The Immune System and Lymphoid Organs - Coburn
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
innate vs adaptive immunity: surface barriers (skin and mucous membranes)
innate
innate vs adaptive immunity: internal defenses (phagocytes, natural killer cells, inflammation, antimicrobial proteins, fever)
innate
innate vs adaptive immunity: humoral immunity
adaptive
innate vs adaptive immunity: cellular immunity
adaptive
innate vs adaptive immunity: non-specific
innate
innate vs adaptive immunity: fast, but limited
innate
innate vs adaptive immunity: specific
adaptive
innate vs adaptive immunity: slow, but vast range and generates memory
adaptive
(t/f) the first line of defense are surface barriers, the second line of defense includes humoral and cellular immunity, and the final line of defense includes phagocytes and natural killer cells
false; the first line of defense are surface barriers, the second line of defense includes phagocytes and natural killer cells, and the final line of defense includes humoral and cellular immunity
what are 3 cells that can perform phagocytosis?
1. macrophages
2. dendritic cells
3. neutrophils
which innate cells induce apoptosis in cancer cells and virus-infected cells?
natural killer cells
what are the innate non-phagocytic, large granular lymphocytes that police blood and lymph?
natural killer cells
what are 3 ways natural killer cells will be activated before adaptive immunity is activated?
1. recognize stress markers (expressed in response to infections, damage, or cancer)
2. recognize the downregulation of mhc I proteins
3. recognize antibodies coating target cells
(t/f) natural killer cells have receptors for IgG which is helpful in recognizing antibodies that coat target cells
true
what is humoral immunity?
activation and clonal selection of B cells (and plasma cells)
what happens when an antigen binds to a receptor on the surface of a B cell?
the complex is internalized (receptor-mediated endocytosis) and a fragment of the antigen is presented to CD4+ t cells
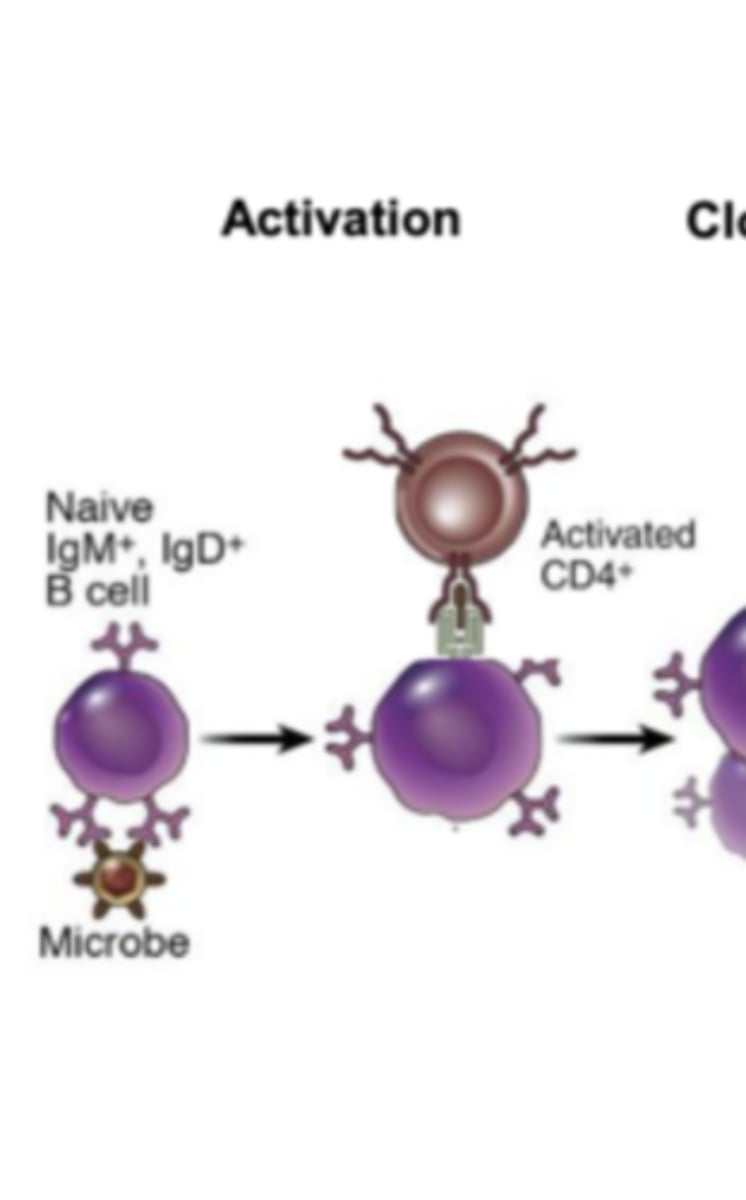
what cells will activate b cells to allow them to proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells and memory b cells? what cytokine will they release to activate the b cells?
CD4+ t cells; interleukin-4 (IL-4); this happens after the b cells present the internalized antigen to the CD4+ t cells
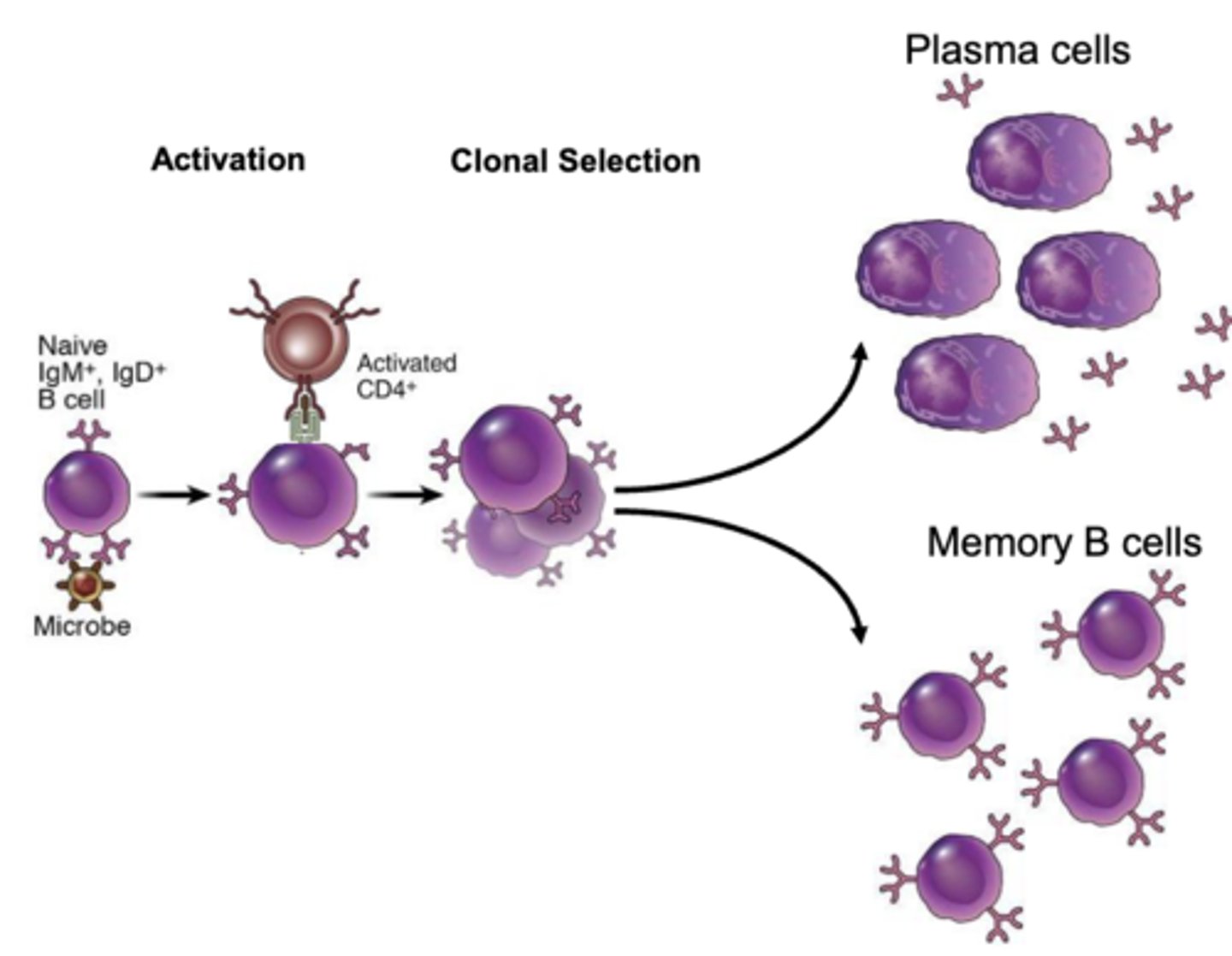
proteins secreted by plasma cells are capable of binding specifically with ______________
antigens
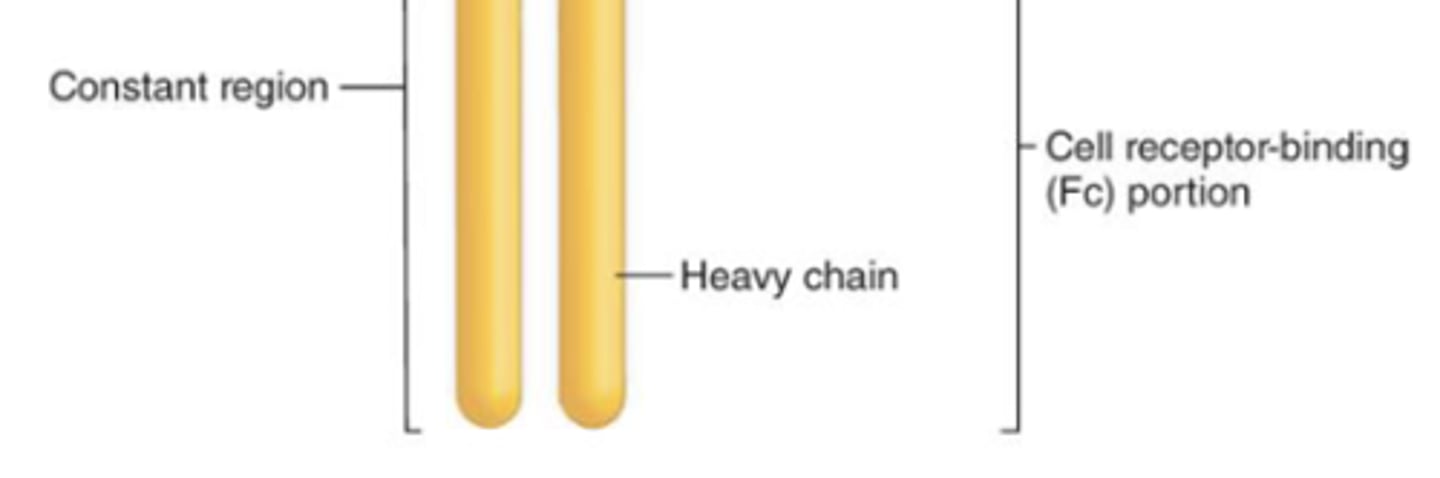
what are the 2 regions of an immunoglobulin?
1. variable region
2. constant region
which region of the antibody is the antigen binding site?
variable region
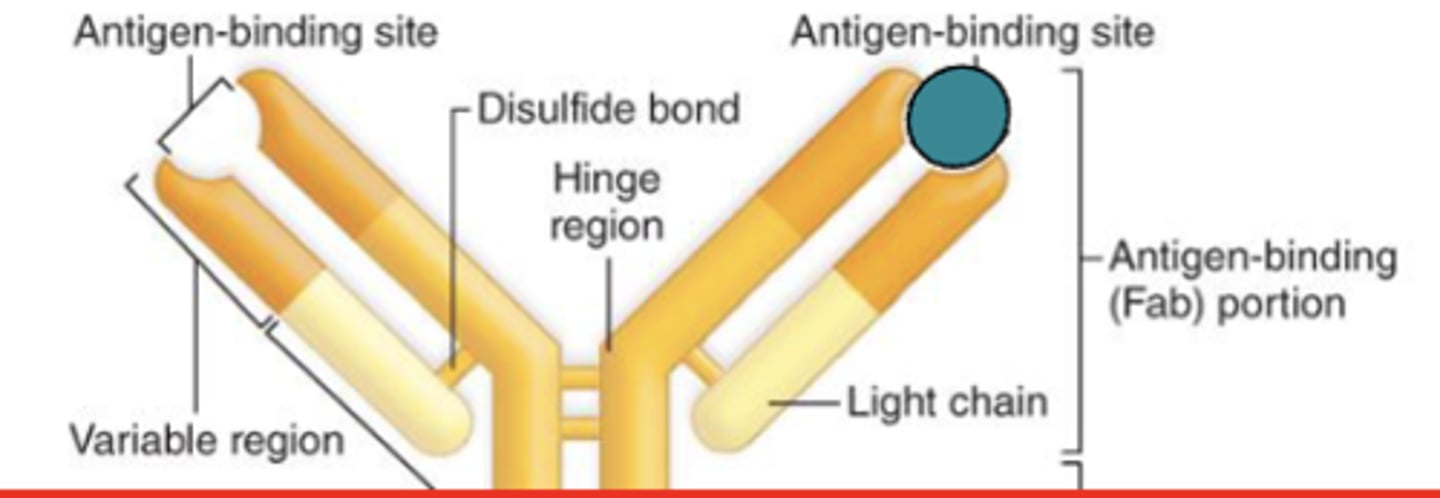
which region of the antibody is also known as the Fab region?
variable region
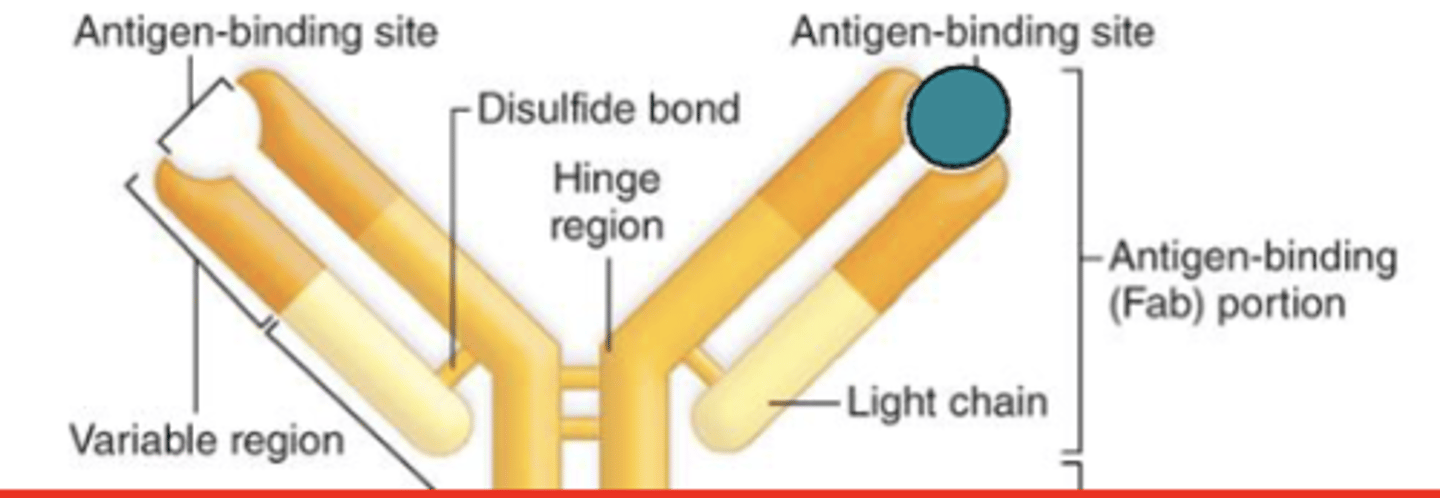
which region of the antibody is also known as the Fc region?
constant region
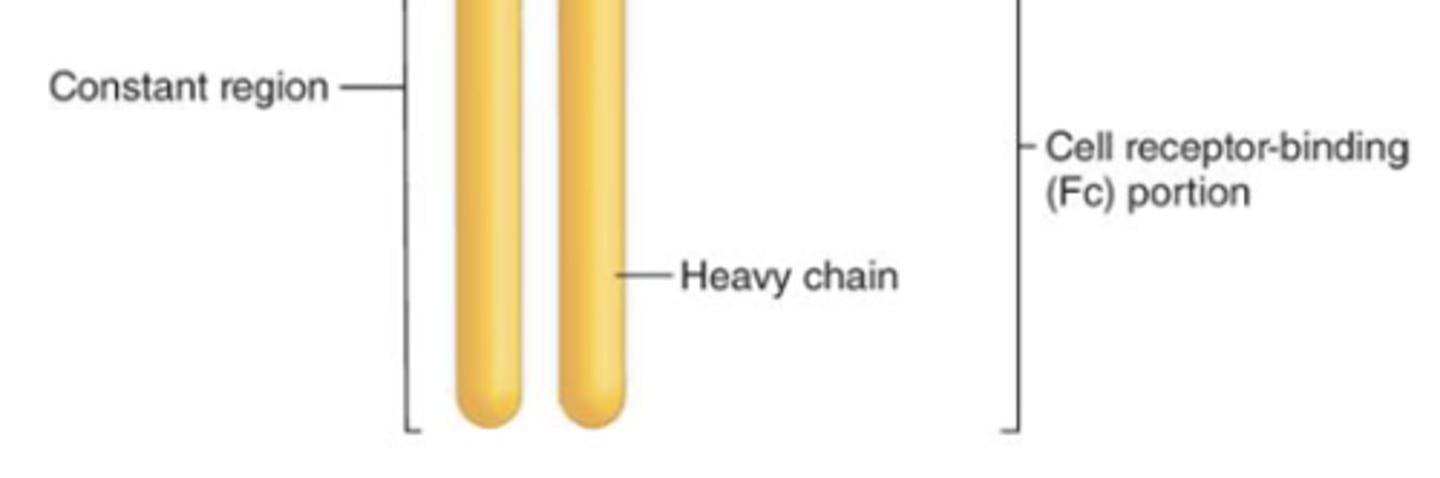
which region of the antibody determines the antibody class?
