DTHY 186: Introduction to Terms
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Perm dentition
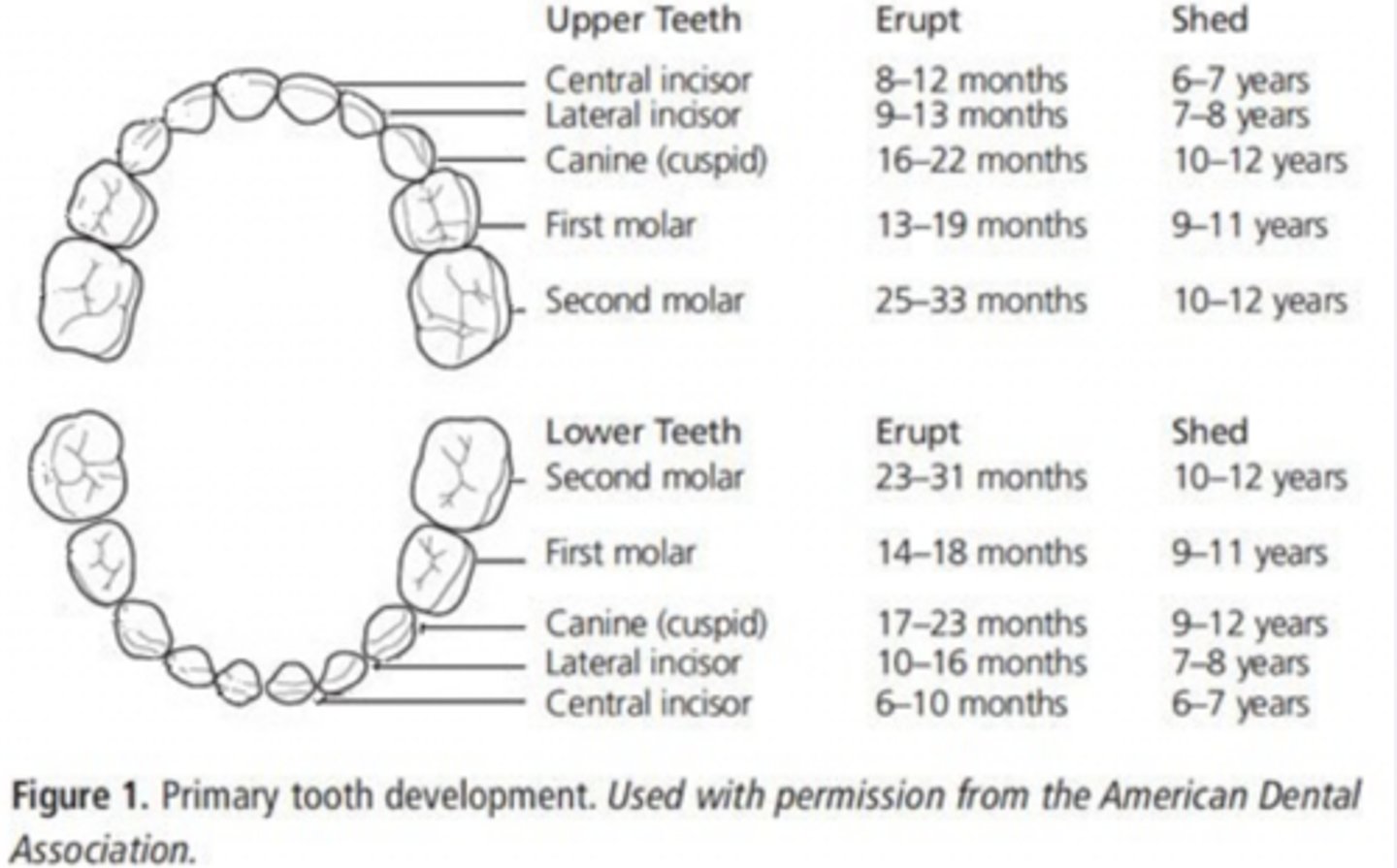
Primary (decduous) dentition
Canines are...
...The corner stones of the mouth
Arch straits of Mand. and Max. primary teeth
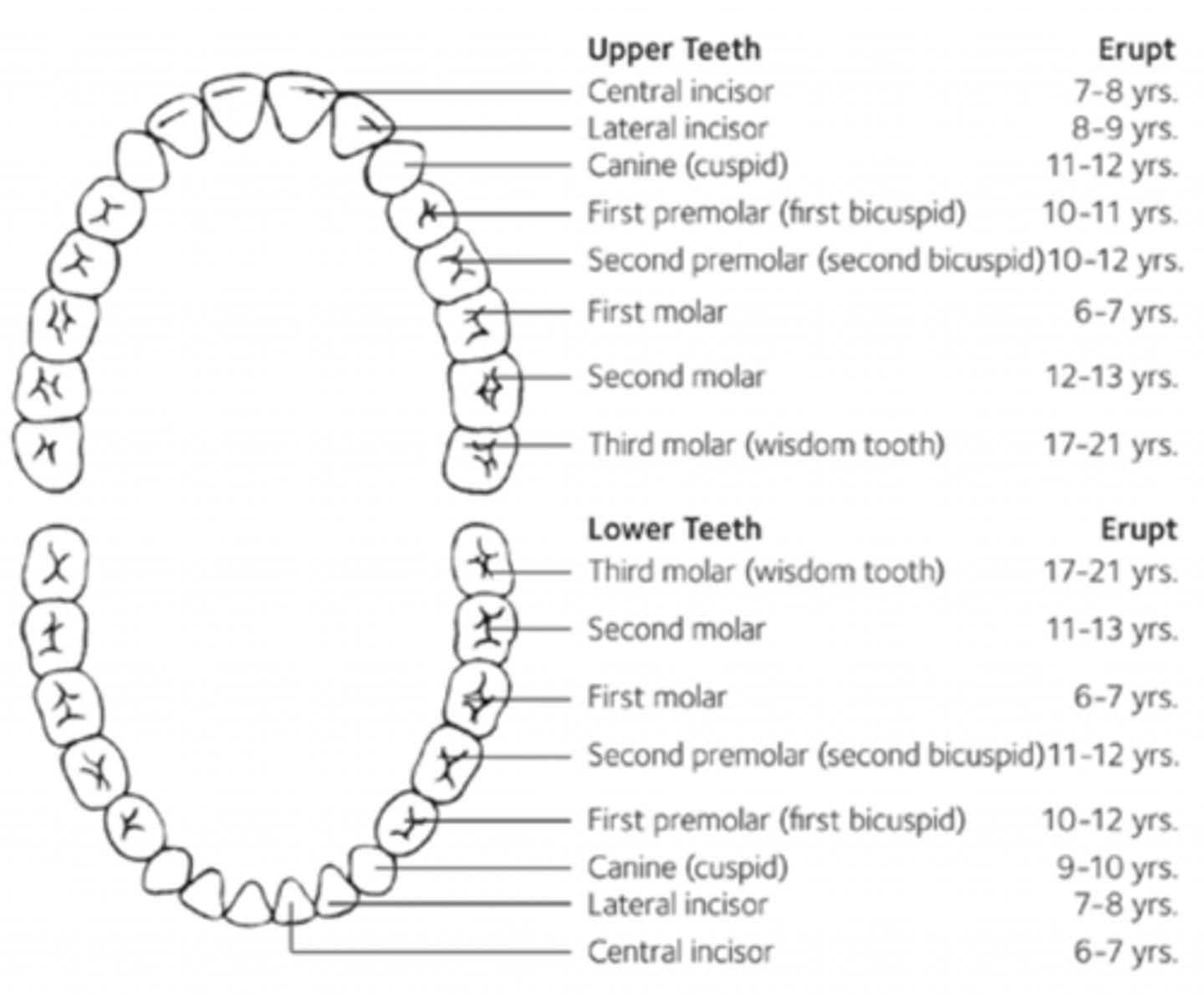
Arch traits of Mand. and Max permanent teeth
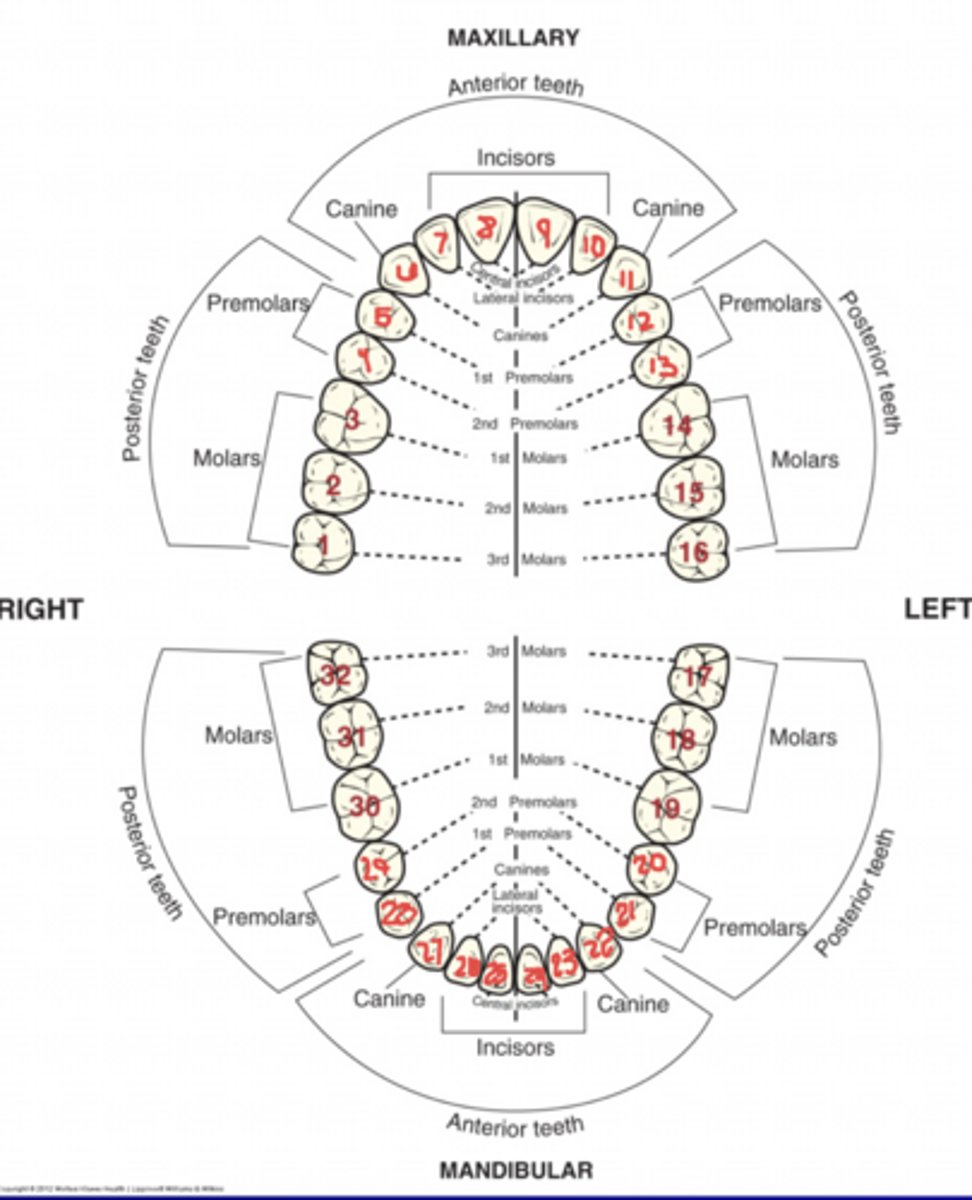
IMPORTANT= How to name tooth
1. Arch= Max. or Mand.
2. Quadrent= Right or left
3. Type of tooth= Cen., la., 1st, 2nd, 3rd
4. Class of tooth= incisor, canine, premolar, or molar
4 Class Traits
Incisors (central or lateral), canines, premolars, and molars
Universal Numbering System
