NeuroBio EXAM 1
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
What is the difference between GABA and Ach Synaptic Vesicle
Gaba gets re-uptaken, Ahc gets degraded.
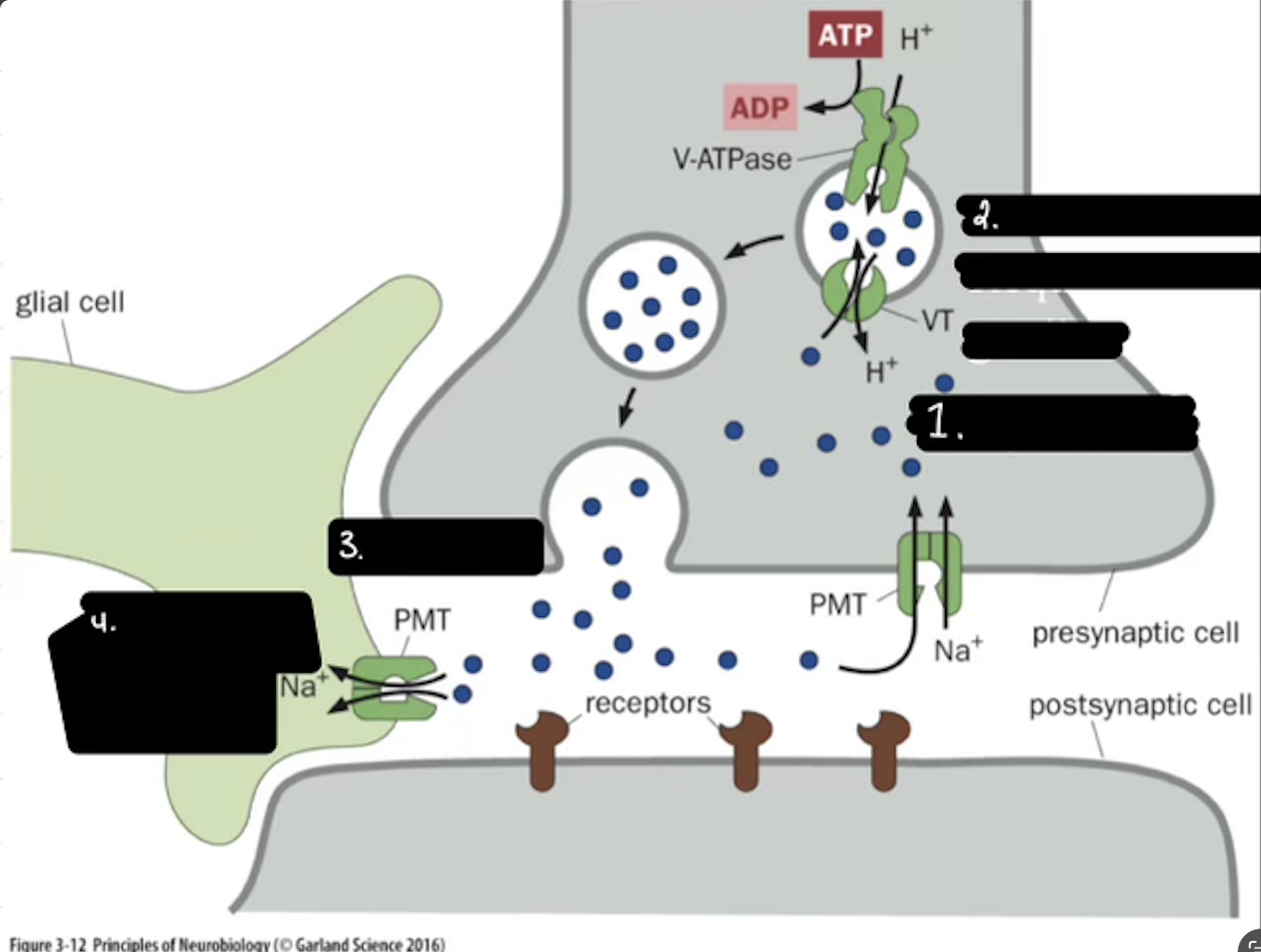
What is 1
Synthesis
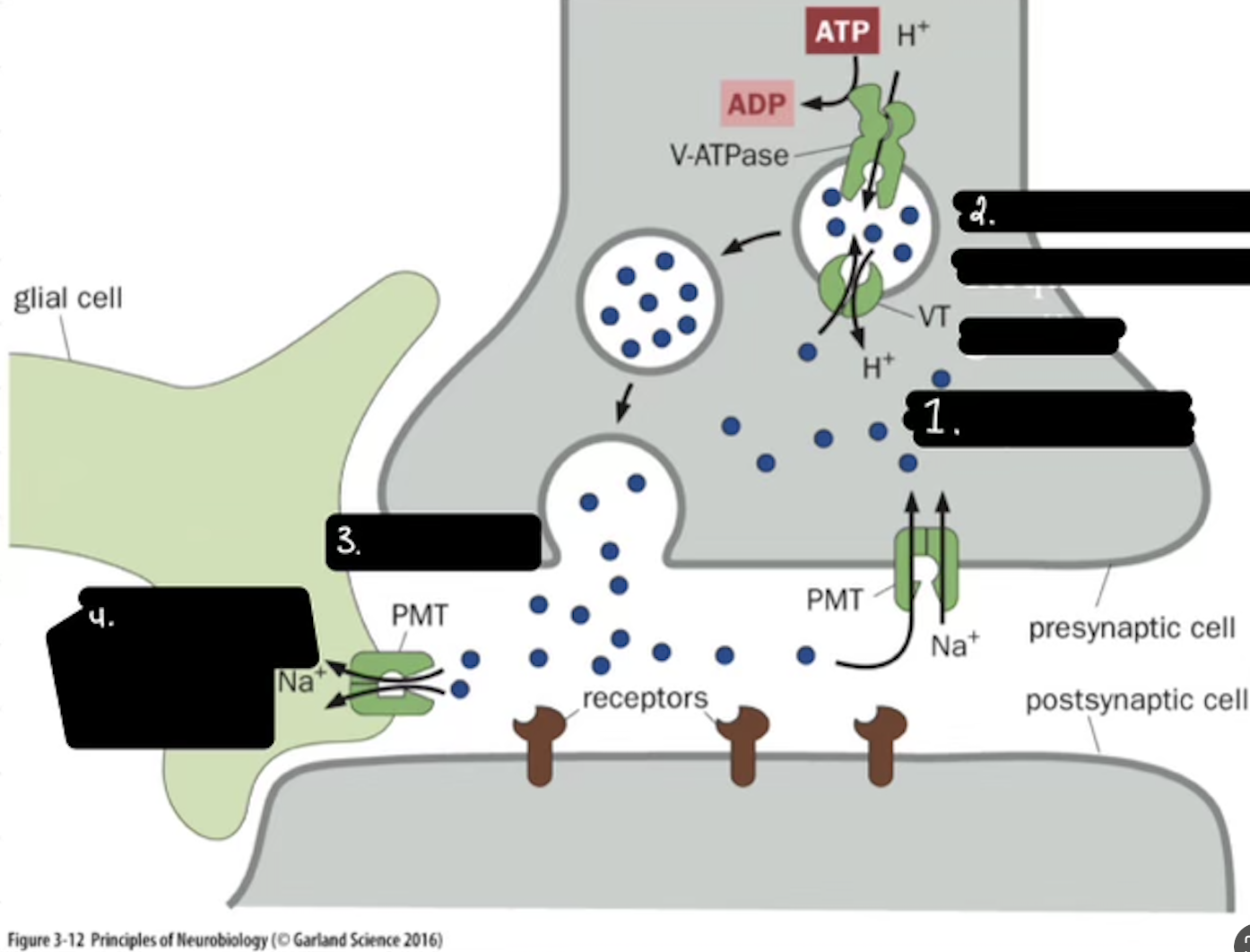
What is 2
Packaging Requiers Proton Graident
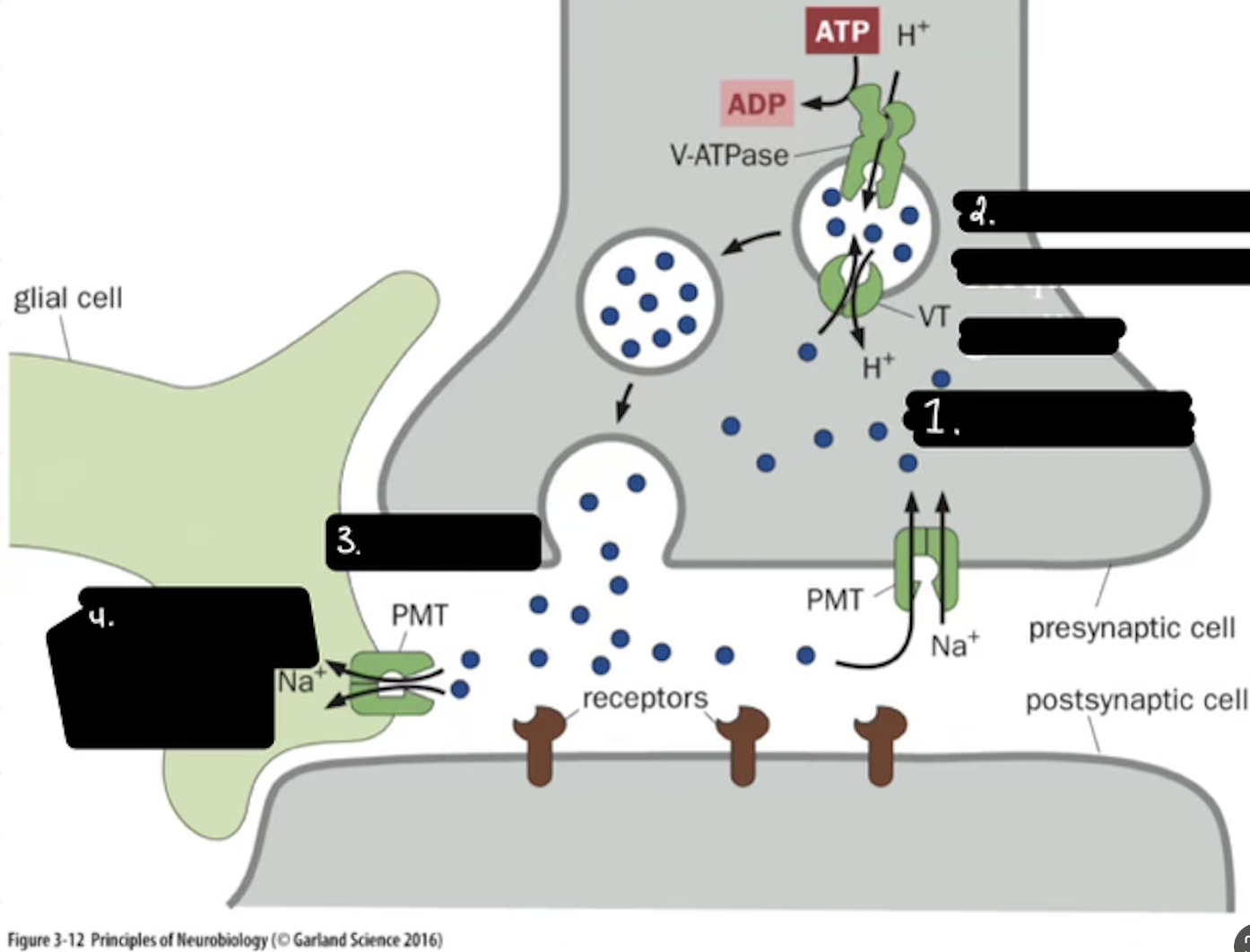
What is 3
Release
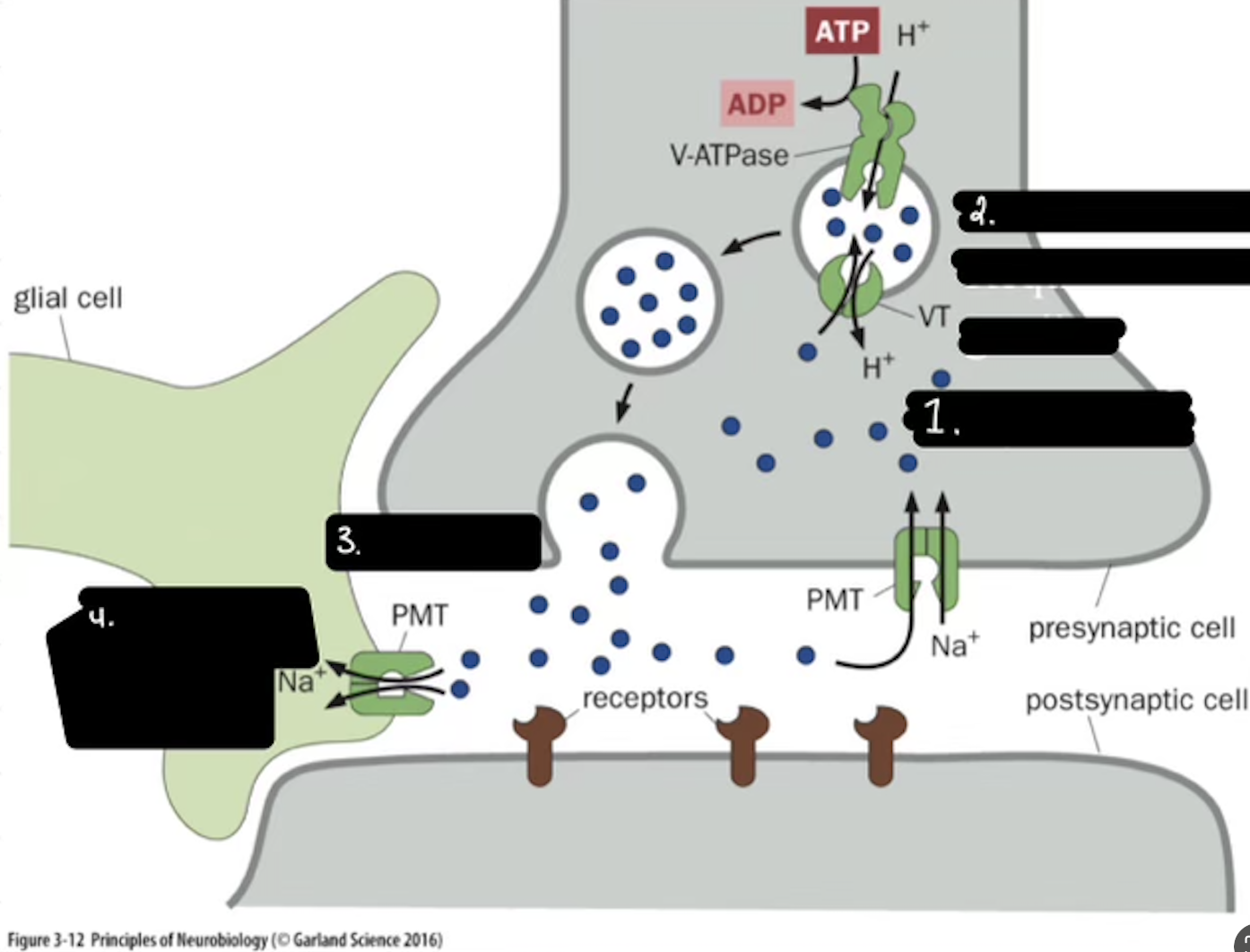
What is 4
Re-uptake or Degration
In the Life cycle of the Neurotransmitter, what does V-ATPase do?