constant region
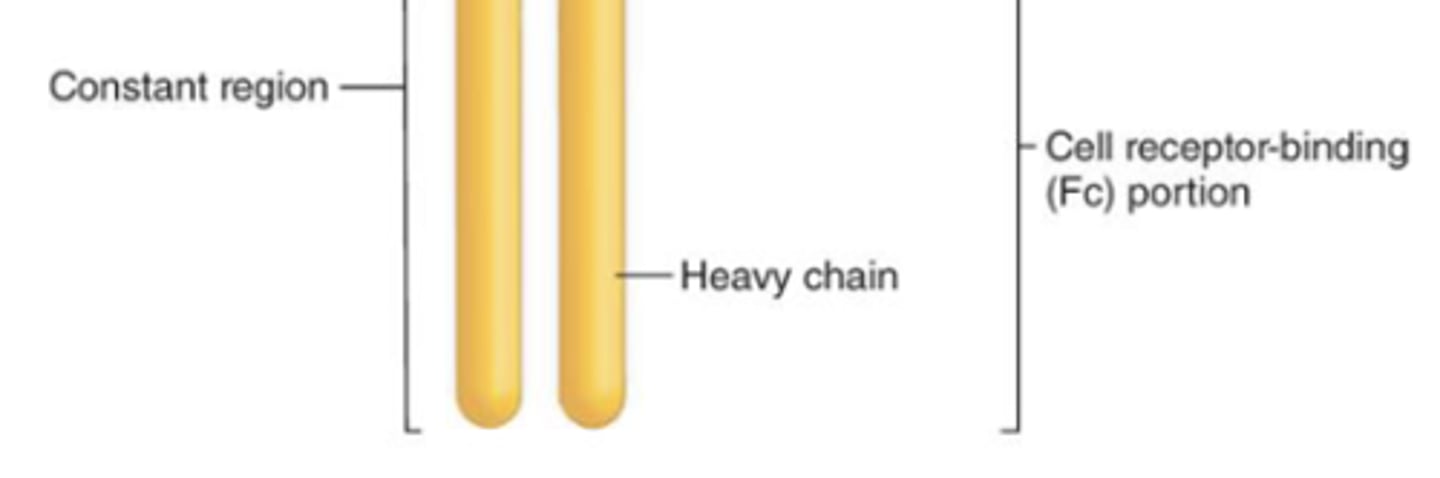
which region of the antibody controls the activity and type of cells that the antibody can bind to?
constant region
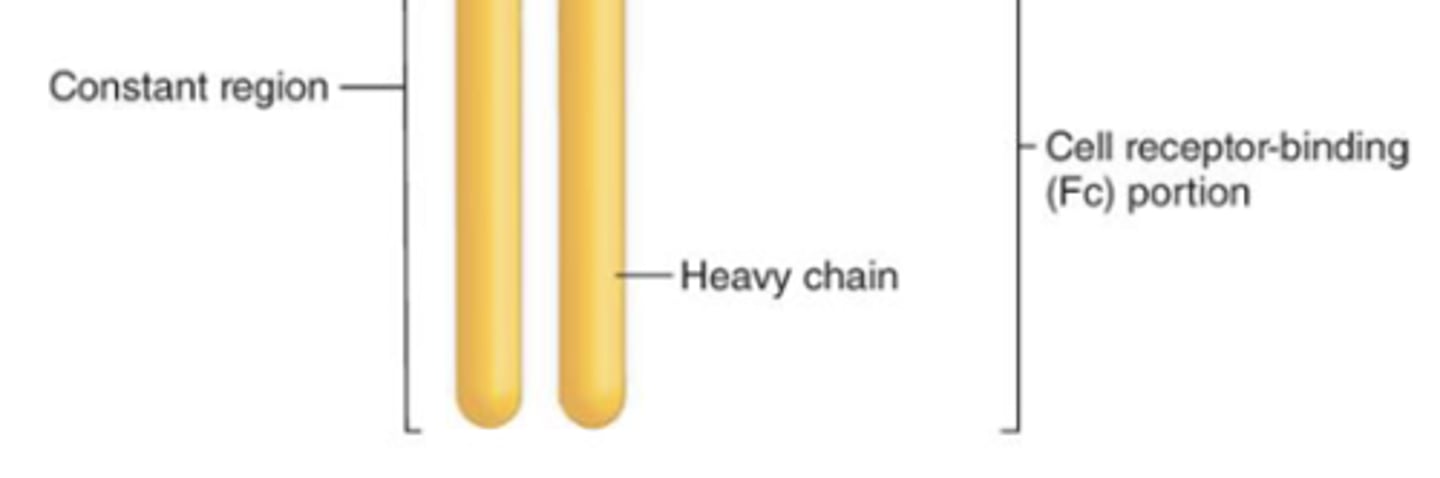
what are the 5 antibody classes in the (constant/variable) region?
constant;
1. IgG
2. IgA
3. IgM
4. IgE
5. IgD
what are 3 consequences of binding to the antigen-binding site of an antibody?
1. neutralization
2. agglutination (clumping)
3. precipitation
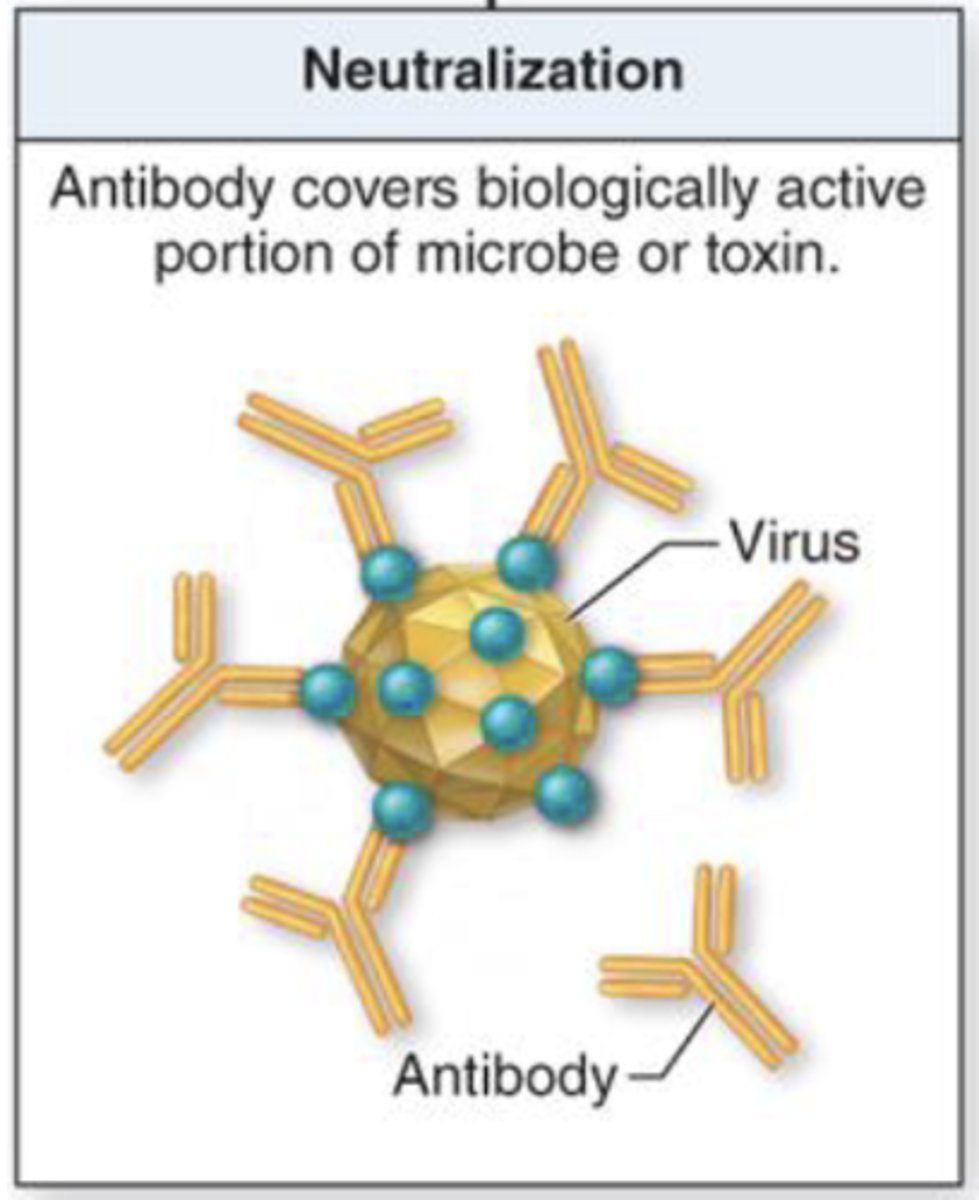
what term refers to antibodies covering biologically active portions of a microbe or toxin?
neutralization
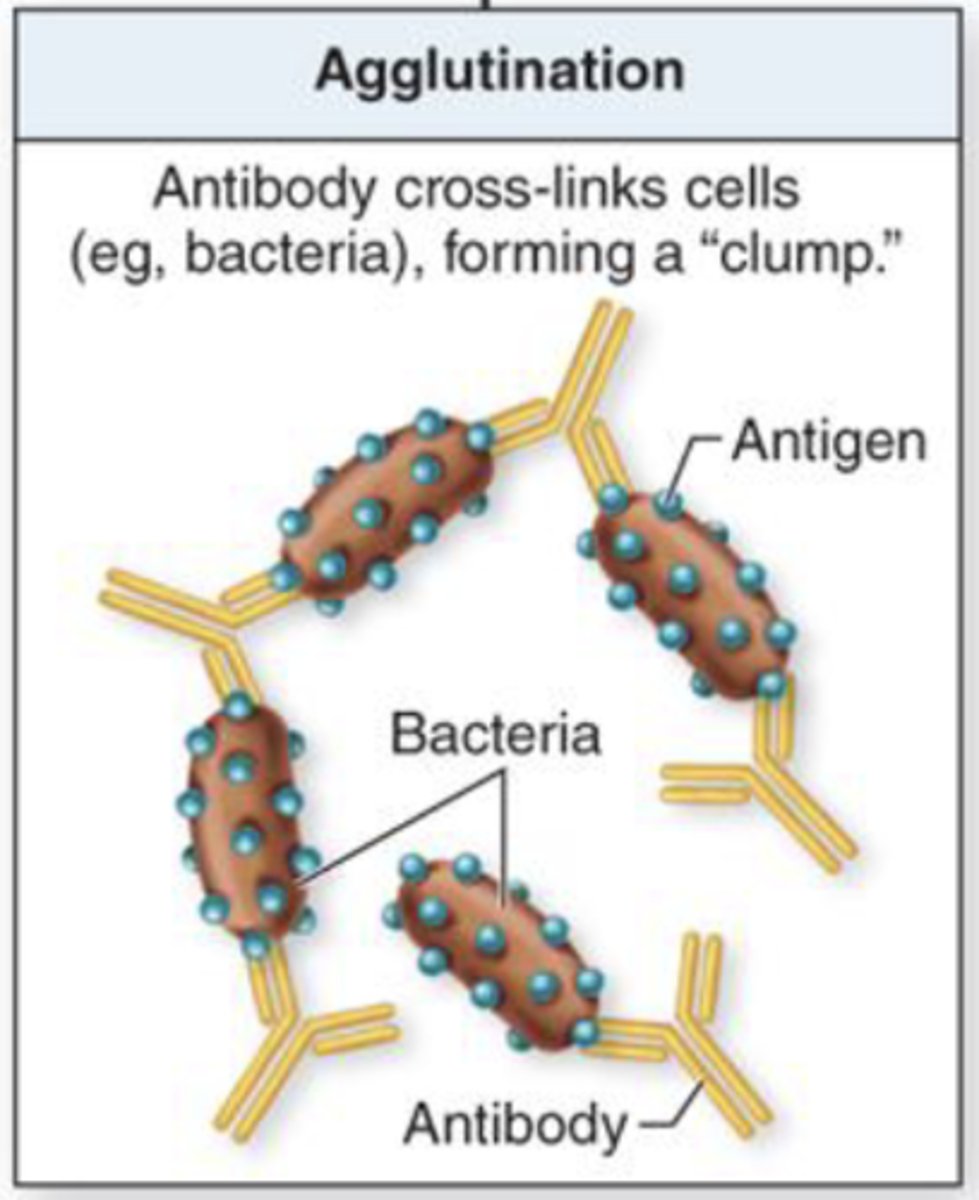
what term refers to antibodies cross-linking cells and forming a clump?
agglutination
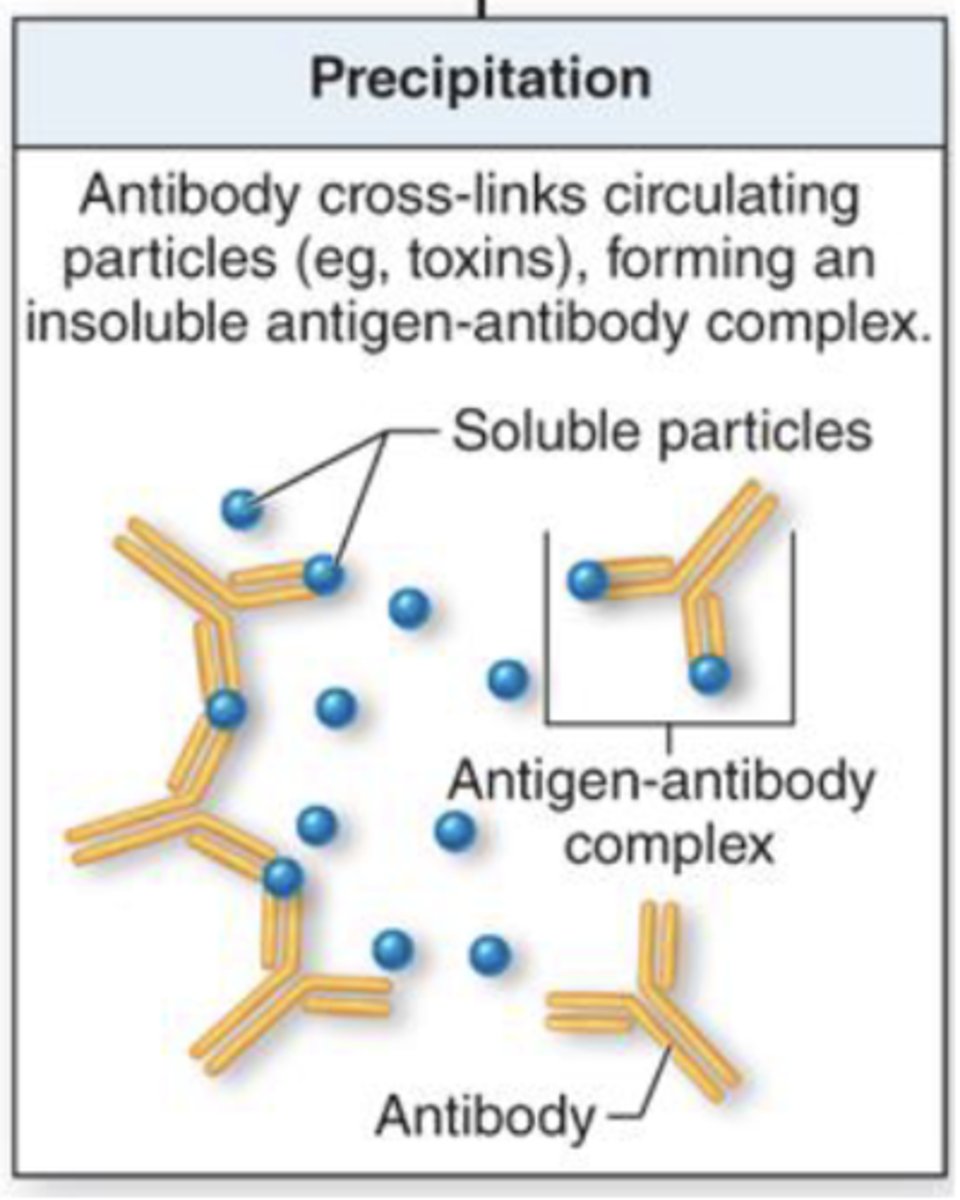
what term refers to antibodies cross-linking circulating particles and forming an insoluble antigen-antibody complex?
precipitation
which region of the antibody will bind to complement proteins to become activated?
constant region
which region of the antibody binds to surface receptors on certain cells?
constant region
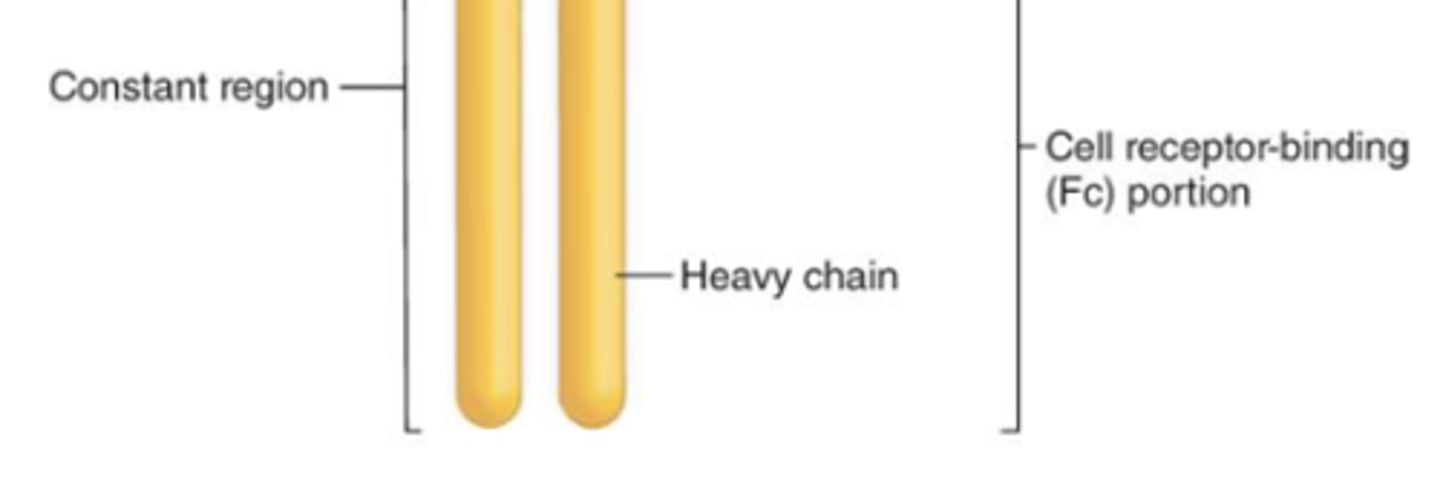
which region of the antibody will result in more efficient phagocytosis (opsonization) and natural-killer cell activation?