WHAT WE USE
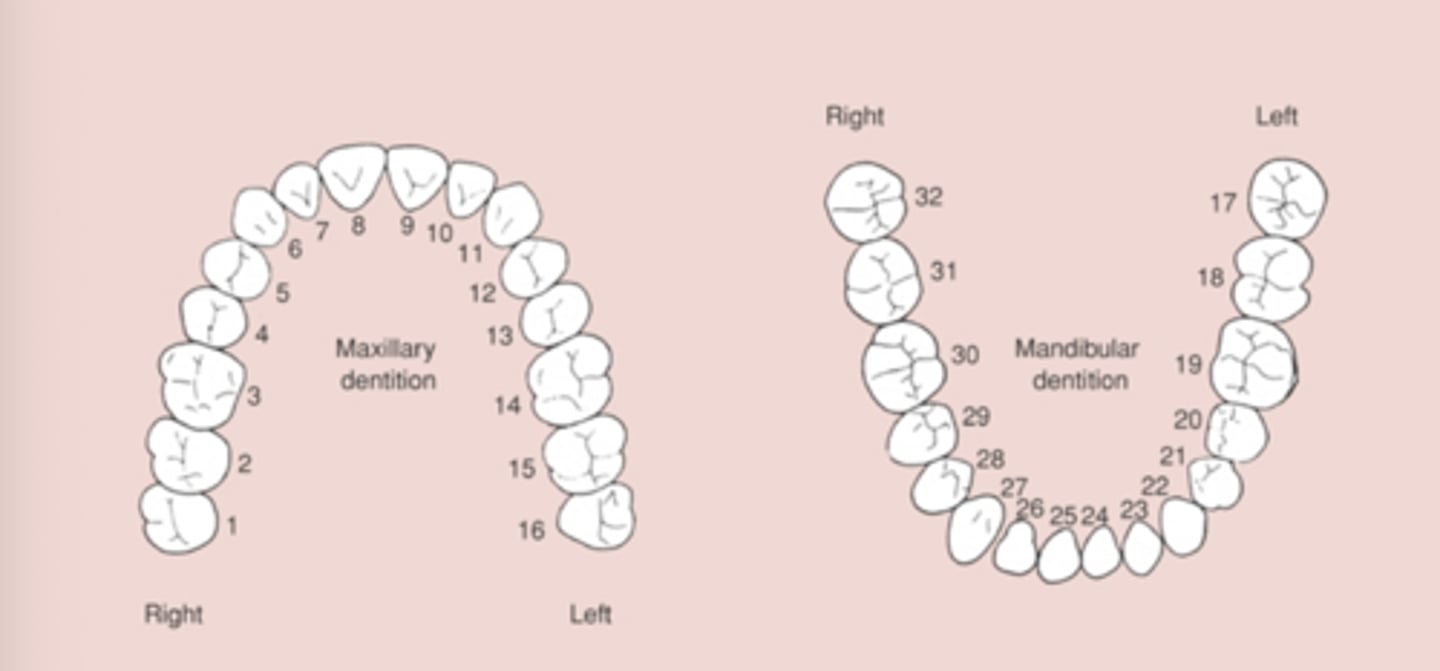
Universal Numbering System Perm Dentition
MAX = #1-16
Mand = #17-32
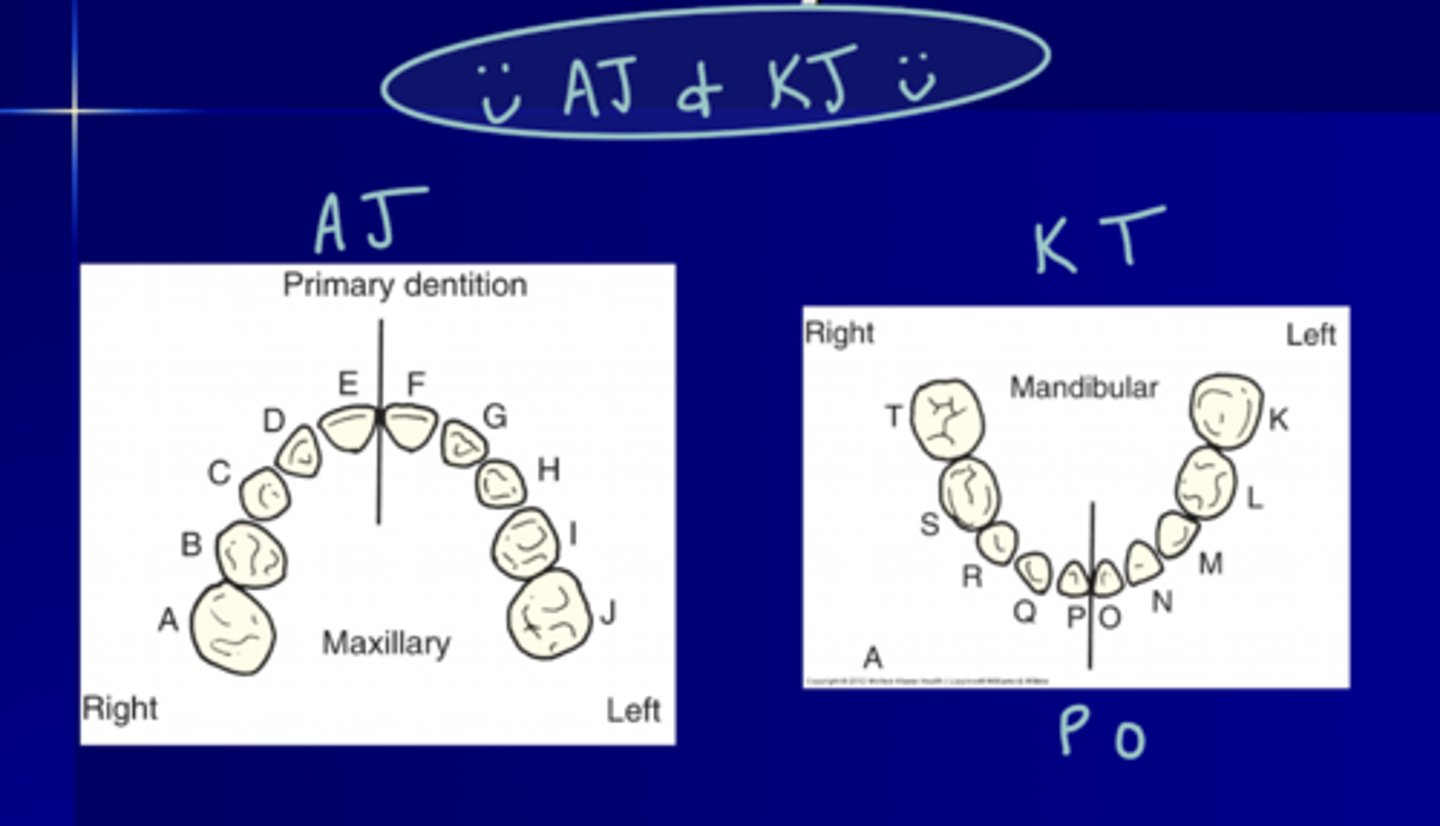
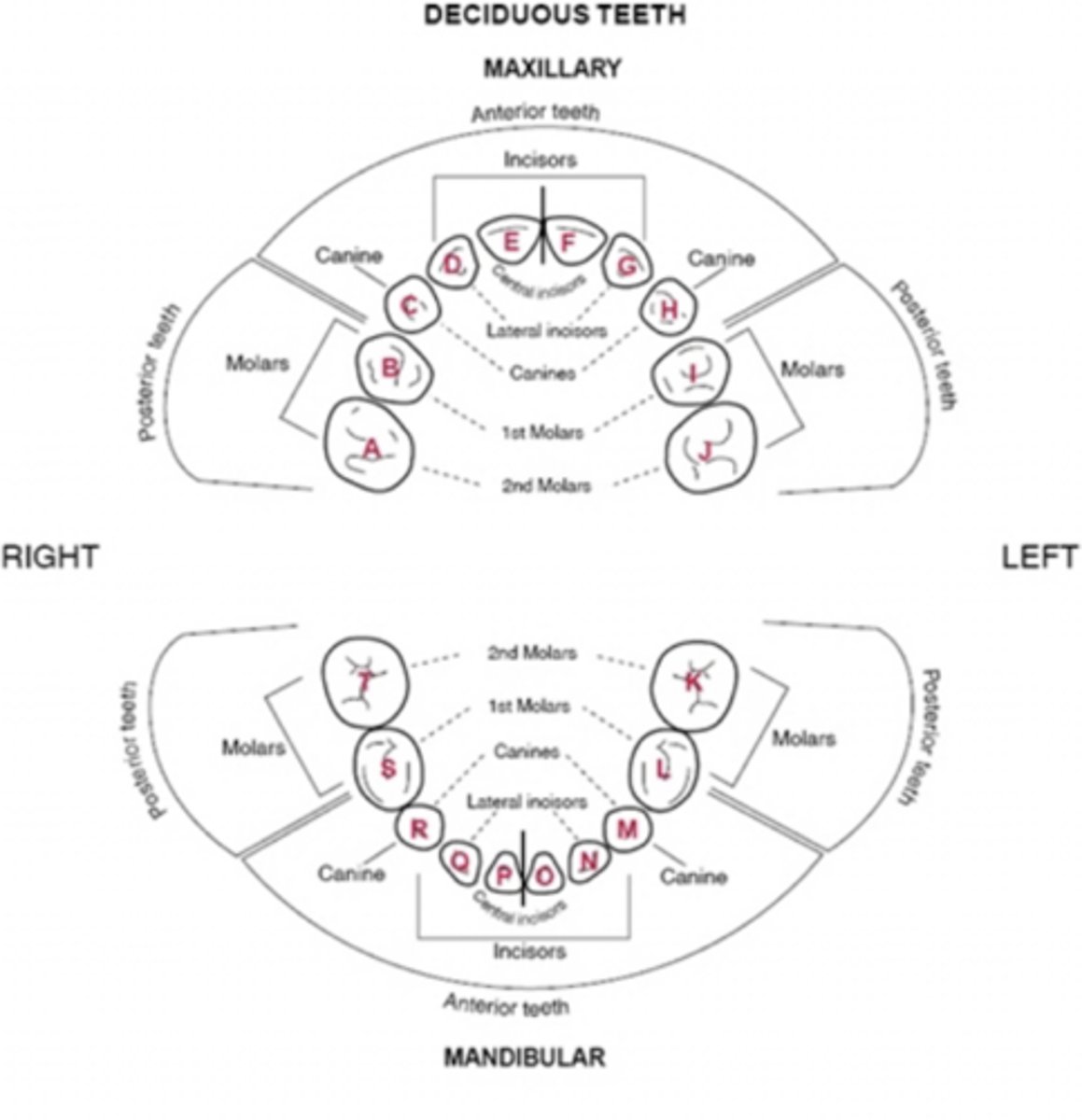
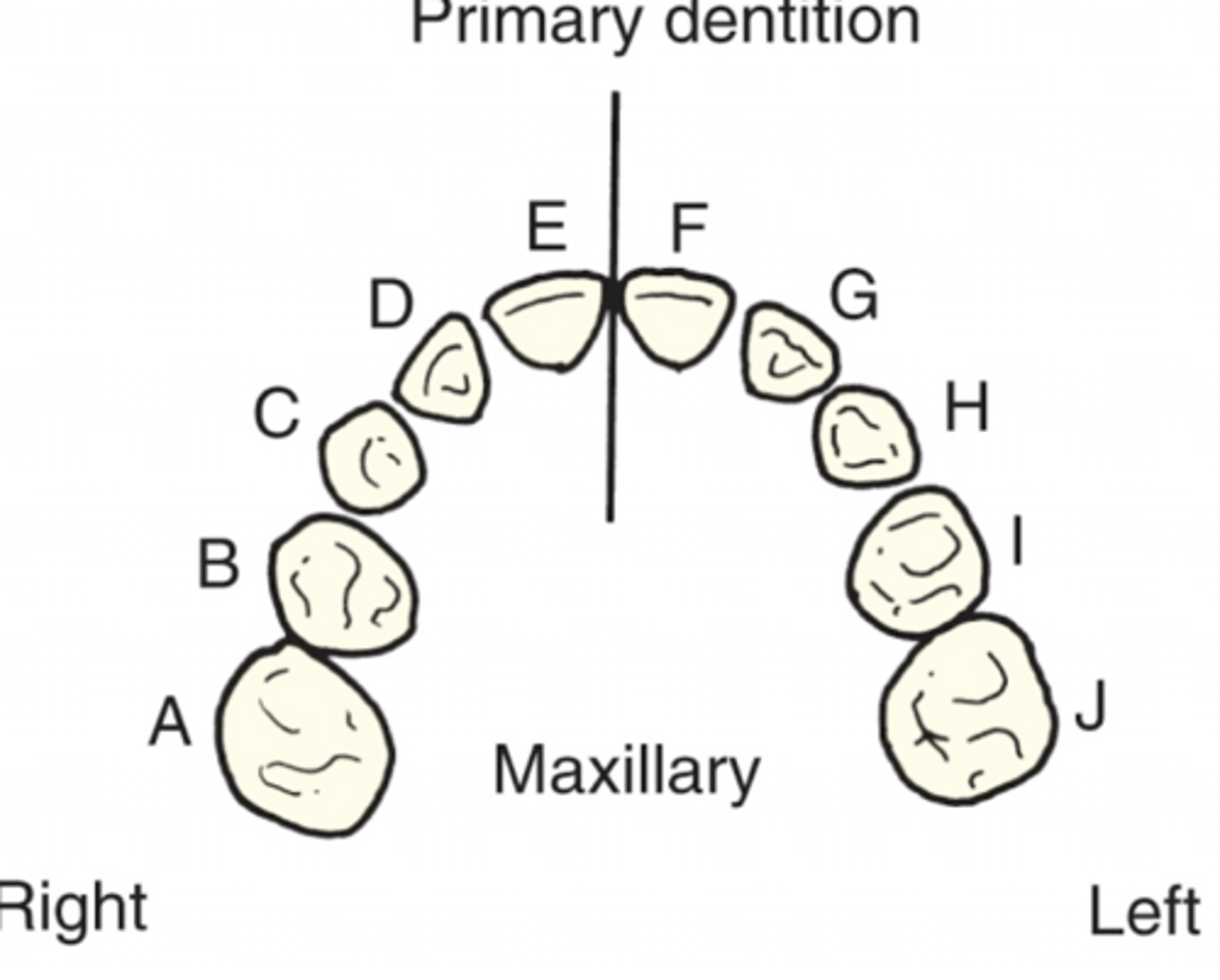
Universal Numbering System Primary Dentition
MAX = A-J
MAND = K-T
3rd molars
#1, #16, #17, and #32
Centrals
#8, #9, #24, and #25
1st Molars
#3, #14, #19, #30
1st PreMolars
#5, #12, #21, and #28
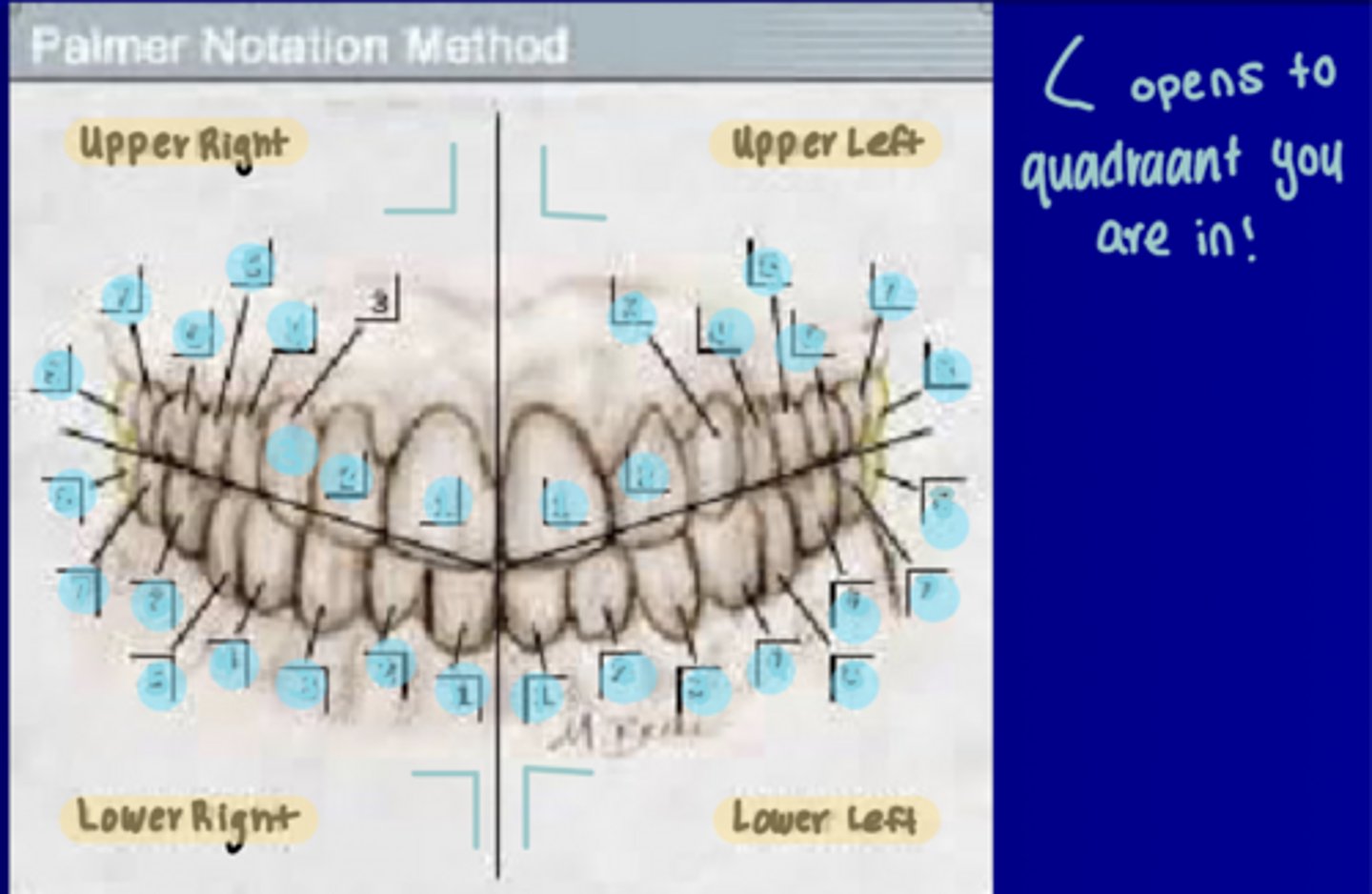
Palmer Numbering System for Permanet and Primary Dentition
Uses quadrants 1-4 UR to LR and numbers #1-8 starting at midline and numbers are in brackets
FDI Numbering System for Permanent Dentition