Sets up a proton gradient that powers VT
In the Life cycle of the Neurotransmitter, what does VT do?
Vesicular Transporter lets protons out and Neurotransmitters in.
In the Life cycle of the Neurotransmitter, what fuses for release?
Calcium-mediated SNARE fusion.
In the Life cycle of the Neurotransmitter, What is the PMT
Plasma Membrane Transport
In the Life cycle of the Neurotransmitter, What does the PMT on the glia do?
it degrades and shunts, maintaing the “off rate”
In the Life cycle of the Neurotransmitter, how does ACh get degraded?
Acetylcholinesterase Enzyme.
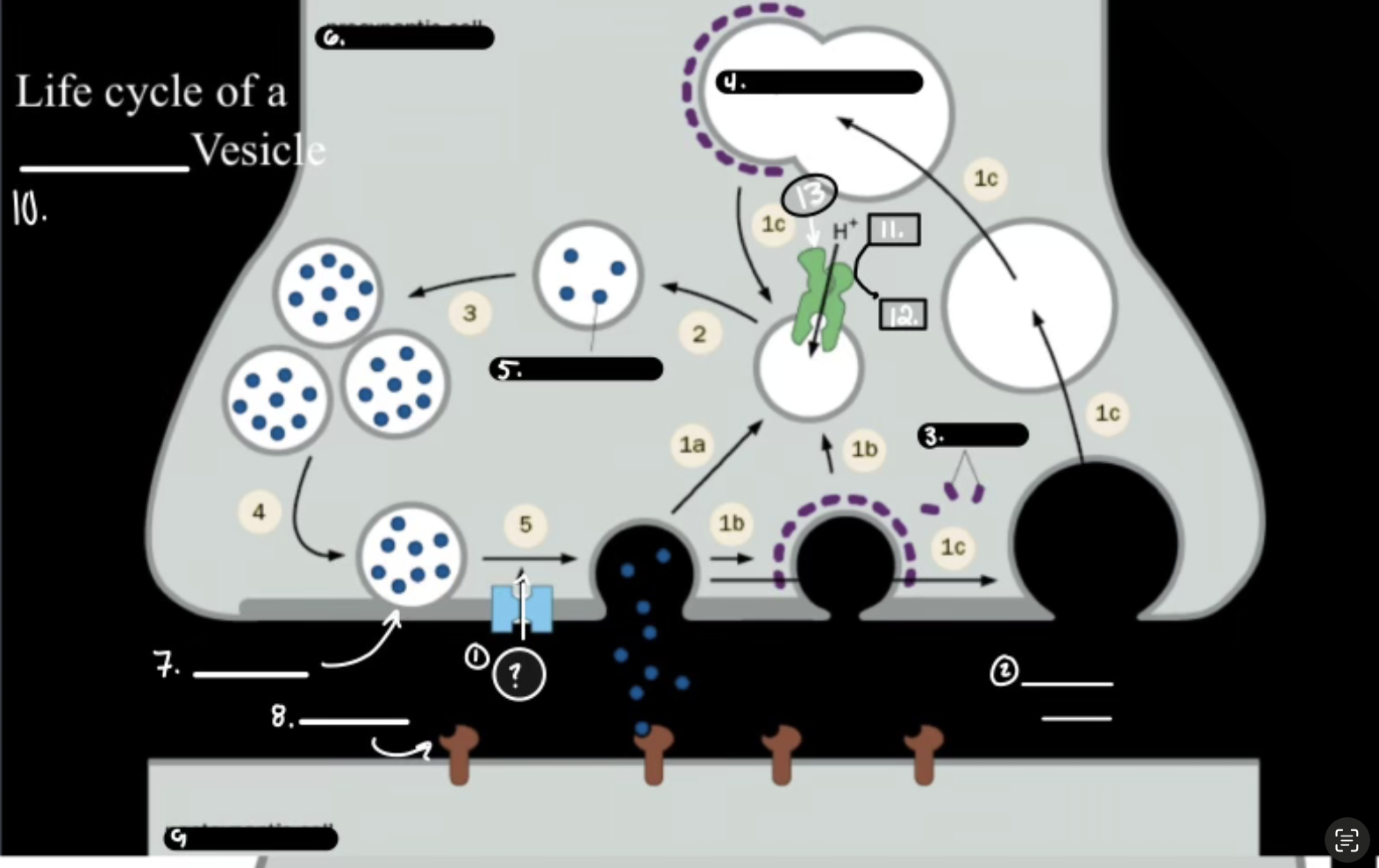
What is 1
Ca2+
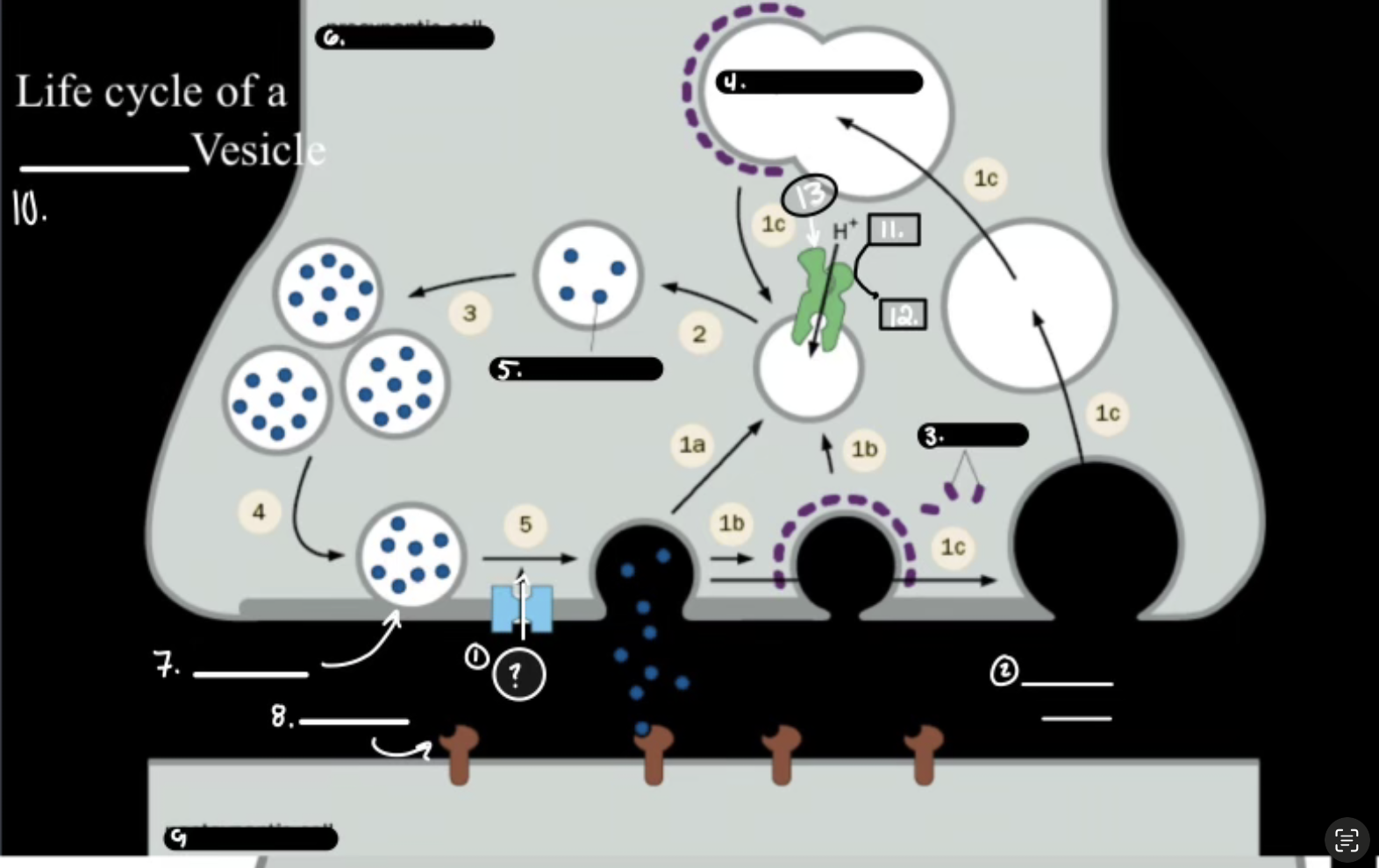
What is 2
Synaptic Cleft
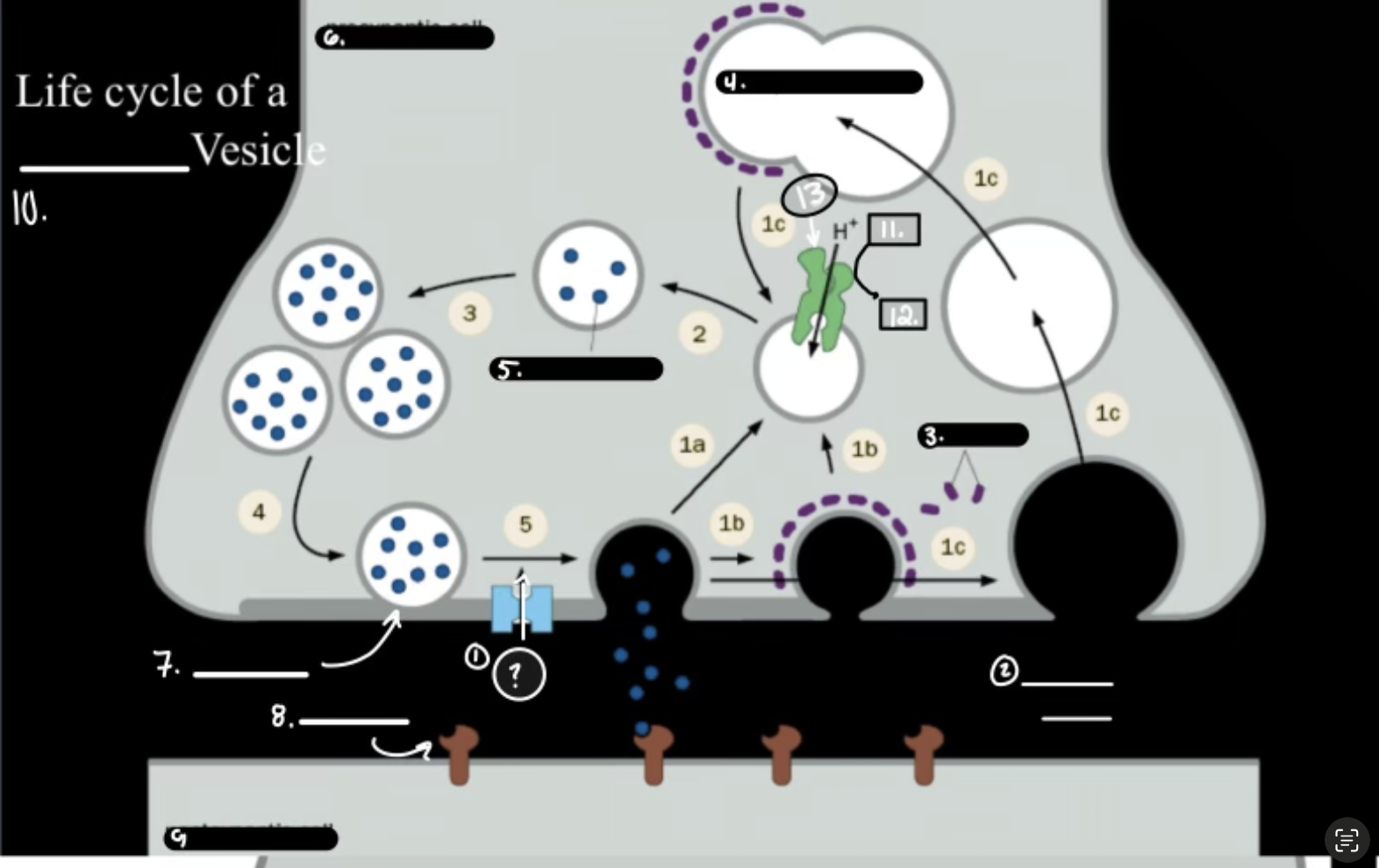