constant region
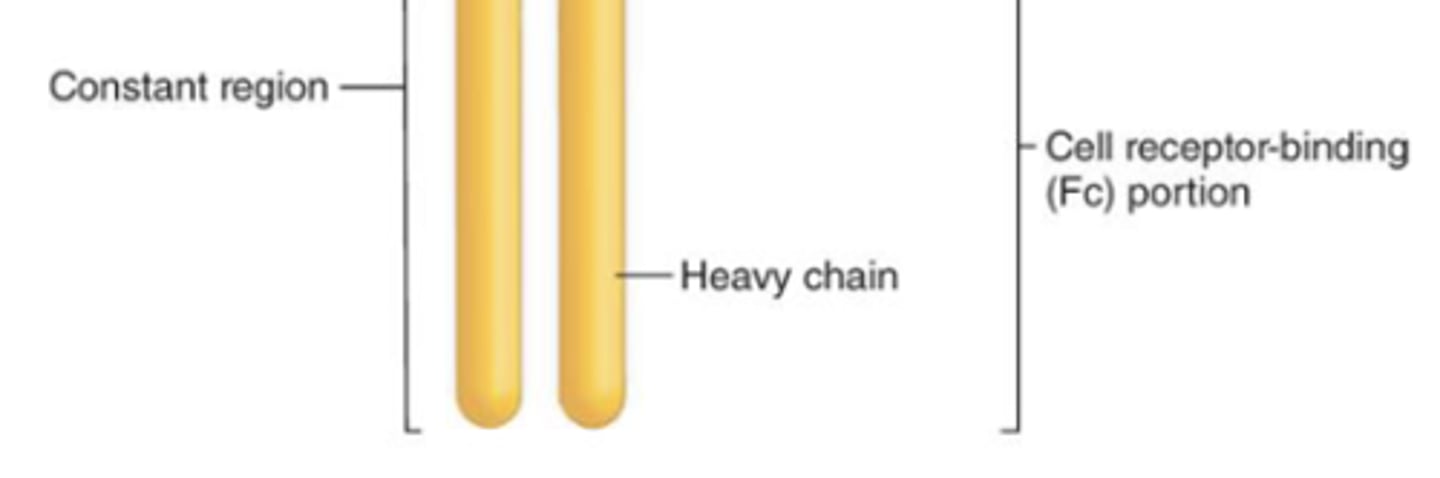
which region of the antibody, when activated, will result in degranulation from mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils?
constant region
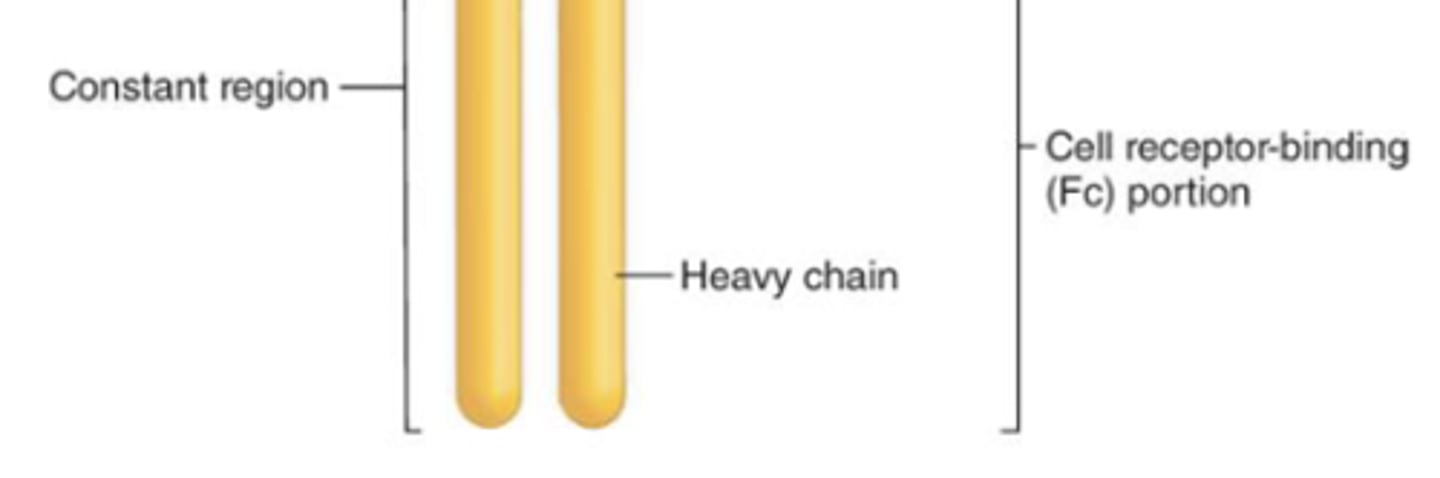
what are 2 antibody classes that have an Fc region (of the monomer form) that bind to B cells and functions as a B cell receptor?
1. IgD
2. IgM
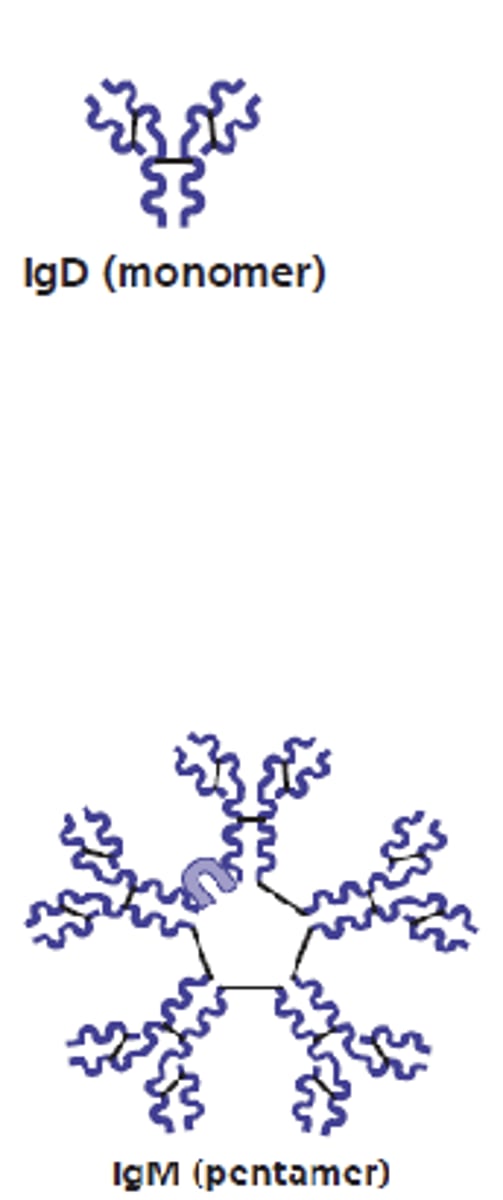

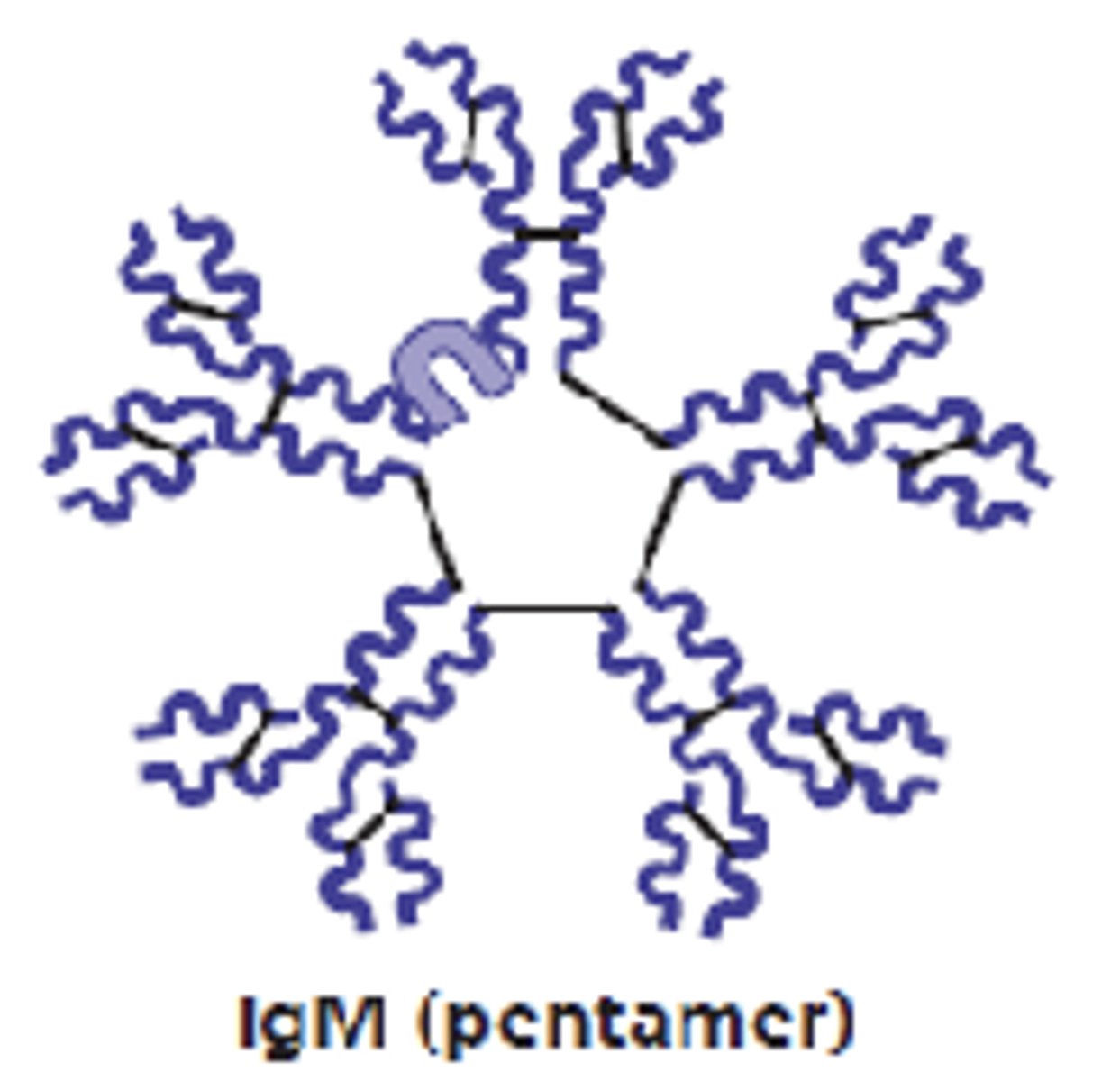
which antibody class will form pentamers in plasma?
IgM
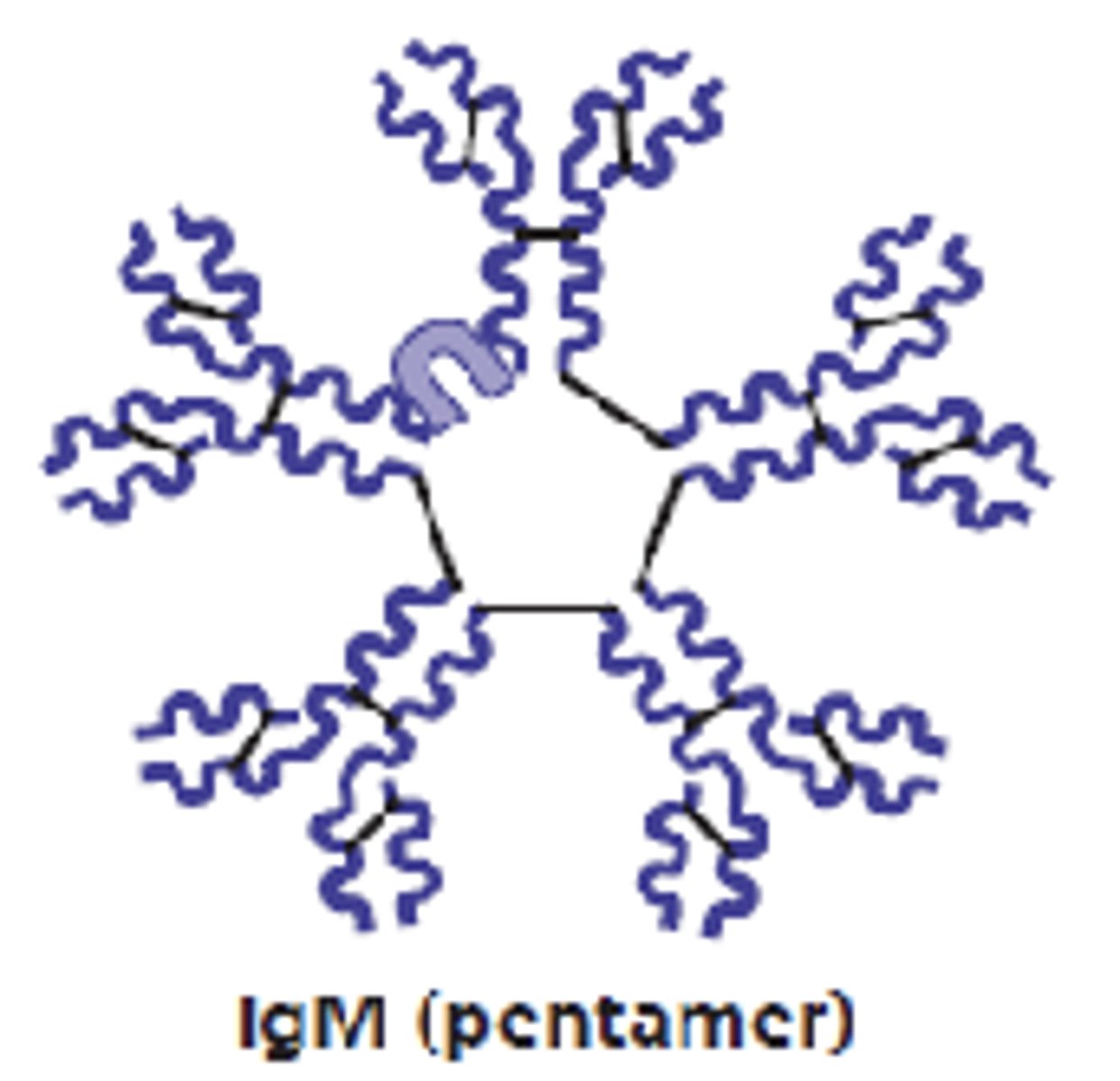
which antibody class is the first antibody released and the largest?
IgM
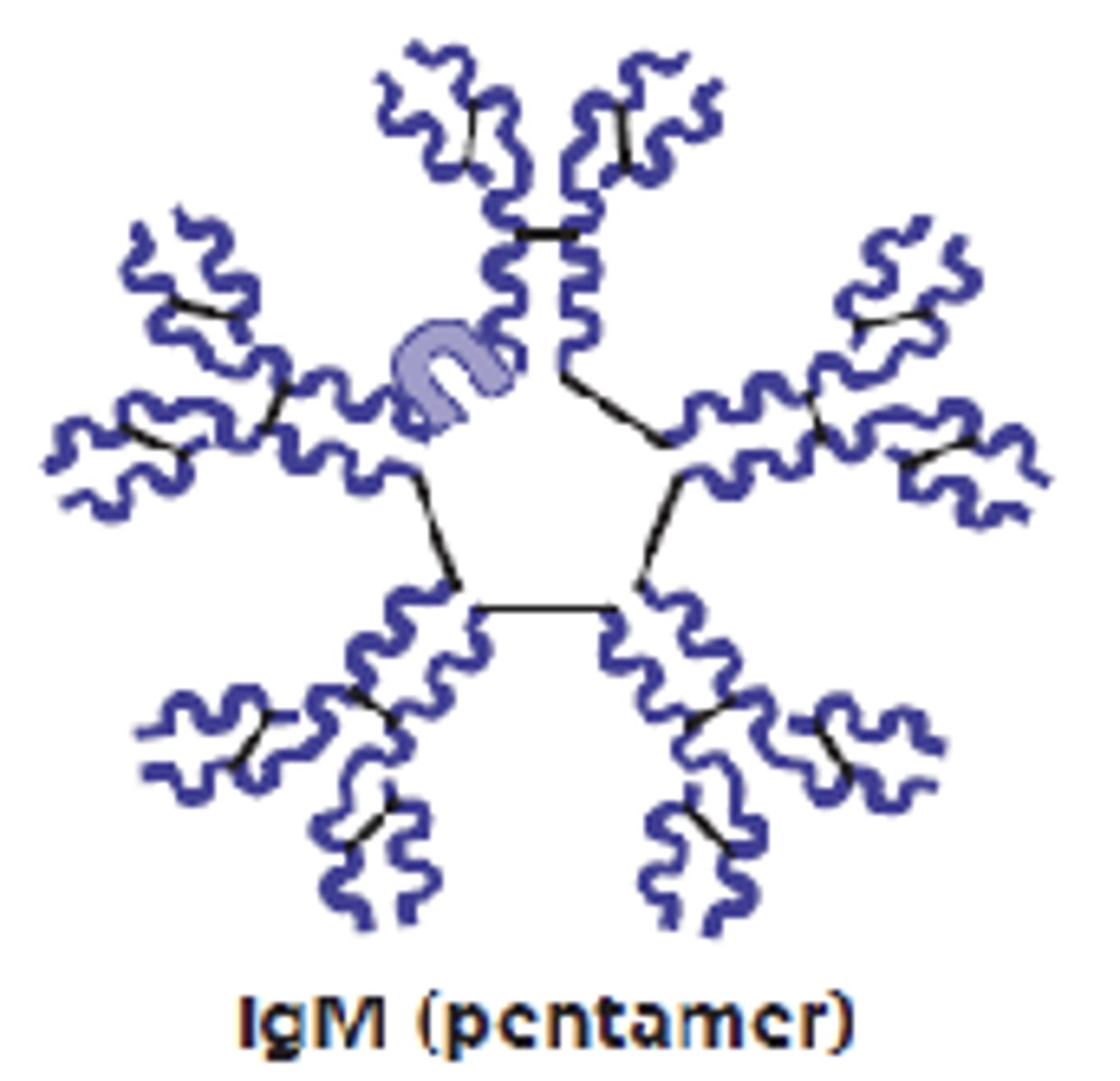
which antibody class is a potent agglutinating agent and activates the complement?
