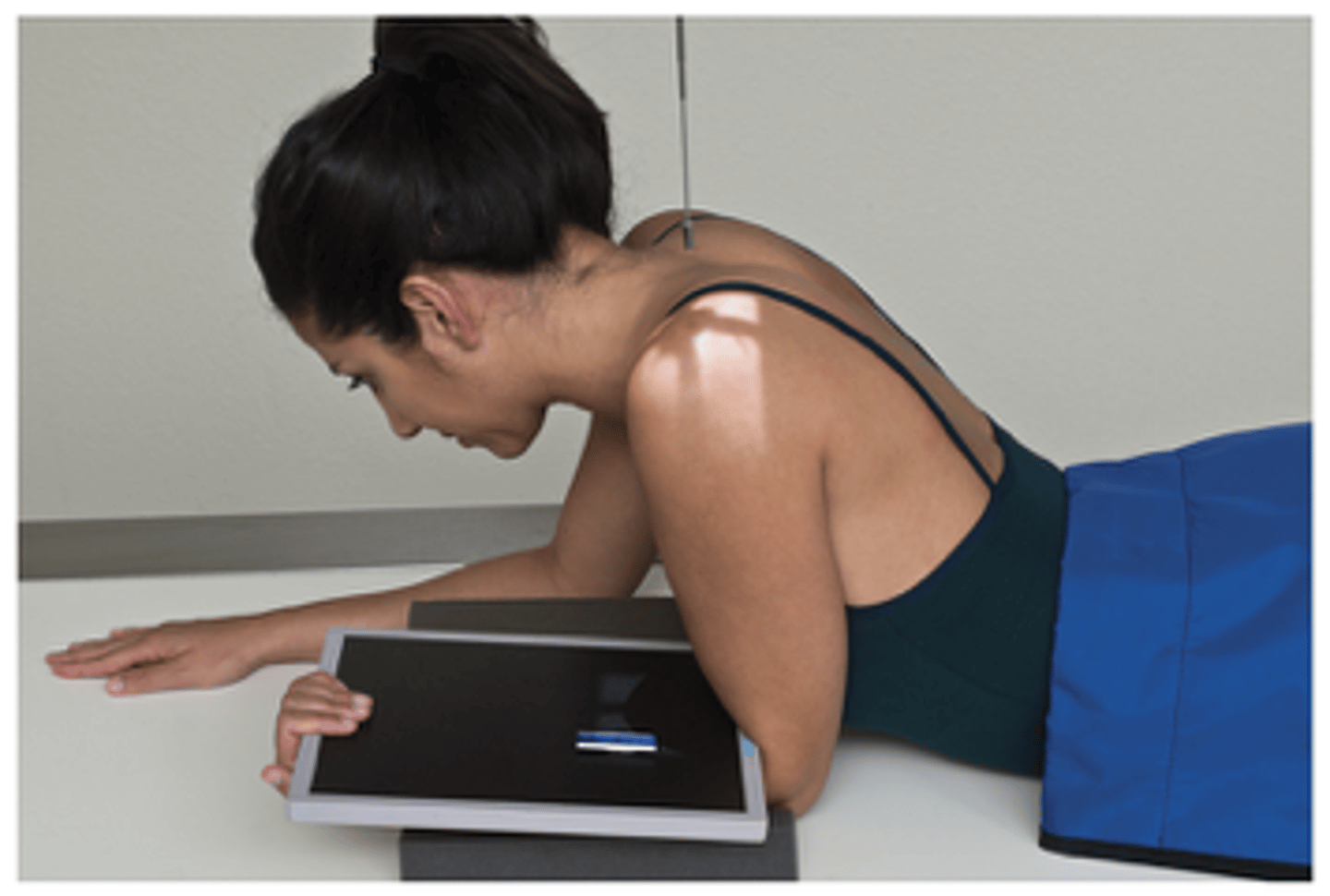
Shoulder - Tangential Projection Intertubercular Groove (Supine)
What projection is this?