What is 3
Clathrin
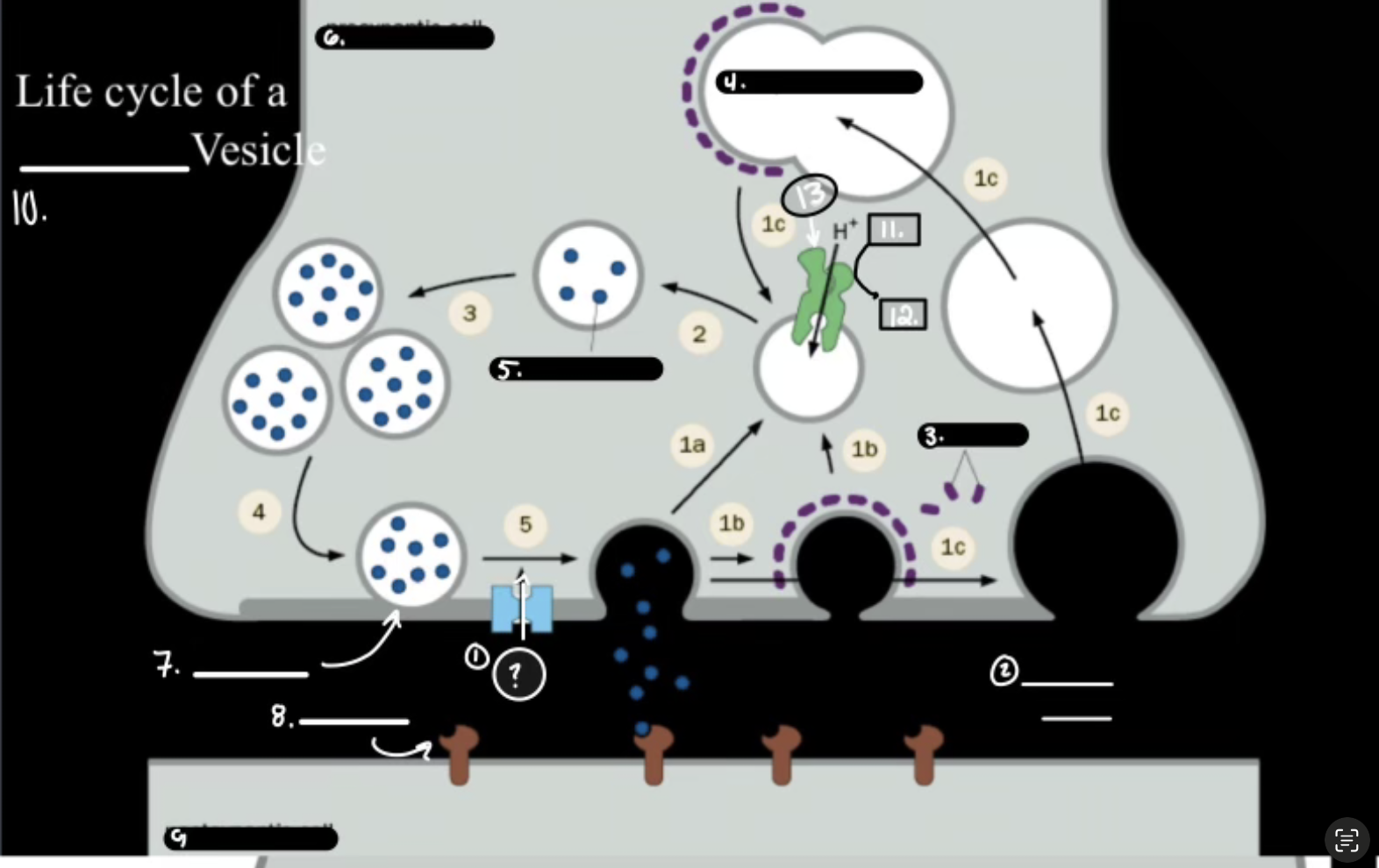
What is 4
Synaptic Endosome
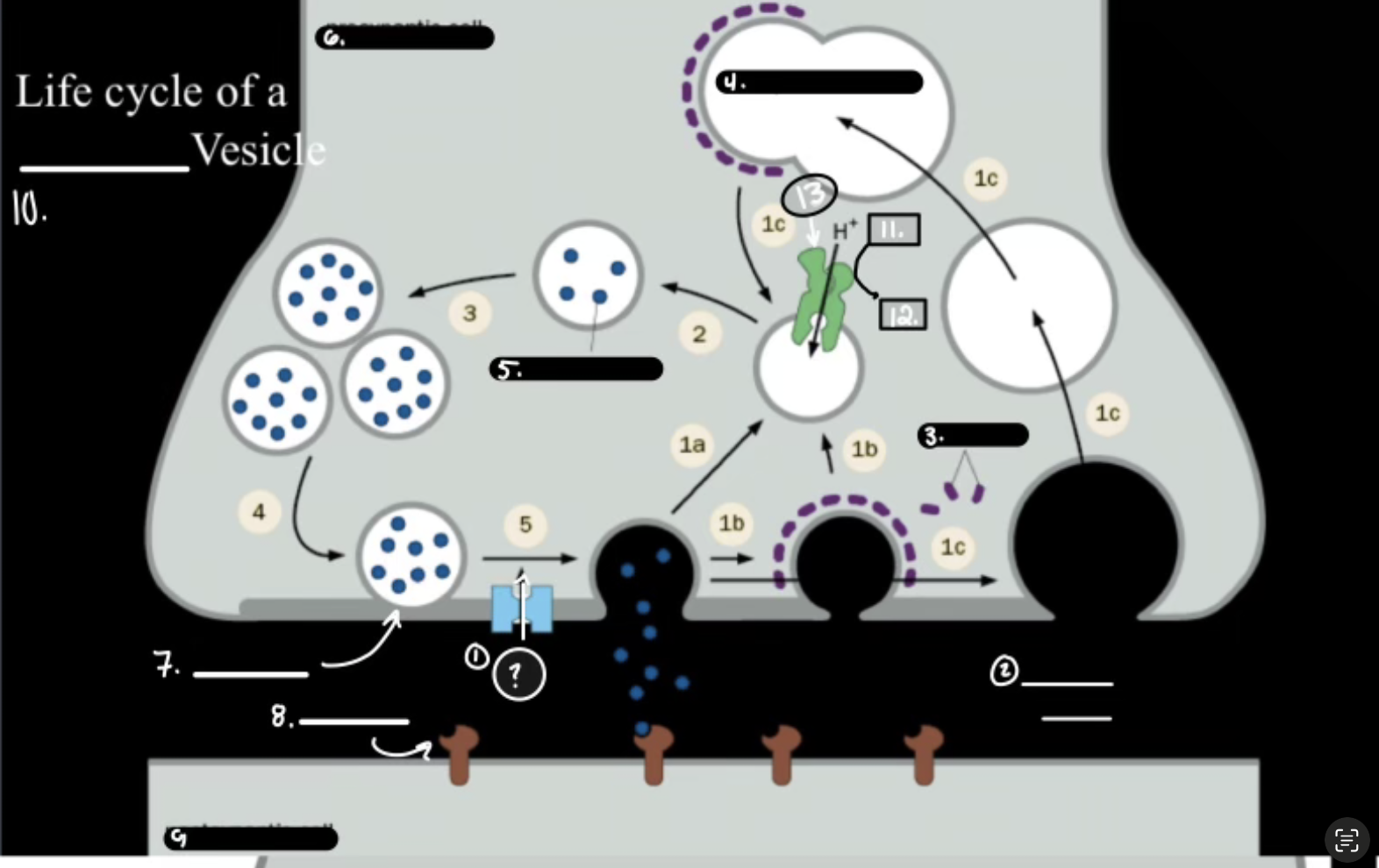
What is 5
Neurotransmitter
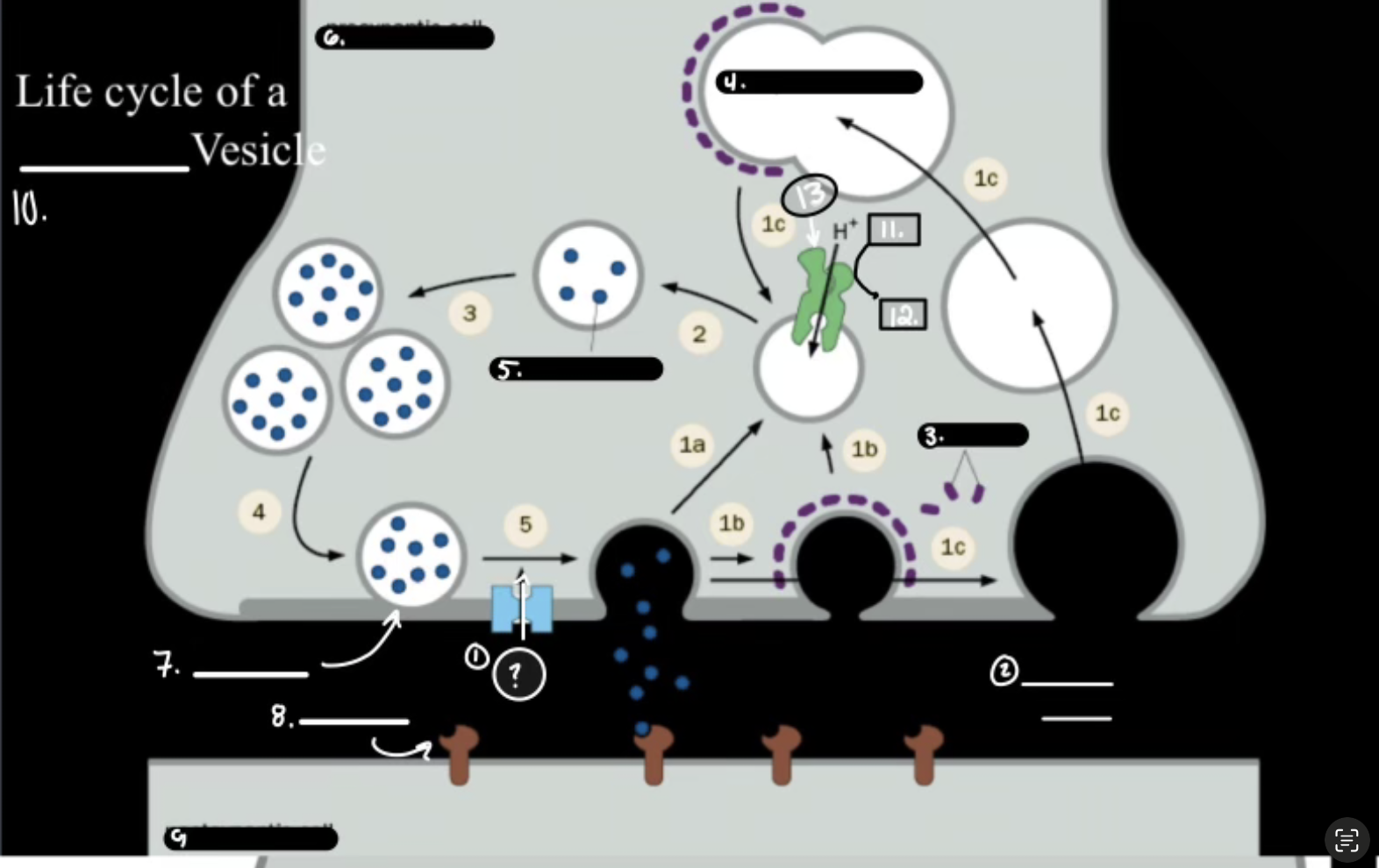
What is 7
Active Zone
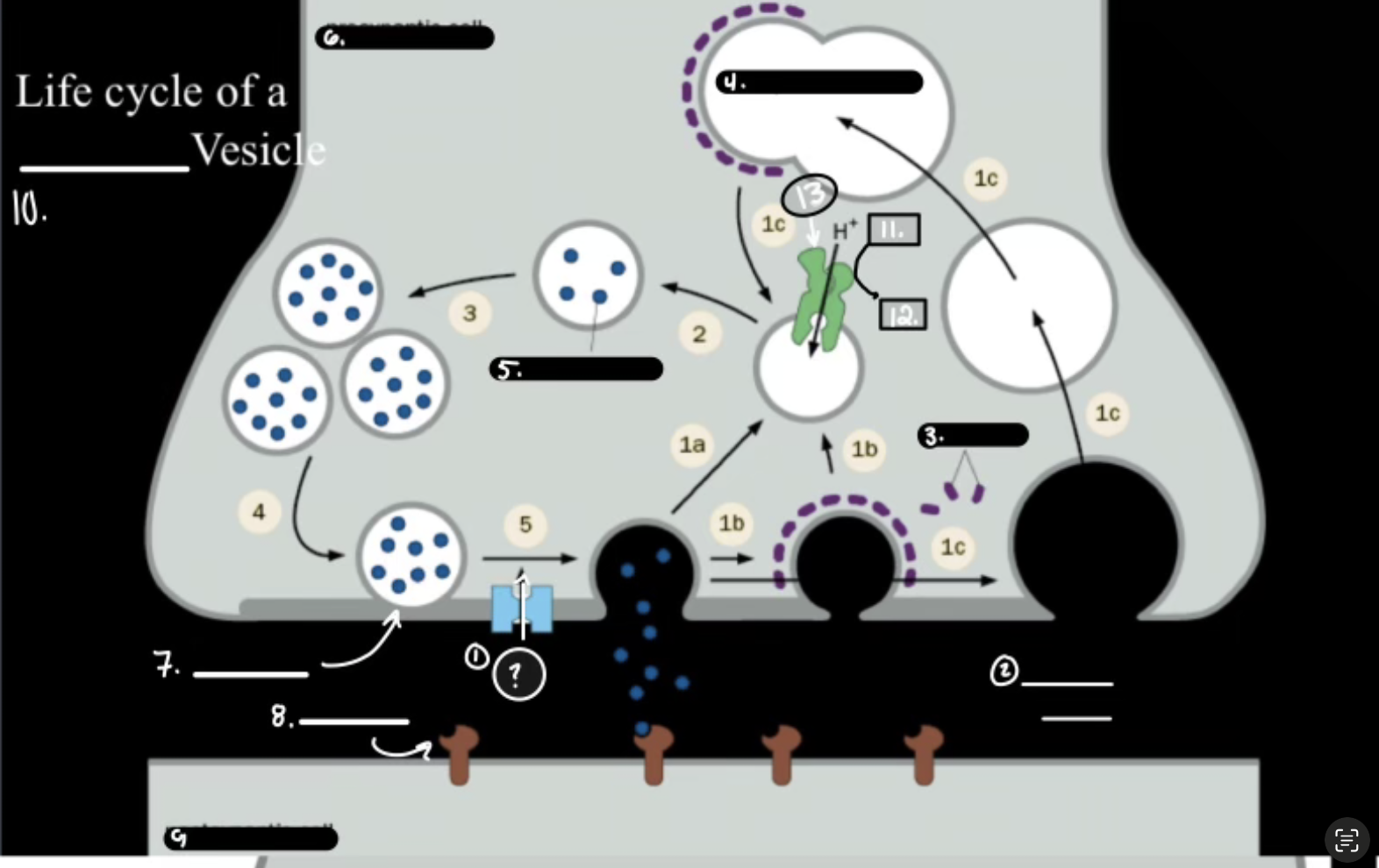
What is 8
Receptor
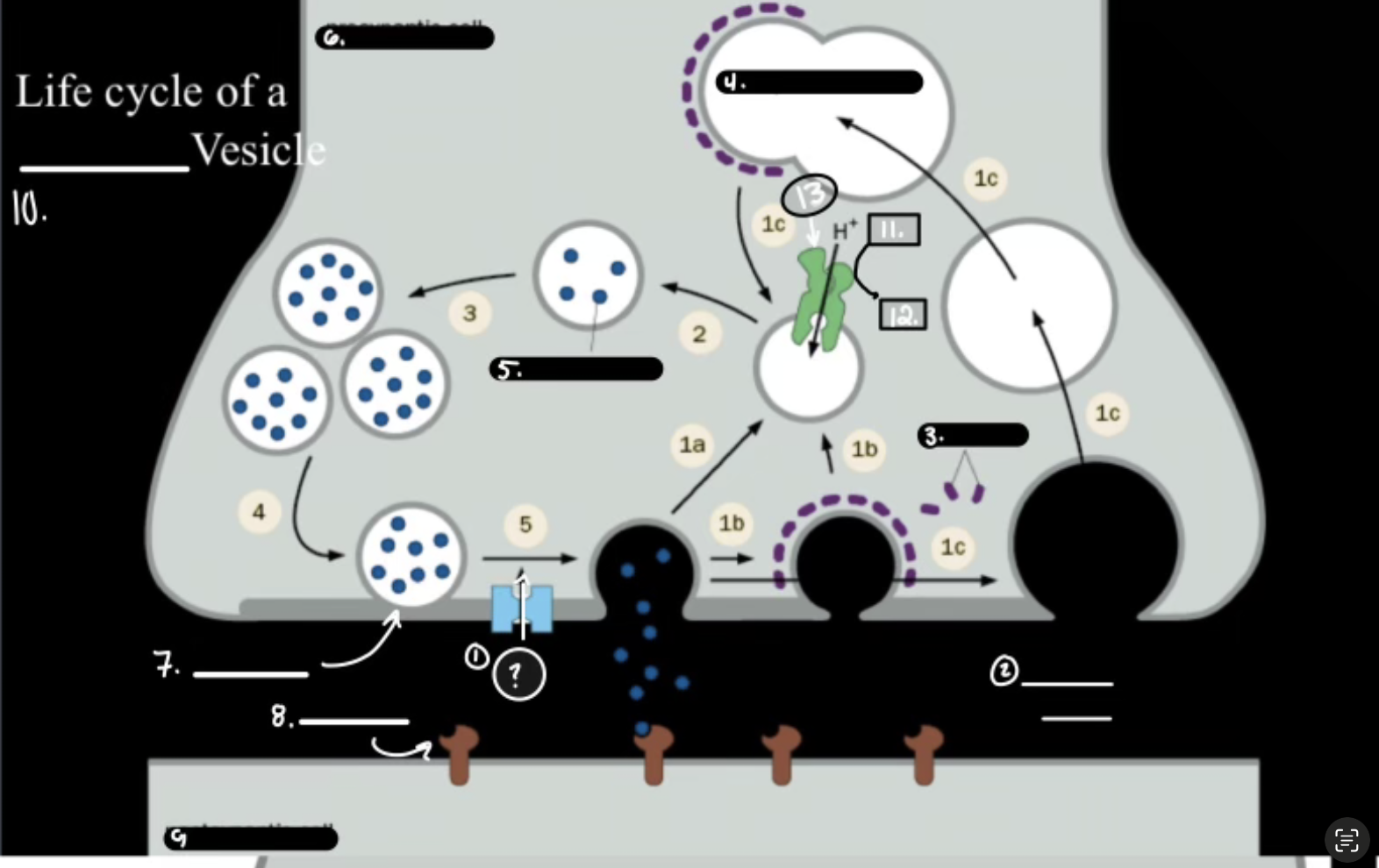
What is 9
Postsynaptic Cell
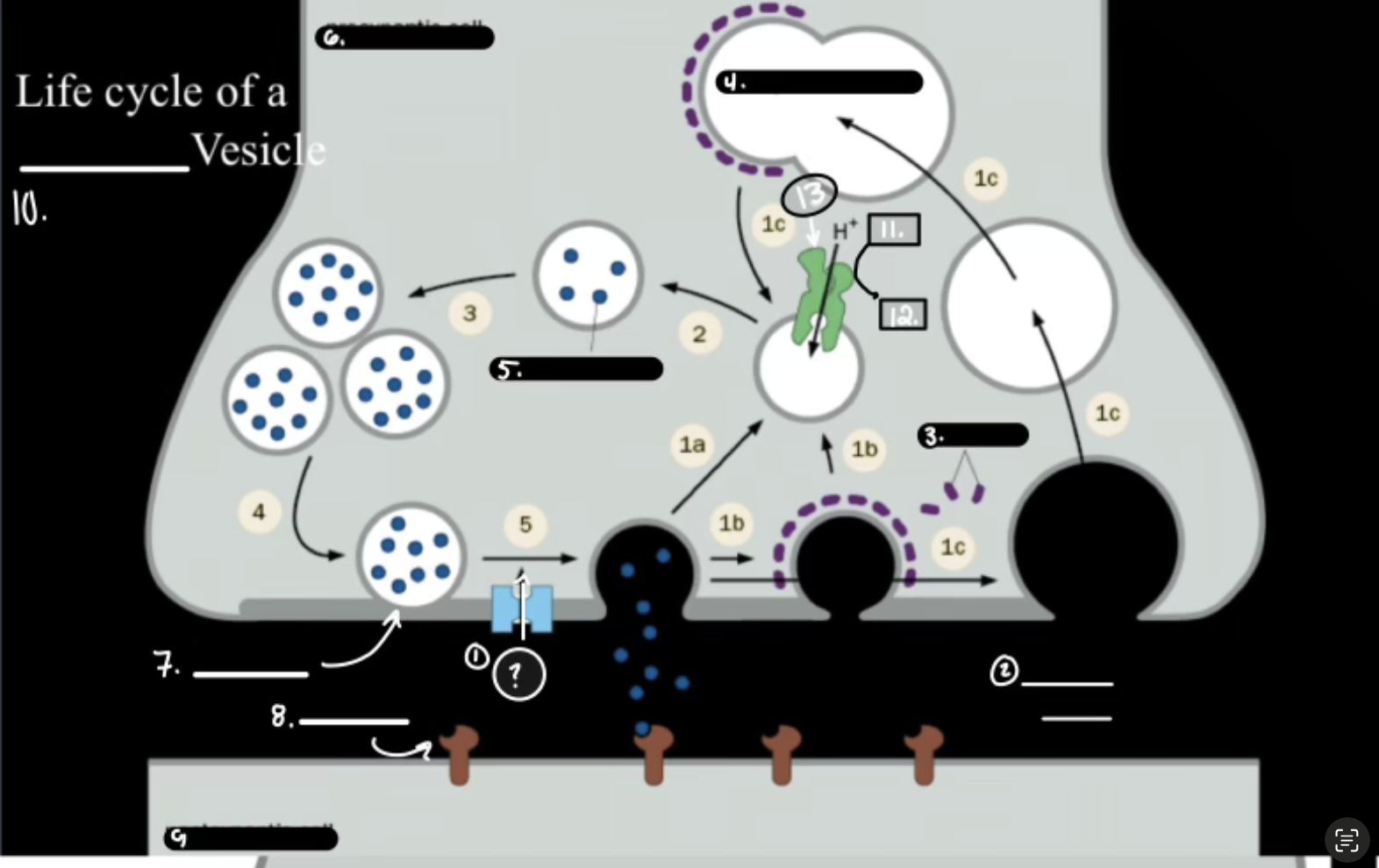
