transition metals
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
coloured compounds, d orbital splitting, catalysis equations, autocatalysis, ligand substitution, vanadium, redox, oxidation states, pH, everything !!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
defintions !!
characteristics of transition metals
variable oxidation states
catalytic activity
forms coloured compounds
forms complexes
how do these characteristics arise?
incomplete d subshell
co-ordinate bond (dative covalent)
where one atom donates both the electrons in the covalent bond
ligand
a molecule or ion which forms a co-ordinate bond with a transition metal by donating a pair of electrons
catalysis!!
adsorption
solid catalysts adsorbs molecules onto active site on surface of the catalyst
increases proxmitiy of molecules and weakens the covalent bonds
what can happen to heterogeneous catalysts? industrial/economic impact of this?
become poisoned by impurities which adsorb to the active site, preventing reactants from binding.
needs to be replaced, increasing costs as production may have to stop.
example of catalytic poisoning
sulfur impurities in methane during the haber process will adsorb to iron catalyst
what is the contact process
making SO₃ from SO₂ (involved in manufacturing sulphuric acid)
type of catalyst used in contact process
heterogeneous
catalyst used in contact process
Vanadium V - V₂O₅
contact process equations with catalyst
V₂O₅ + SO₂ → SO₃ + V₂O₄
V₂O₄ + 0.5O₂ → V₂O₅
number of activation energy profiles for homogeneous catalysts
2
Catalyst used in oxidation of iodide ions with persulfate ions and type of catalyst
Fe²⁺ in solution, homogeneous
Equations for oxidation of iodide ions with persulfate ions
S₂O₈²⁻ + 2Fe²⁺ → 2SO₄²⁻ + 2Fe³⁺
2Fe³⁺ + 2I⁻ → 2Fe²⁺ + I₂
autocatalysis example
Mn²⁺ formed from reaction of MnO₄⁻ with C₂O₄²⁻
MnO₄⁻ half equation
MnO₄⁻ + 8H⁺ + 5e⁻ → 4H₂O + Mn²⁺
C₂O₄²⁻ ethanedioate ion half equation
C₂O₄²⁻ → 2CO₂ + 2e⁻
Autocatalysis equations for C₂O₄²⁻ with MnO₄⁻
MnO₄⁻ + 4Mn²⁺ + 8H⁺ → 4H₂O + 5Mn³⁺
C₂O₄²⁻ + 2Mn³⁺ → 2Mn²⁺ + 2CO₂
Colour !!
How does colour arise with transition metals?
Some wavelengths are absorbed and the rest of the wavelengths are reflected or transmitted.
What happens when light is absorbed?
d electrons move from ground state to excited state when light is absorbed
Calculation for energy difference between ground state and excited state
∆E = hv = hc/λ
Frequency of light absorbed depends on…
∆E
Factors which affect ∆E
Change in oxidation state
Change in type of ligand
Change in co-ordination number
How does type of ligand affect ∆E
different ligands will split the d orbital by a different amount of energy
ligands will cause different levels of repulsion to d orbital
how does co-ordination number influence ∆E
affects the strength of the metal ion-ligand interactions
technique used to find concentration of compounds using the colour of the ions
spectroscopy
principles of spectroscopy, colorimeter
shine white light through a coloured filter ( complementary to colour of solution) aimed at the sample
more light it absorbs, higher the concentration of the solution
compare the amount of light absorbed to a calibration curve
ligand sub, shapes and complexes !!
example of incomplete substitution of ligands, and colour of this compound
[Cu(NH₃)₄(H₂O)₂]²⁺ deep blue
Size of Cl⁻ ligand compared to NH₃ and H₂O
Larger, forms compounds with co-ordination number 4 and tetrahedral shape
Bidentate ligands examples
C₂O₄²⁻ ethanedioate ion and H₂NCH₂CH₂NH₂ 1,2-diaminoethane
Shape of complexes bidentate ligands form and isomerism they exhibit
Octahedral and optical
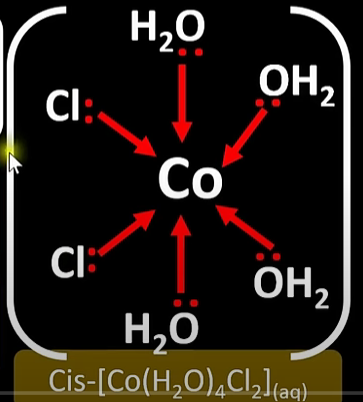
Isomerism shown by octahedral complexes like [Cu(H₂O)₄Cl₂] and how to identify each one
cis-trans
trans isomer has the ligands opposite eachother
cis isomer has the ligands on the same same
Multidentate ligands examples
EDTA⁴⁻ and haem with iron(II)
How is oxygen transported in the blood
Oxygen forms a co-ordinate bond to Fe(II) in haemoglobin
How is CO toxic
forms a stronger co-ordinate bond with Fe(II) in haemoglobin, replacing oxygen
Chelate effect
Replacing monodentate ligands with bidentate or multidentate ligands, increases number of moles of products, negative ∆G means reaction is spontaneous and favourable
Example of square planar complex
Cisplatin
cisplatin is used in cancer treatment, what does it do?
