Rules of Metabolic Reactions
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Last updated 9:28 PM on 11/28/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
potential energy
The change in ________ occurs because the new bonds formed in the products are much stronger than those in ATP.
2
New cards
kinetic energy
An increase in temperature will raise the average ________ of the reactant molecules.
3
New cards
Temperature
________: An increase in ________ typically increases the rate of reaction.
4
New cards
Surface area
________: Large surface area helps more reactant molecules to undergo reaction at the same time to convert into the product, as the number of molecules undergoing reaction at the same time increases, the rate of reaction increases.
5
New cards
positive ΔG
A(n) ________ indicates that the reaction is endergonic, or that it requires energy to go from reactants to products.
6
New cards
substrate concentration
Increasing ________ also increases the rate of reaction to a certain point.
7
New cards
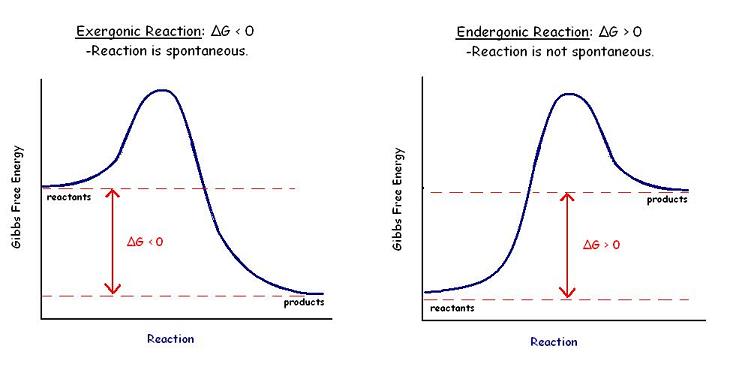
Gibbs free energy graph
The ________ shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-- whether it is exergonic or endergonic.
8
New cards
ATP hydrolysis
________ is exergonic because the entropy of the product molecules is higher than that of the reactants, and because there is a large drop in potential energy when ATP is hydrolyzed to form ADP and Pi.
9
New cards
Concentration
________: Increasing the ________ of one or more reactants will often increase the rate of reaction.
10
New cards
Temperature
An increase in temperature typically increases the rate of reaction
11
New cards
Concentration
Increasing the concentration of one or more reactants will often increase the rate of reaction
12
New cards
Surface area
Large surface area helps more reactant molecules to undergo reaction at the same time to convert into the product, as the number of molecules undergoing reaction at the same time increases, the rate of reaction increases
13
New cards
The Gibbs free energy graph shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-
whether it is exergonic or endergonic
14
New cards
potential energy
The change in ________ occurs because the new bonds formed in the products are much stronger than those in ATP.
15
New cards
kinetic energy
An increase in temperature will raise the average ________ of the reactant molecules.
16
New cards
Temperature
________: An increase in ________ typically increases the rate of reaction.
17
New cards
Surface area
________: Large surface area helps more reactant molecules to undergo reaction at the same time to convert into the product, as the number of molecules undergoing reaction at the same time increases, the rate of reaction increases.
18
New cards
positive ΔG
A(n) ________ indicates that the reaction is endergonic, or that it requires energy to go from reactants to products.
19
New cards
substrate concentration
Increasing ________ also increases the rate of reaction to a certain point.
20
New cards
Gibbs free energy graph
The ________ shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-- whether it is exergonic or endergonic.
21
New cards
ATP hydrolysis
________ is exergonic because the entropy of the product molecules is higher than that of the reactants, and because there is a large drop in potential energy when ATP is hydrolyzed to form ADP and Pi.
22
New cards
Concentration
________: Increasing the ________ of one or more reactants will often increase the rate of reaction.
23
New cards
Temperature
An increase in temperature typically increases the rate of reaction
24
New cards
Concentration
Increasing the concentration of one or more reactants will often increase the rate of reaction
25
New cards
Surface area
Large surface area helps more reactant molecules to undergo reaction at the same time to convert into the product, as the number of molecules undergoing reaction at the same time increases, the rate of reaction increases
26
New cards
The Gibbs free energy graph shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-
whether it is exergonic or endergonic
27
New cards
potential energy
The change in ________ occurs because the new bonds formed in the products are much stronger than those in ATP.
28
New cards
kinetic energy
An increase in temperature will raise the average ________ of the reactant molecules.
29
New cards
Temperature
________: An increase in ________ typically increases the rate of reaction.
30
New cards
Surface area
________: Large surface area helps more reactant molecules to undergo reaction at the same time to convert into the product, as the number of molecules undergoing reaction at the same time increases, the rate of reaction increases.
31
New cards
How does substrate concentration impact the rate of reaction?
Increasing ________ also increases the rate of reaction to a certain point.
32
New cards
Gibbs free energy graph
The ________ shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-- whether it is exergonic or endergonic.
33
New cards
How is ATP hydrolysis exergonic?
________ is exergonic because the entropy of the product molecules is higher than that of the reactants, and because there is a large drop in potential energy when ATP is hydrolyzed to form ADP and Pi.
34
New cards
How does Concentration affect the rate of reaction?
________: Increasing the ________ of one or more reactants will often increase the rate of reaction.
35
New cards
Temperature
An increase in temperature typically increases the rate of reaction
36
New cards
Concentration
Increasing the concentration of one or more reactants will often increase the rate of reaction
37
New cards
Surface area
Large surface area helps more reactant molecules to undergo reaction at the same time to convert into the product, as the number of molecules undergoing reaction at the same time increases, the rate of reaction increases
38
New cards
The Gibbs free energy graph shows whether or not a reaction is spontaneous-
whether it is exergonic or endergonic
39
New cards
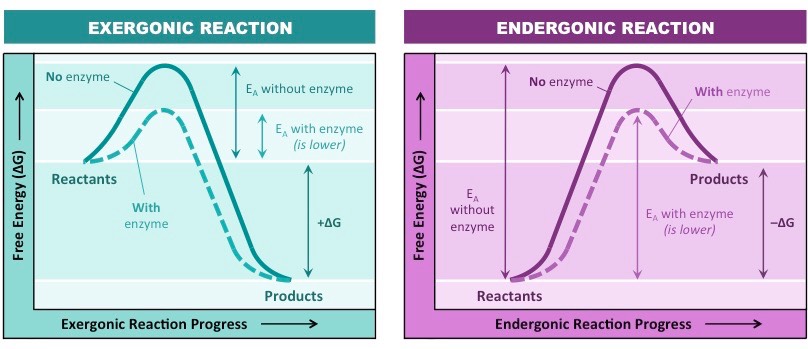
Exergonic And Energonic Reaction
Therefore, if the reaction goes from higher free energy to lower free energy, there will be a negative ΔG, and the reaction will be spontaneous. A positive ΔG indicates that the reaction is endergonic, or that it requires energy to go from reactants to products.