What is 10
Synaptic Vesicle
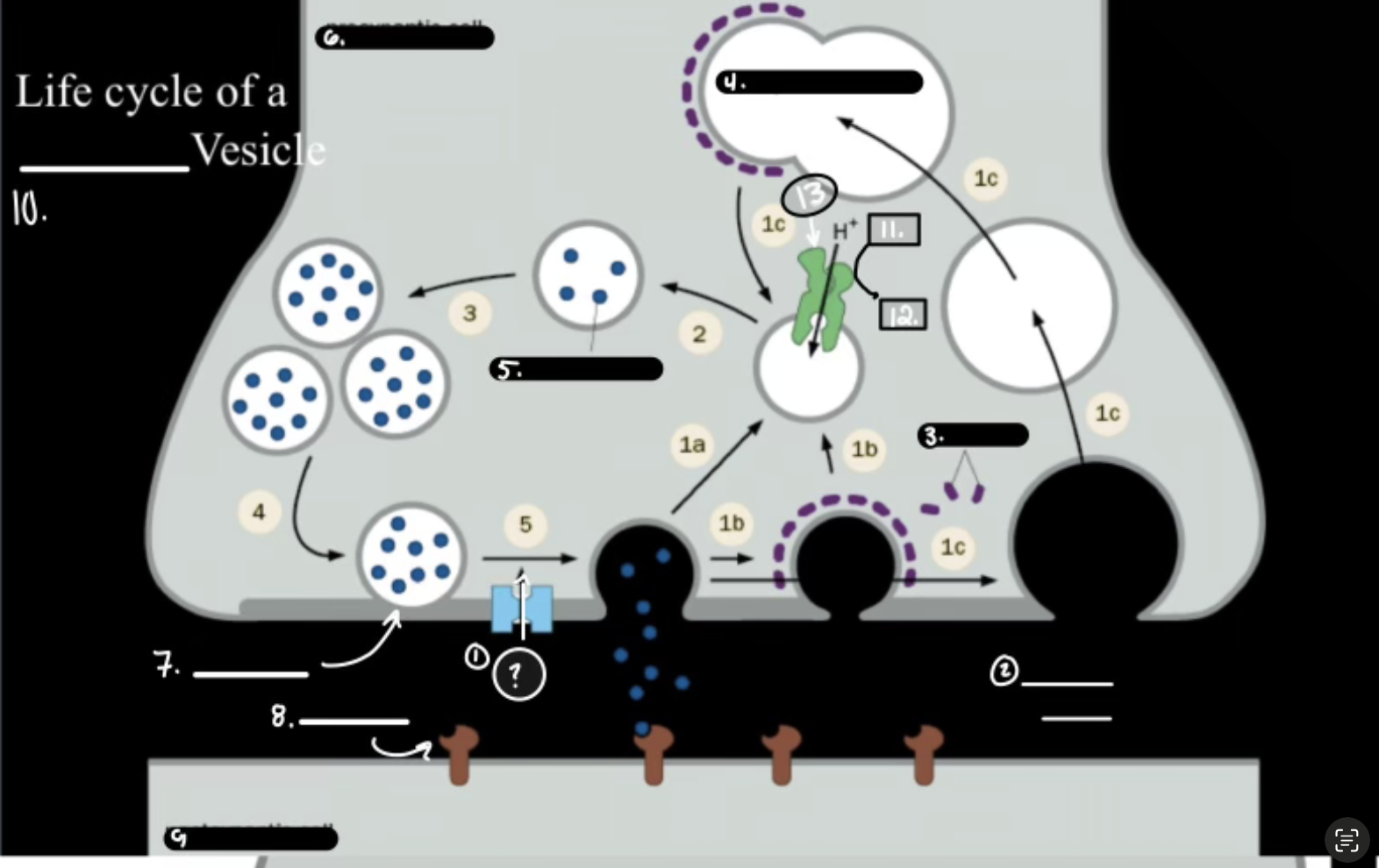
What is 11
ATP
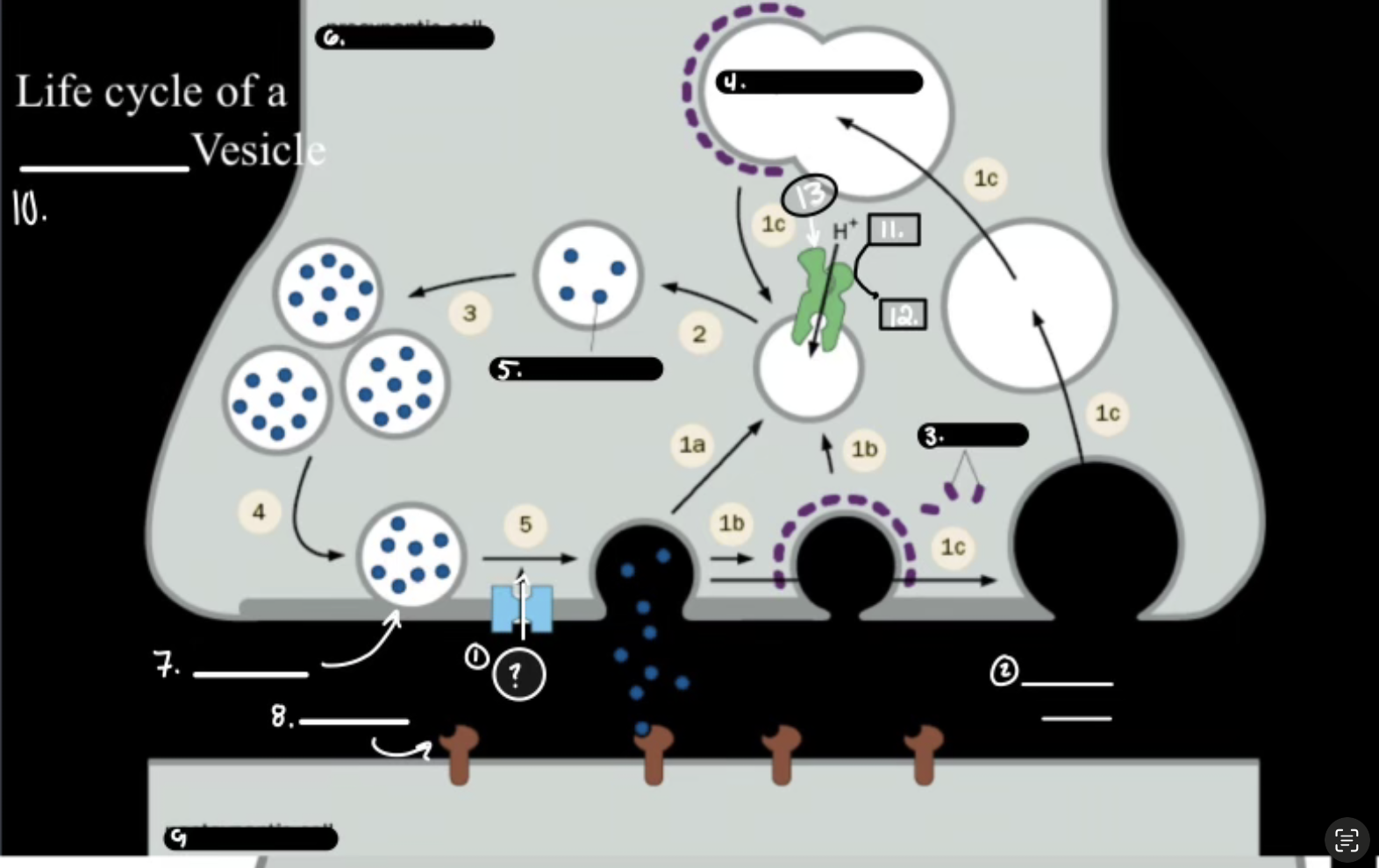
What is 12
ADP
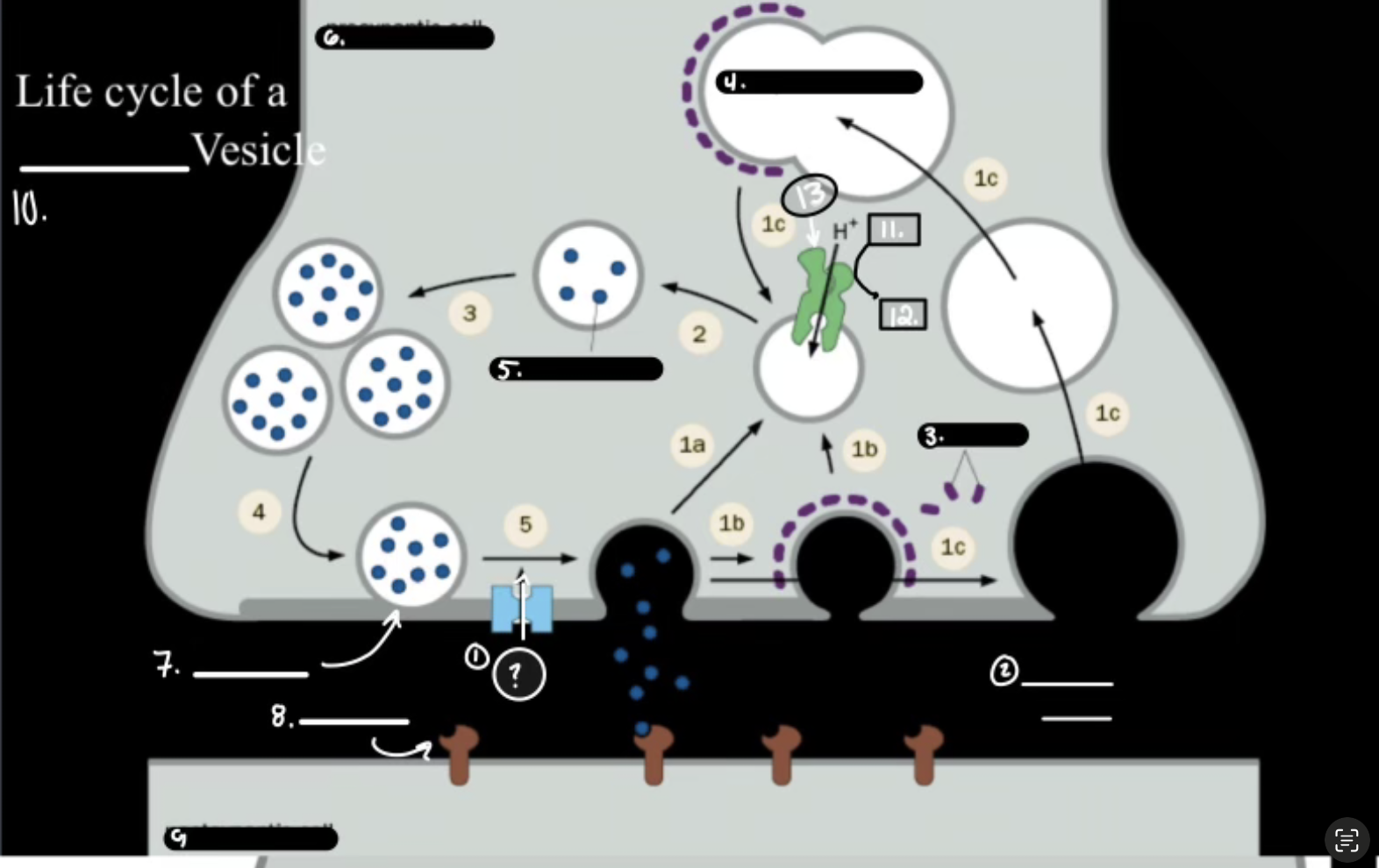
What is 13
V-ATPase
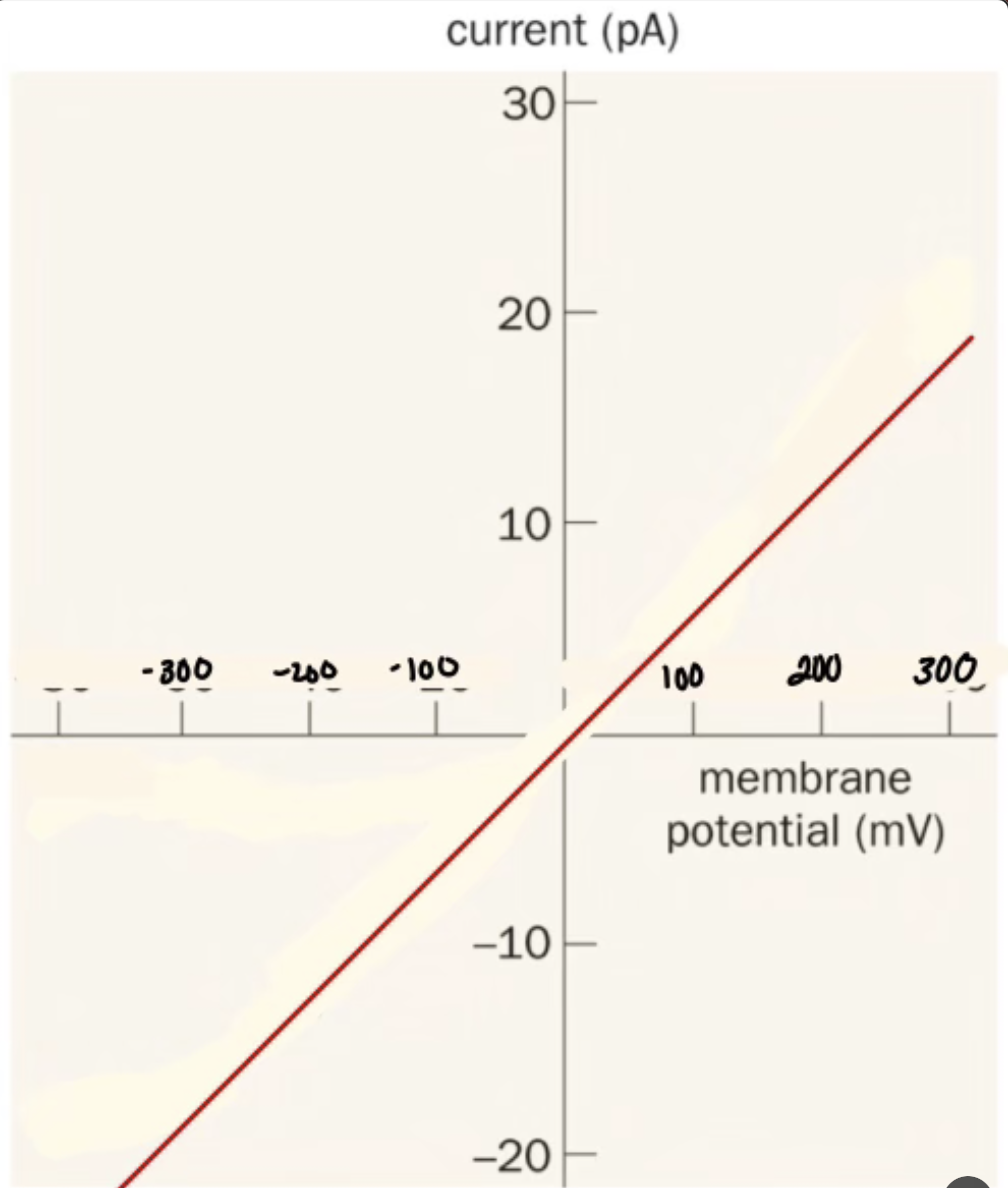
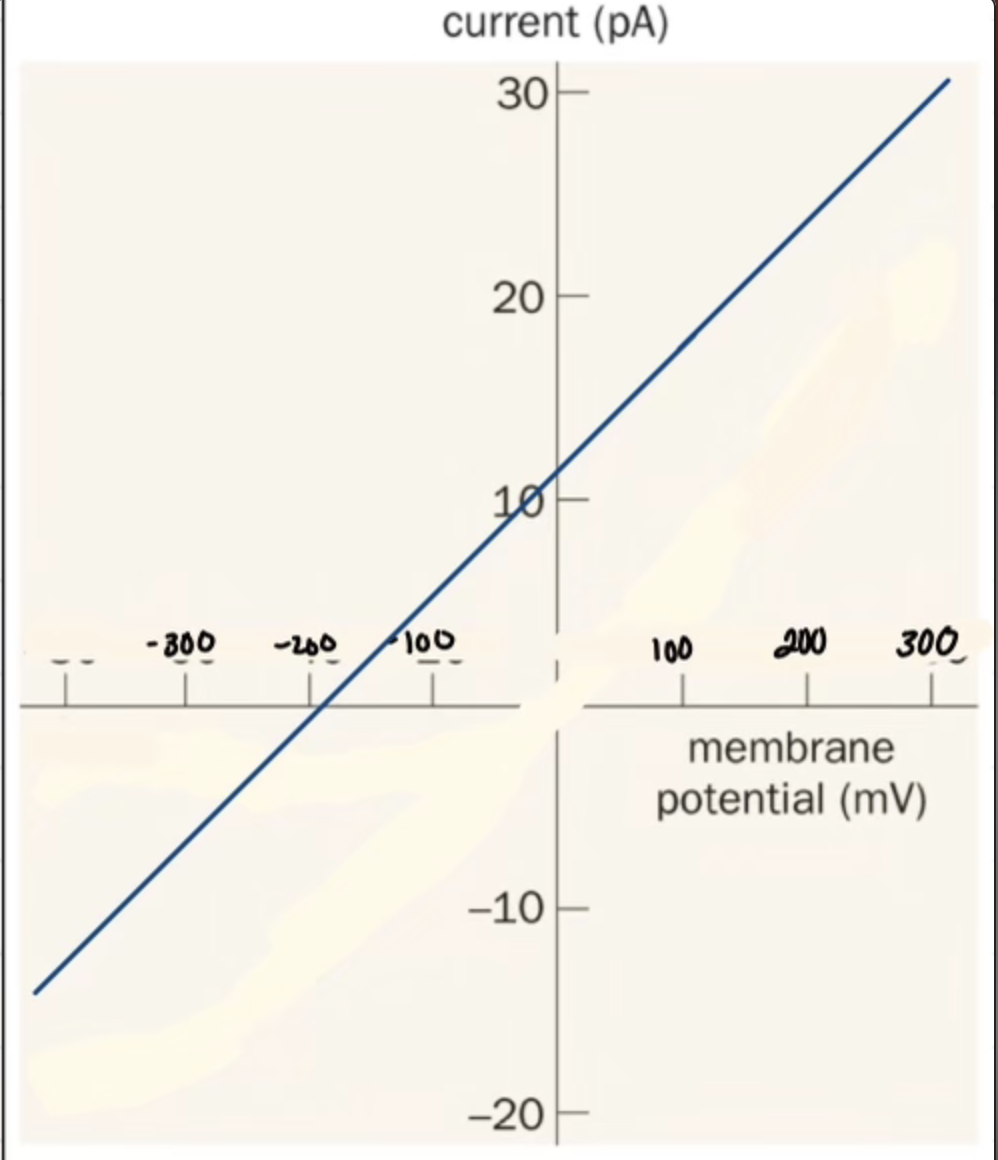
What does this IV plot show
Nicotine Acetylcholine Receptor