- Uses quadrants 1-4 UR to LR and numbers #1-8 starting at midline
- Numbers are boxed, first number is the quadrant tooth is in and the second is the number tooth (1-8 starting at midline)
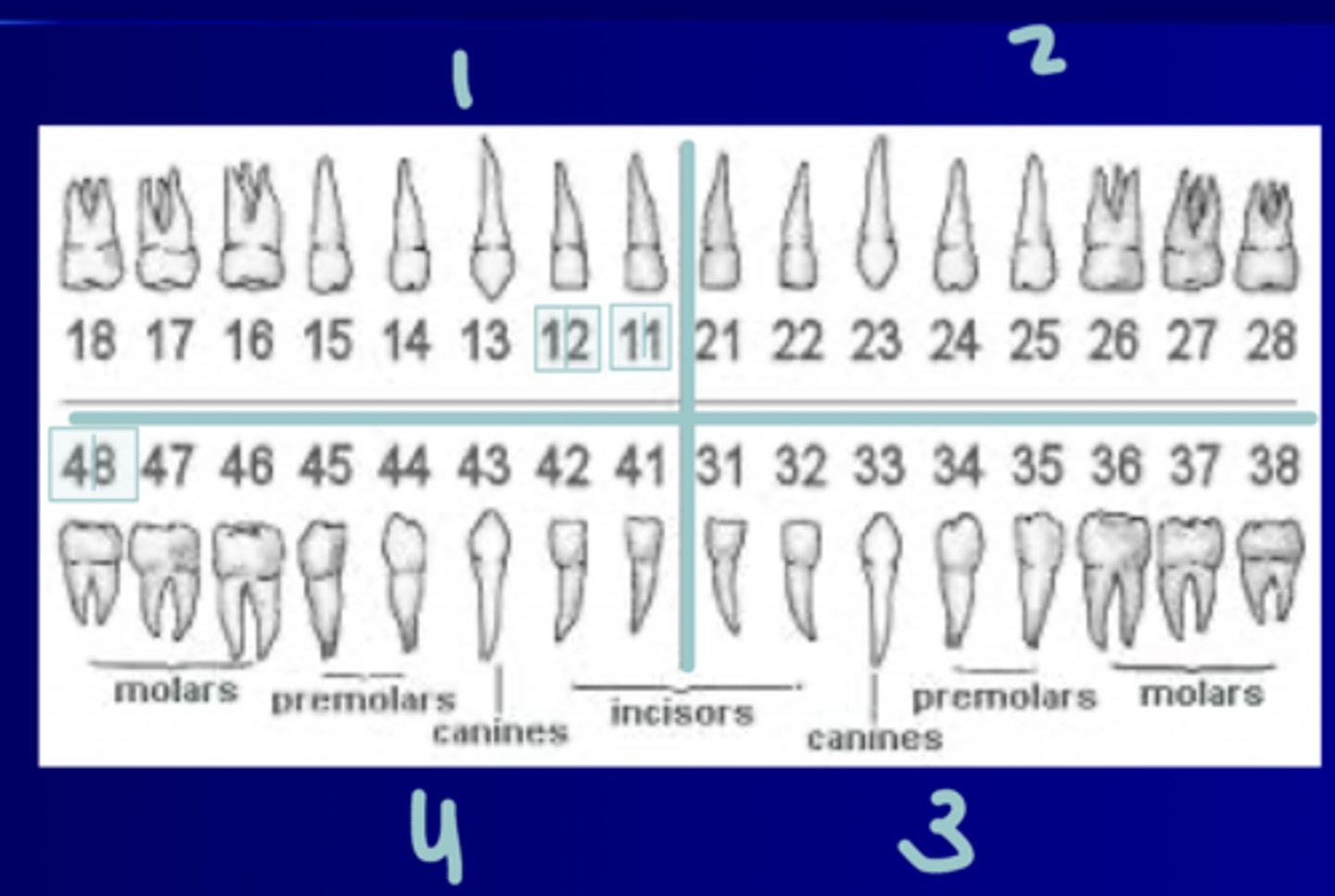
FDI Numbering System for Primary Dentition
- Uses quadrants #5-8 UR to LR and numbers #1-5 starting at midline
- Numbers are boxed, first number is the quadrant tooth is in and the second is the number tooth (1-5 starting at midline)
Terminology used to describe tooth
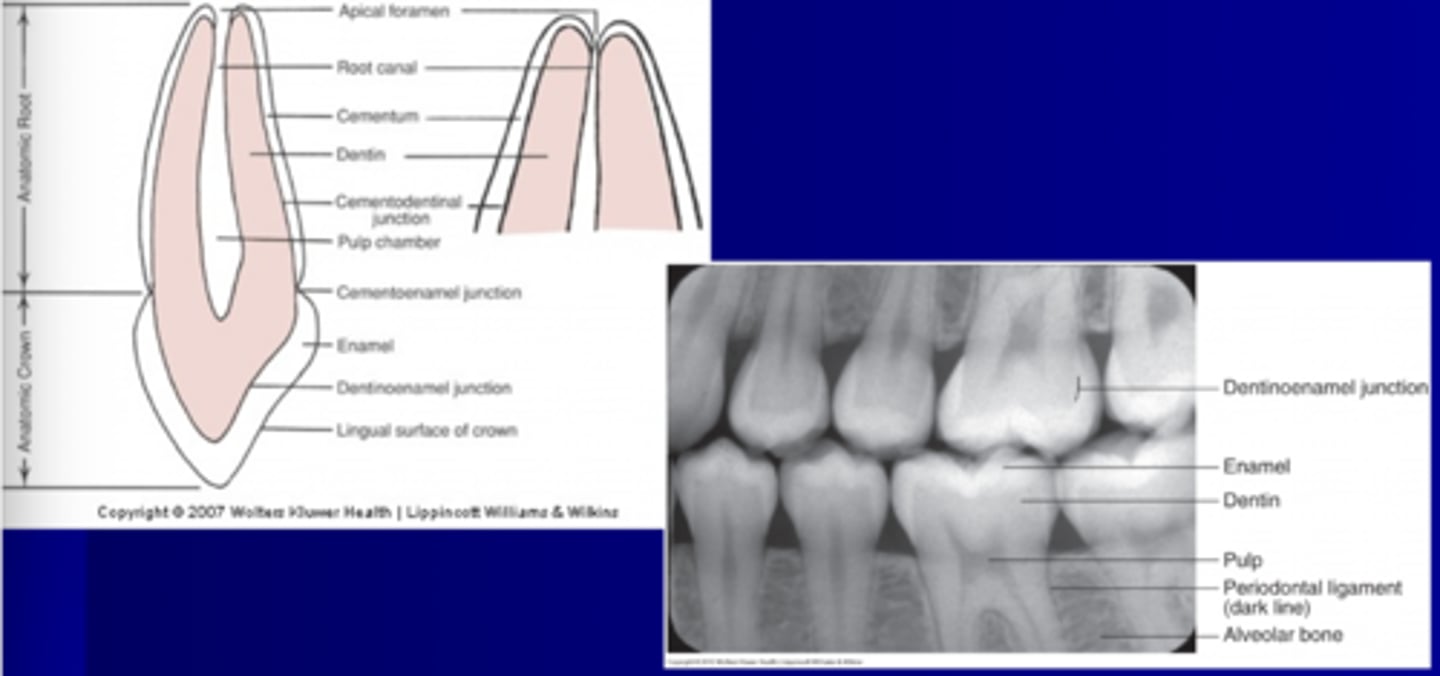
Relative positions
- Mesial, Distal
- Facial, Lingual
- Apical
- Occlusal, Incisal
- Cervical