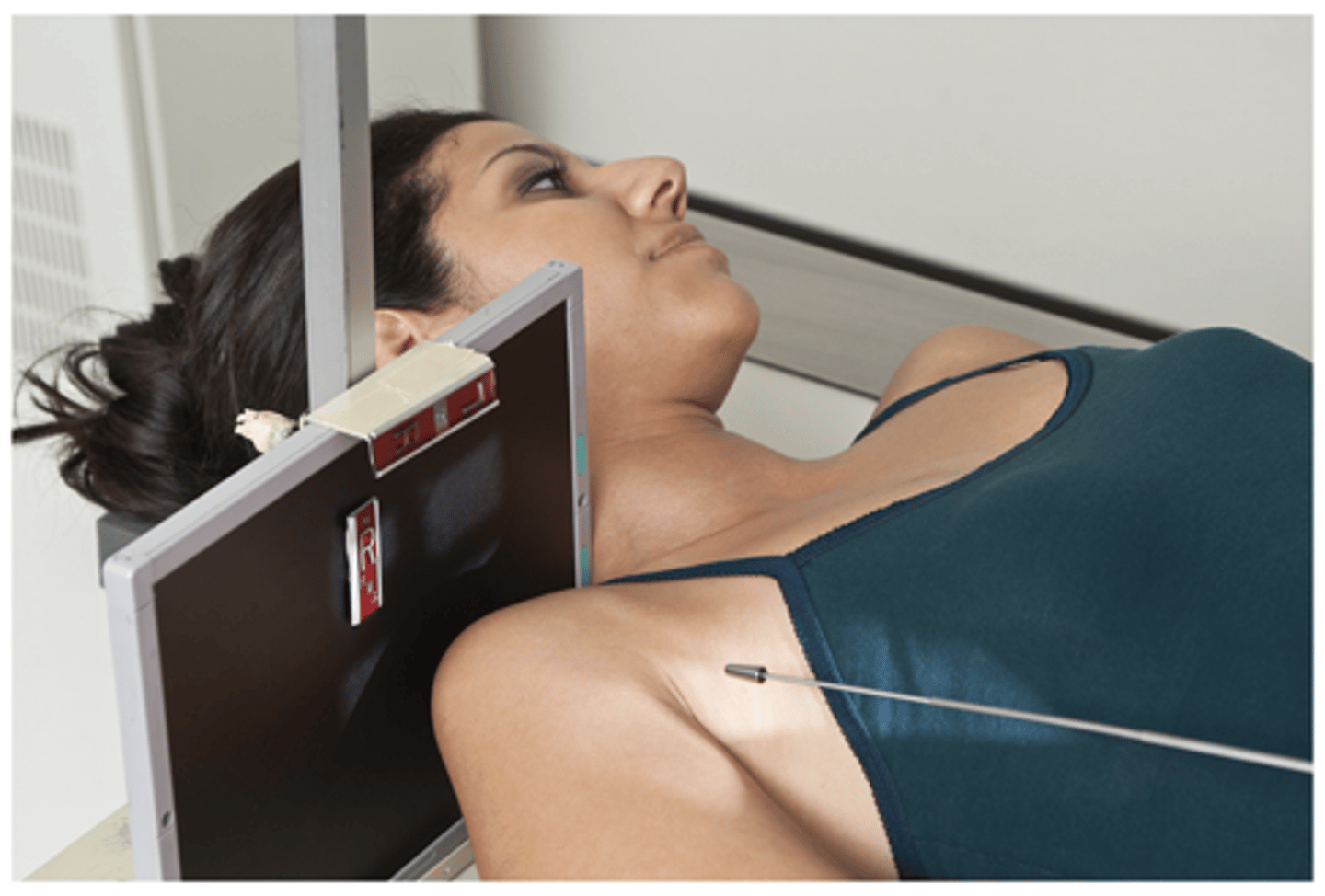
CR Shoulder - Tangential Projection Intertubercular Groove (Supine)
- CR 15° to 20° posterior to humerus
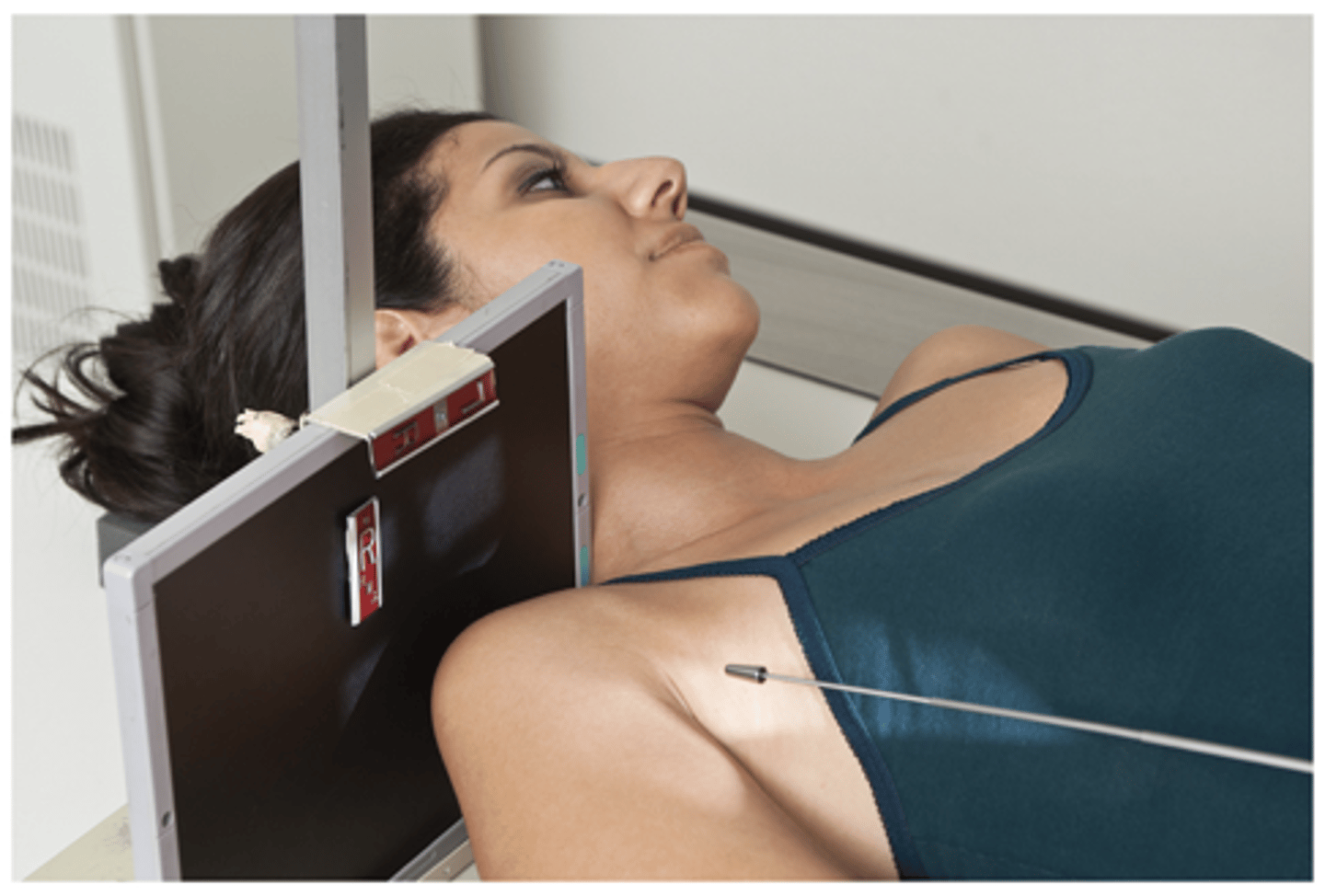
Evaluation Criteria Shoulder - Tangential Projection
- Anterior humeral head profiled