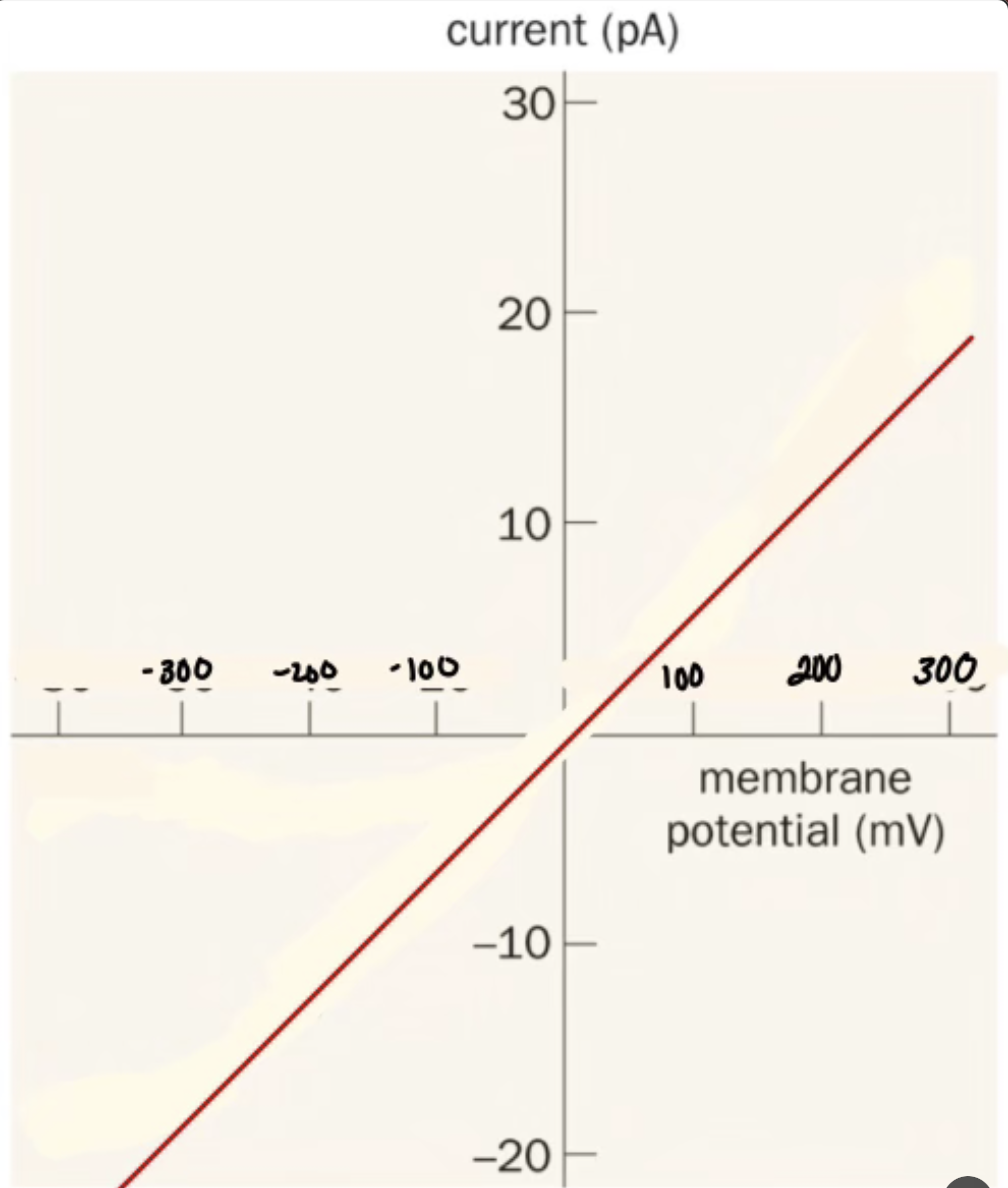
What is important about Nicotine Acetylcholine Receptor
Mixed I ion channel (Na+. K+. Ca+2)
Slightly above 0
Excitatory
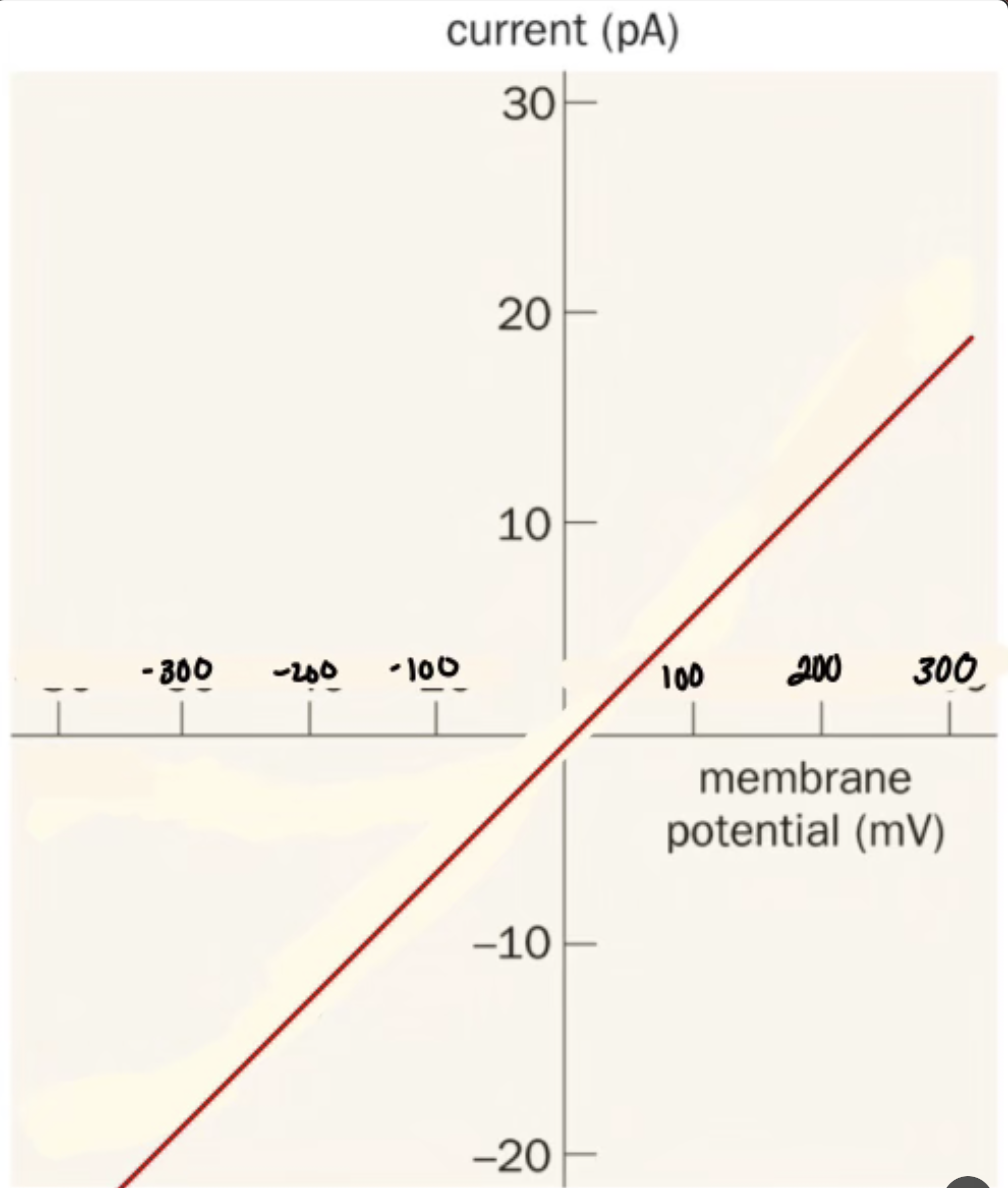
What does it mean when the Nicotine Acetylcholine Receptor depolarizes at 060 current
Positive Ions INTO Cell
It depolarizes and hits the threshold to hit an action potential.
