Chemistry - C3 Chemicals of the natural environment
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:48 AM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
Metallic bonding
This is a giant structure containing stationary positive metal ions and a sea of delocalized electrons. This creates strong forces of electrostatic attraction. This make metals generally solid at room temp, has high melting/boiling points, good conductors and malleable.
2
New cards
Ionic equations

3
New cards
Acid + Metal
→ Salt + Hydrogen
4
New cards
Water + Metal
→ Metal hydroxide + hydrogen
5
New cards
Ore
A rock that is typically a metal oxide and is economically worth extracting the metal from
6
New cards
Extracting with carbon
This only works for metals less reactive than carbon. The ore is heated with the carbon and the carbon displaces the metal in it, extracting the metal
7
New cards
phytoextraction
This involves growing a plant in an area of soil with metal compounds. The plant cannot get rid of the metal so it builds up in the leaves. These plants then can be harvested, dried and burned in a furnace and the ash will contain metal compounds.
8
New cards
Bioleaching
This uses bacteria to convert insoluble metal compounds in the ore to soluble compounds which extracts the metal in the process. leachate which is produced during the reaction contains an aqueous solution of metal ions.
9
New cards
Oxidation
loss of electrons
10
New cards
Reduction
gain of electrons
11
New cards
Cathode
the negative electrode where reduction occurs. This is where metals form during electrolysis
12
New cards
Anode
the positive electrode where oxidation occurs. This is where non-metals form during electrolysis.
13
New cards
Electrolysis (Molten)
This is the process of extracting metals from ores that are more reactive than carbon
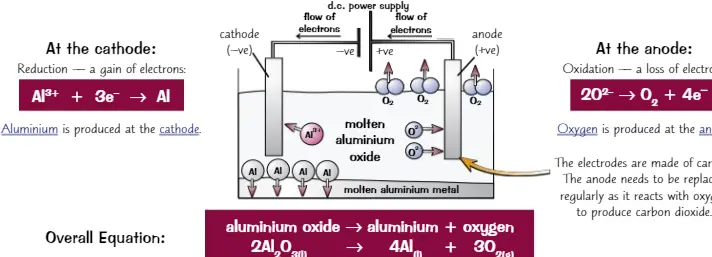
14
New cards
Electrolysis (aqueous)
This is the process of extracting metals from ores that are more reactive than carbon but have too high a melting point to melt. at the cathode if H+ and metal ions are present hydrogen gas will be formed (if the metal is more reactive than hydrogen). Unless chlorine ions are present, oxygen will be formed at the anode.
15
New cards
Covalent bonds
When two non-metals bond together and share electrons on their outer shell
16
New cards
Dot cross diagram
a way of displaying covalent bonds
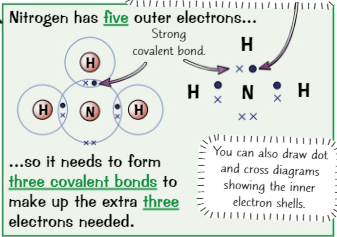
17
New cards
Displayed formula
a way of displaying covalent bonds
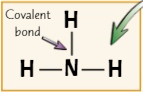
18
New cards
Ball and stick diagram
a way of displaying covalent bonds
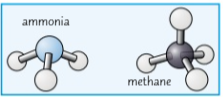
19
New cards
Simple covalent structures
These are covalent structures that are only made up of a few atoms like water, oxygen and methane. They cannot conduct electricity and have low melting/boiling points as they have weak intermolecular forces.
20
New cards
Homologous series
A family of molecules that share the similar general formula and have the same functional group. They also carry similar properties. (For example alkane and alkenes)
21
New cards
Alkanes
These are the simplest homologous series. They have a general formula of **C***n***H***2n+2*. The shorter hydrocarbon chains are less viscous, are more volatile (Low melting/boiling point) and are more flammable. They all have c-c single bonds
22
New cards
Fractional distillation
This is the process of separating long chain hydrocarbons from short chain hydrocarbons. Long chain hydrocarbons have a higher boiling point so are collected at the bottom and short chain hydrocarbons have a lower boiling point so are collected at the top.
23
New cards
Crude oil
This is what is used in a fractioning tower. It provides the fuel for most modern vehicles and can be used to create new compounds like lubricants. However it is a finite resource and therefore non-renewable
24
New cards
Cracking
This is the process of splitting up long chain hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbons are heated then combined with wither a powdered catalyst or steam which splits them up. it produces a shorter alkane and an alkene. E.G. Decane → Octane + ethene
25
New cards
Alkenes
A homologous series of hydrocarbons that have a C=C double bond. They have a general formula of **C***n***H***2n*.
26
New cards
Bromine water + alkene
goes from orange to clear
27
New cards
Alcohols
These have a functional group of OH and a general formula of **C***n***H***n+1***OH** and are used as solvents and fuels. They are flammable can be dissolved into water and can be oxidised.
28
New cards
Carboxylic acids
These have a functional group of COOH and a general formula of **C***n***H***n+1***COOH**. They are weak acids that can dissolve in water and are used in foods and soaps