- Groove profiled between greater and lesser tubercles
- Optimal exposure factors
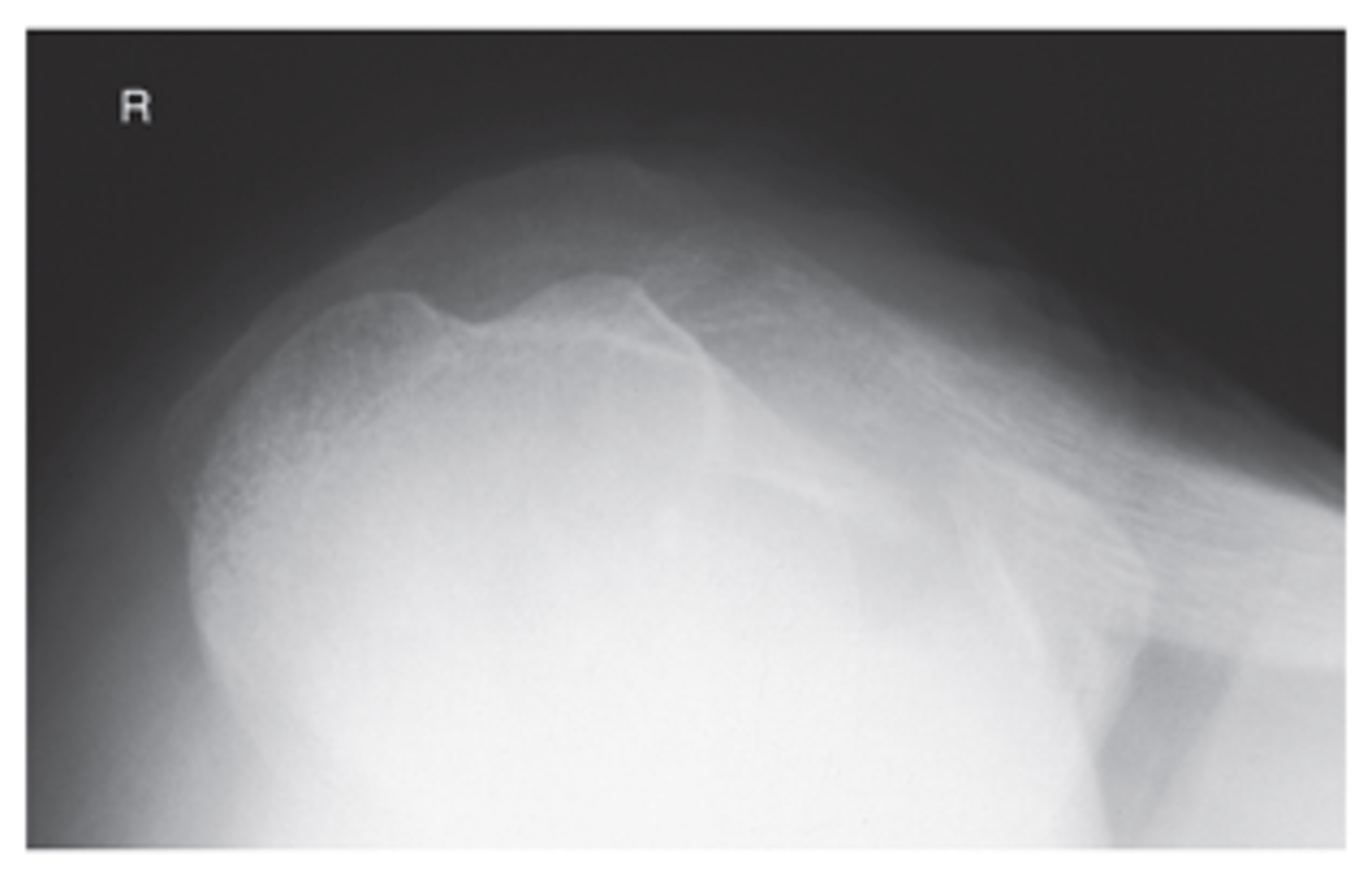
Trauma Shoulder Routine
- AP—neutral rotation
- Scapular Y
- Transthoracic lateral (if required)
AP Neutral Rotation
What projection is this?