stops DNA replication
ligand replacement reaction with DNA
bond forms between nitrogen atom on guanine and platinum in cisplatin
Linear complex example and common use
[NH₃→Ag←NH₃]⁺ Tollens’ reagent for testing aldehydes
Vanadium chem !!
Vanadium species. different oxidation states and colours
Yellow VO₂⁺ +5
Blue VO²⁺ +4
Green V³⁺ +3
Violet V²⁺ +2
How are the IV, III, II oxidation states formed?
Reduction of VO₂⁺ using Zinc in acidic solution
Vanadium(V) —> Vanadium (IV) and colour change
2VO2+(aq) + Zn(s) + 4H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) + 2VO2+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
Yellow to blue
Vanadium IV to Vanadium III and colour change
2VO²⁺(aq) + Zn(s) + 4H⁺ → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2V³⁺(aq) + 2H₂O(l)
Blue to green
Vanadium III to Vanadium II and colour change
2V³⁺(aq) + Zn(s) → Zn²⁺(aq) + 2V²⁺(aq)
Green to violet
Redox potential
Show how easily a metal can be reduced (same as electrode potential)
Higher values mean ion is less stable and more easily reduced
Redox potentials depend on…
Ligands
pH (higher H⁺ concentration means a higher redox potential)
Colours of hexaaqua ion complexes
[Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺
blue
[Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺
green
[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺
yellow (purple)
[Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺
colourless solution
hexaaqua ions with OH⁻/NH₃ and colour of complex formed !!
[Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺
[Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺(aq) + 2OH⁻ (aq)→ [Cu(OH)₂(H₂O)₄](s)
blue ppt
[Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺
[Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺(aq)+ 2OH⁻(aq) → [Fe(OH)₂(H₂O)₄](s)
green ppt, brown ppt on standing (as 3+ is formed as it reacts with O₂ in the air)
[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺
[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺(aq)+ 3OH⁻(aq) → [Fe(OH)₃(H₂O)₃](s)
brown ppt
[Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺
[Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺(aq)+ 3OH⁻(aq) → [Al(OH)₃(H₂O)₃](s)
white ppt
with excess NH₃
[Cu(H₂O)₆](s) + 4NH₃ → [Cu(NH₃)₄(H₂O)₂](aq) + 4H₂O
deep blue SOLUTION
with excess OH⁻
[Al(OH)₃(H₂O)₃](s) + OH⁻ → [Al(OH)₄]⁻ + 3H₂O
colourless solution reformed
[Al(OH)₃(H₂O)₃](s) with H⁺
[Al(OH)₃(H₂O)₃](s) + 3H⁺ → [Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺
this shows [Al(OH)₃(H₂O)₃](s) is…
amphoteric - can act as both an acid and a base
reactions of hexaaqua ion complexes with CO₃²⁻…
2⁺ ions form…
XCO₃(s) ppt
3⁺ ions form…
same as OH⁻/NH₃ ppt, with CO₂ gas
colour of complex formed when [Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺ reacts with CO₃²⁻
CuCO₃ is green/blue ppt
colour of complex formed when [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺ reacts with CO₃²⁻
FeCO₃ is green ppt
pH !!
Explain why an aqueous solution containing [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺ ions has a lower pH than an aqueous solution containing [Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺ ions.
[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺ has higher charge to size ratio/ higher charge density
[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺ polarises the water molecules more
More O-H bonds break, releasing more H⁺ ions.
Explain, with the use of an equation, why a solution containing [Al(H2O)6] 3+ has a pH ˂7
[Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺ ⇌ [Al(H₂O)₅(OH)]²⁺ + H⁺
[Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺ has a high charge density
weakens the O-H bond, releasing H⁺ ions