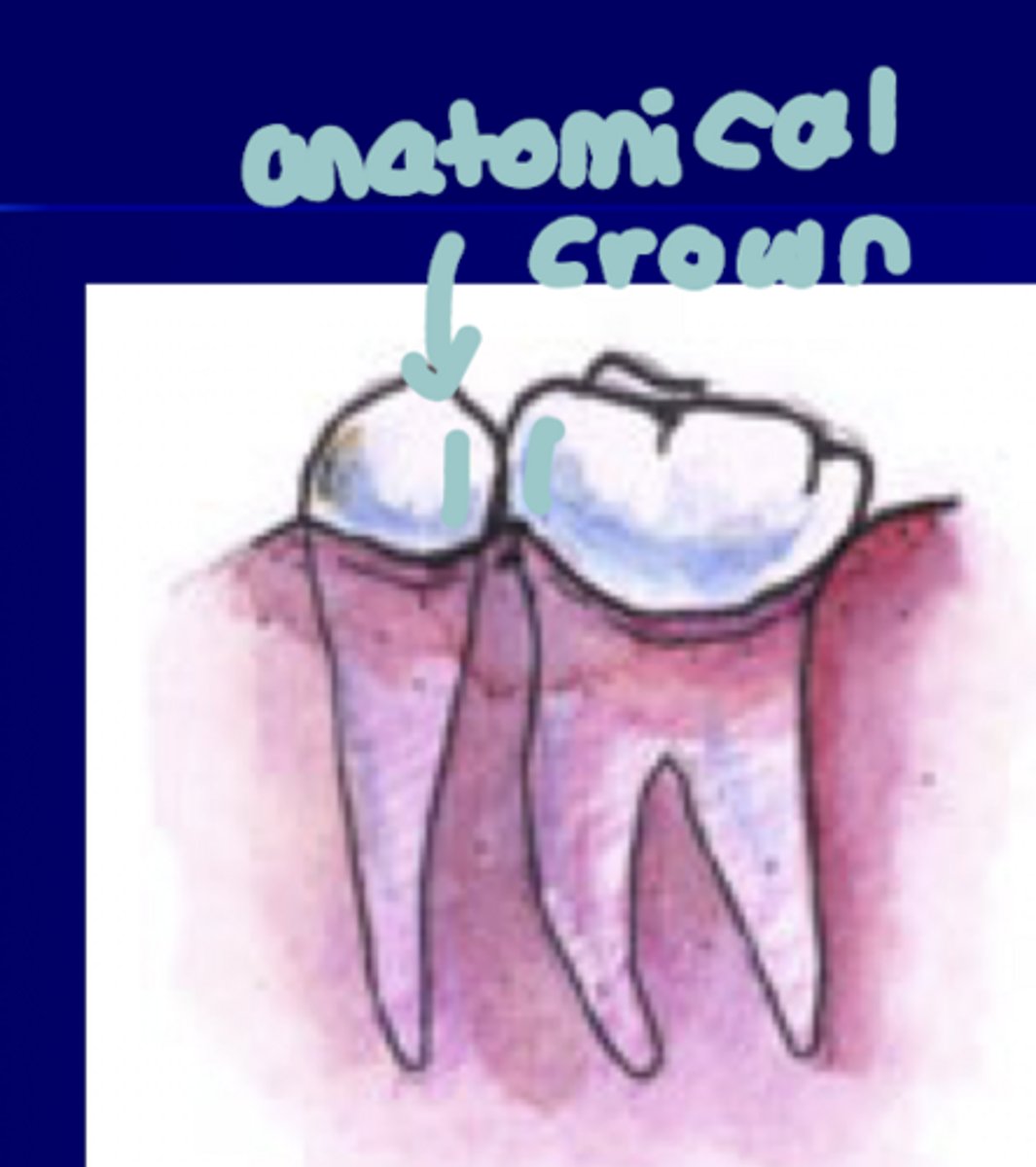
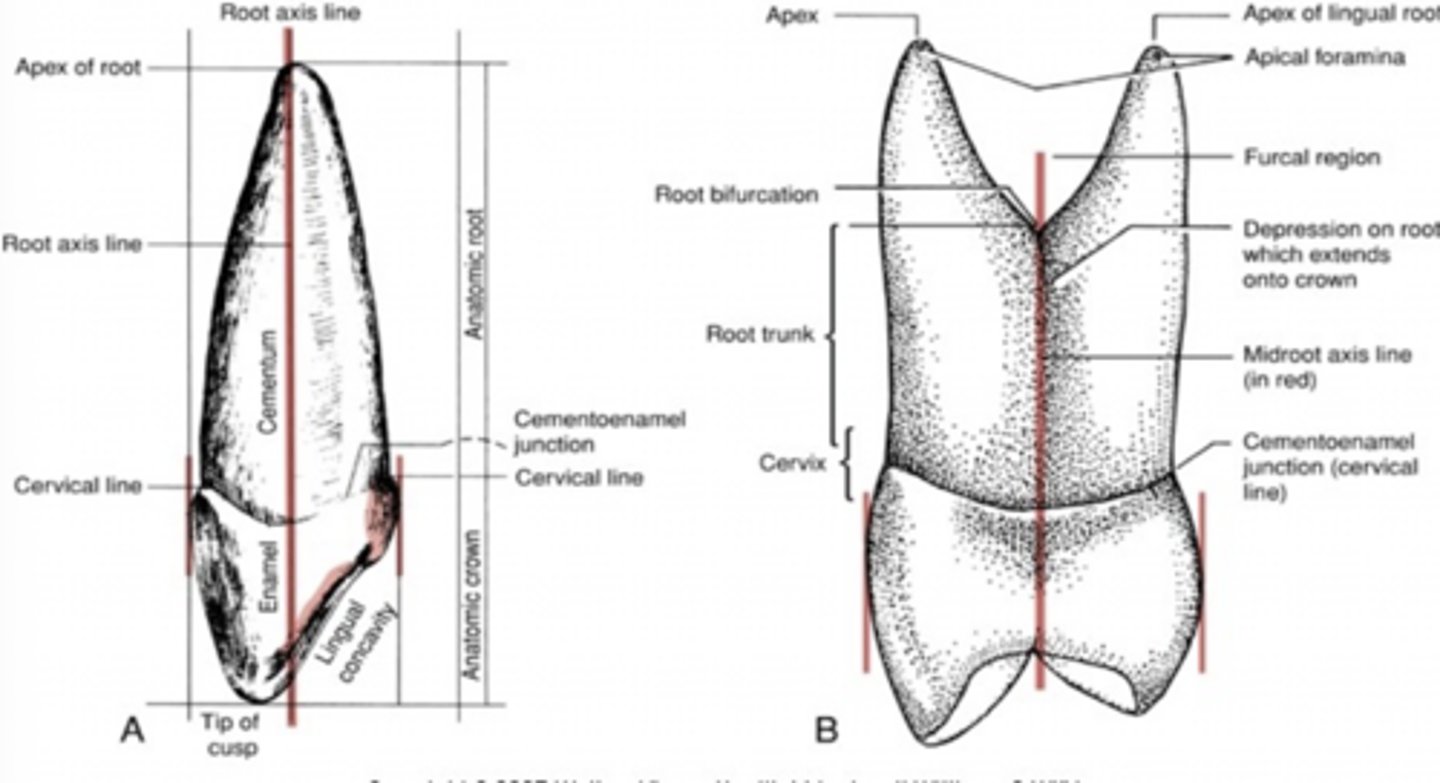
Clinical Crown
Whats seen, everything
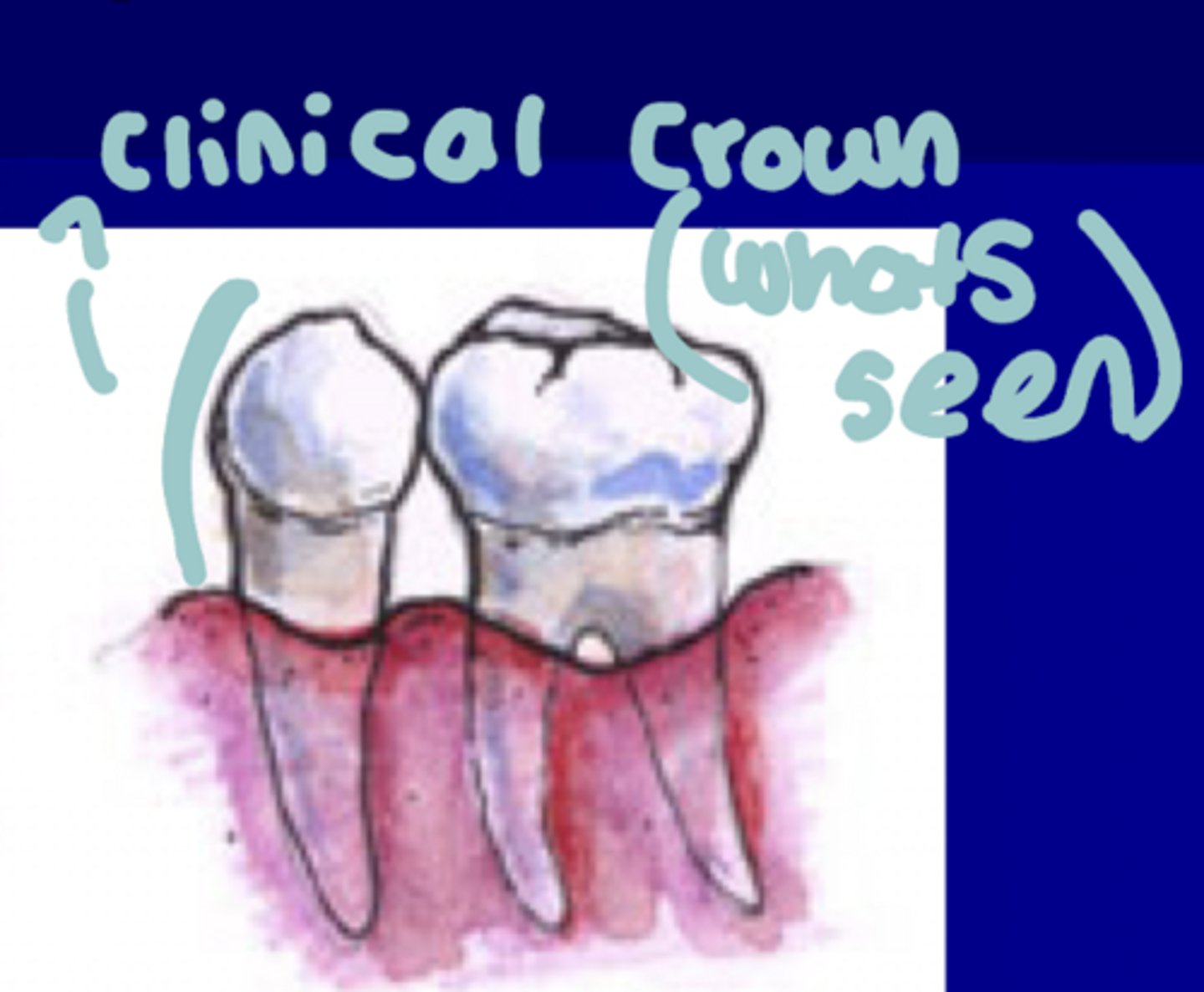
Clinical Root
DOES not show
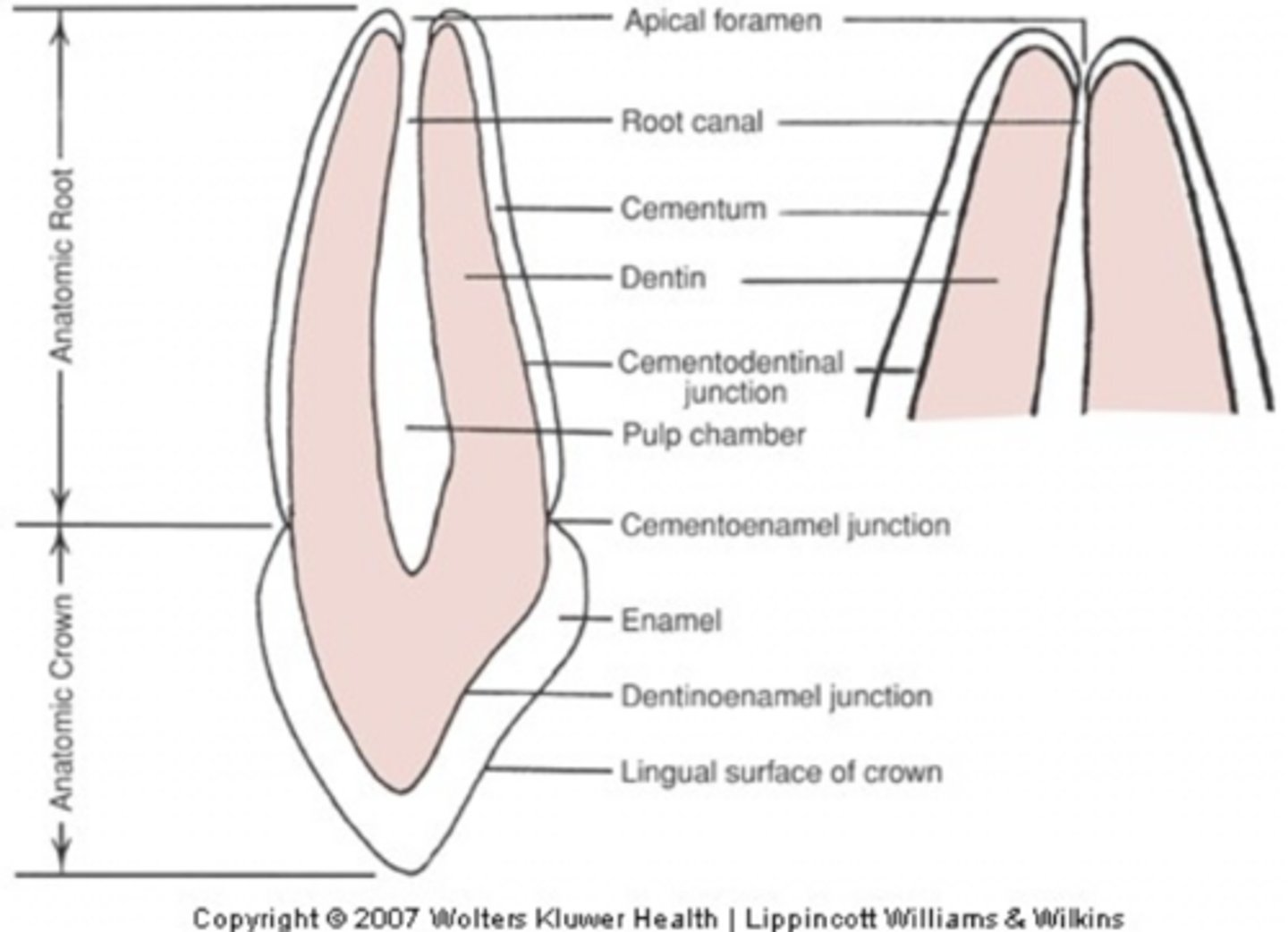
Anatomical root
Covered in cementum
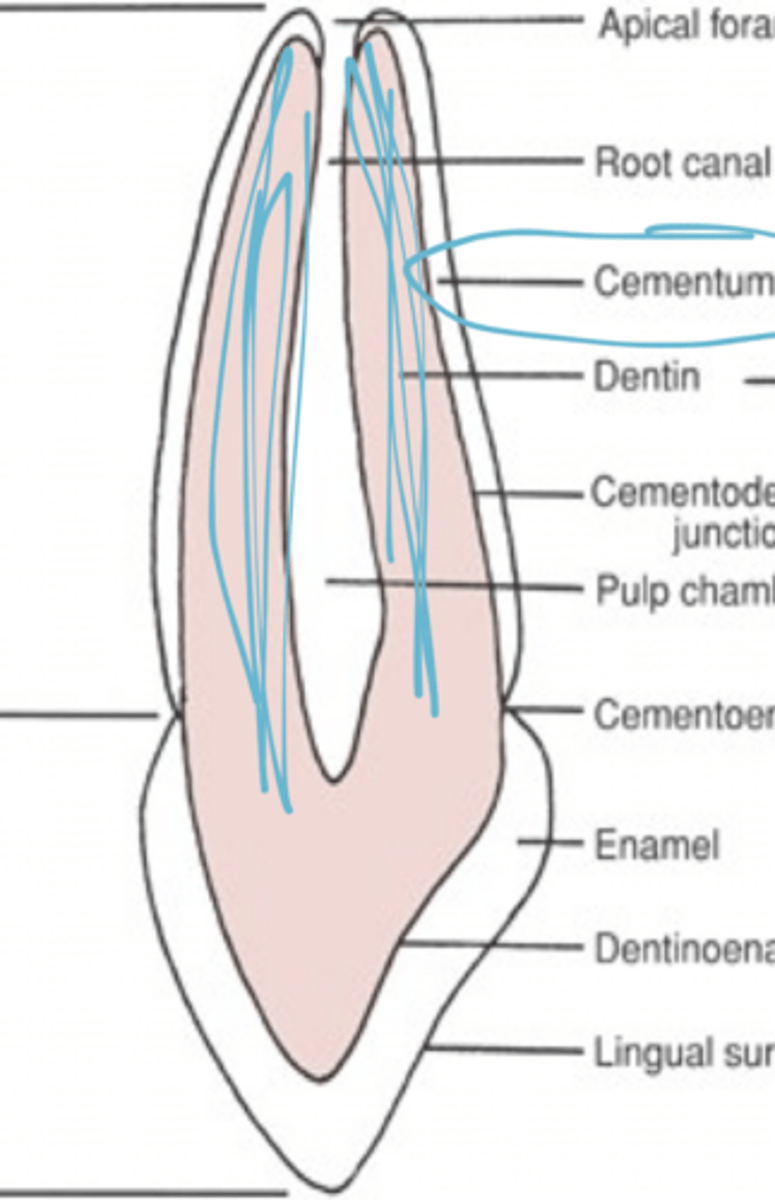
Anatomical Crown
Covered by enamel
External morphology of the anatomical root
CEJ separates the anatomic crown from the anatomic root
Proximal
Between the teeth
- Mesial surfaces are proximal and face the midline
- Distal surfaces are proximal surfaces that face away from midline
Facial Surface
Buccal and labial
Anterior teeth biting surface
Incisal edge