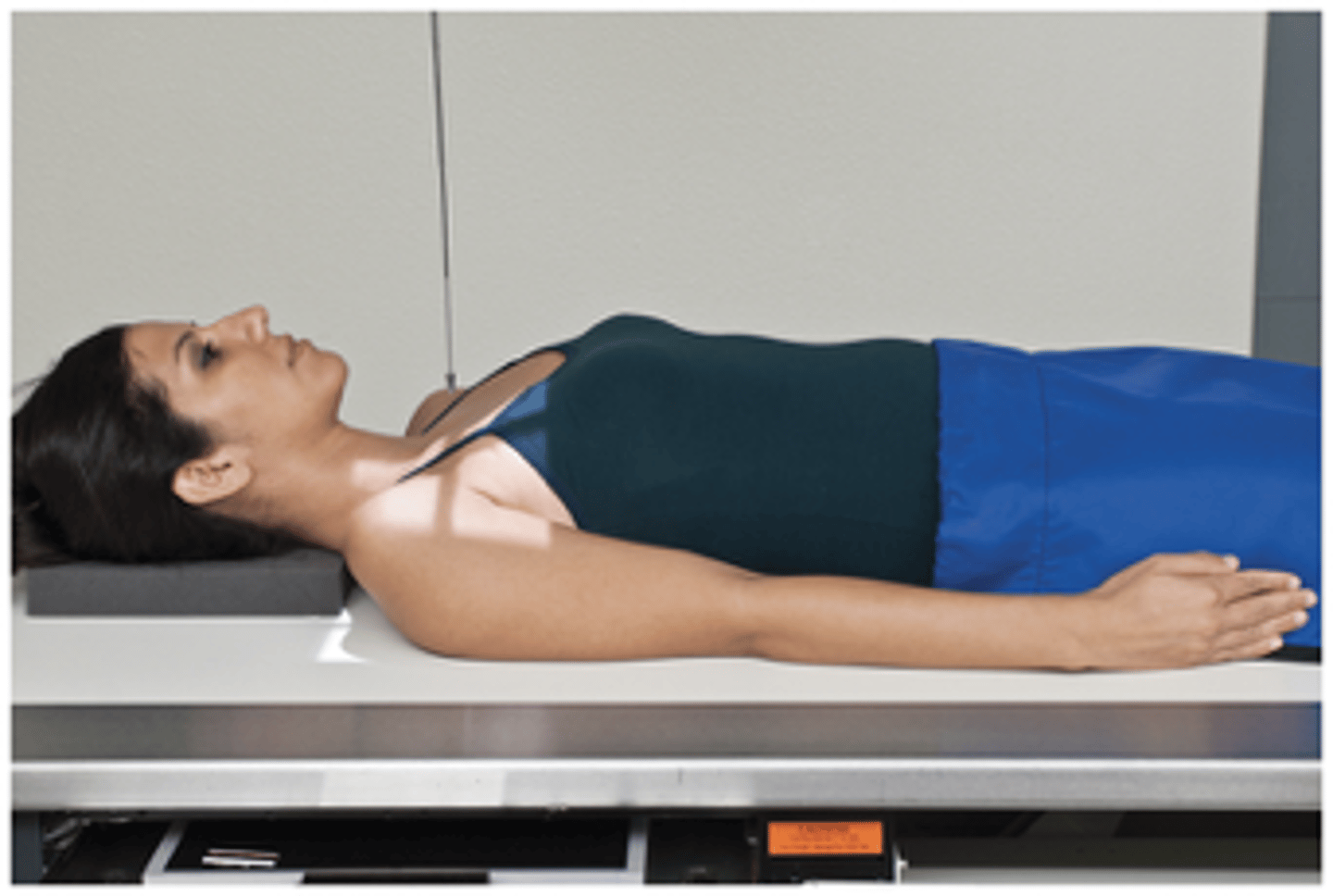
Evaluation Criteria for AP Neutral Rotation
- CR to scapulohumeral joint (¾ inch inferior and slightly lateral to coracoid process)
- Greater tubercle superimposed