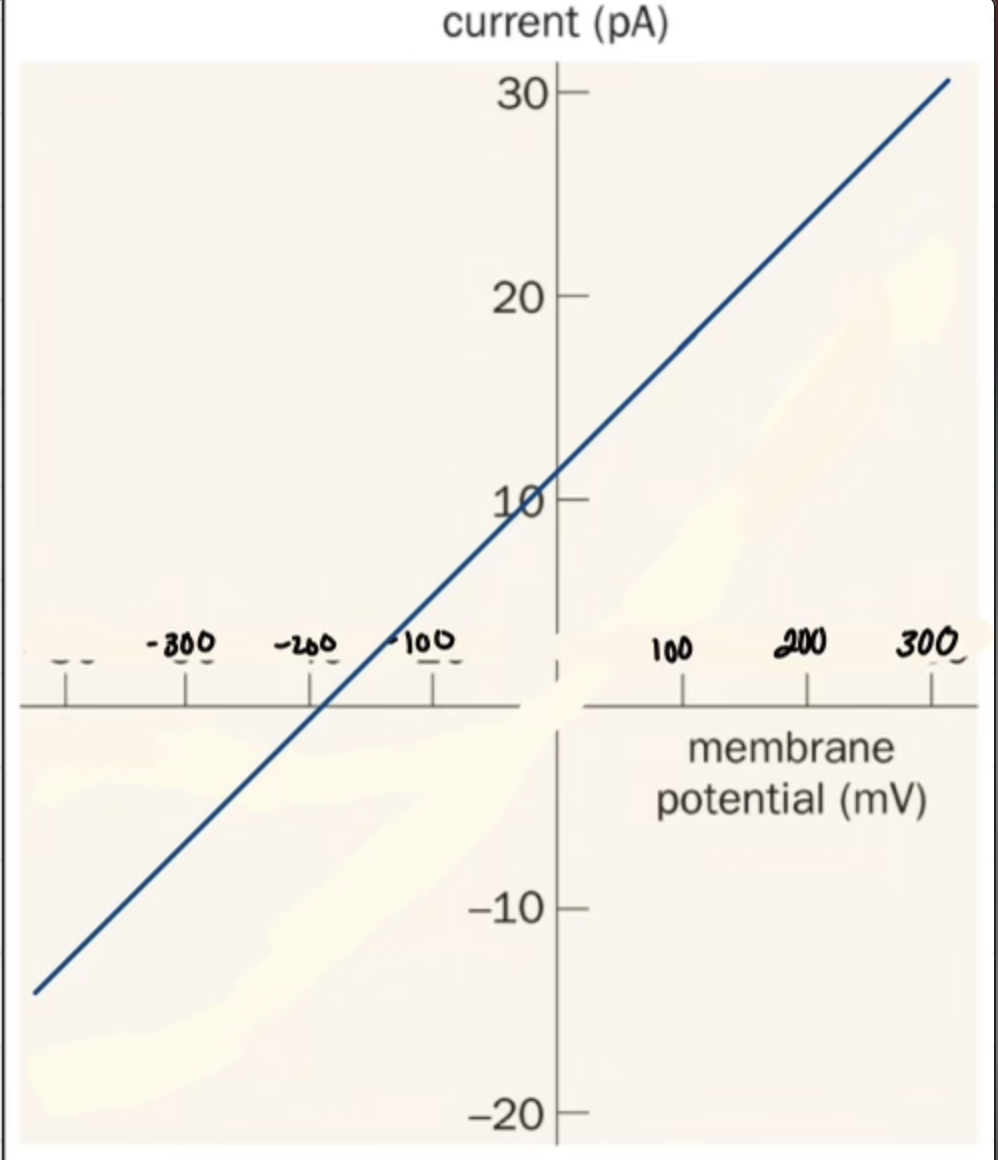
What is important about GABA-A Receptors
Inhibitory
Cl^- receptors only
+ slope from - ions
+ slope form - ions works how?
from -60 current, + slope from the - current flowing in
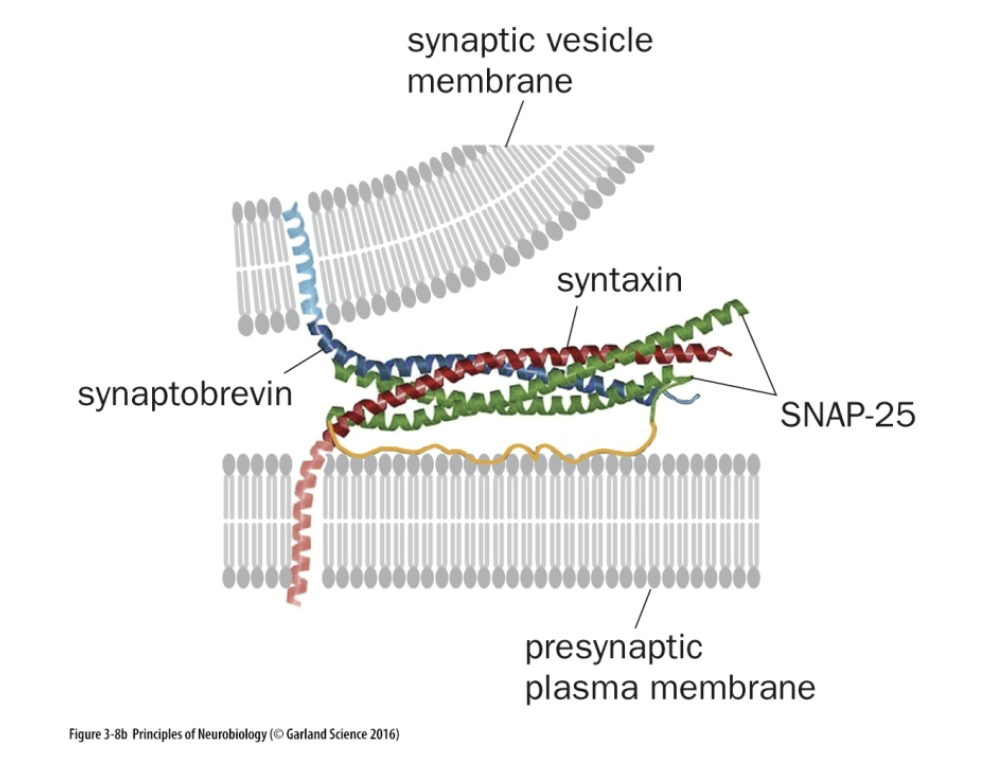
Snyaptobrevin/VAMP stands for
“Vesicle-Associated Membrane Protein”
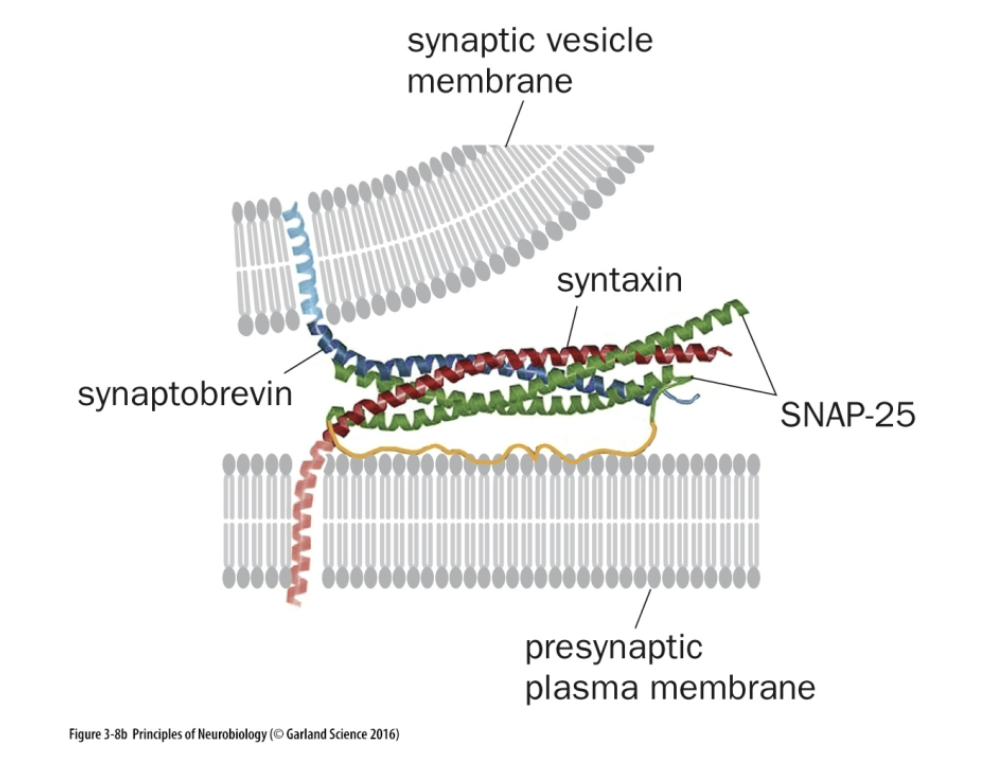
Snyaptobrevin/VAMP if found in
The Synaptic Vesicle (BLUE)
Side of Neurotransmitters
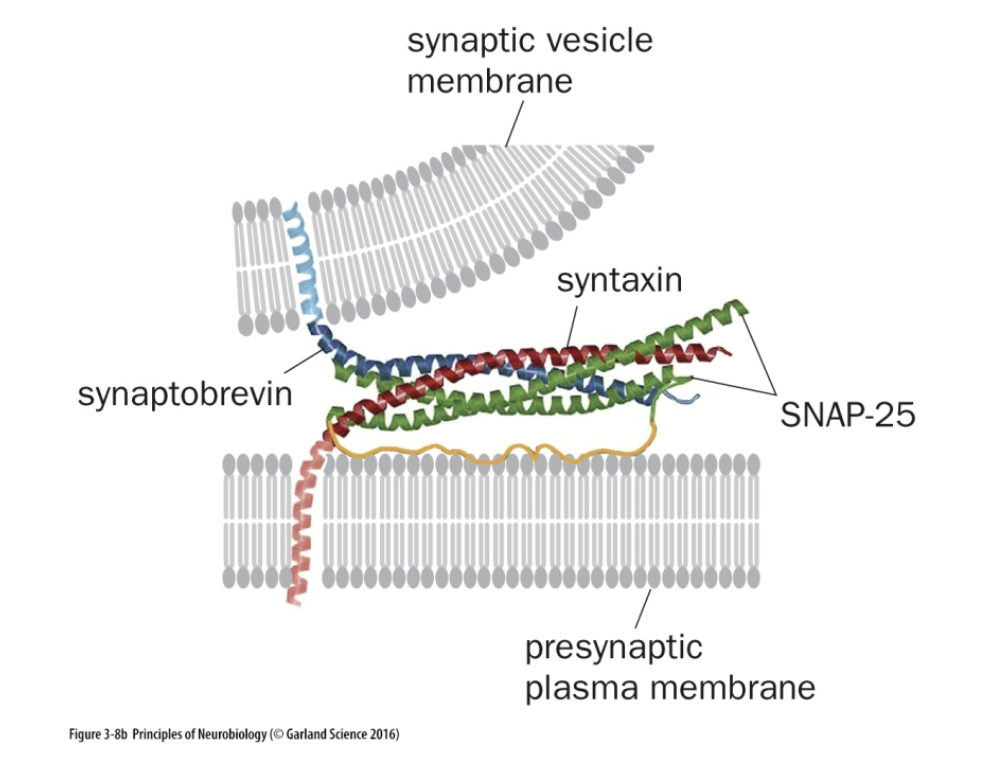
Snyaptobrevin/VAMP does what
Mediates vesicle fusion (v-SNARE)