IgM
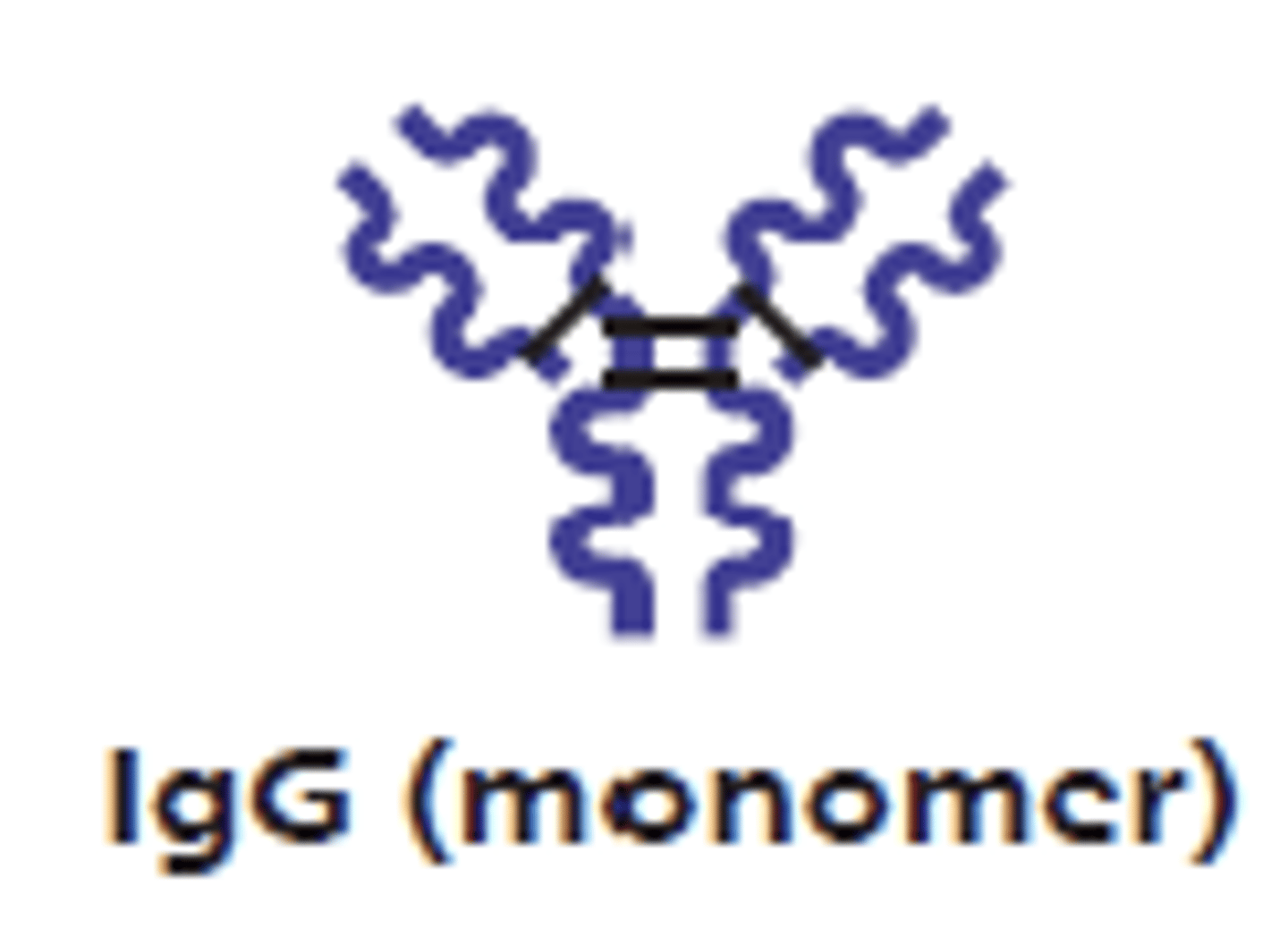
which antibody class make up 75-85% of antibodies in plasma?
IgG
which antibody class is the main antibody of late primary and secondary responses (readily activates the complement)?
IgG
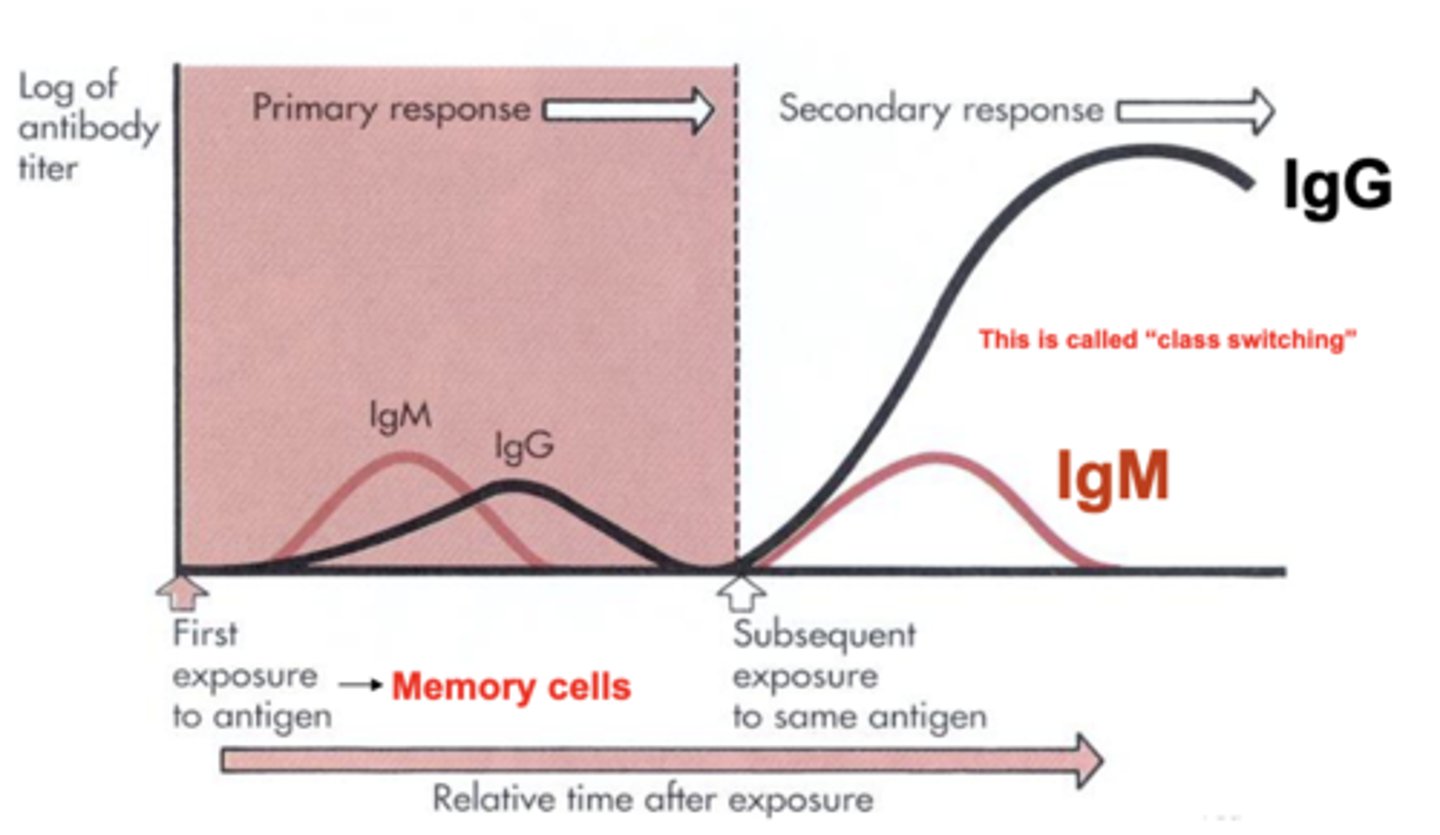
what is class switching?
a biological process that allows a B cell to change the type of antibody it produces
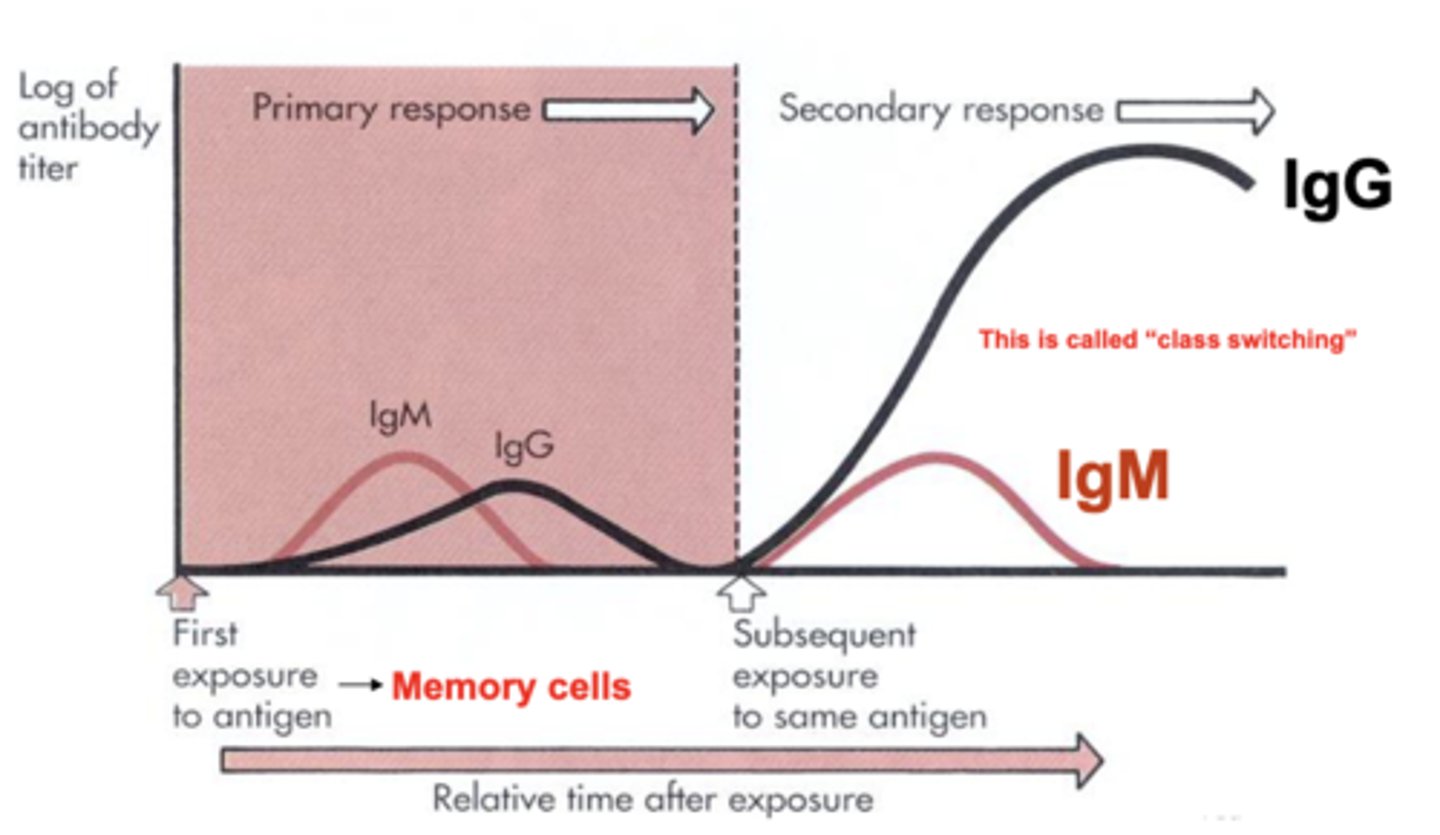
which antibody class is the only one that crosses the placental barrier?
IgG
which antibody class has an Fc region that binds to neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer cells?
IgG
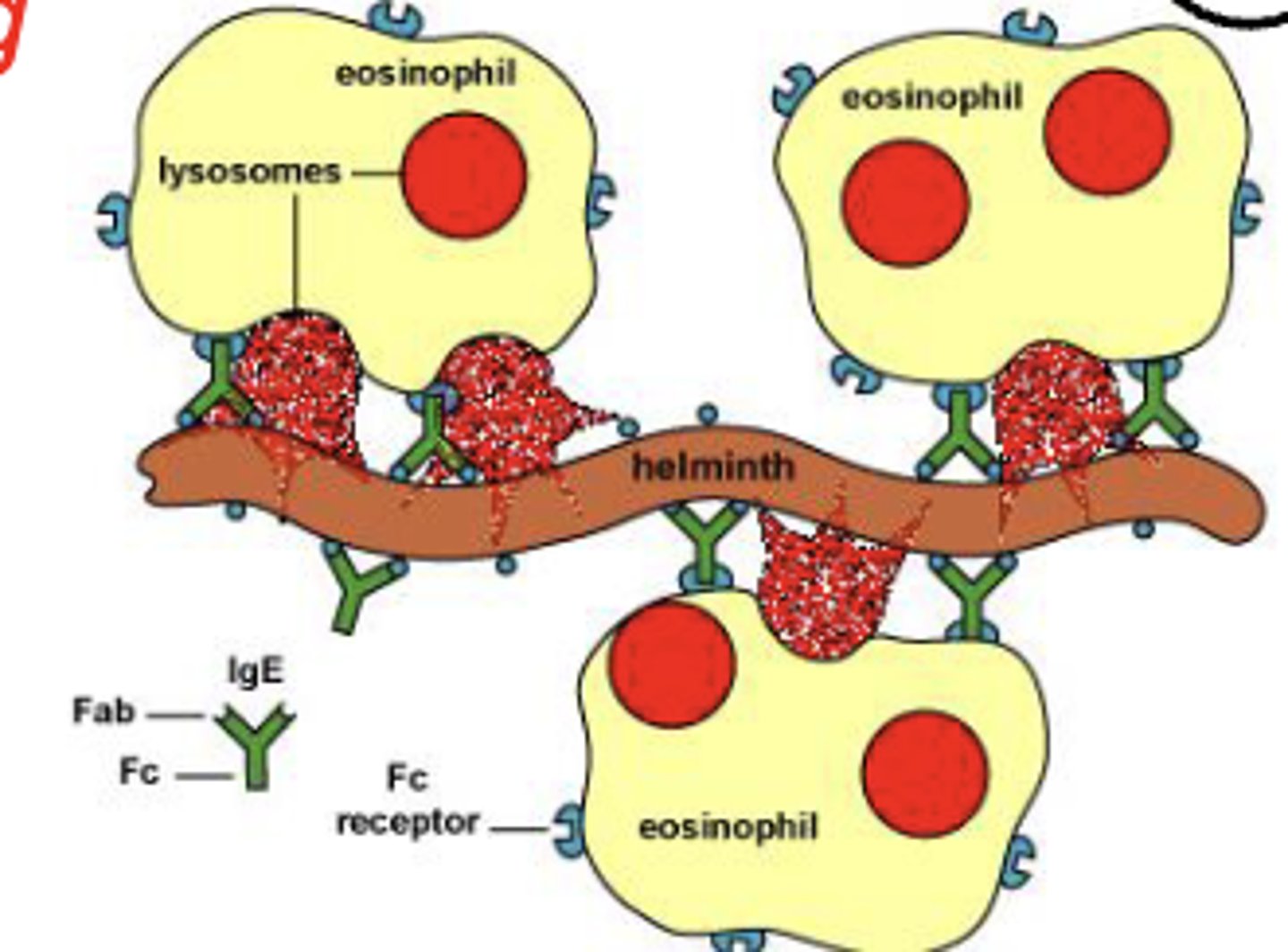
which antibody class has an Fc region that binds to mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils to trigger degranulation?