- Scapulohumeral joint centered
- Optimal exposure factors
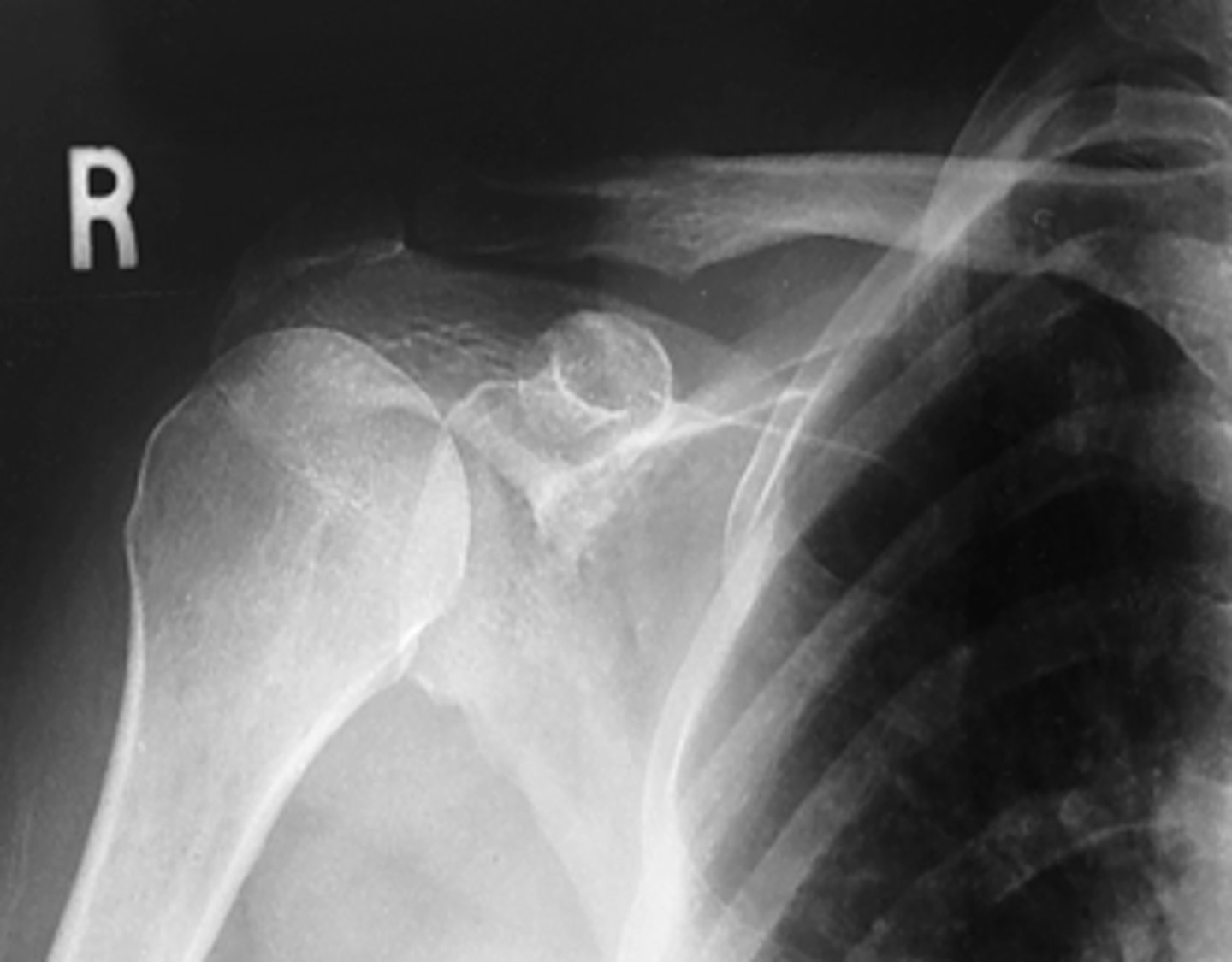
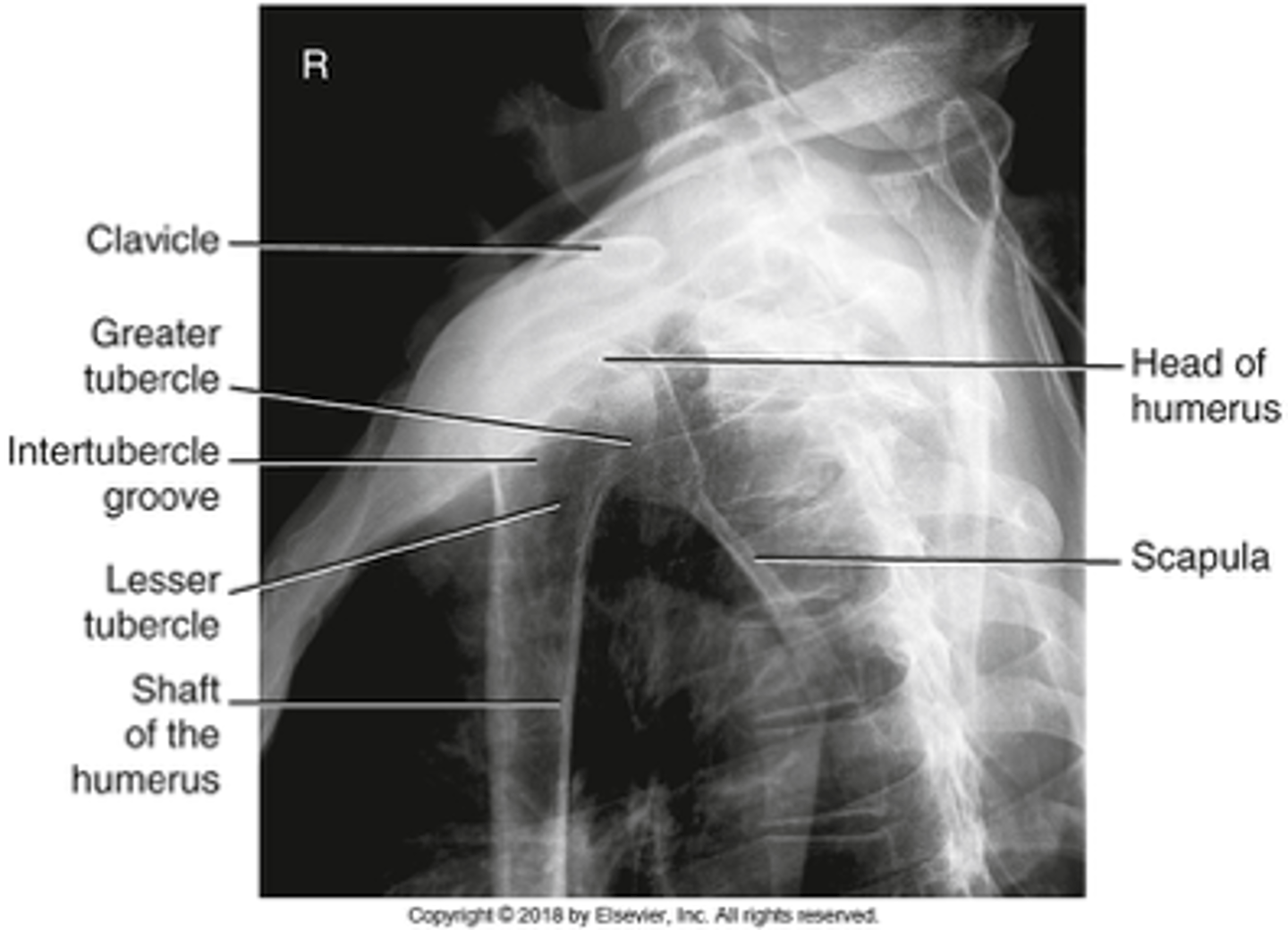
Transthoracic LateralProximal Humerus/Shoulder
What projection is this?
