Headaches and Migraines
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PEBC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
red flags
Thunderclap onset = severe HA with peak intensity at onset
Positional HA = gets worse when standing up
Progressive severity or increased frequency (pattern change)
Papilledema (feels like nausea, throwing up, tinnitus)
Stiff neck, focal signs, reduced/altered LoC
Post-traumatic onset (like hematoma)
painful eye with eye redness, tearing, facial flushing
HA caused by sneezing, coughing
HA with paralysis, weakness, numbness, slurred speech, behavioural changes, or seizure
unilateral eye pain with diminished vision
important questions to ask
onset of HA
Pain location (where does it hurt?)
Headache associated symptoms (any other symptoms present?)
Precipitating factors?
Remitting factors (drug therapy?)
Presence of comorbidities?
tension type headache
mild, dull constant aching, pressure
occurs bilaterally
NO AURA
not triggered by food or activity; precipitated by stress
duration= hrs - days (up to 7 days)
at least 2 of:
bilateral HA
non-pulsating
mild-mod pain
not worsened by activity
no nausea and cant have photophobia or phonophobia
cluster headache
severe attack of piercing pain —> behind the eye or over lateral aspect of nose
unilateral
accompanied with nasal secretions, lacrimation
possible aura
precipitated by: alcohol, changes in season, naps
duration = < 3 hrs (several times a day)
migraine
pulsing, throbbing (may start as tension type)
unilateral
temporal, eye region
accompanied with GI sx (nausea) and/or light sensitivity
AURA = 10-30 mins before
triggered by food (cheese, chocolate), fatigue, stress
aggravated by activity
duration = 4-72 hrs
at least 2 of:
nausea
light sensitivity
interference with activities
presence of nausea or vomiting and/or photophobia and phonophobia
risk factors (TTH)
stress
excessive caffeine
excessive alcohol
lack of sleep
poor nutrition/ dehydration
poor posture
odours
smoke
sunlight
risk factors (migraines)
stress
caffeine
alcohol
fatigue
fasting
genetics
menses
changes in atmospheric pressure
altitude changes
trigger foods (changes per individual)
medication overuse headache
HA occurring at least 15 days per month
cycle where HA returns as soon as effects of analgesics wear off, causing patient to use more medication for relief
occurs with:
simple analgesics (acetaminophen, NSAIDs) used ≥15 days/ month for > 3 months
Opioids, triptans, analgesic opioid combinations used ≥10 days/month for >3 months
symptoms present as tension type HA
recommended treatment:
gradual D/C opioid containing agents
abrupt or gradual D/C with simple analgesics/triptans
may need to start prophylactic medications = triptans
manage comorbidities that contribute to HA like depression
drug causes
alcohol
cocaine
methylphenidate
caffeine withdrawal
corticosteroids
nitrates (nitroglycerin) and nitrate containing deli meats
SSRIs
oral contraceptives
drugs associated with intracranial HTN (leading to HA)
tetracyclines
isotretinoin
tamoxifen
oral contraceptives
precipitate migraine attacks in females w no Hx of migraines
onset = first few months - years of OC use
D/C OC = see improvement in HA w/in few months
cause = estrogen content
estrogen containing OC = CONTRAINDICATED IN MIGRAINE WITH AURA = Increased STROKE risk