Posterior teeth biting surface
Occlusal surface
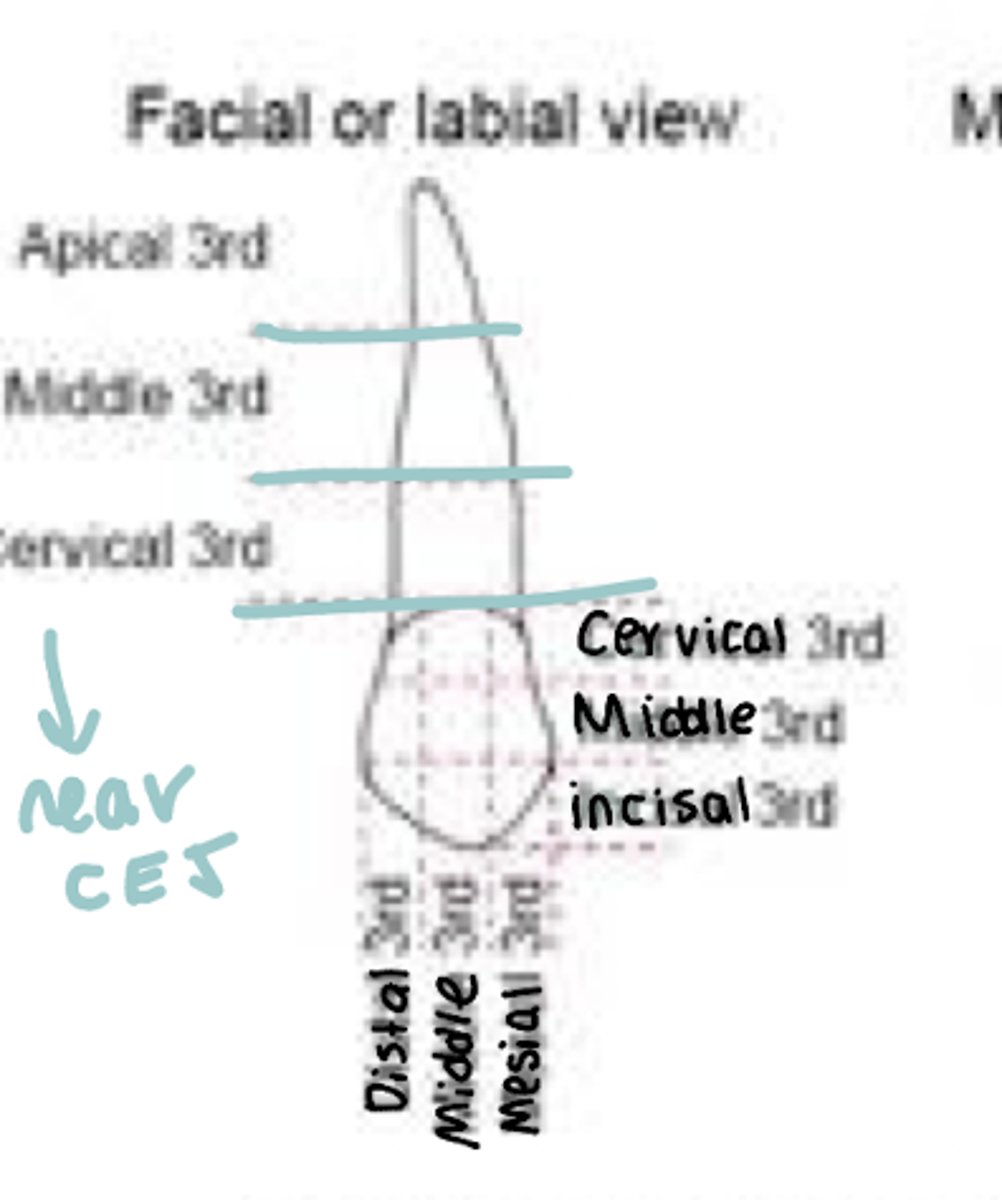
Facial/labial 1/3s division
- Root: apical, middle, cervical
- Crown: Cervical, middle, incisal
- Edge: Distal, middle, medial
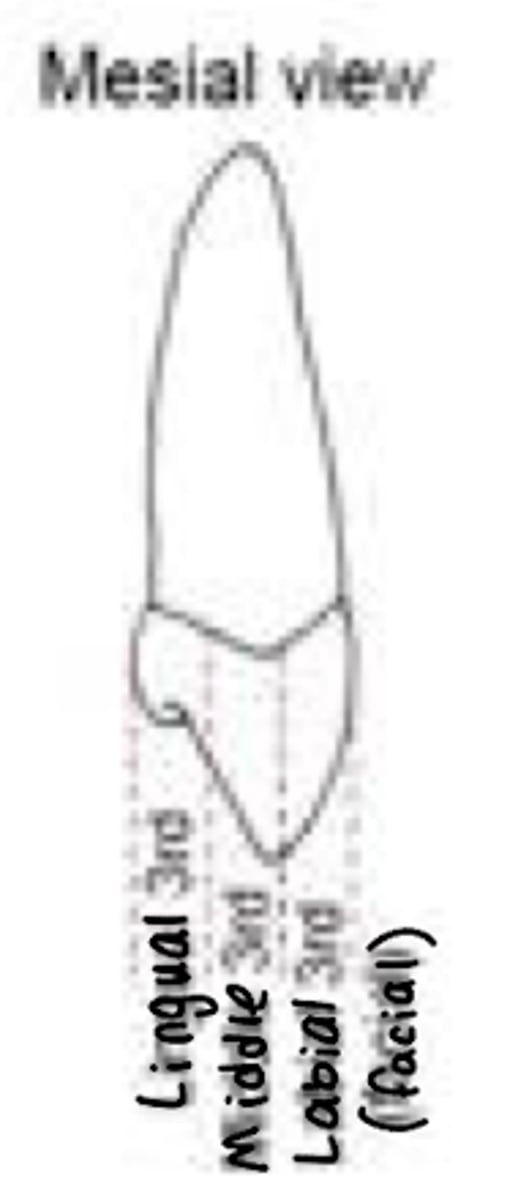
Mesial 1/3s division
Labial (facial), middle, lingual
Facial/buccle 1/3s division
- Root: Apical, middle, cervicle
- Crown: Occlusal, middle, cervicle
- Edge: Distal, middle, mesial
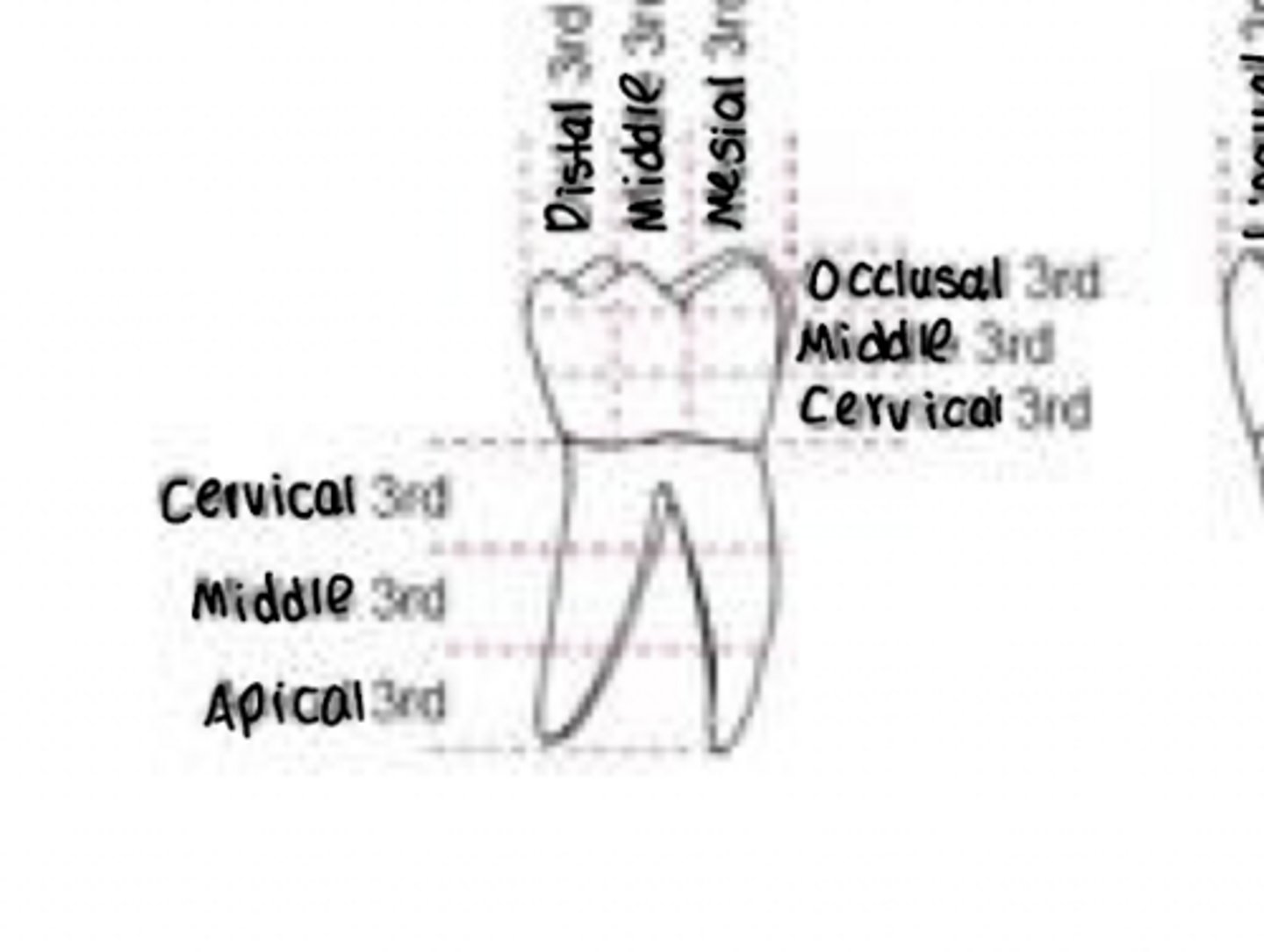
Distal 1/3s division
Lingual, middle, buccle

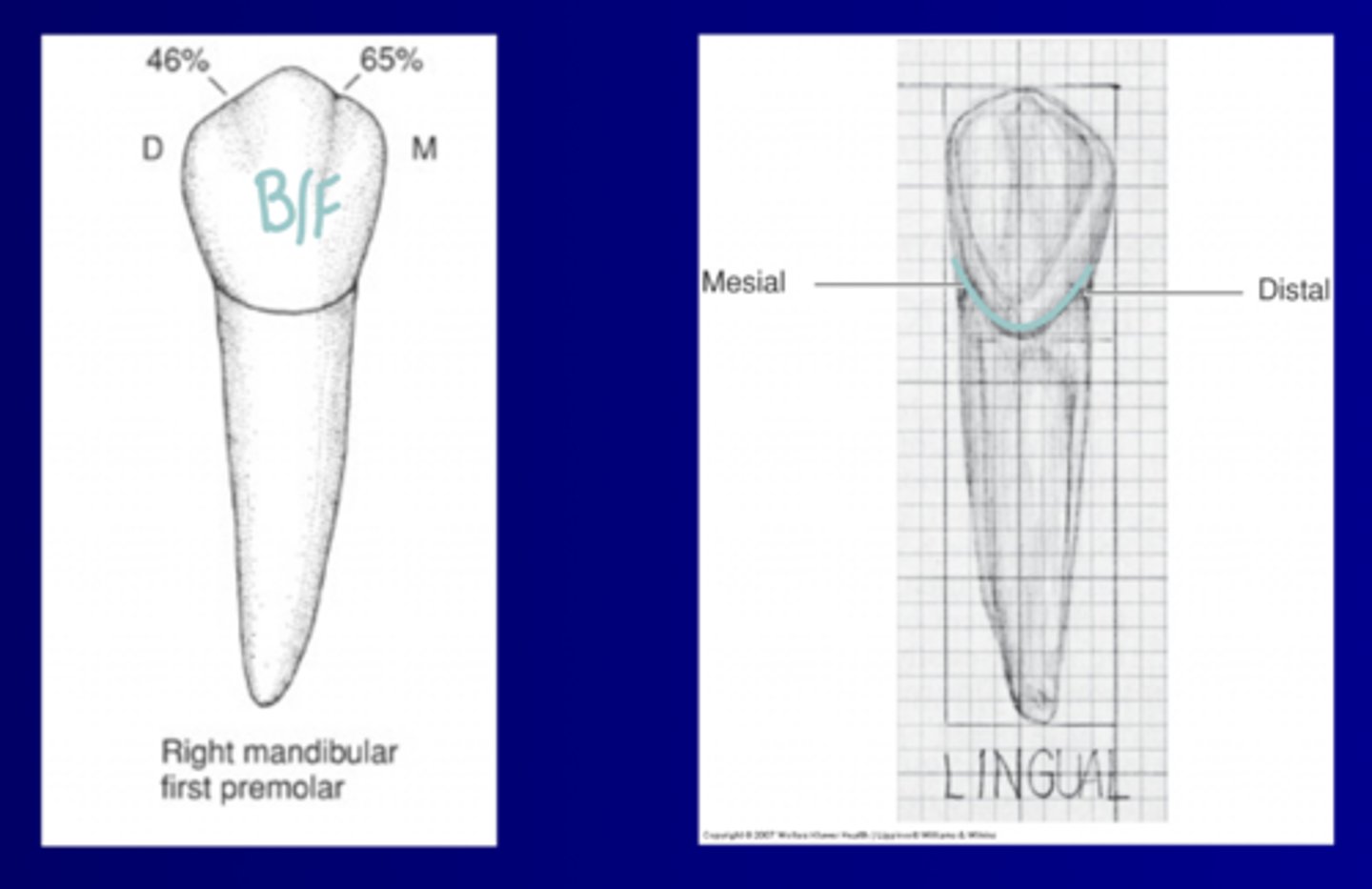
Dimensions: B/F View
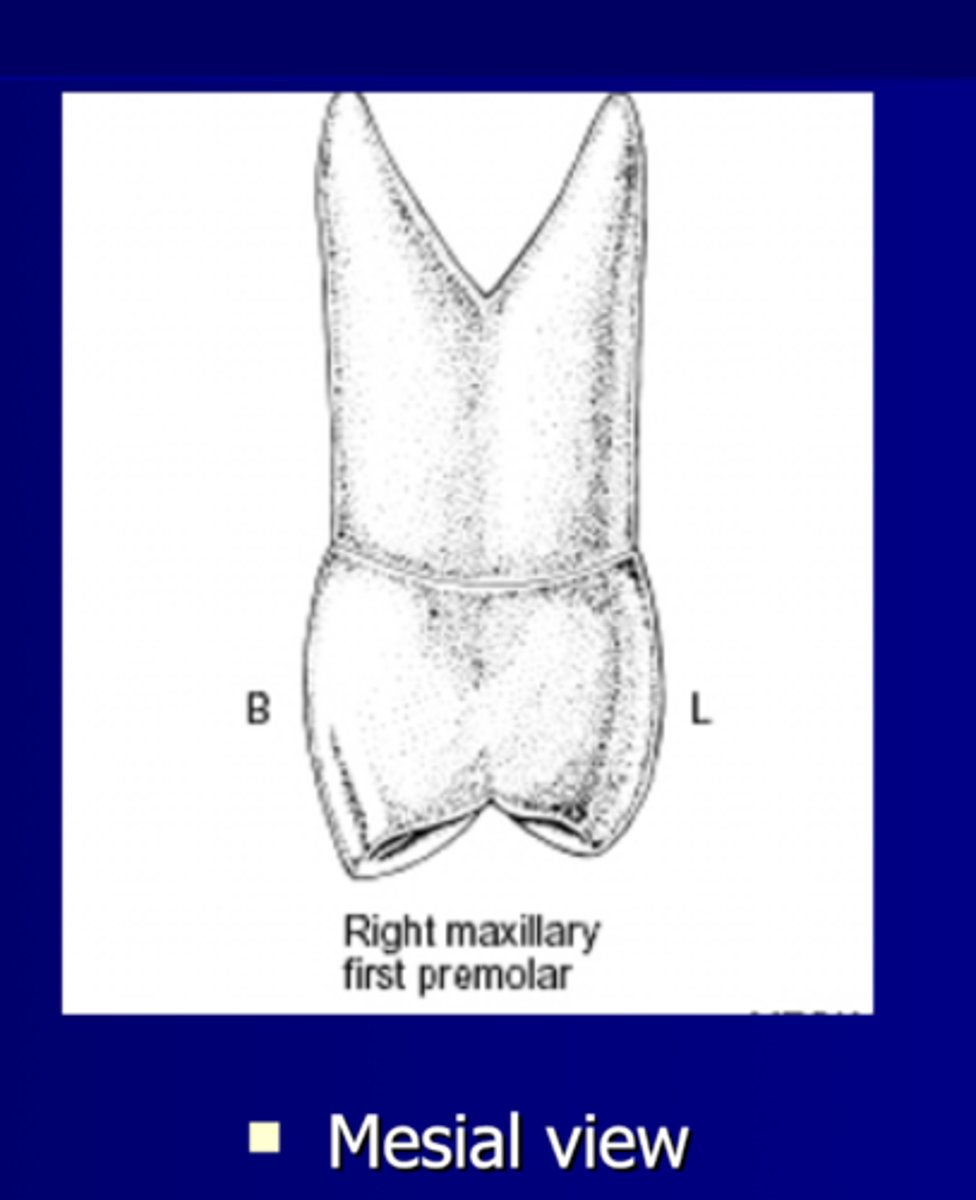
Dimensions: Mesial view