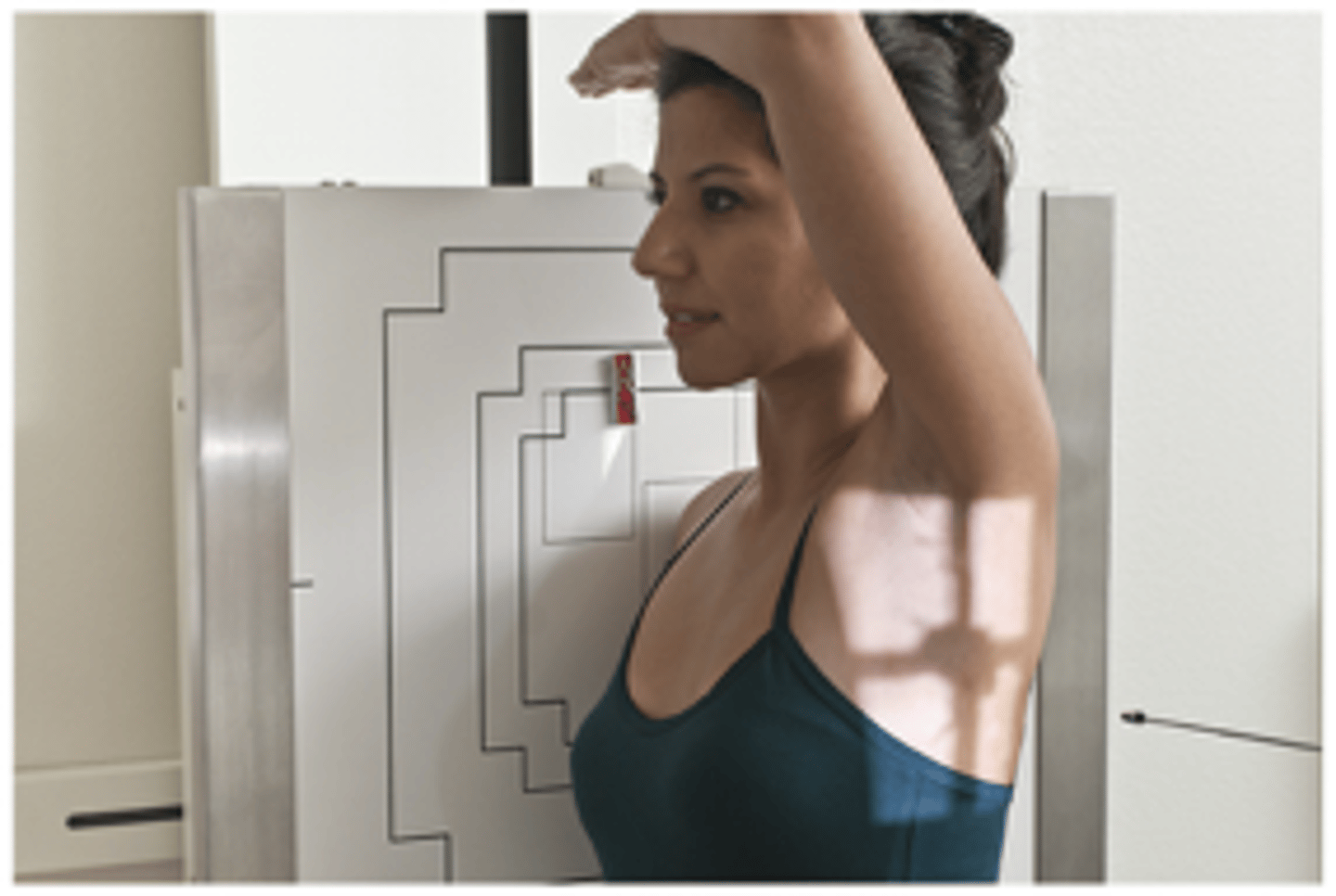

Evaluation Criteria for Transthoracic LateralProximal Humerus/Shoulder
- CR perpendicular to surgical neck
- Breathing technique
- Proximal humerus clearly seen
- Humeral head and glenoid cavity seen
- Humeral head in neutral rotation
- Optimal exposure factors
Scapular Y Lateral
What projection is this?