IgE
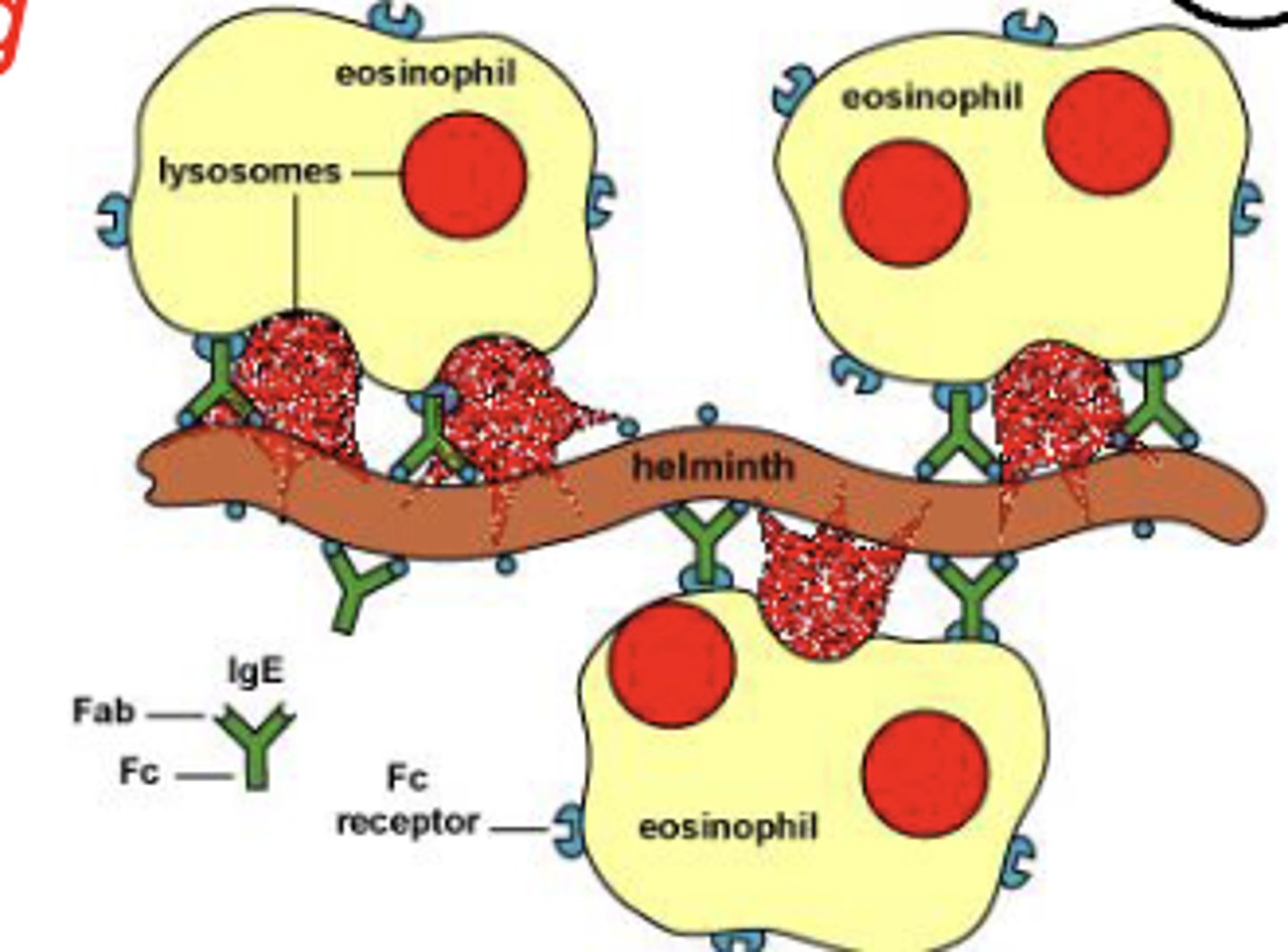
which antibody class is involved in allergies, asthma, and parasitic infections?
IgE
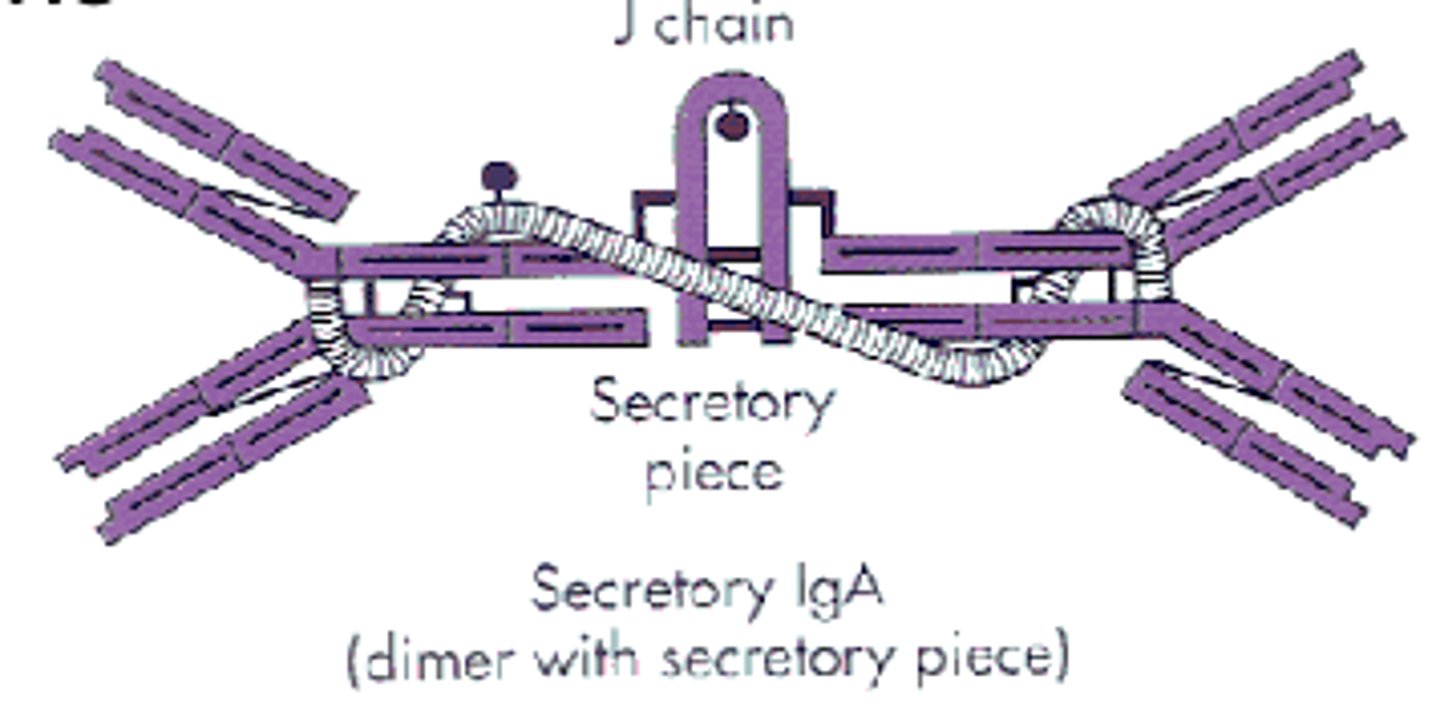
which antibody class is a monomer in plasma and helps stop pathogens from attaching to epithelial cell surfaces?
IgA
which antibody class can dimerize with an epithelial component?
IgA (secretory IgA)
which antibody class is found in body secretion like saliva, sweat, milk, intestinal juice, and prostate and vaginal secretions?
IgA
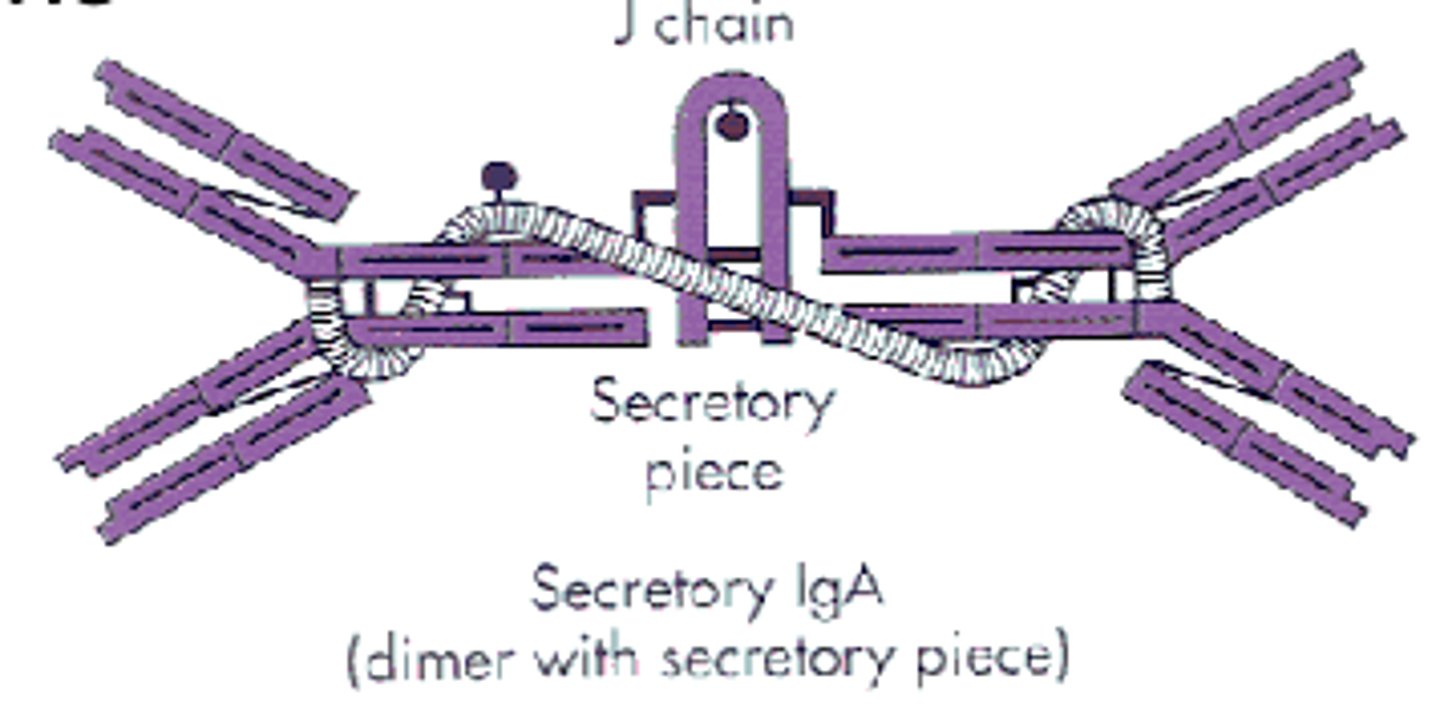
(t/f) IgA is fairly resistant to proteolysis
true
which adaptive immunity directly kills cells and regulates immune responses?
cellular immunity
(t/f) b cells exhibit cell markers called cluster of differentiation (CD), allowing cells to be identified, based on what molecules are present on their surface
false; t cells exhibit cell markers called cluster of differentiation (CD), allowing cells to be identified, based on what molecules are present on their surface
what t cells make up 75% of t cells?
helper t cells
what t cells are the major regulators of immune responses and produce lymphokines?
helper t cells
what t cells stimulate b cells, other t cells, and macrophages?
helper t cells
what t cells kill infected, tumorigenic, or transplanted cells?
cytotoxic t cells
what t cells induce apoptosis by secreting perforins and granzymes?
cytotoxic t cells
(t/b) lymphocytes are MHC restricted. what does this mean?
