AP Biology - DNA Replication
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Double helix structure
DNA's twisted ladder shape
Directionality of DNA
DNA strands have a 5' to 3' orientation
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA
Numbering of carbons in a sugar
1' to 5'
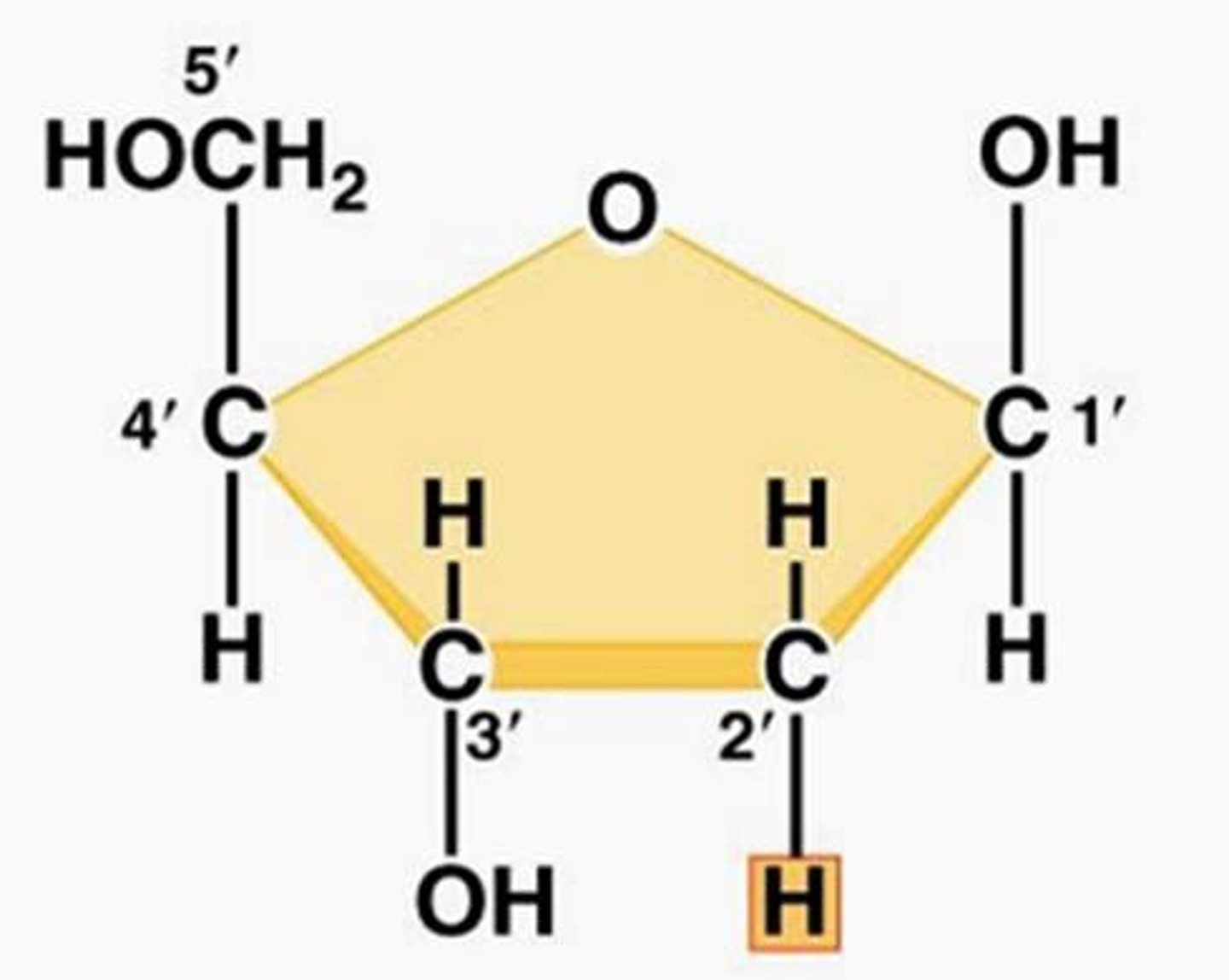
Putting the DNA backbone together
Connecting the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA
Anti-parallel strands
DNA strands run in opposite directions
Hydrogen bonds
Weak bonds between nitrogenous bases in DNA
Covalent phosphodiester bonds
Strong bonds between sugar and phosphate groups in DNA
Base pairing in DNA
Specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA
Purines
Adenine (A) and Guanine (G) nitrogenous bases
Pyrimidines
Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C) nitrogenous bases
Replication of DNA
making a copy of a DNA molecule.
Unwind DNA
Separating the two strands of DNA
Helicase enzyme
Enzyme that unwinds DNA helix
Single-stranded binding proteins
Proteins that stabilize unwound DNA strands
Polymerase III
Enzyme that adds new bases to a DNA strand
Energy of Replication
DNA bases arrive as nucleosides. The extra phosphate groups split off to provide the energy for the endergonic synthesis of DNA.
Lagging strand
The DNA strand synthesized in short fragments
Okazaki fragments
Short DNA fragments on the lagging strand
Leading strand
The DNA strand synthesized continuously
Replication fork
The point where DNA strands separate
RNA primers
Short RNA sequences that initiate DNA synthesis
DNA polymerase I
Enzyme that removes RNA primers and replaces them with DNA
Chromosome erosion
Loss of bases at the ends of chromosomes
Telomeres
Repeating sequences at the ends of chromosomes
Telomerase
Enzyme that extends telomeres