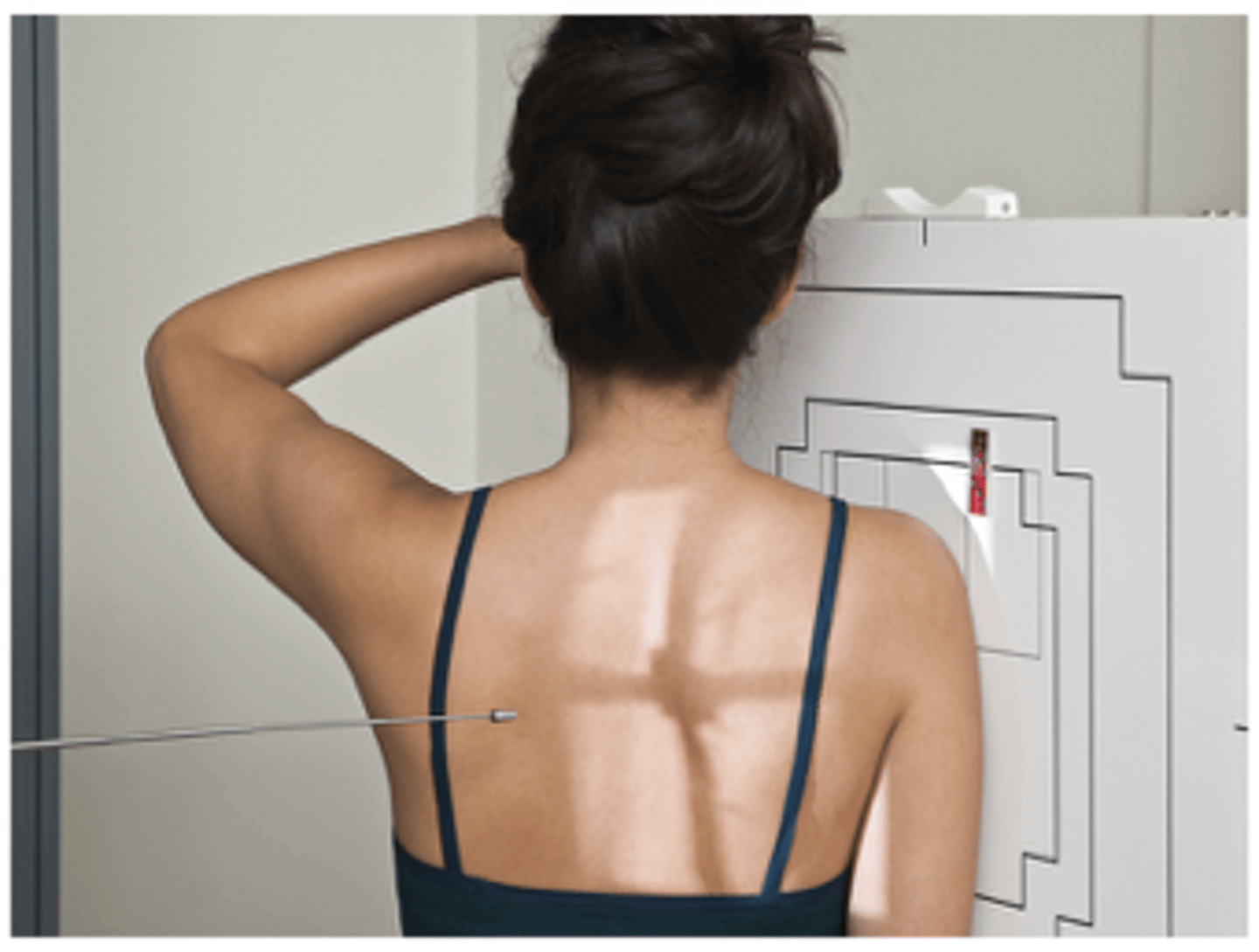
Evaluation Criteria for Scapular Y Lateral
- For lateral shoulder and proximal humerus
- CR to proximal humerus—2 inches (5 cm) below top of shoulder
- Body of scapula superimposed on end
- Acromion and coracoid processes in profile
- Humeral head and glenoid cavity superimposed
- Optimal exposure factors