goals of therapy
identify red flags and immediate referral
prevent medication overuse headache
identify drug-induced/ reversible causes
relieve pain and associated sx with drug and non drug therapy
reduce frequency, severity, duration and disability of attacks
non pharm
headache diary = trigger management/ avoidance if possible
apply ice and rest in a dark, noise free room
stress management = CBT, relaxation therapy, psychotherapy
acupuncture and/or nerve blocks
routine = healthy diet, regular exercise, good sleep hygiene
good posture, ergonomics at work (TTH)
algorithm
NSAIDs
1st line for mild-moderate migraines (not requiring bedrest) or as adjunct with triptan
1st line for tension-type HA
COX-2 Selective = Celecoxib
non-selective = ASA
semi-selective = Increased affinity for COX-2 but still retain activity for COX-1
diclofenac
indomethacin
Meloxicam
Piroxicam
Ibuprofen
Naproxen (closer to non-selective)
Pregnancy = avoid in third trimester because they may cause constriction of the fetal ductus arteriosus
Celecoxib
COX-2 selective NSAID
low GI bleed risk
HIGH CV risk
s/e = Constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, upset stomach, or throwing up, Heartburn, Gas, Dizziness or headache
aspirin
non-selective NSAID
cardioprotective at low doses
HIGH GI BLEED RISK
triptans
1st line for migraines
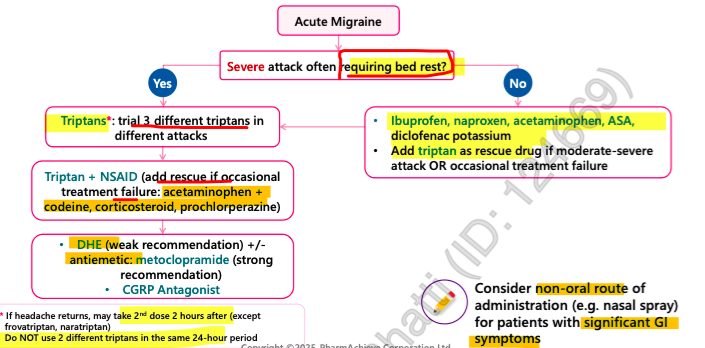
administration = Take at first sign of migraine —> repeat dose after 2 hrs if partial relief (EXCEPT Frovatriptan, Naratriptan)
onset = 30-60 mins
2nd triptan dose unlikely to be effective if 1st dose was not helpful
EARSZ = have 2 ears therefore can rpt dose in 2 hrs = Eletriptan, Almotriptan, Rizatriptan, Sumatriptan and Zolmitriptan
Do not use a different triptan within 24 hrs of another triptan
use 3 diff options before deeming class ineffective
use <10 days/ month to avoid medication overuse headache
formulations:
oral wafer = rizatriptan 10mg or Zolmitriptan 2.5 mg - if fluid ingestion worsens nausea
Nasal spray = zolmitriptan 5mg or sumatriptan 20mg - if pt nauseated
Subcutaneous = sumatriptan 6mg - if vomiting early in attack/ resistant to oral triptans
s/e = chest discomfort, fatigue, dizziness, paresthesia, drowsiness, nausea, throat irritation
CAUTION:
Serotonergic drugs (SSRI, SNRI, MAOI, Ergots, triptans) = increased risk serotonin syndrome
CI: HUMP
Heart disease (incl. angina)
Uncontrolled HTN
Migraine (Basilar or hemiplegic)
Pregnancy
sumatriptan
earliest repeat dose = 2h (2 doses/day)
formulations:
PO = onset 30-60 mins
SC = onset 10 mins
Nasal = onset 10 mins
SC has the fastest onset of action and is the most effective of all triptans, followed by the nasal spray
do NOT use with MAOIs
available in combo with Naproxen sodium
zolmitriptan
earliest repeat dose = 2h (2 doses/day)
EARSZ = have 2 ears therefore can rpt dose in 2 hrs = Eletriptan, Almotriptan, Rizatriptan, Sumatriptan and Zolmitriptan
formulations:
orally dispersible tabs = can take without water
Nasal spray = faster onset and greater efficacy
do NOT use with MAOIs
rizatriptan
earliest repeat dose = 2h (2 doses/day)
EARSZ = have 2 ears therefore can rpt dose in 2 hrs = Eletriptan, Almotriptan, Rizatriptan, Sumatriptan and Zolmitriptan
formulations:
fast melt wafers = for those who have worsening nausea with fluid ingestion; can be taken without water and have rapid onset
has one of the fastest onsets vs other oral triptans
use with caution in patients taking propranolol = increased bioavailability of this drug
do NOT use with MAOIs
almotriptan
earliest repeat dose = 2h (2 doses/day)
EARSZ = have 2 ears therefore can rpt dose in 2 hrs = Eletriptan, Almotriptan, Rizatriptan, Sumatriptan and Zolmitriptan
do NOT use with MAOIs
inhibitors of CYP3A4 may increase bioavailability
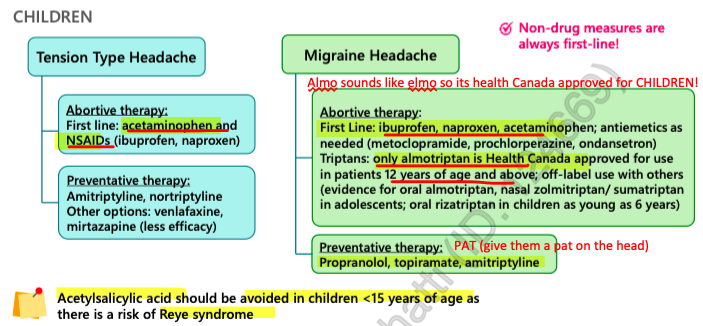
can be used in children 12+. → Almo = Elmo = kids
eletriptan
Earliest repeat dose = 2h (2 doses/day)
EARSZ = have 2 ears therefore can rpt dose in 2 hrs = Eletriptan, Almotriptan, Rizatriptan, Sumatriptan and Zolmitriptan
contraindicated within 72 hrs of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors
other triptans
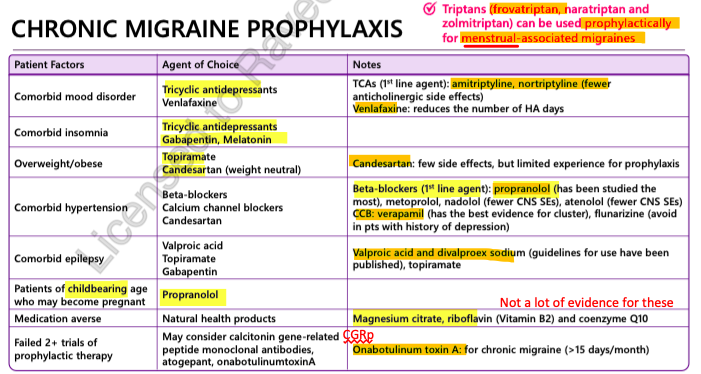
Frovatriptan = prophylactic for menstruation related migraines
Naratriptan = lowest efficacy and slowest onset vs any other triptan
2nd dose = 4 hrs later

CGRP antagonists
newest class of migraine meds —> 2nd line treatment
blocks action of CGRP = stops/ prevents migraine
can be used as preventative therapy
injection once a month
antiemetics
target nausea and vomiting
dimenhydrinate, metoclopramide, domperidone
dimenhydrinate
gravol
s/e = sedation, anticholinergic effects, confusion
metoclopramide
anti-emetic/ prokinetic
s/e = diarrhea, cramping, HA, drowsiness, extrapyramidal sx, tardive dyskinesia
domperidone
anti-emetic/ prokinetic
s/e = diarrhea, cramping, HA, QTc prolongation
chronic migraine prophylaxis
criteria:
attacks have significant impact on QoL despite appropriate use of abortive therapy
or
frequency of attacks puts patient at risk of MOH
or
≥4 headaches/ month
used in pts with contraindication to medications for acute migraine attacks = symptomatic treatment difficult
duration of therapy
continue for 6-12 months then consider tapering dose
assessment of benefit= min 2 months following dose titration (takes at least 2 months for benefit)
successful prophylaxis = ≥ 50% reduction in HA or days with HA
propylaxis options
tension type headaches treatment
acute treatment
mild = non-pharm
if meds needed = acetaminophen or NSAIDs (ibuprofen, Naproxen)
if frequency ≥15 days/month = chronic = prophylaxis
prophylaxis (AN MVp)
1st line = Amitriptyline, Nortriptyline
2nd line = Mirtazepine, Venlafaxine
pregnancy
1st line = non-pharm
aborptive therapy:
acetaminophen
NSAIDs - ibuprofen/ naproxen = AVOID IF POSSIBLE, ESP 1st and 3RD TRIMESTER!
severe nausea = metoclopramide or prochlorperazine
prophylaxis = propranolol = DC few days before delivery and monitor neonates (bc it can cause fetal growth restriction: bradycardia, hyperglycemia)
triptans = generally avoided —> growing evidence for sumatriptan
ergots = contraindicated
breastfeeding
1st line = non pharm
abortive therapy:
acetaminophen = preferred
ibuprofen = avoid if possible but can use
sumatriptan = can be used but it is crucial to avoid vasoconstricting agents in initial postpartum period
pump and dum! holding breastfeeding for 8-12 hrs after dose = reduce exposure to infant
prophylaxis = propranolol
avoid ergots, barbiturates, opioids and ASA
children