Chemistry Final Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 12:21 AM on 6/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 5
penta
2
New cards
What are Physicals properties
A change in a property that can be observed. (change in color, change in texture, smell)
3
New cards
What are Chemical potteries
When a substance changes into a new chemical
4
New cards
What is the difference between Chemical and physical Changes
Physical is a change in texture or color, chemical is a new substance.
5
New cards
What is Heterogenous matter
Visually different
6
New cards
What is Monogenous matter
Stays the same no difference
7
New cards
What was Ruthfords ’s experiment
Found out the the atom is mostly empty with the gold foil experiment. He shot particles through a atom onto a gold foil and most of the atoms went through
8
New cards
What was JJ Thomson’s experiment
Discovered electrons with a cathode towards positively charged protons.
9
New cards
Alpha decay
Nucleus loses two protons
10
New cards
Beta Decay
Nucleus gains or losses one proton
11
New cards
What is the rule for measuring
write the known values down firs than en estimated one
12
New cards
Hoe many atoms equal one mole
6\.02x10^23 atoms(atm)
13
New cards
What is the Centi base unit
10^2
14
New cards
What is the Milli base unit
10^3
15
New cards
What is the kilo base unit
10^-3
16
New cards
What are the three rules for writing electron configoration
Aufbau, hunds rule, and pauli exclusion principle
17
New cards
What is hunds rule
Each orbital must have one electron(arrow) before two
18
New cards
What is Aufbau
Electrons occupy the lowest energy level first
19
New cards
What is Pauli exclusion principle
2 elections in the same orbital have different spins
20
New cards

What is the red section
S2
21
New cards

What is the blue section
D10

22
New cards

What is the yellow section
P6
23
New cards
Explain the relation between ground and excited state
Ground to Excited - energy is absorbed
Excited to Ground - energy is released
Excited to Ground - energy is released
24
New cards
What happens when an electron goes from excited to ground state
A photon of light is released. the color is determined on the amount of energy released. Purple is the most energy released and red is the least.
25
New cards
What color has the longest wavelengths
Red
26
New cards
What color has the shortest wavelength
Violate
27
New cards
What does C stand for in calculating wavelengths and frequency
speed of light
28
New cards
What does V stand for in calculating wavelengths and frequency
Frequency
29
New cards
What does E stand for in calculating wavelengths and frequency
Energy (J)
30
New cards
What does h stand for in calculating wavelengths and frequency
Planks constant 6.63x10^-34 JxS
31
New cards
What does λ stand for in calculating wavelengths and frequency
Wavelength (m)
32
New cards
How do you tell atomic radious
As you go down the periodic table the radios gets bigger, left to right gets it smaller
33
New cards
What is a covalent bond
Non-metal + Non-metal
34
New cards
What is a Ionic Bond
Metan and non Metal
35
New cards
What is a Non-Polar molecule
When the molecules are evenly distributed
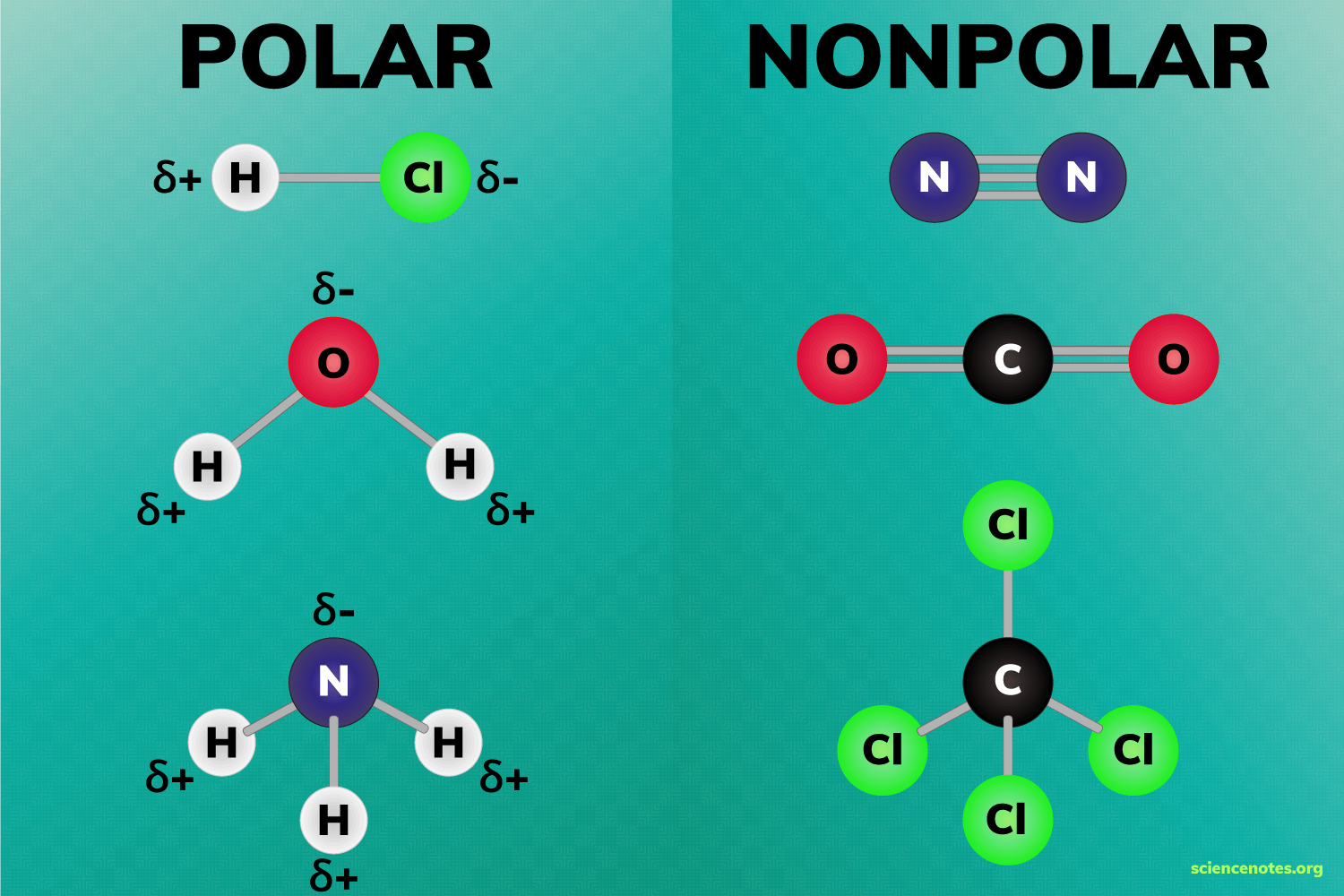
36
New cards
What is a Polar molecule
When the molecules aren’t evenly distributed
37
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 1
Mono
38
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 2
di
39
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 3
tri
40
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 4
tetra
41
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 6
Hexa
42
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 7
Hepta
43
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 8
octo
44
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 9
nano
45
New cards
what is the abbreviation for 10
deca
46
New cards
Is energy required or released in order to break bonds
Required
47
New cards
What are the strongest from strongest to least IMF forces
Hydrogen Bond, Dipple Dipple, london dispersion
48
New cards
What are the three factors that increase solubility
stirring, temperature, and size
49
New cards
What is the relationship between pressure, volume, and number of moles
PV = nRT
50
New cards
is a salt ionic or covalent
ionic
51
New cards
What is the Law of conservation of mass
Mater is not created or destroyed