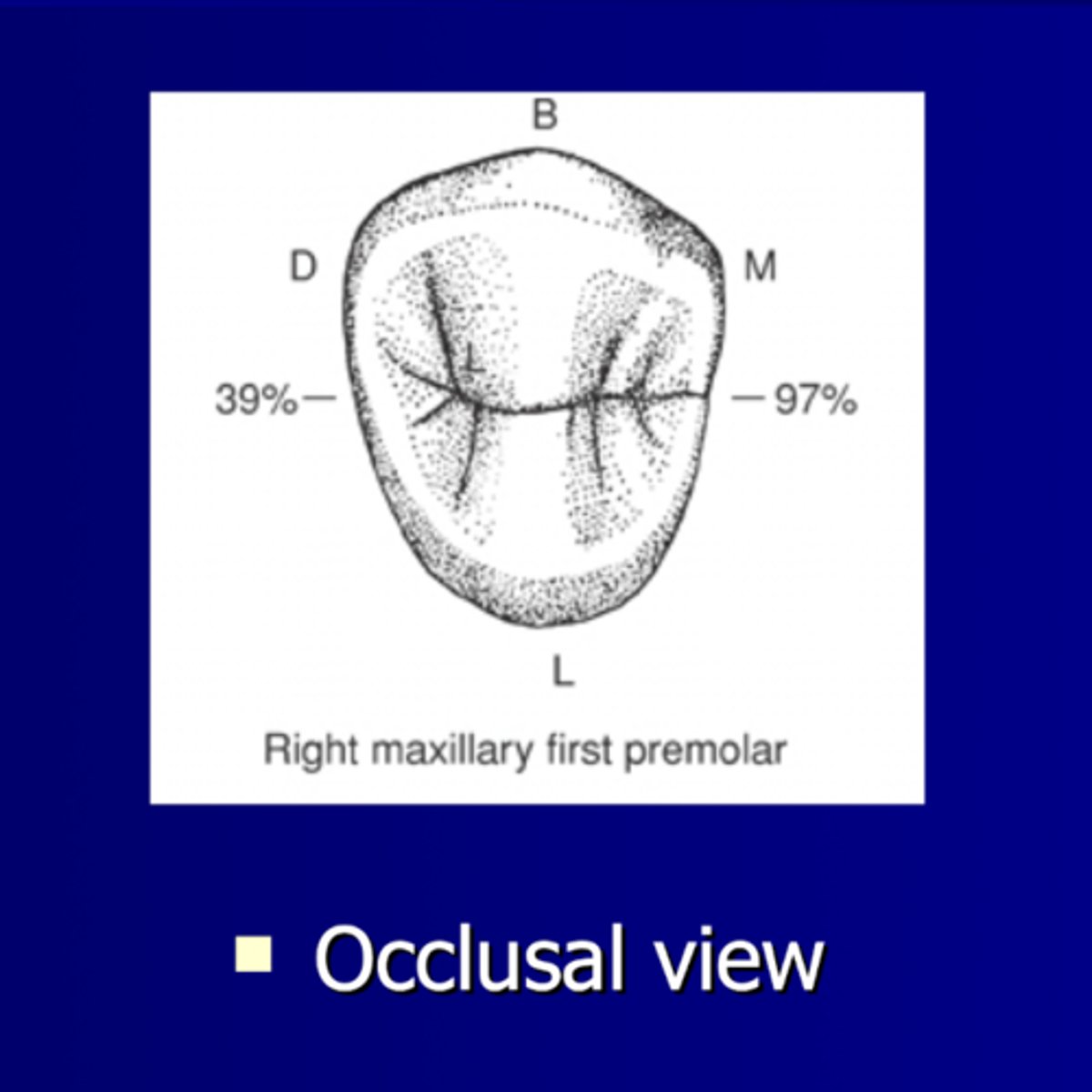
Dimensions: Occlusal view
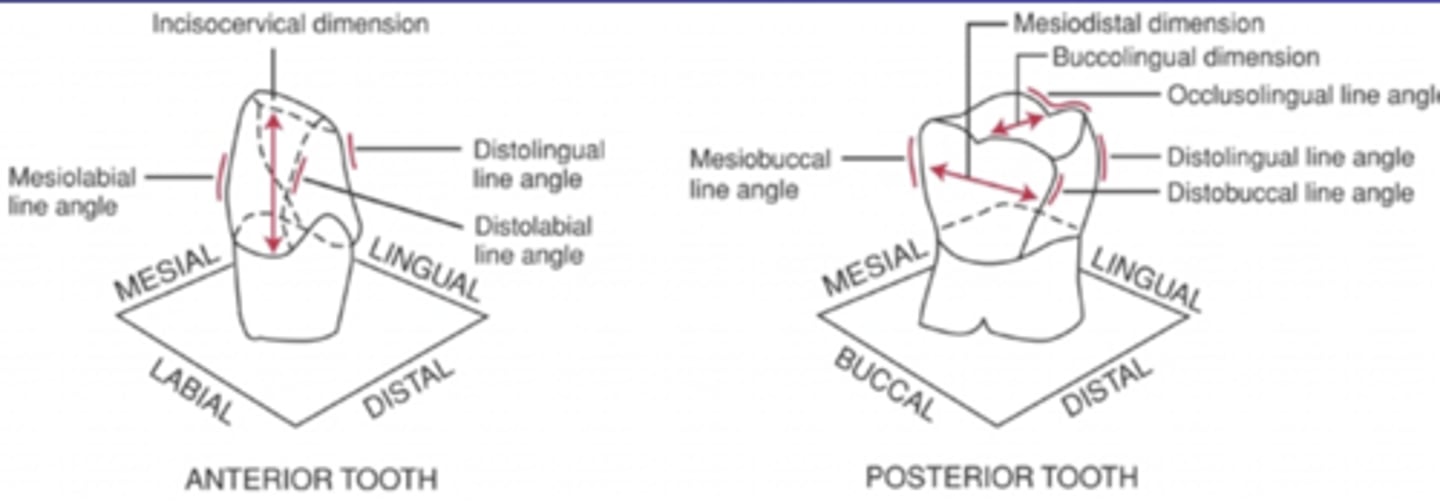
Line angles
Where 2 surfaces meet
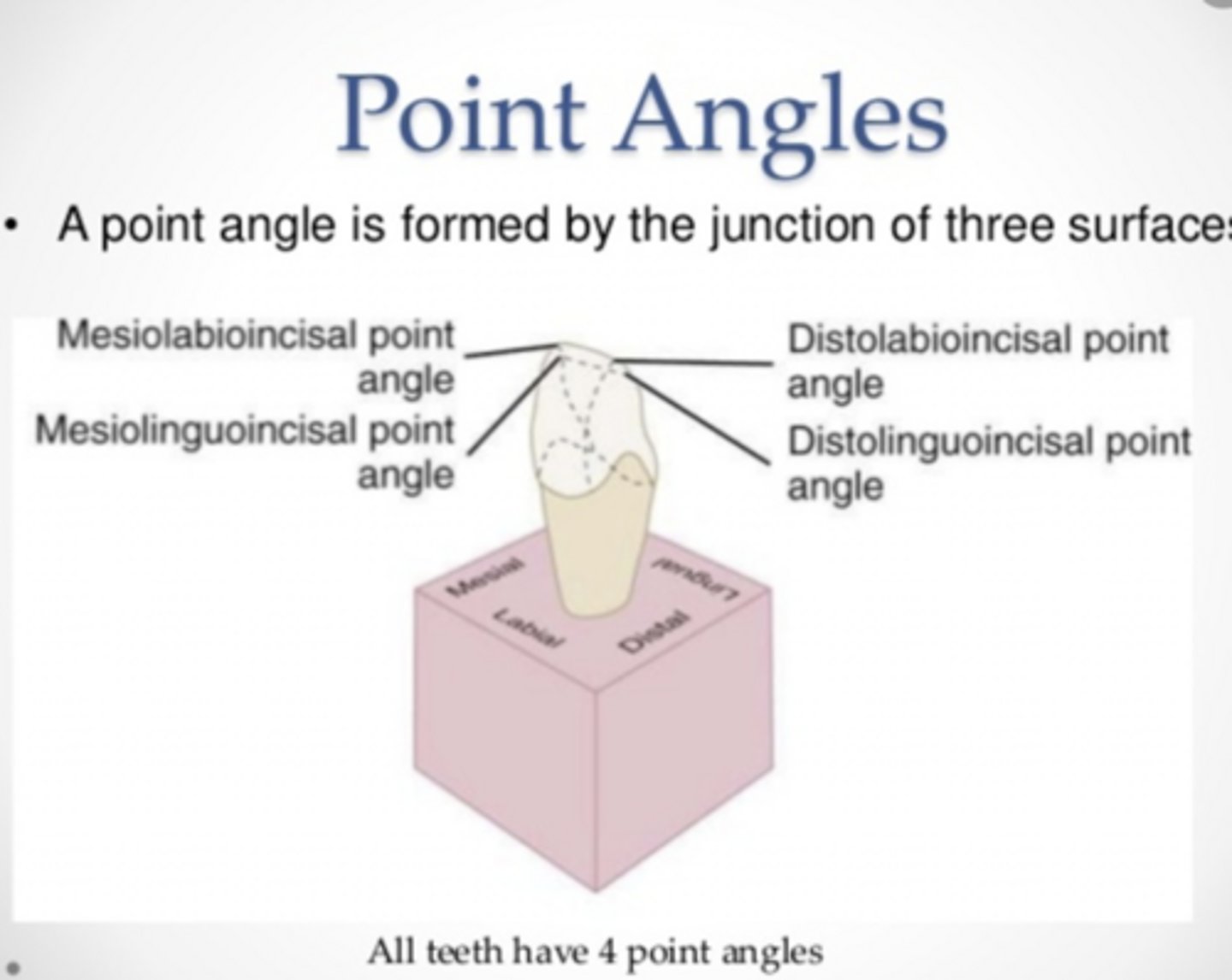
Point angles
Where surfaces meet
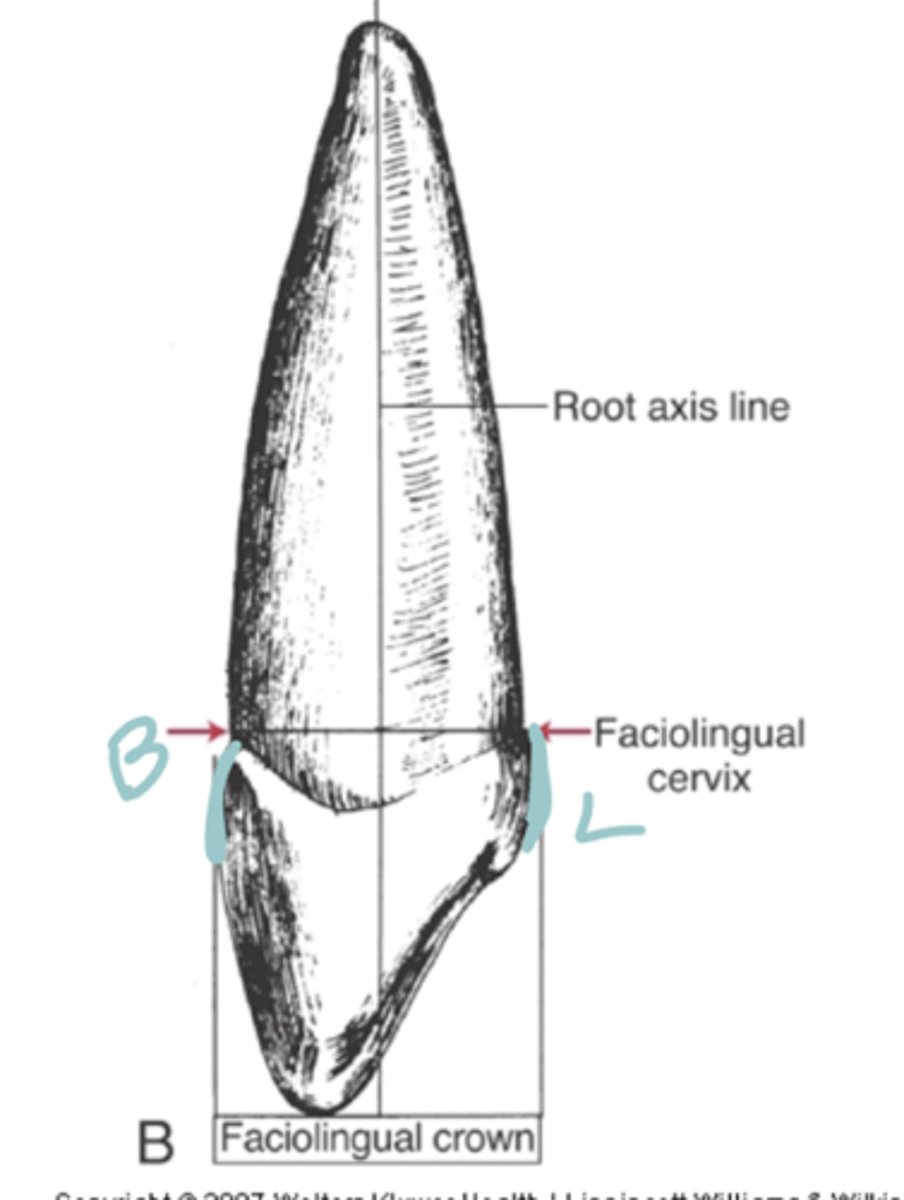
Facial height of curvature
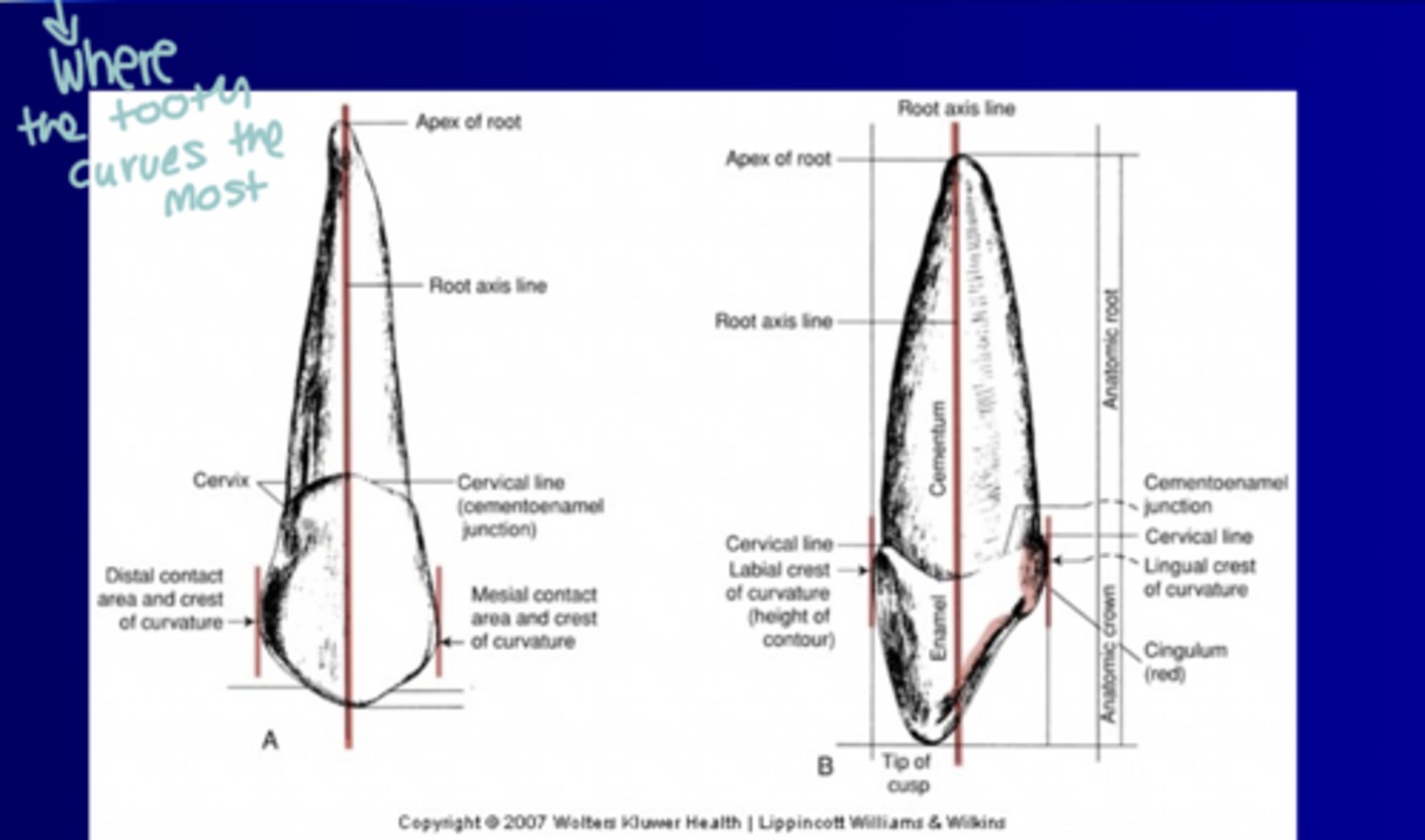
Hight of contour (crest of curvature) of contact areas
Where the tooth curves the most
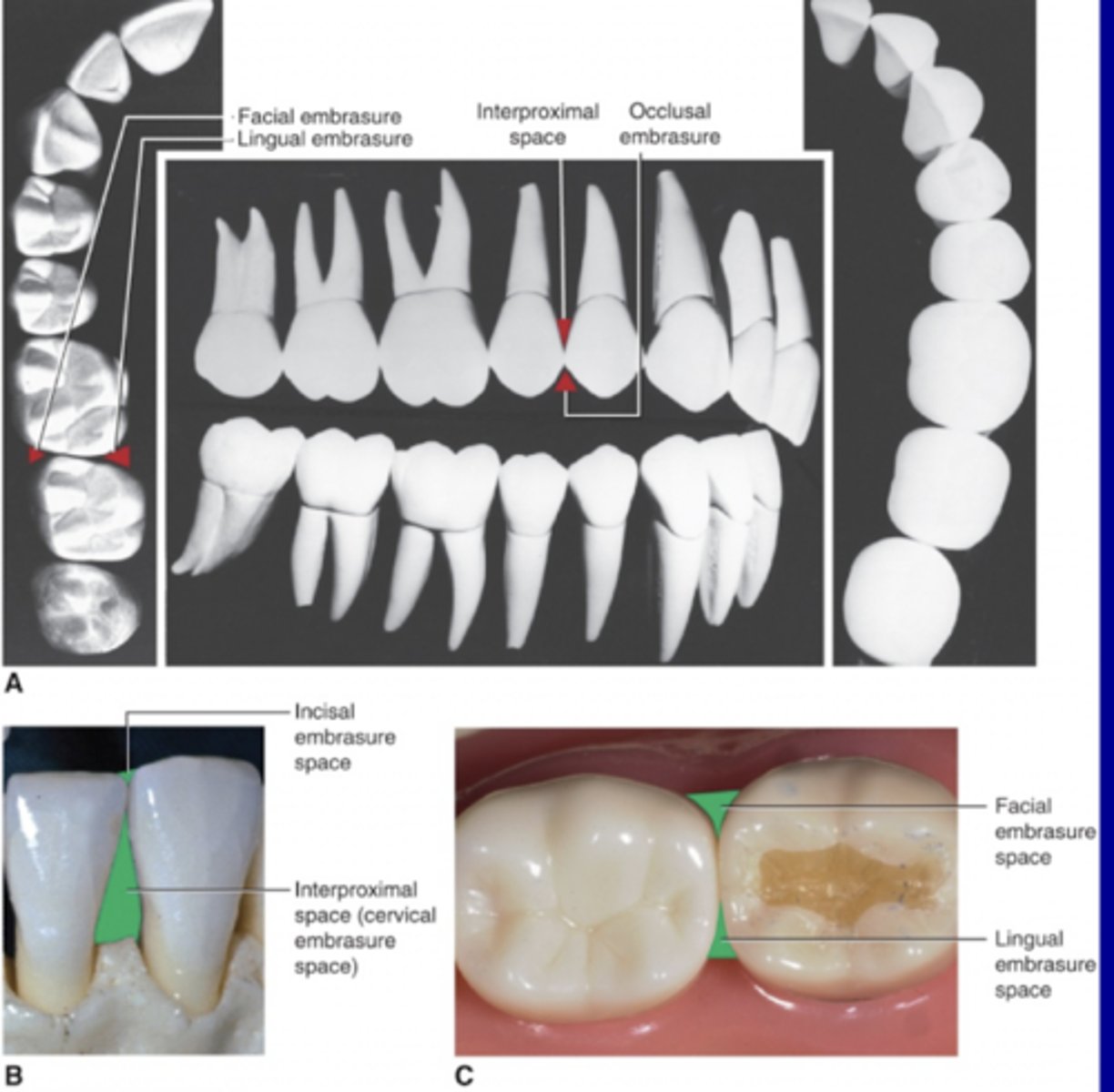
Embrasures
Only present wen two adjacent teeth touch
The four embrasures
- Facial
- Lingual: Larger than facial
- Occlusal or incisal: Small
- Cervical: Filled with gingiva
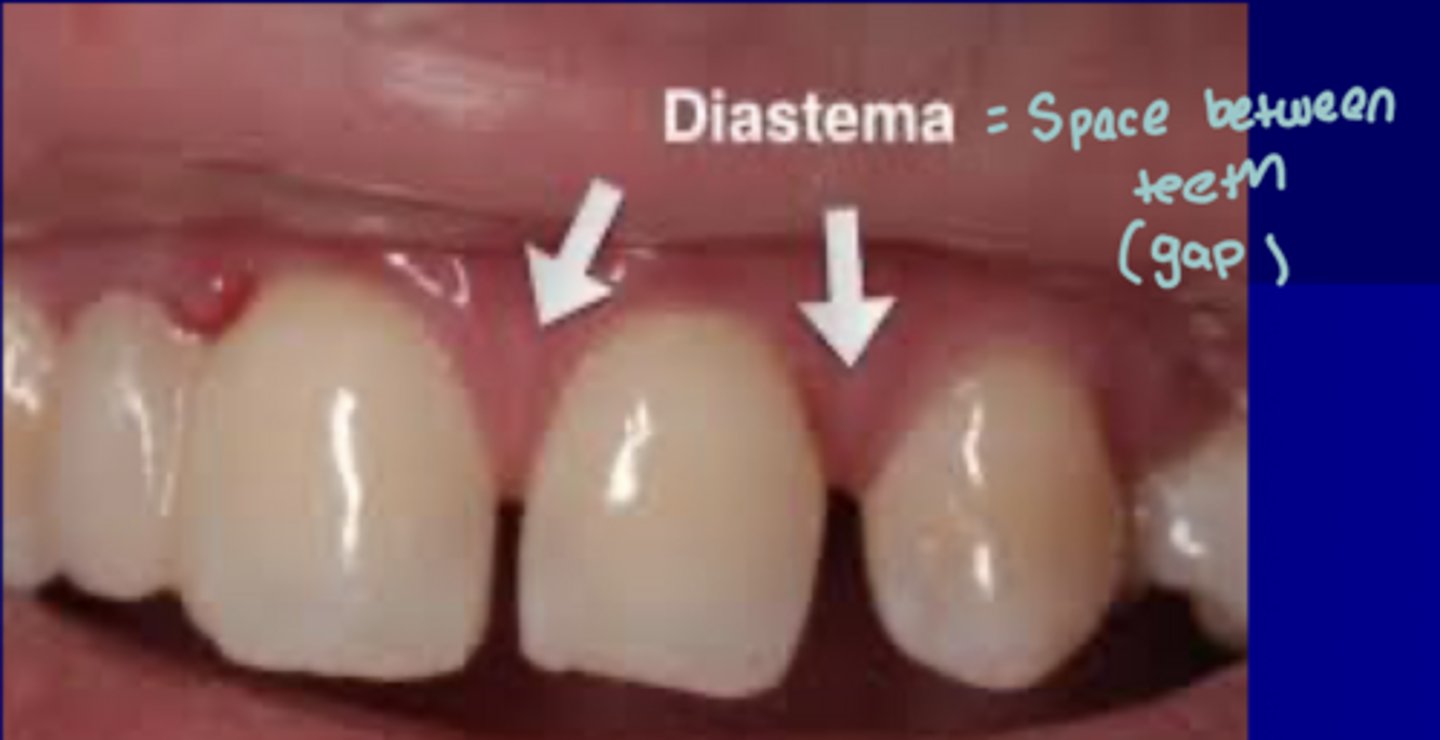
Diastema