t; can only recognize antigens that are presented through MHC proteins (determines histocompatibility)
what are the 2 major classes of MHC?
1. mhc I
2. mhc II
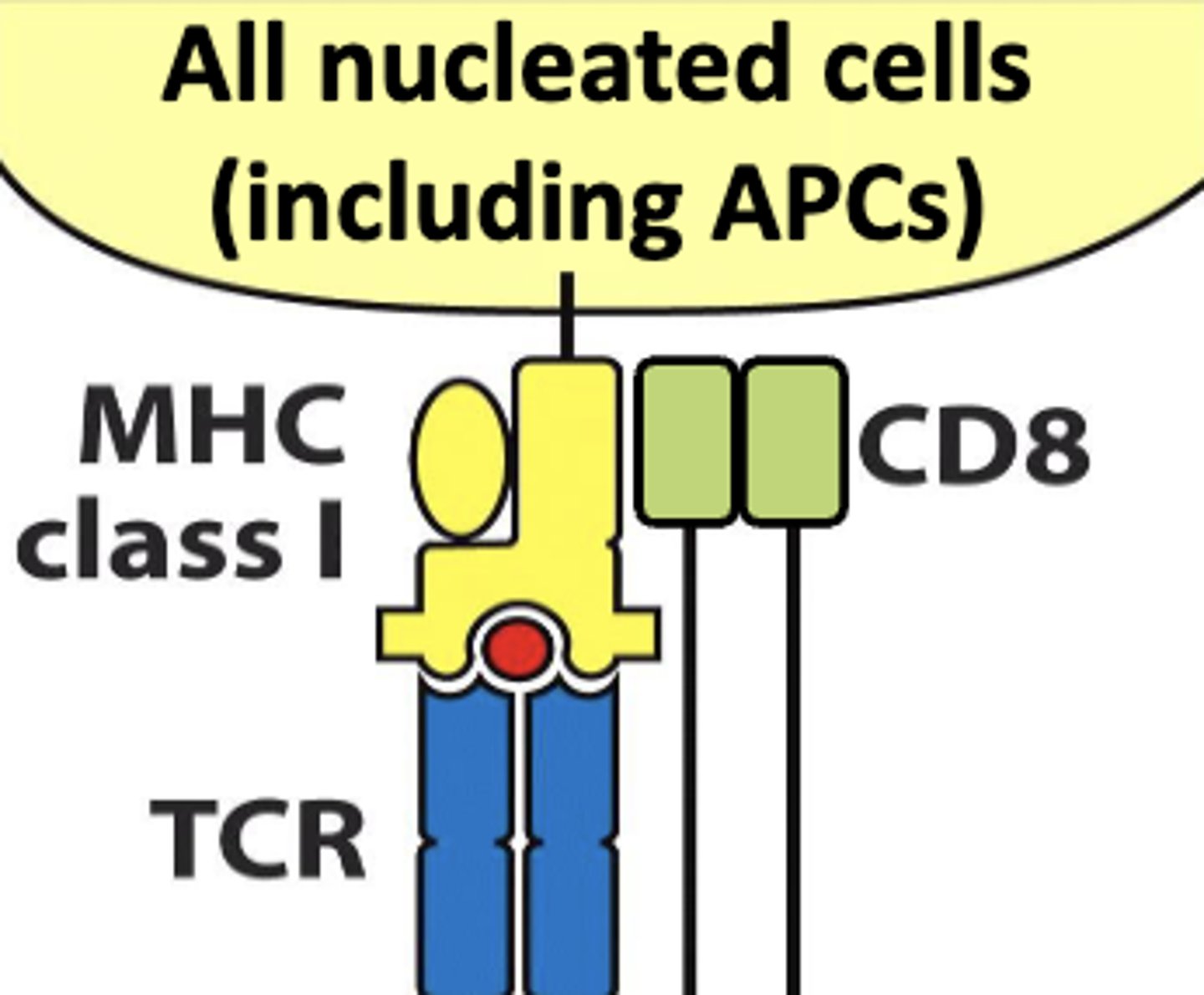
all nucleated cells (including antigen presenting cells) are associated with mhc class (I/II)
I
antigen presenting cells are associated with mhc class (I/II)
II
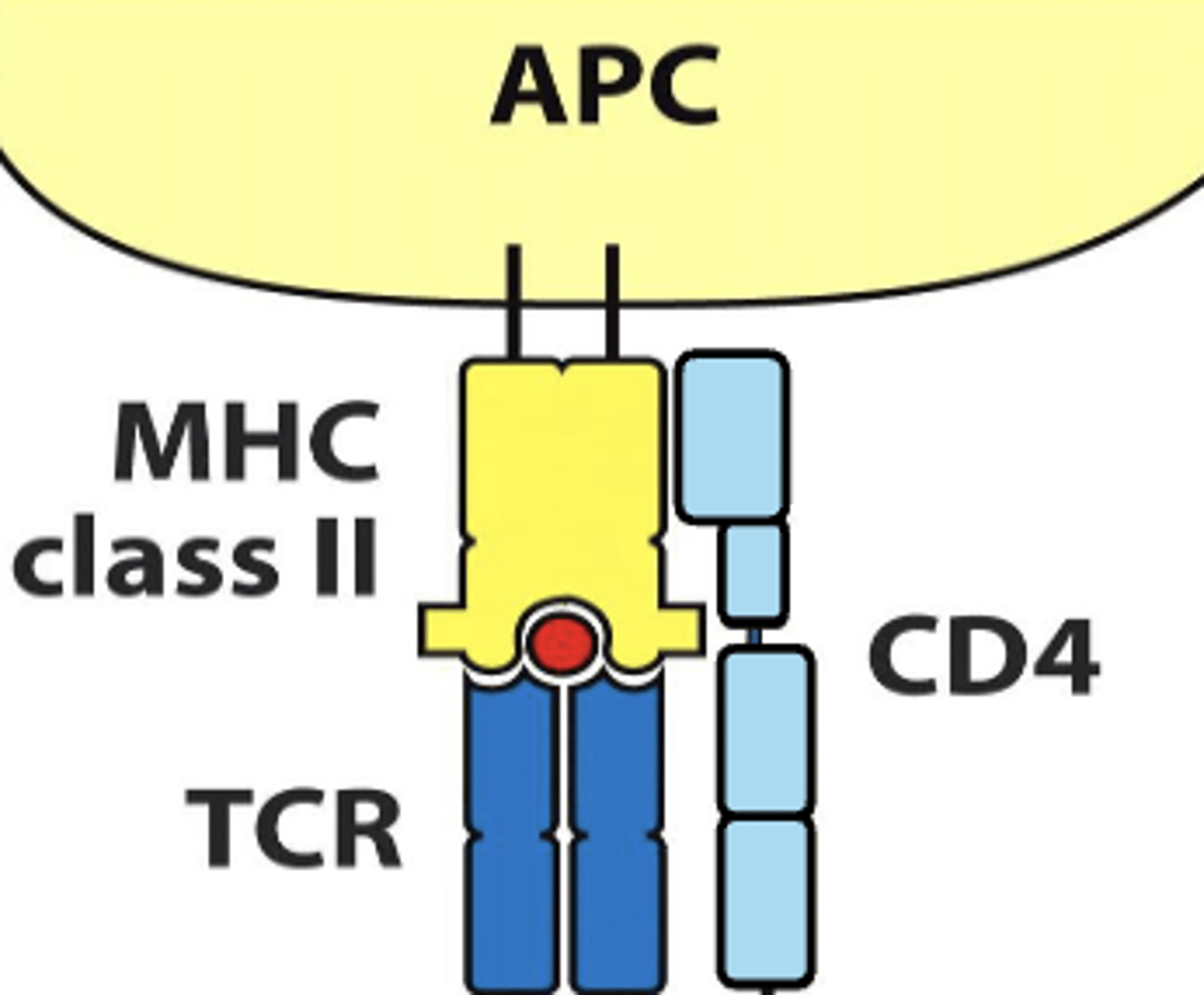
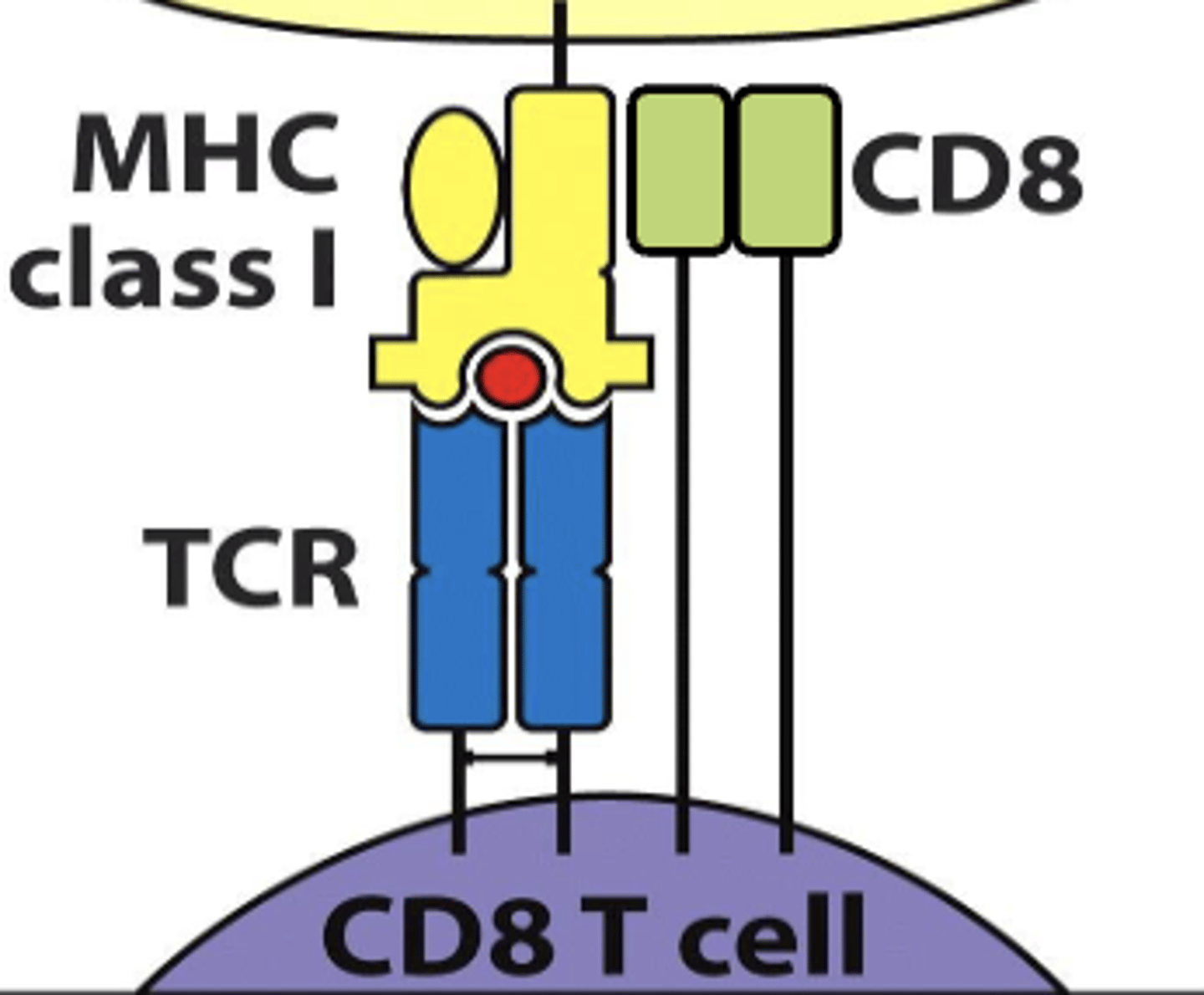
CD8 TCR interacts with mhc class (I/II)
I
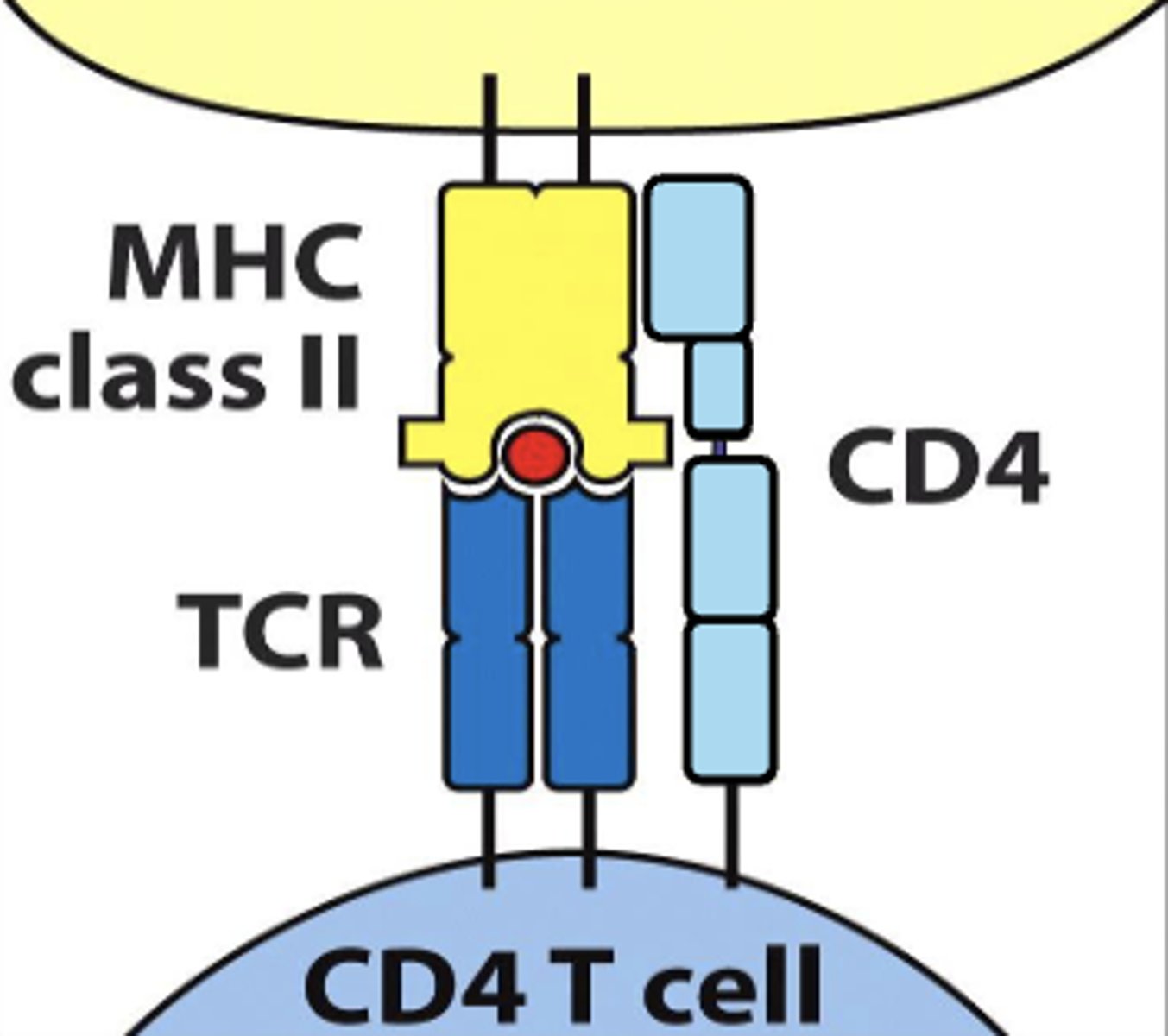
CD4 TCR interacts with mhc class (I/II)
II
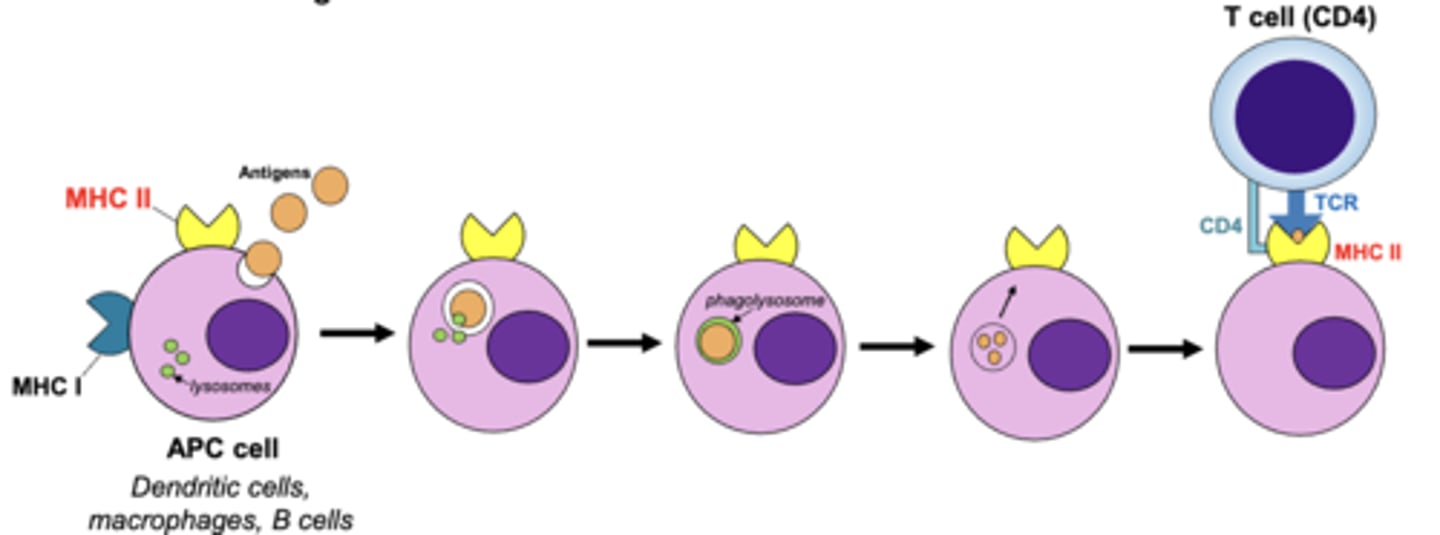
what are 3 antigen presenting cells?
1. dendritic cells
2. macrophages
3. b cells
what are 2 ways antigen presenting cells internalize antigens to present antigen fragments to t cells for recognition?
1. phagocytosis (macrophages and dendritic cells)
2. receptor-mediated endocytosis (b cells)
which t cells are known as helper t cells?
CD4
which t cells are known as cytotoxic t cells?
CD8
which mhc class will bind with exogenous antigens?
mhc class II
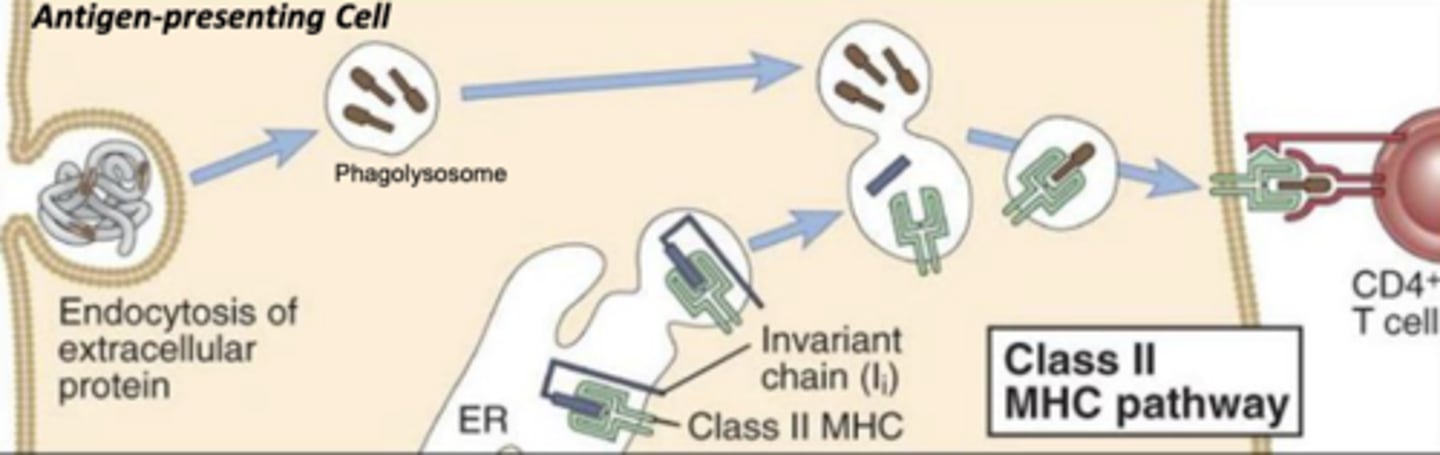
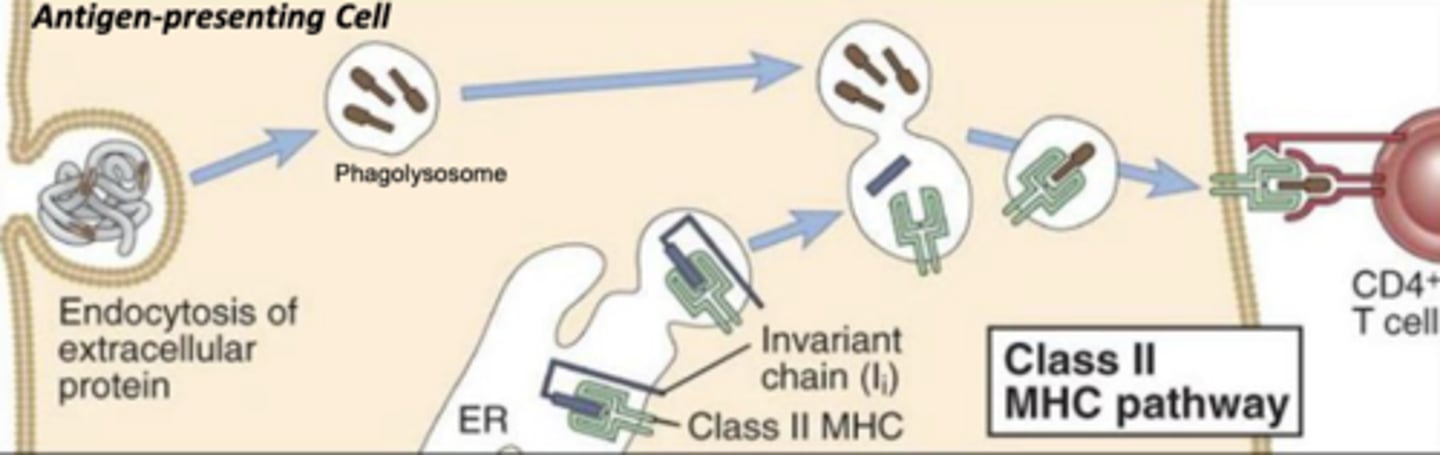
which mhc class will bind with antigens that have been internalized and broken down in a phagolysosome?
mhc class II
which mhc class will lead to the death of the infected cell?
mhc class I
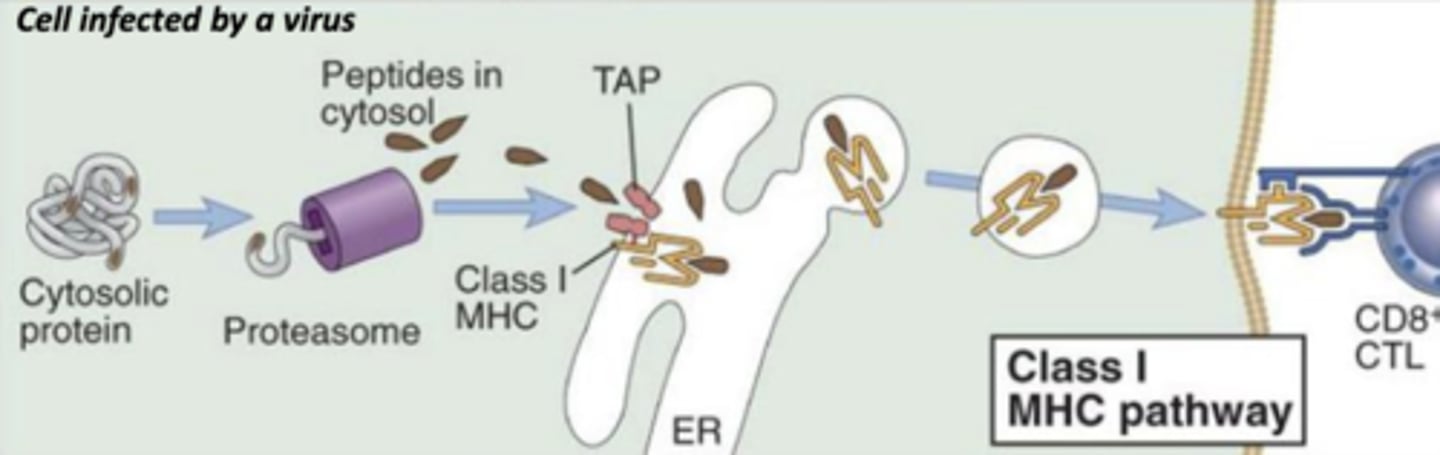
which mhc class binds with endogenous antigens?