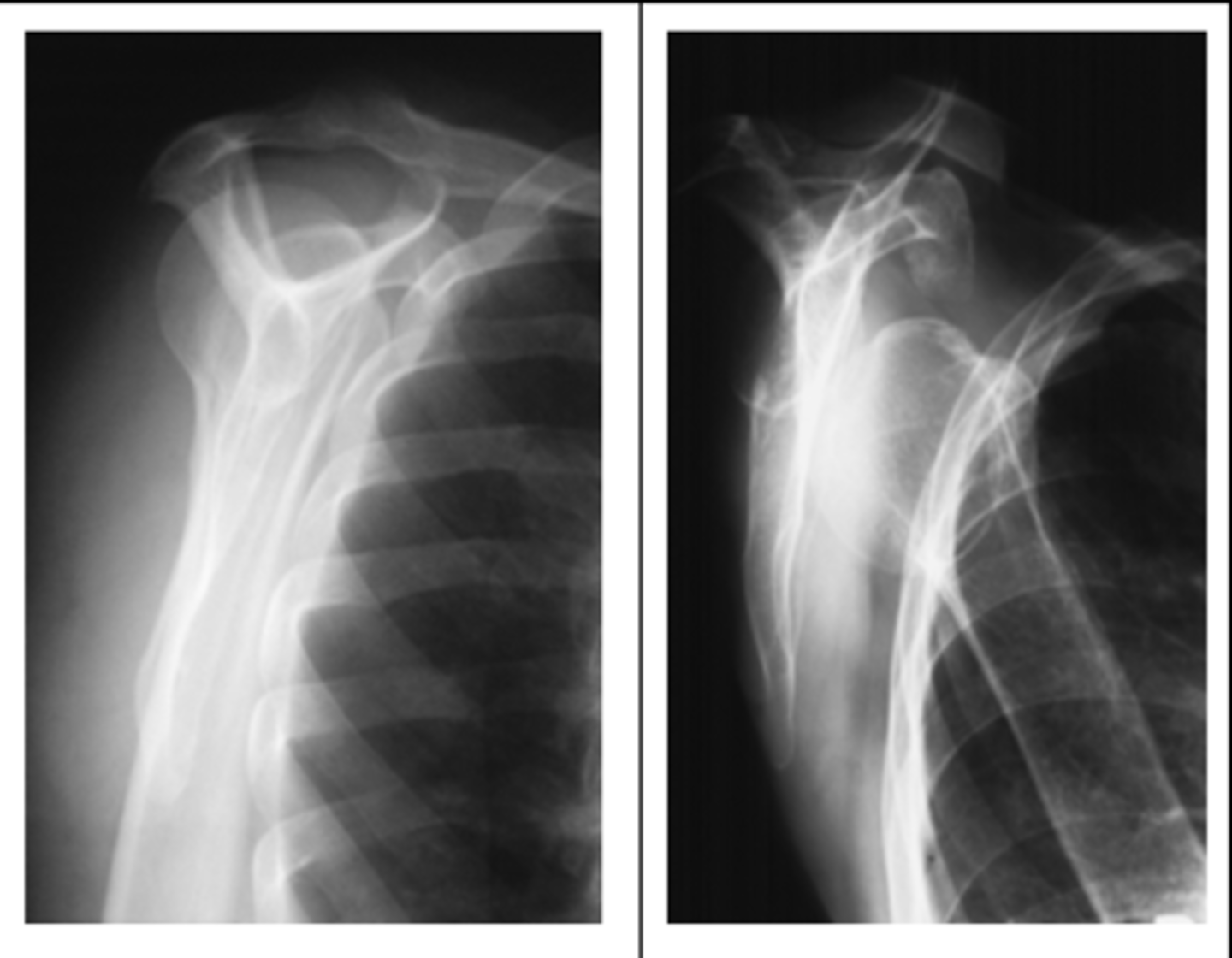
Outlet Projection (Neer Method)
What projection is this? (note: CR angle)
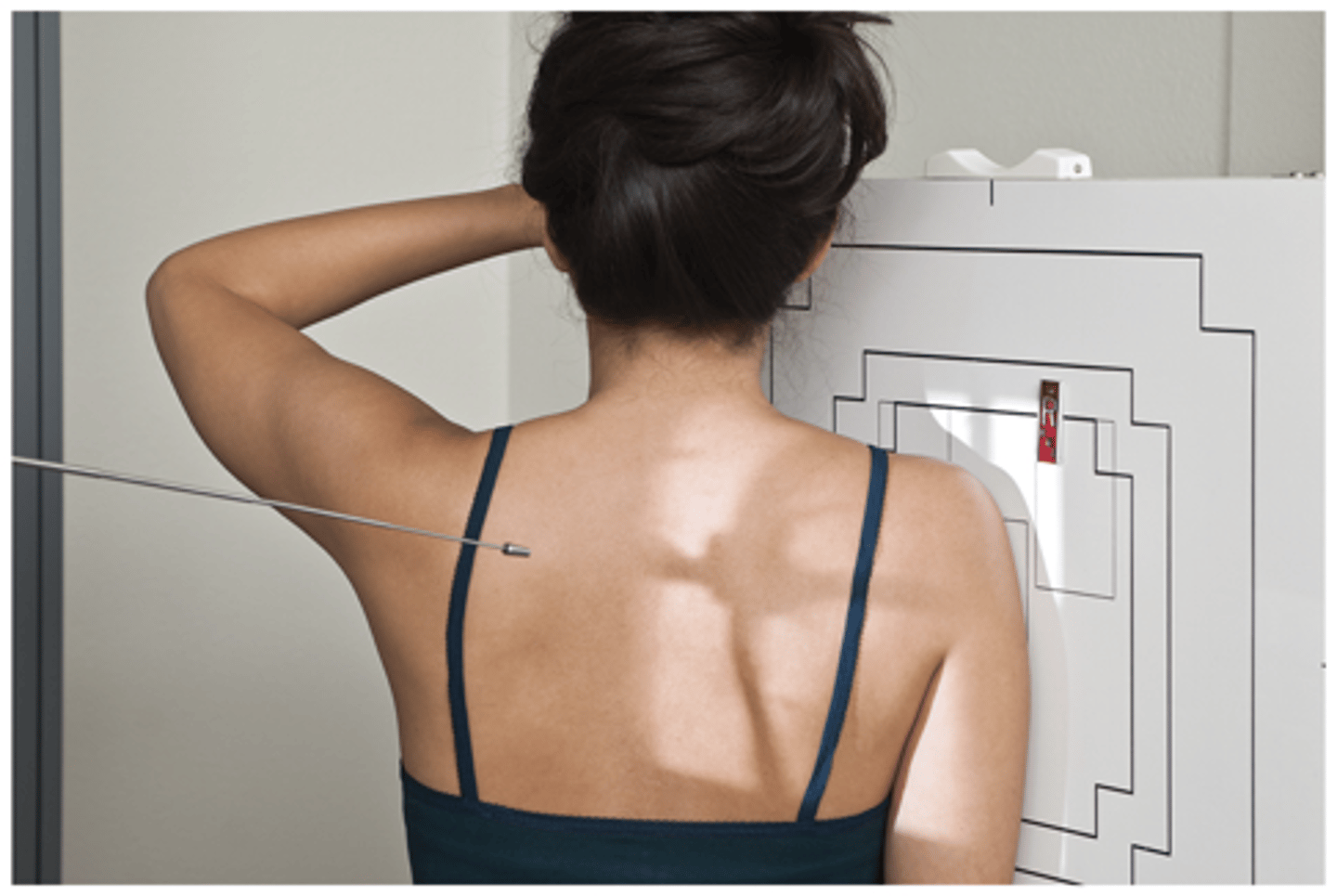
Evaluation Criteria for Outlet Projection (Neer Method)
- CR 10° to 15° caudad
- Supraspinatus outlet open and in profile
- Demonstrates coracoacromial arch
- Optimal exposure factors