Space between teeth
Contact areas
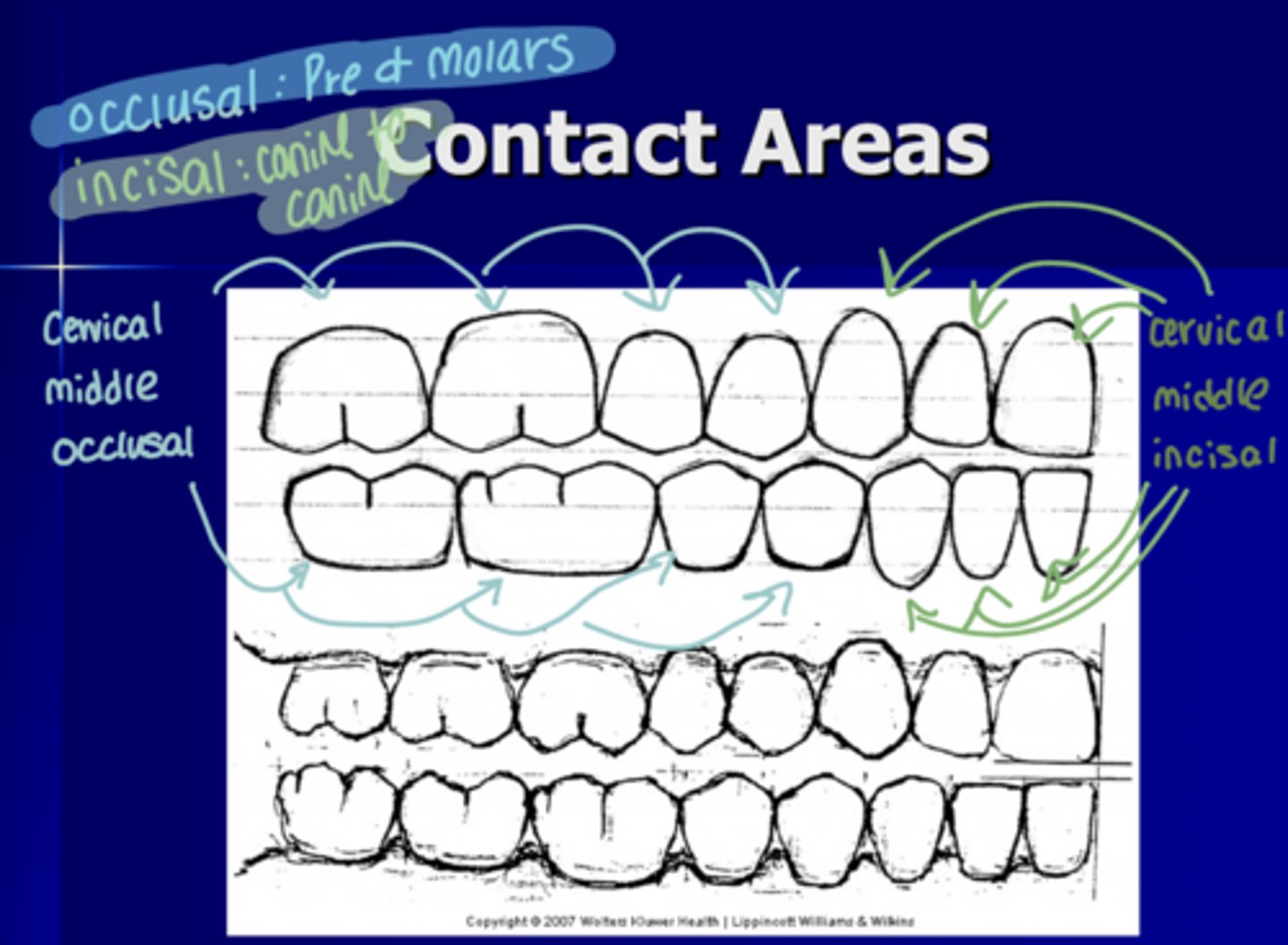
Examples of short hand for note taking

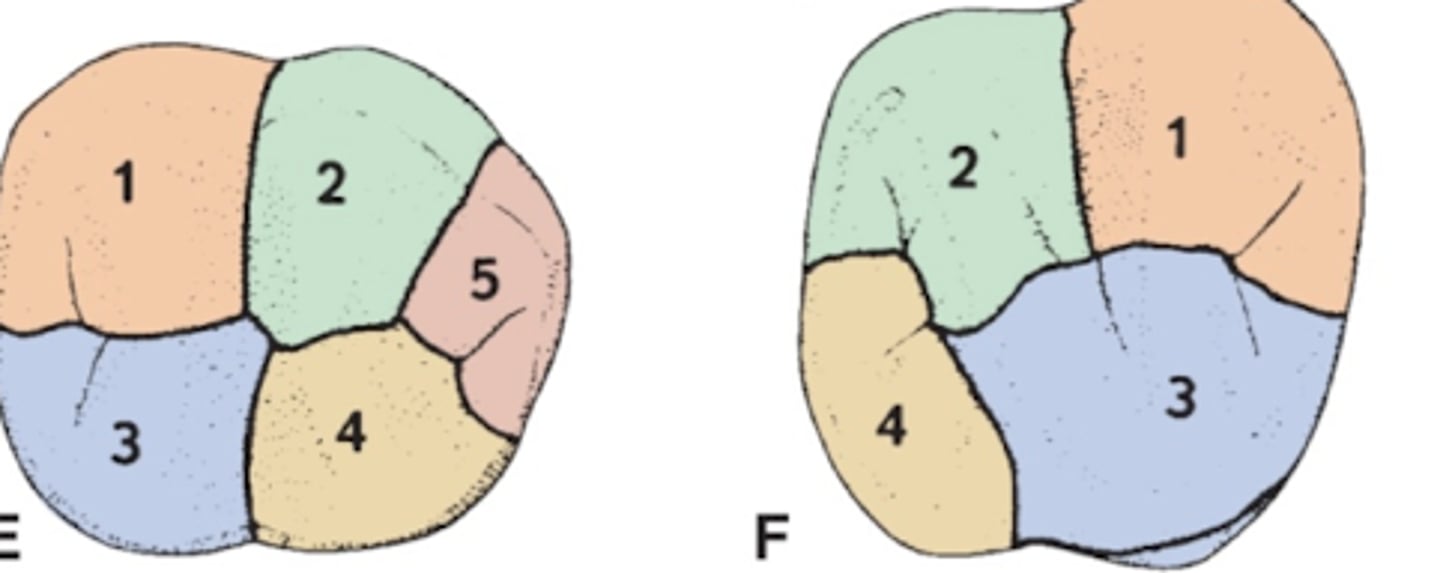
Developmental lobes- Anterior
4 lobes: 3 F and 1 L
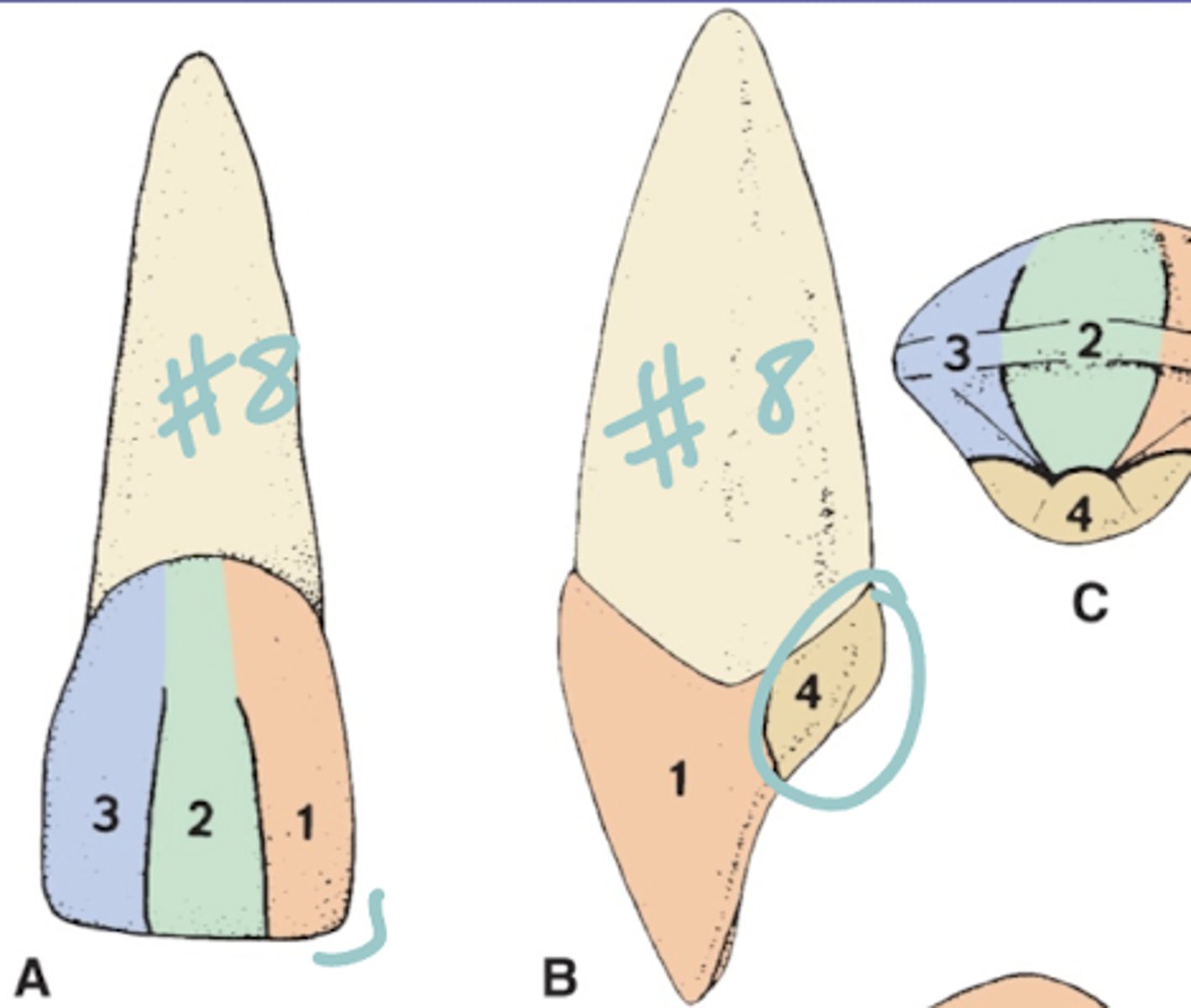
Developmental lobes- Premolars
3 F lobes and 1 lobes per lingual cusp
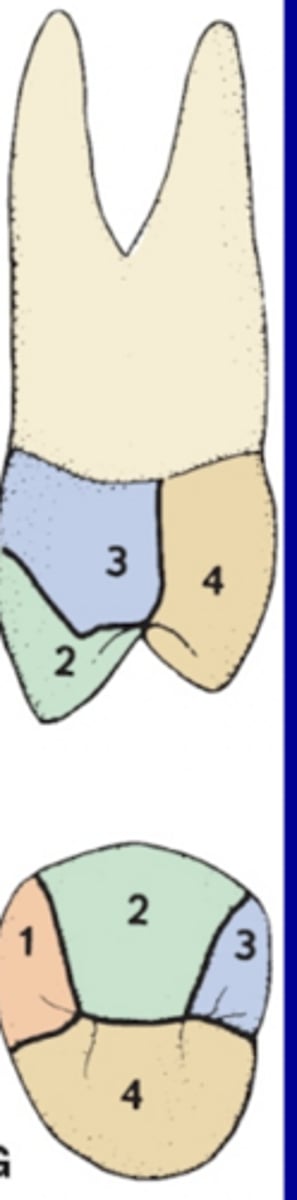
Developmental lobes- Molars
1 lobe per major cusp
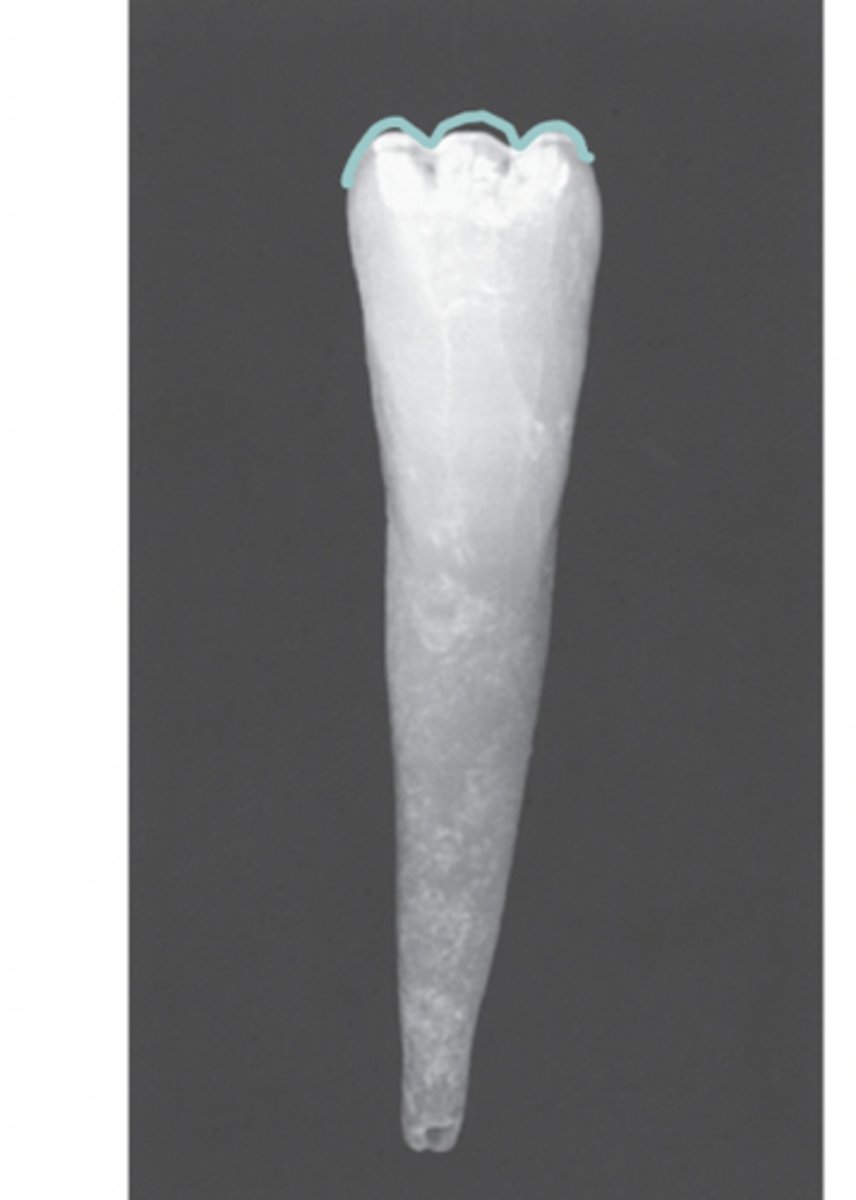
Mamelons
Form on adult incisors, 3 labial lobes and usually wear away
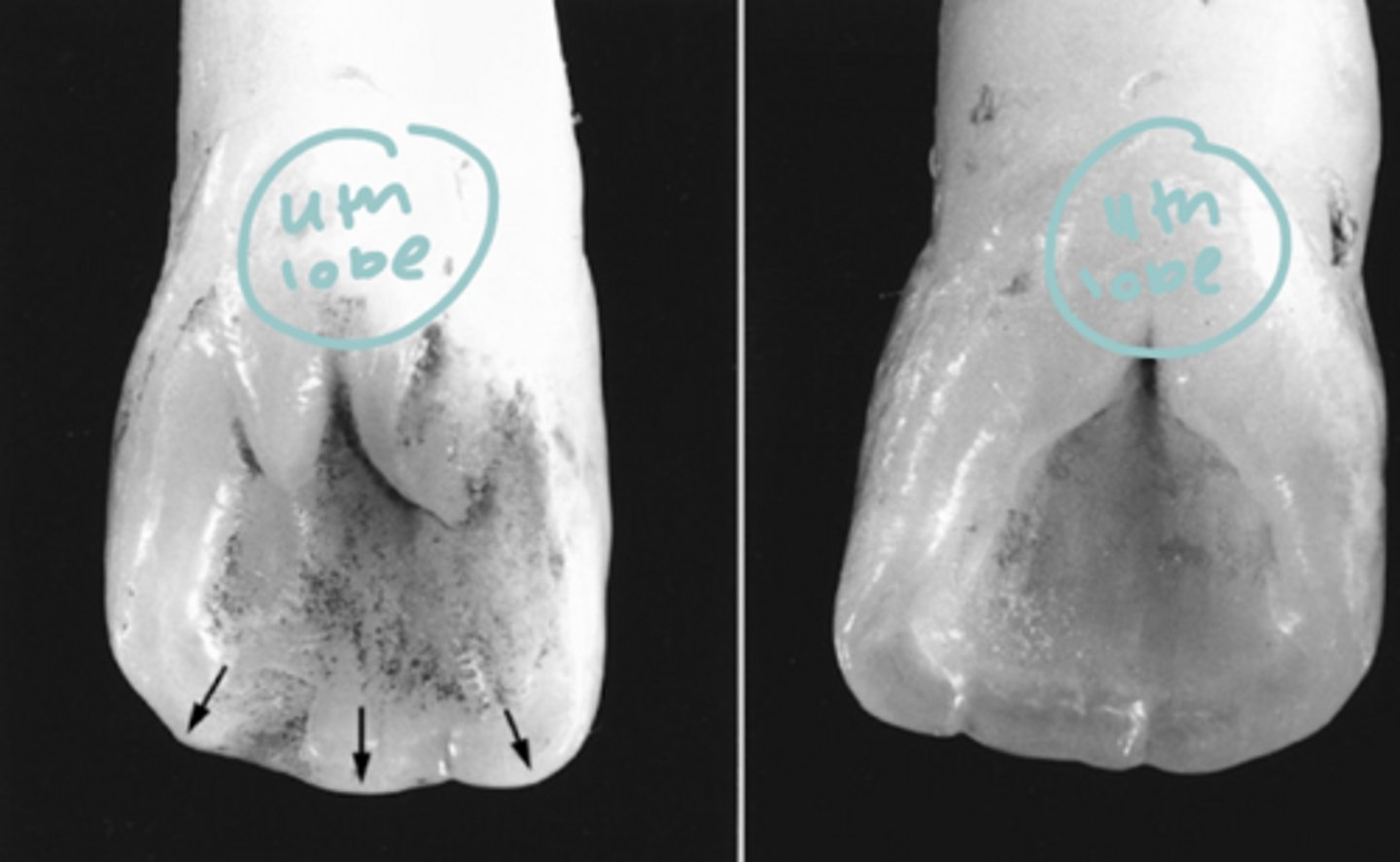
Cingulum
The cingulum forms the 4 developmental lobe
Wear facets