mhc class I
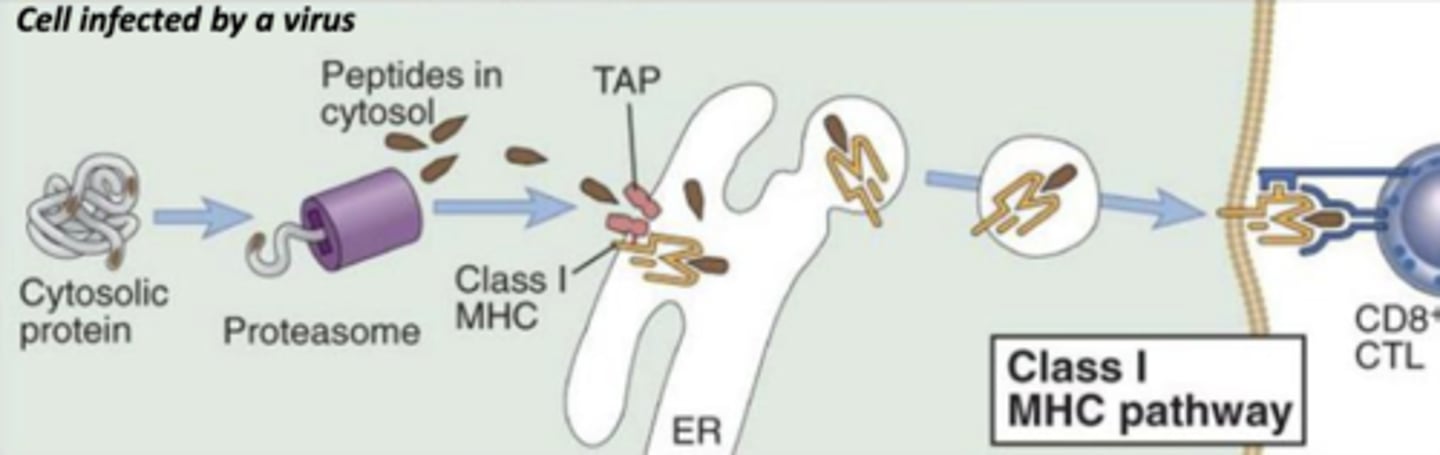
which mhc class will bind to abnormal proteins found in infected or cancer cells?
mhc class I
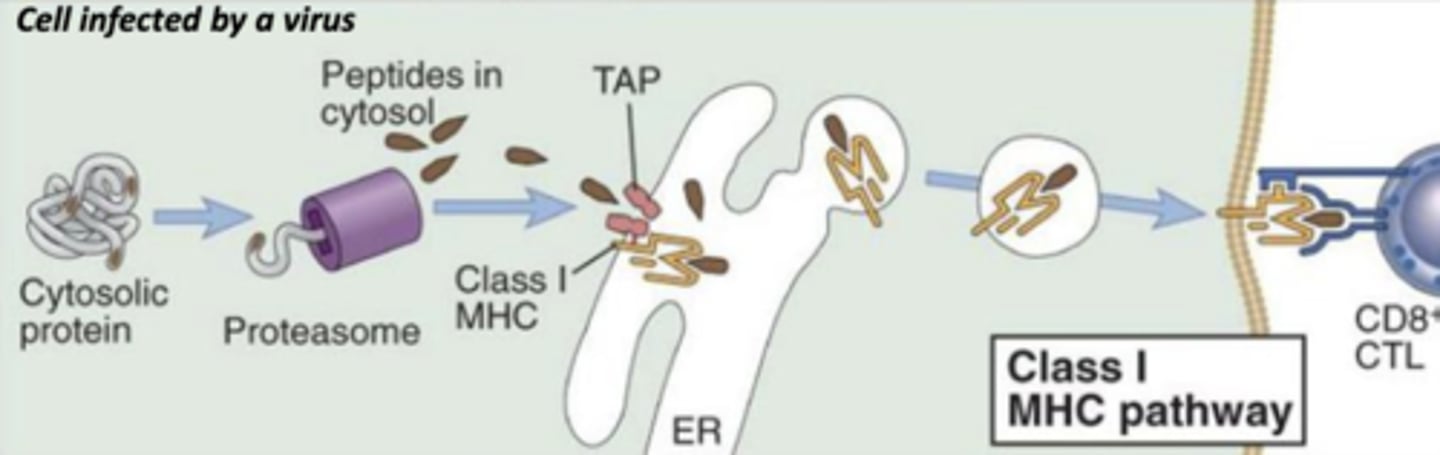
which antigen presenting cells will engulf pathogens that enter tissues, become activated, and then enter lymphatics to present antigens to t cells in the lymph node?
dendritic cells
which antigen presenting cells are found in connective tissues and the epidermis (known as Langerhans cells)?
dendritic cells
(t/f) macrophages are the antigen presenting cells that are the key link between innate and adaptive immunity
false; the dendritic cells are the link between innate and adaptive immunity
(t/f) the most effective antigen presenters known are the b cells
false; the most effective antigen presenters known are the dendritic cells
once activated by dendritic cells, helper t cells proliferate and form what 2 populations?
1. long-lived memory helper t cells
2. effector (activated) helper t cells
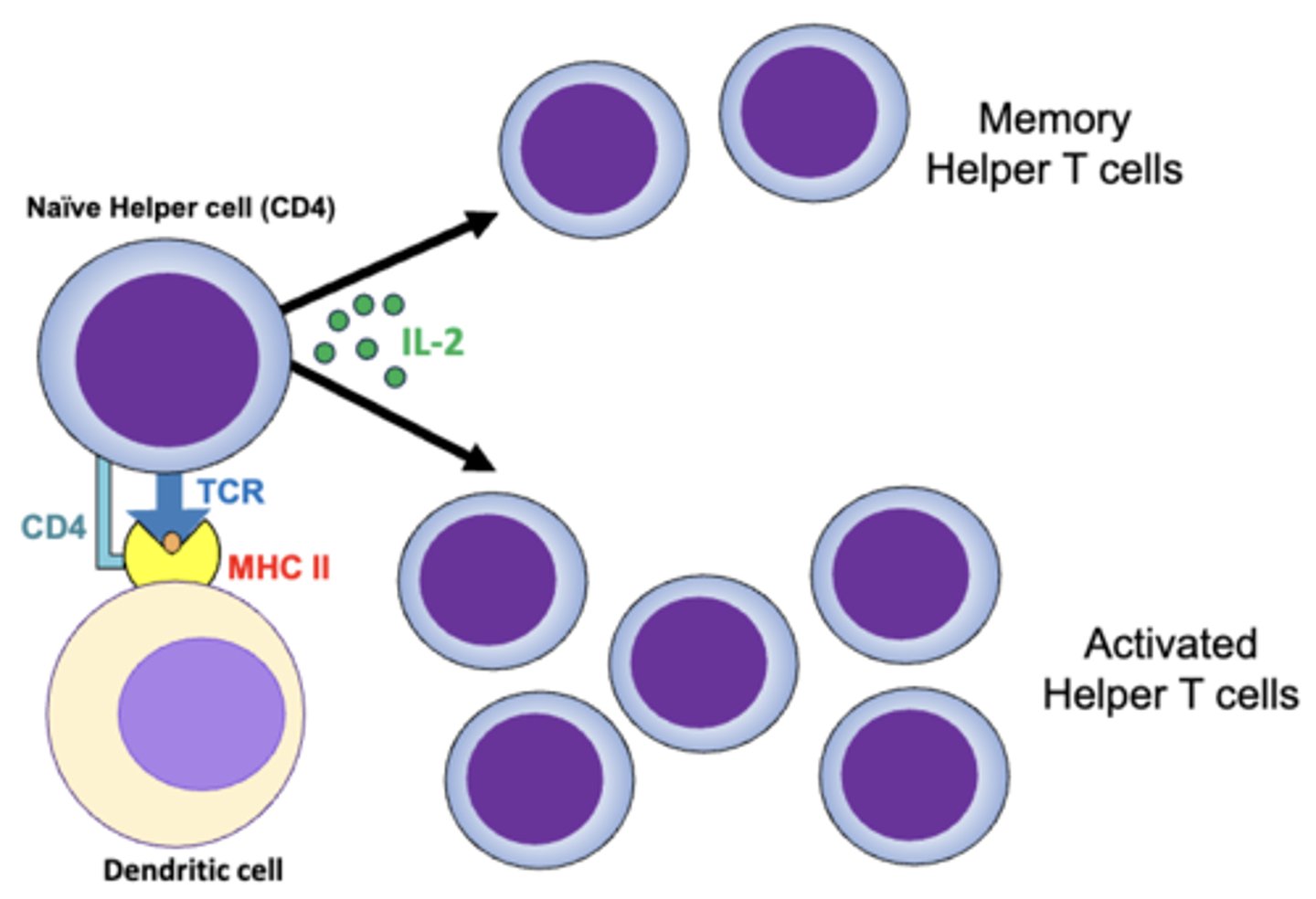
what 3 cells do activated helper t cells activate?
1. b cells (differentiate into plasma cells) through IL-4
2. macrophages (increased phagocytic activity and aggression)
3. cytotoxic t cells (proliferation) though IL-2
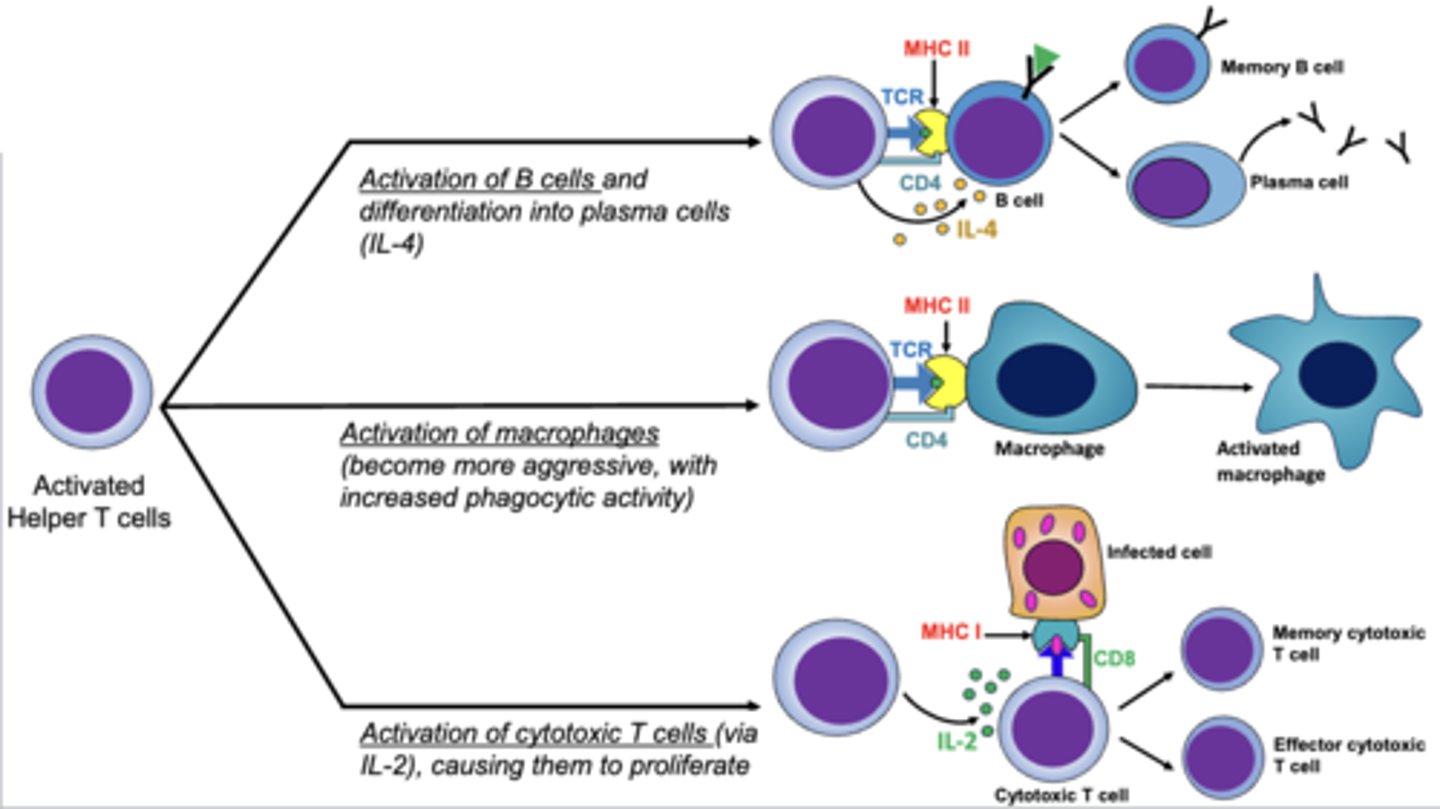
which t cells directly attack and kill infected cells (viruses, parasites, intracellular bacteria), cancer cells, and foreign cells (transfusion and transplants)?
cytotoxic cells
what vessels transport interstitial fluid back to the blood circulation?
lymphatic vessels
what are the 2 primary lymphoid organs?
1. bone marrow
2. thymus
what are 4 secondary lymphoid organs?
1. spleen
2. lymph nodes
3. MALT
4. tonsils
(primary/secondary) lymphoid organs are where t and b cells are formed and matured
primary
(primary/secondary) lymphoid organs is where mature, but naive lymphocytes first encounter their antigen and become activated
secondary
which lymphoid organ is where t cells mature?
thymus
(t/f) the thymus is most active and large in size during adulthood
false; the thymus is most active and large in size during childhood
which lymphoid organ is surrounded by a connective tissue capsule that extends septa into the parenchyma, dividing the organ into many incomplete separated lobules?
thymus
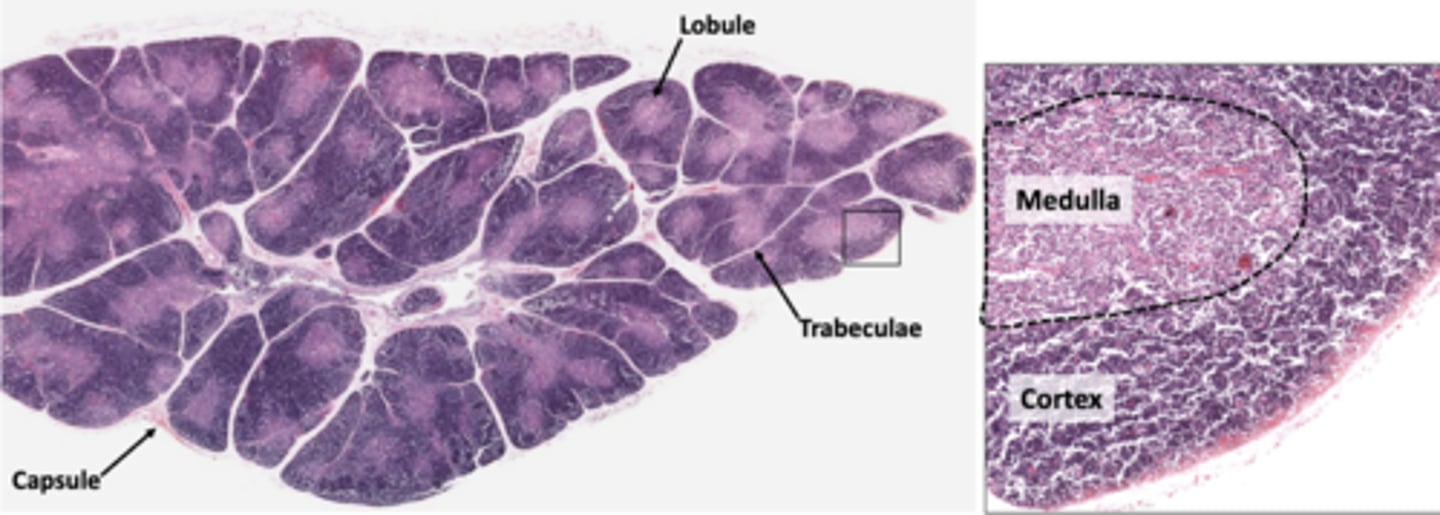
each lobule of the thymus an outer (lightly/darkly) (basophilic/eosinophilic) cortex and an inner (lighty/darkly) stained medulla
darkly, basophilic, lightly
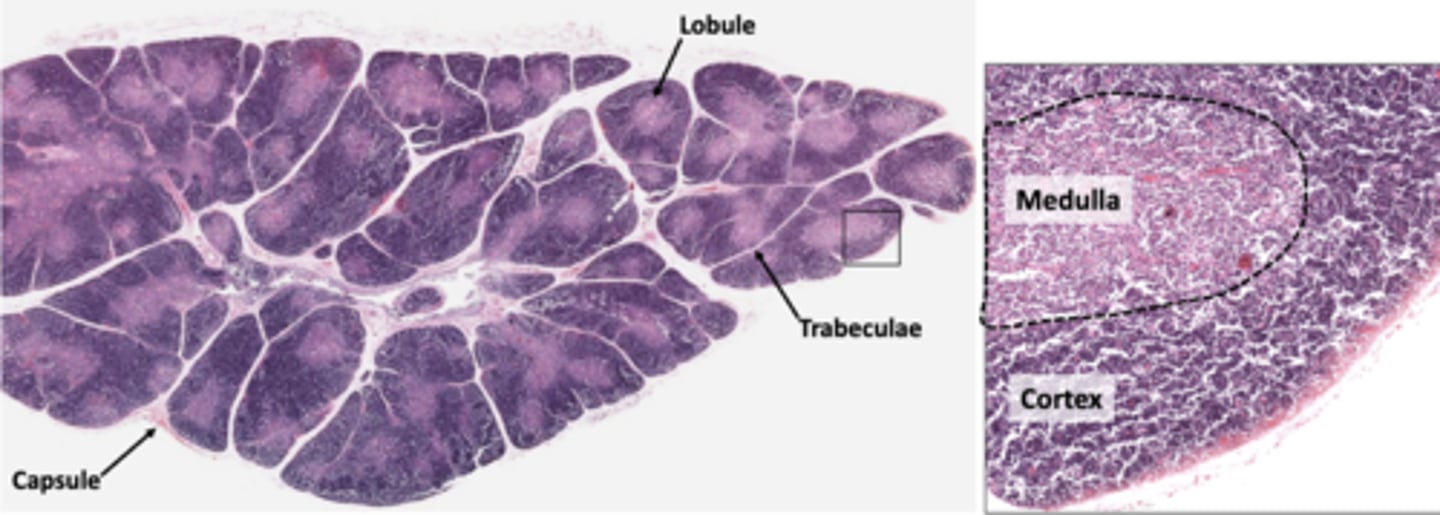
which layer of the thymus contains rapidly dividing lymphocytes, TECs, and macrophages?
cortex
which layer of the thymus provides support and participates in t-cell education?
cortex
which layer of the thymus isolate the cortical compartment and form a blood thymus barrier?
cortex
which layer of the thymus contains fewer lymphocytes and makes it look like the brighter layer?
medulla
the (cortical/medullary) TECs form the boundary between the cortex and medulla
medullary
which layer of the thymus has TECs that form a cytoreticulum that provides support and presents self-antigens to t cells?
medulla
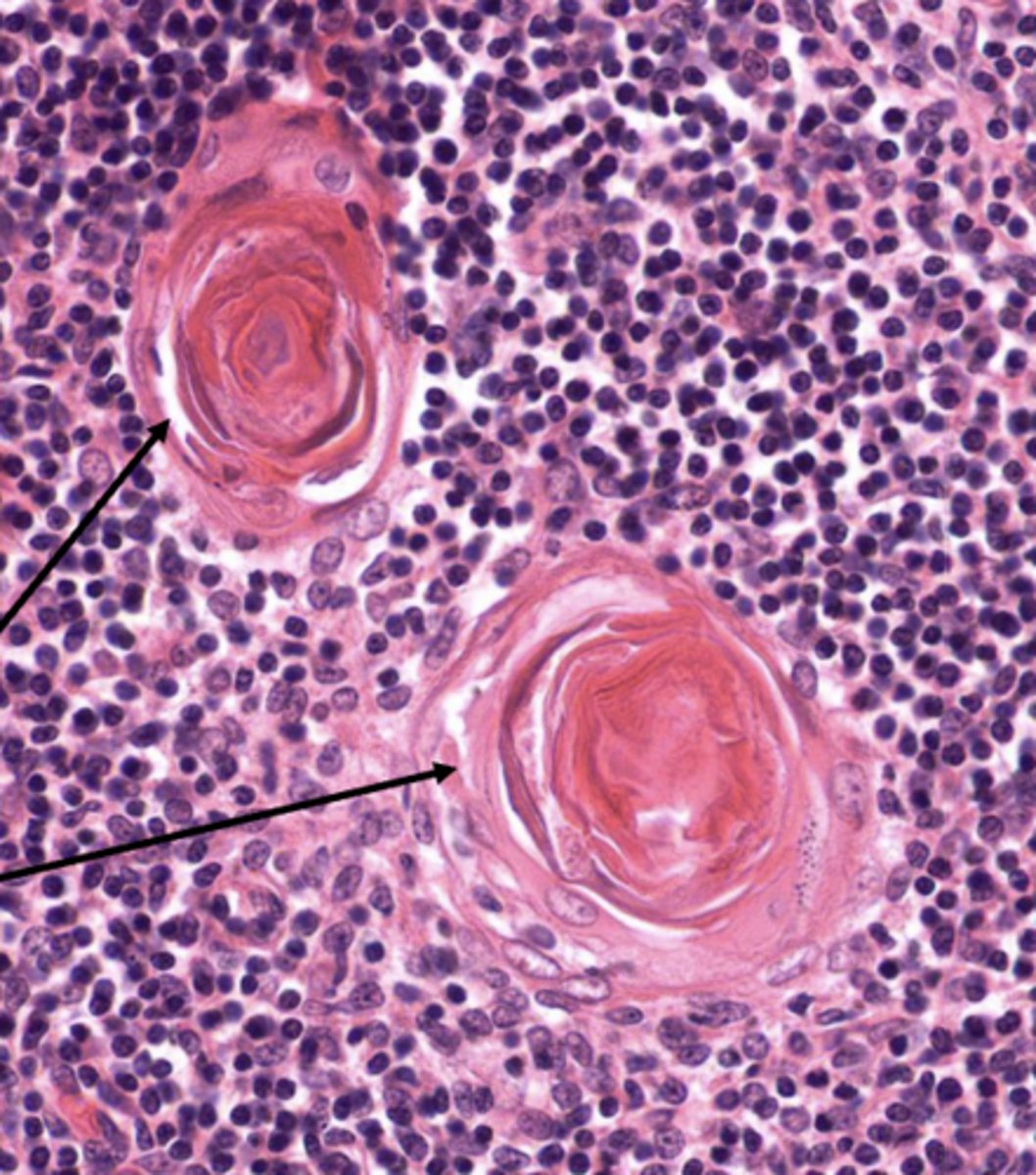
which layer of the thymus has TECs that form large aggregates of TECs called Hassall corpuscles?
medulla
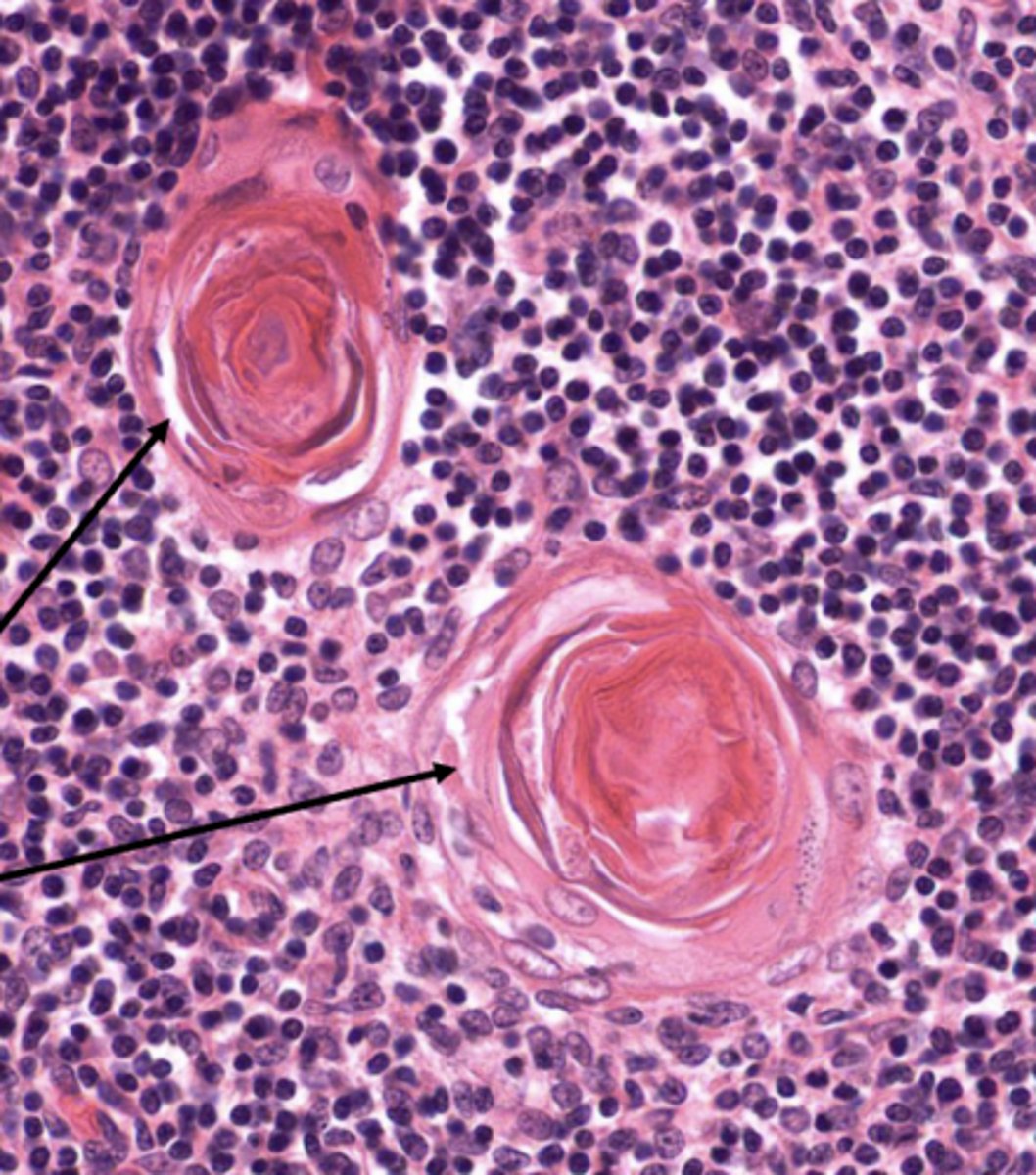
which layer of the thymus releases cytokines that promote the development of regulatory t cells?
medulla (by the Hassall corpuscles)
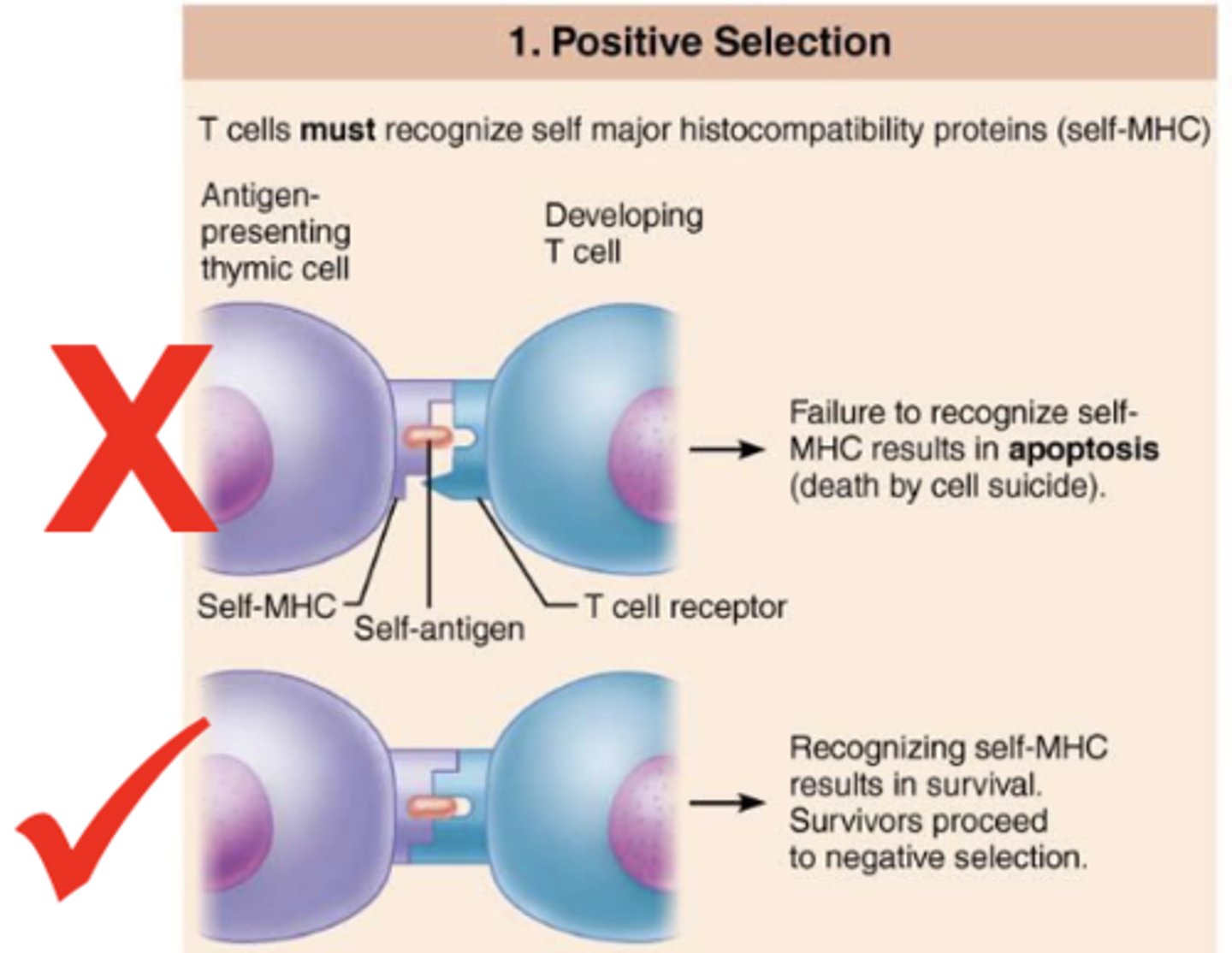
what are the 3 steps of maturing progenitor t-cells (thymocytes) into mature t-cells?
1. expression of TCR (binds MHC)
2. production of surface glycoproteins (CD4 or CD8)
3. thymic education through positive then negative selection
where in the thymus does positive selection occur?
cortex
where in the thymus does negative selection occur?
medulla
what is positive selection?
selection of t cells capable of recognizing self-MHC proteins; failure to recognize results in apoptosis
what is negative selection?
selection of t cells that do not bind tightly to self-antigens; recognition (tightly binding) of self-antigen results in apoptosis
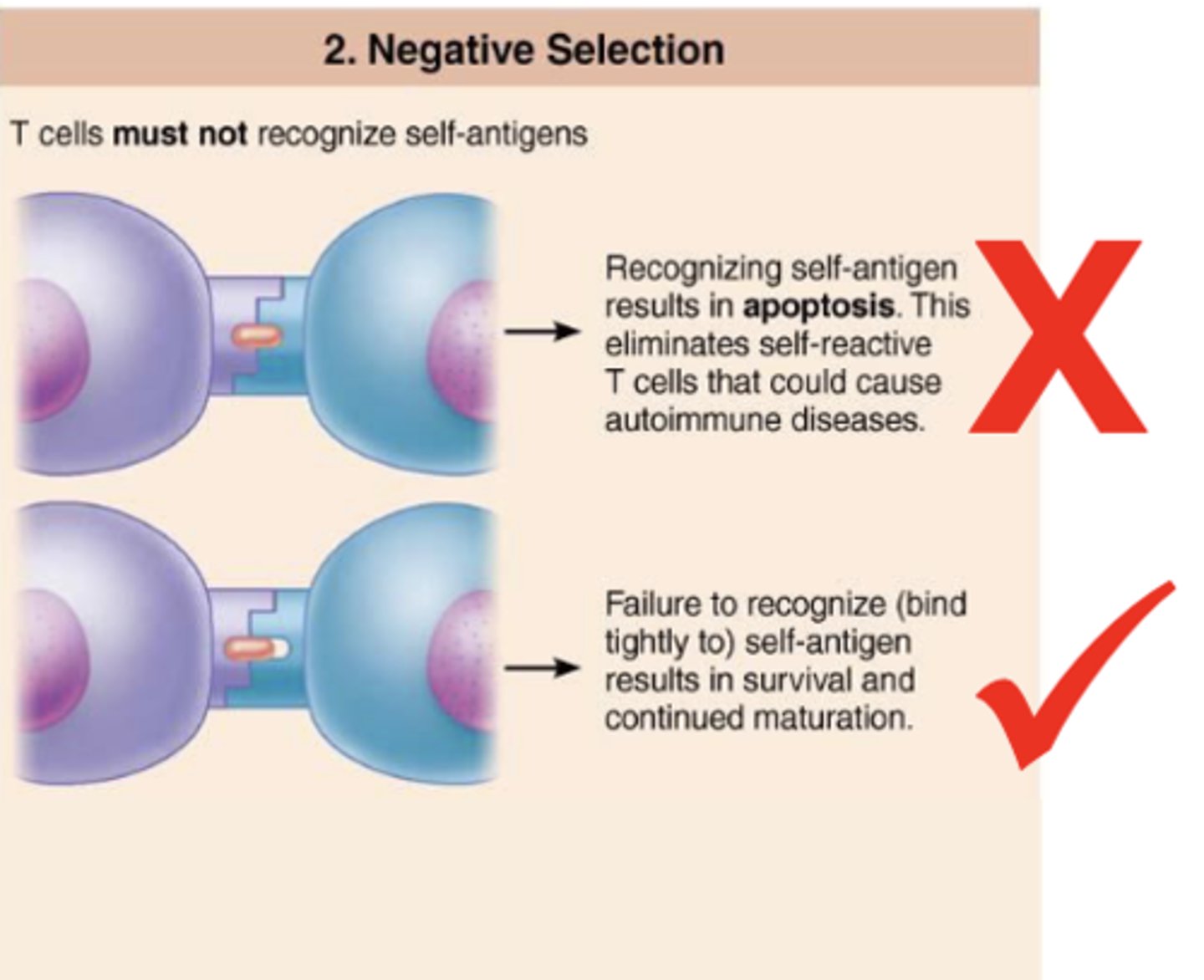
(negative/positive) selection eliminates t cells that could cause autoimmune diseases
negative