Flattened plane produced by wear on convex area of tooth surface and occurs at contact areas
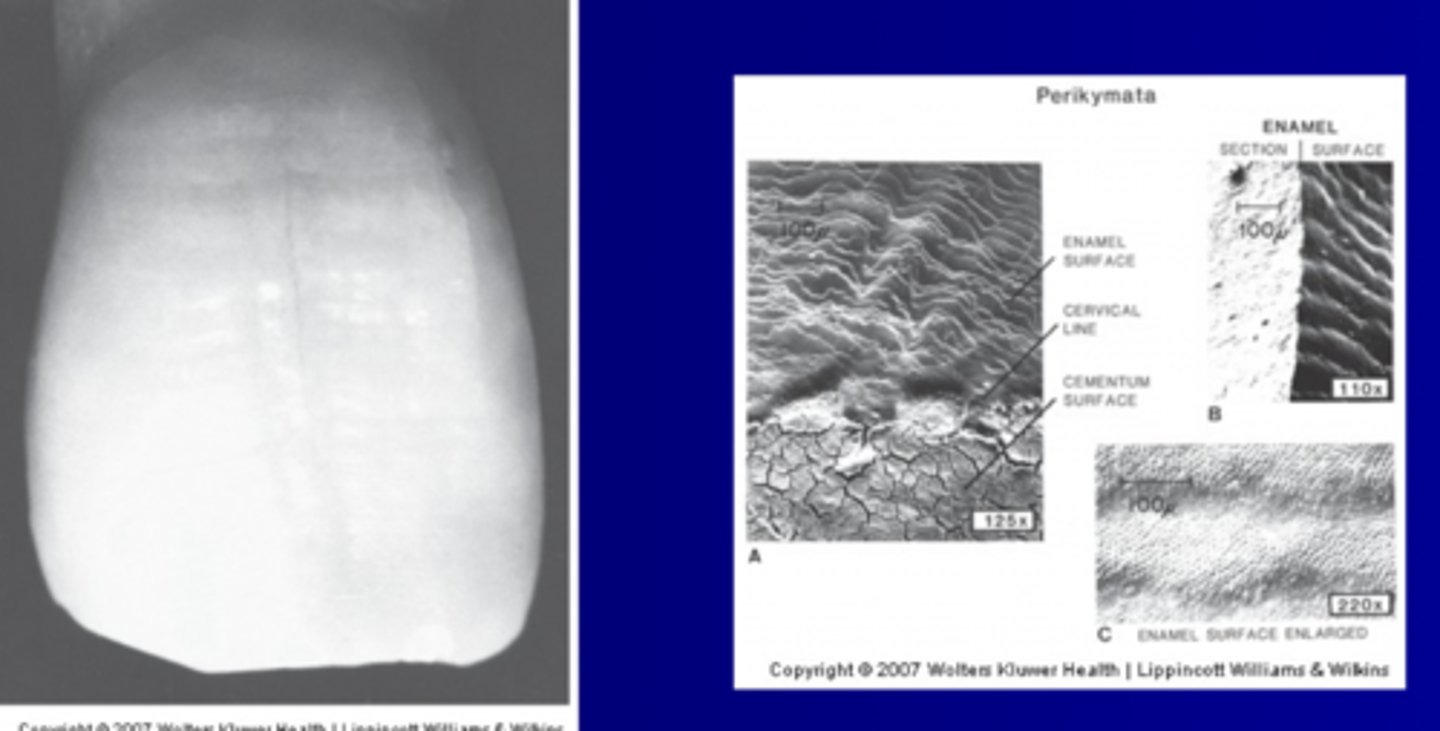
Perikymata
Very small wave-like ripples of enamel on newly erupted teeth
Root axis line
Imaginary line that splits the root in half (mesiodistally or faciolingually)
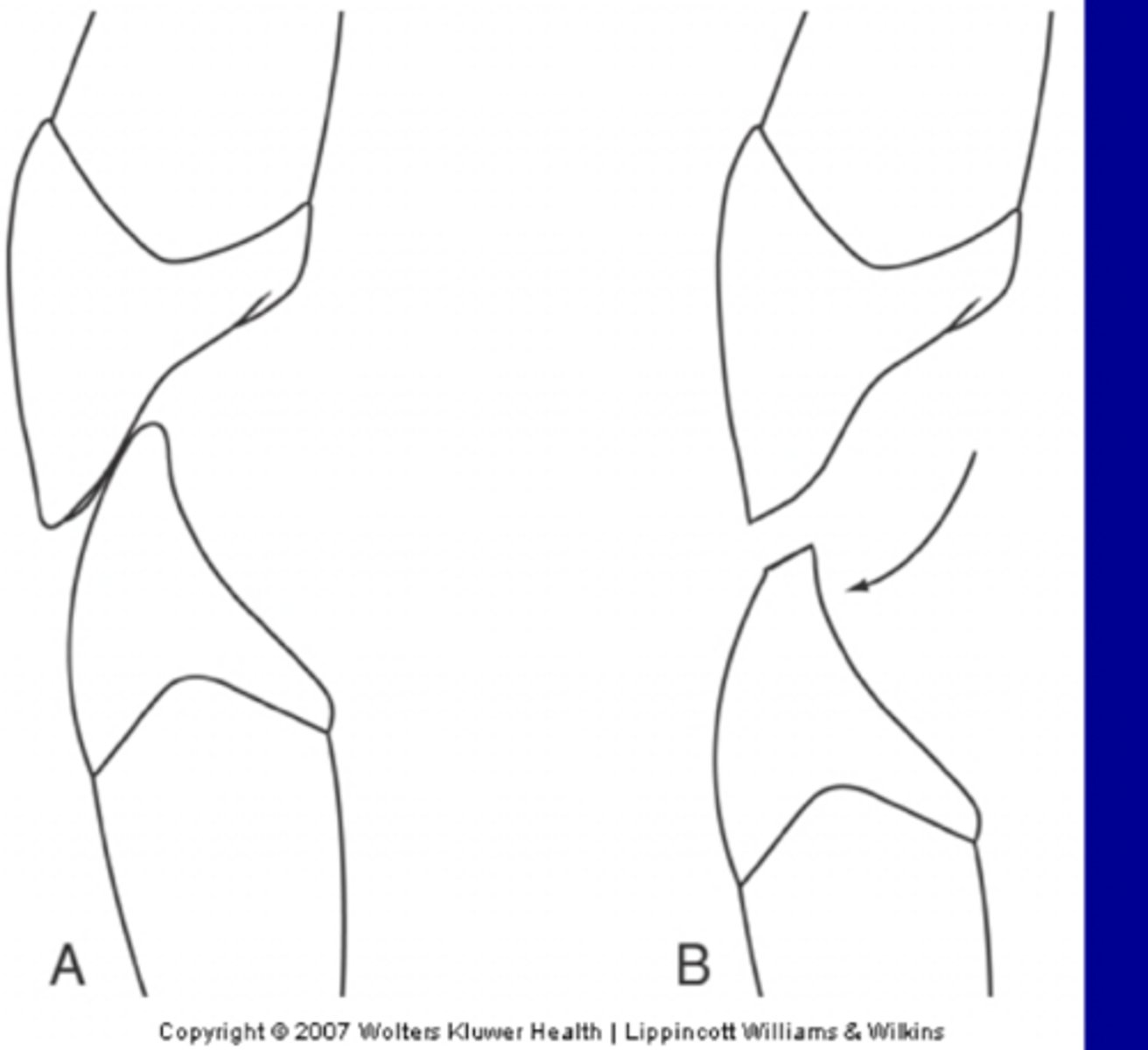
Lingual covergence
Cervical line of Max. molars
CEJ curves more incisally than the distal CEJ
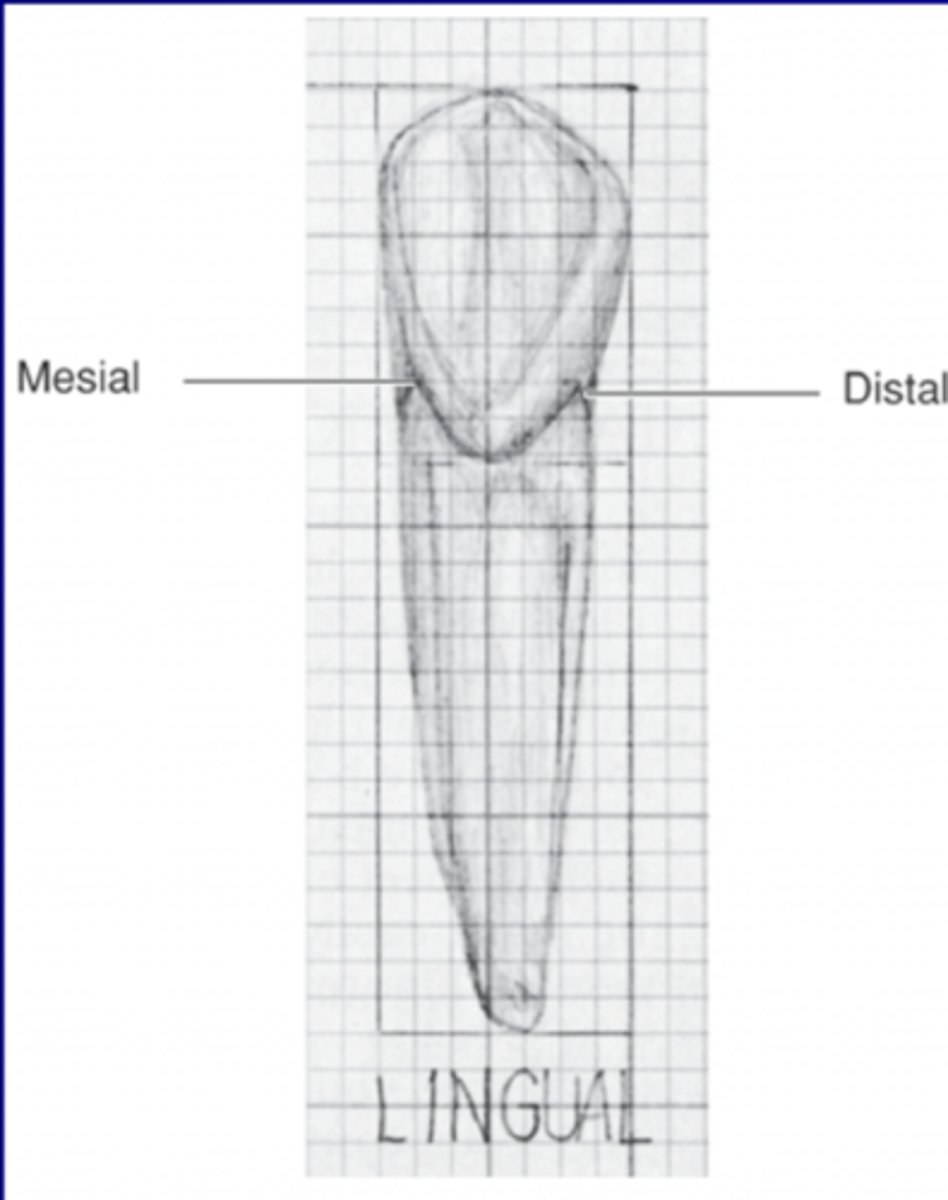
Maxillary incisor: Incisal proximal crown angle: Labial view
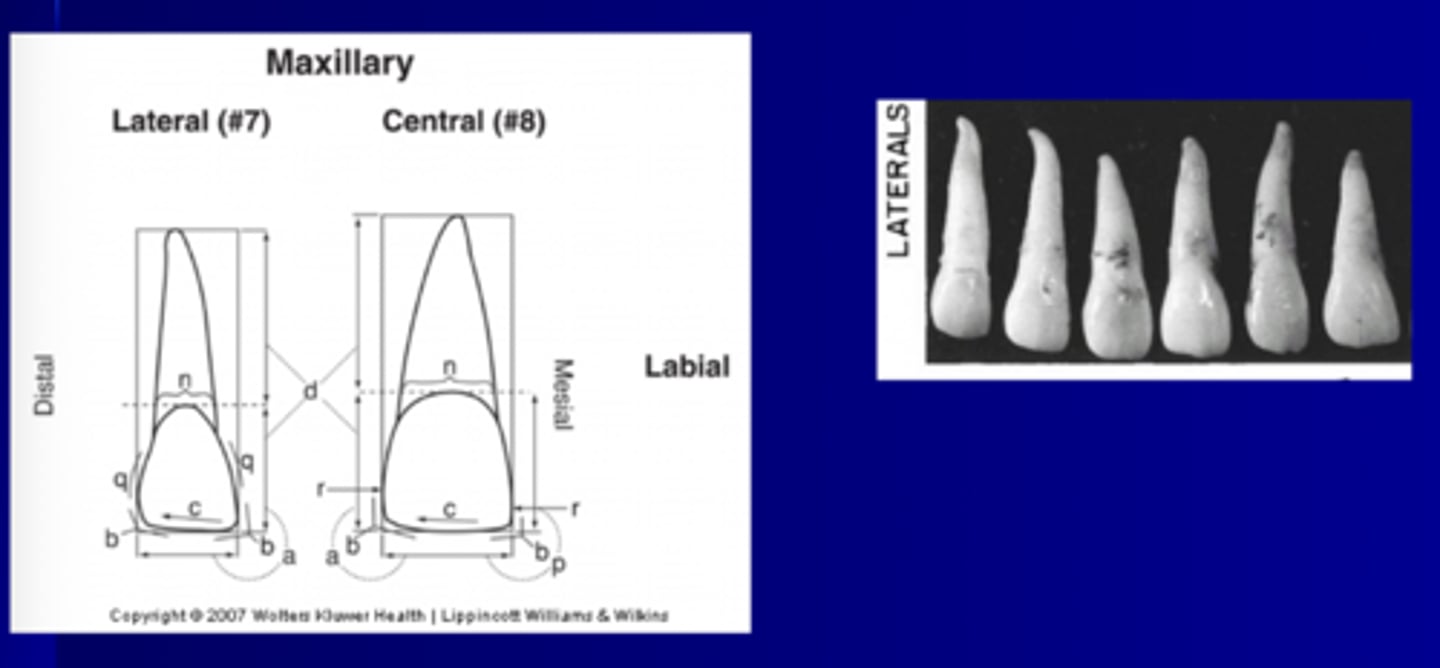
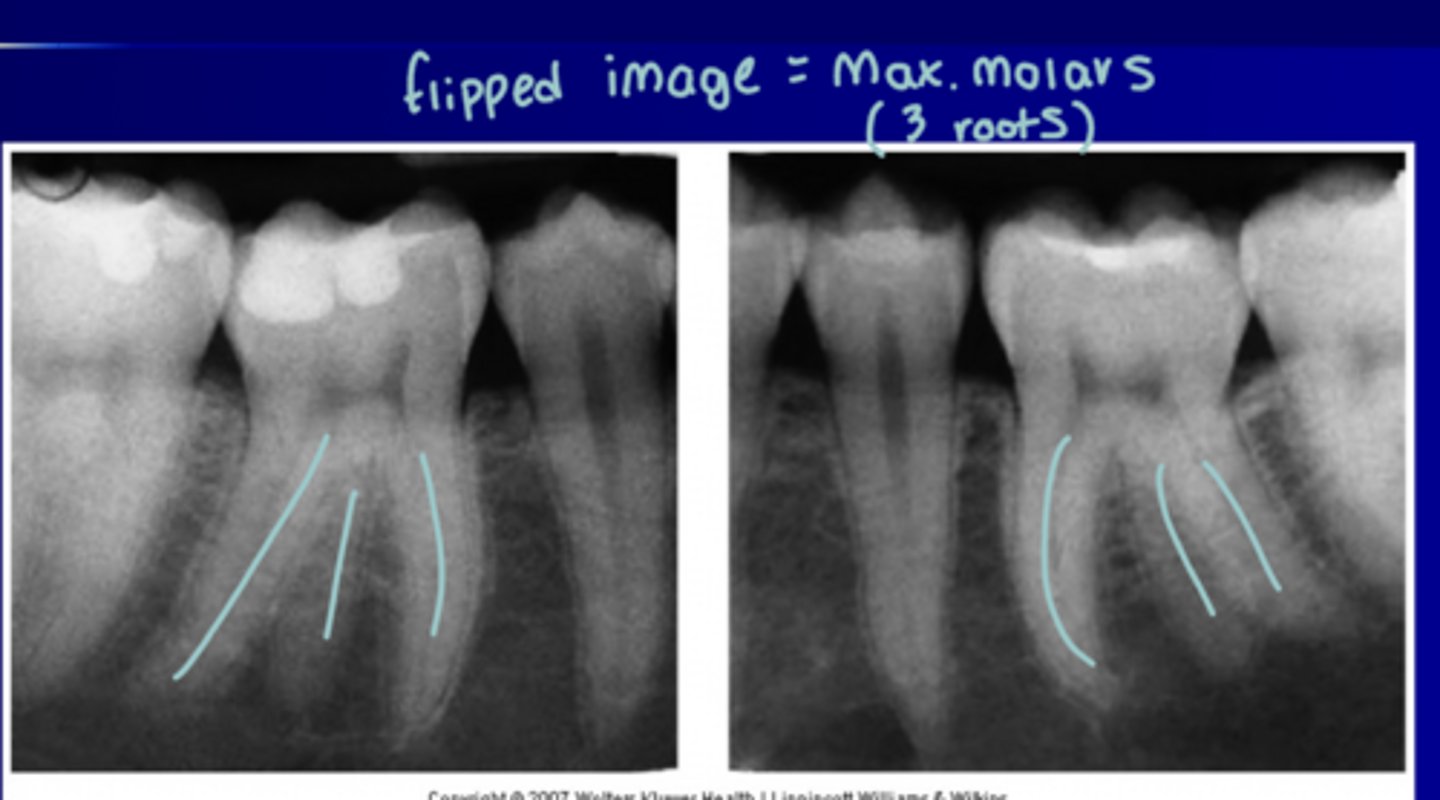
Maxillary roots on molars
3
Mandibular roots on molars
2
Distal curvature of roots