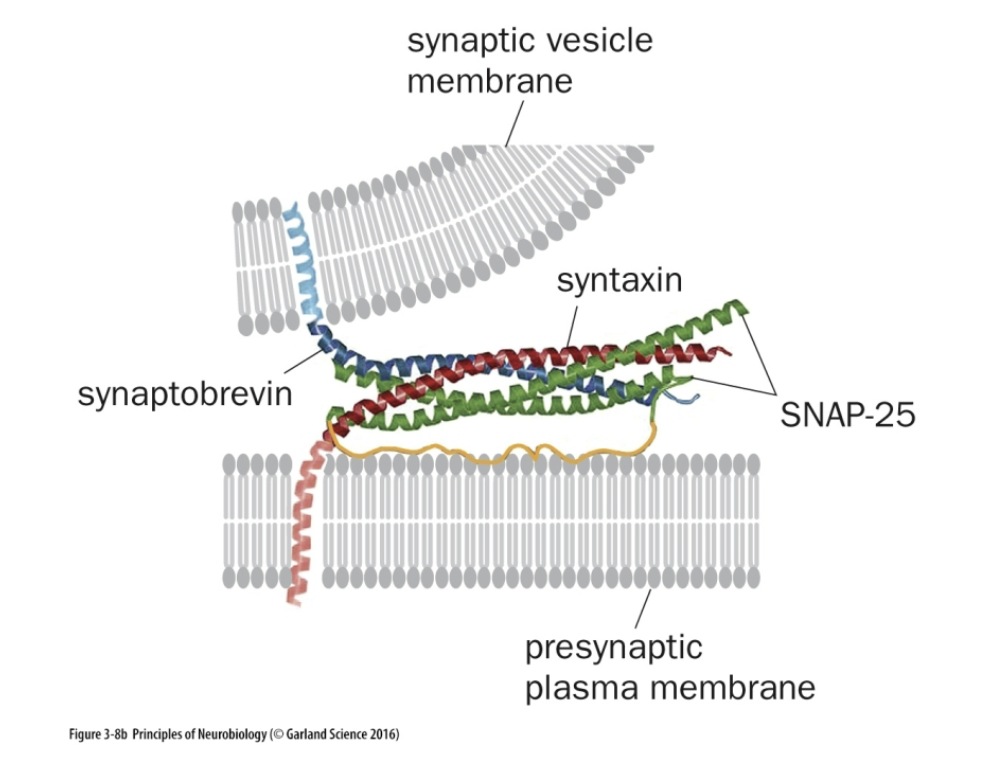
Where is Syntaxin found
From the PreSynaptic Plasma Membrane (RED)
Side of Ca+2 influx
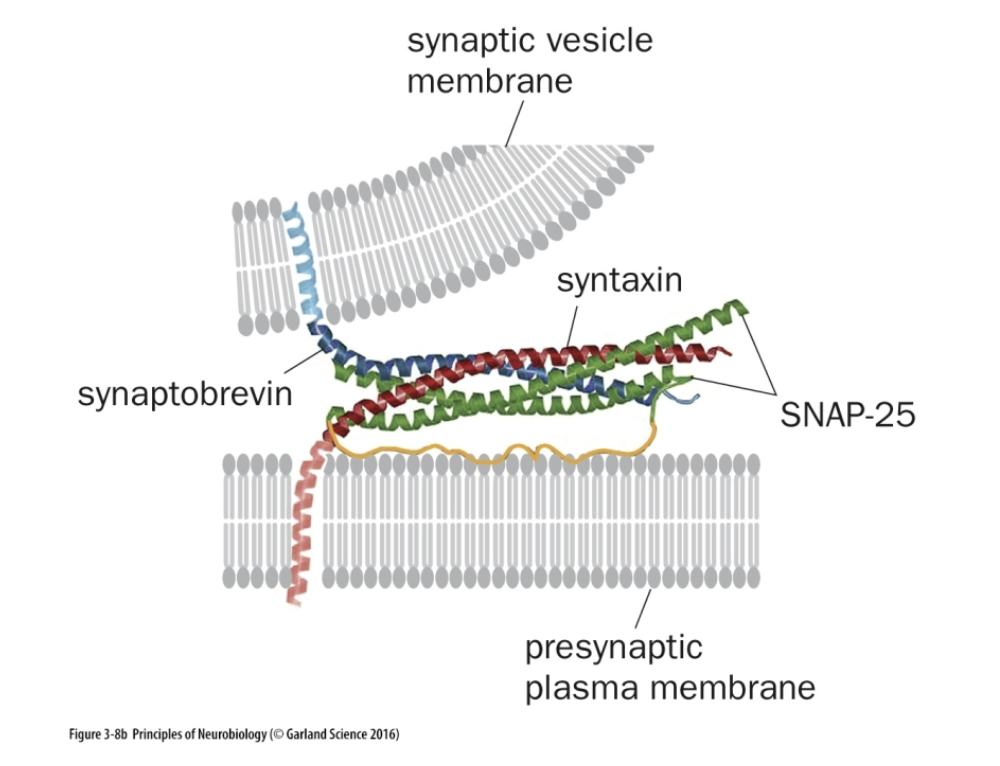
What is Syntaxin function
Mediates vesicle fusion (t-SNARE)
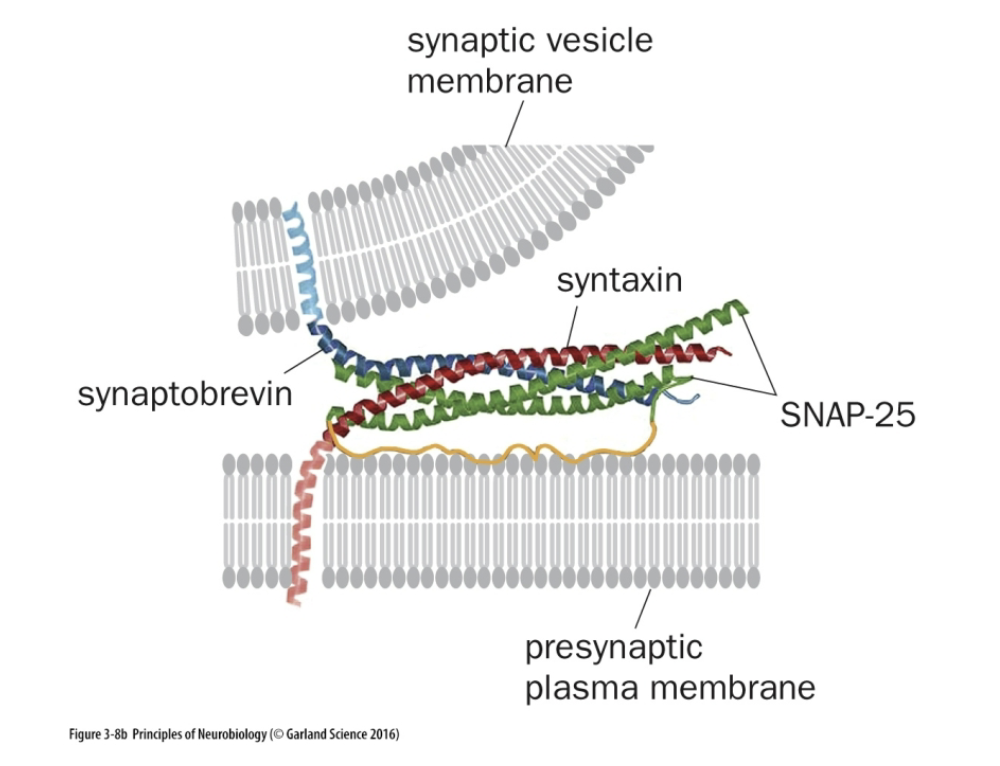
SNAP-25 found in
Presynaptic Plasma Membrane
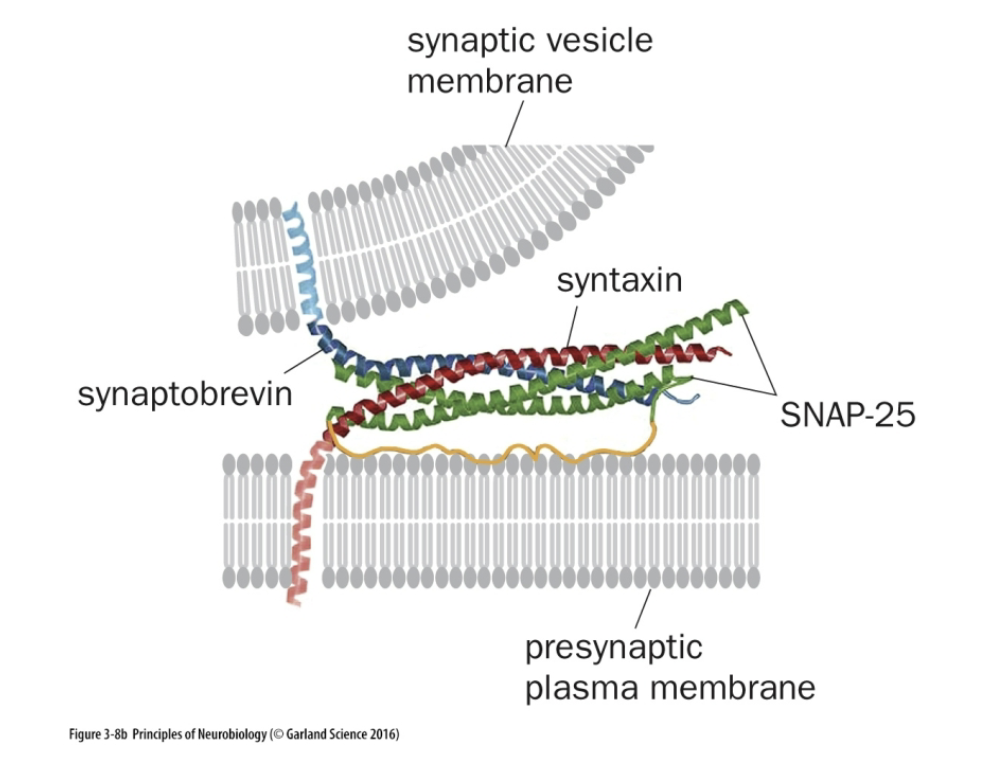
what does the SNAP-25 do
2 alpha helix
Mediates vesicle fusion and interacts with NHF that causes binding.
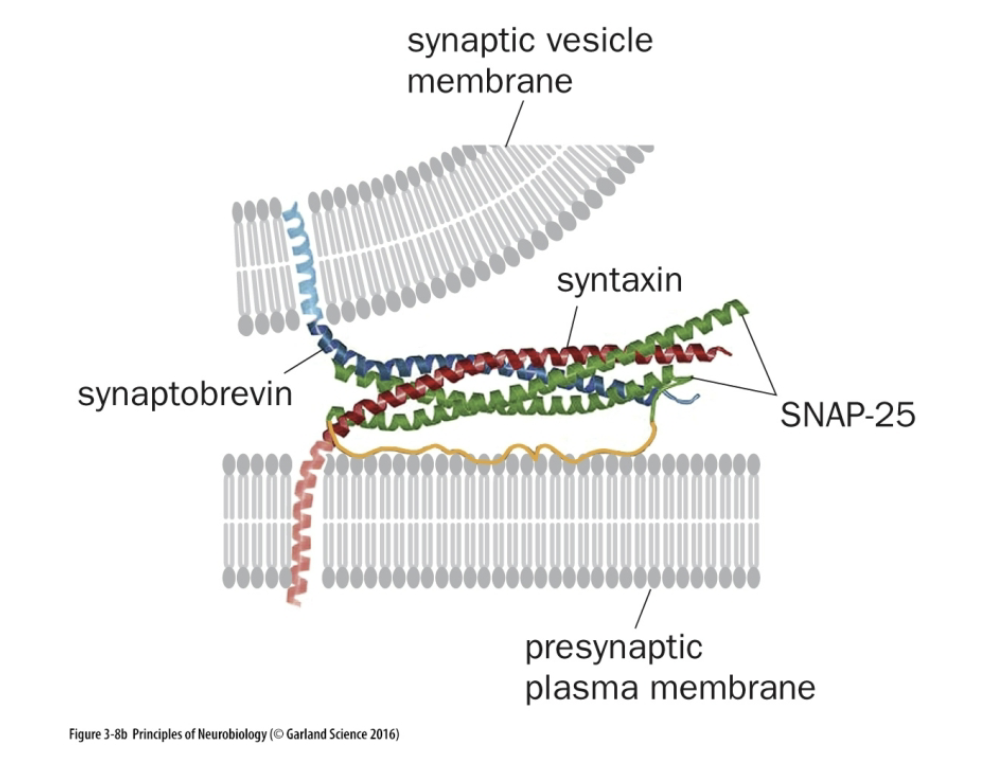
Sec1/Munc18 (SM) found in
Found in the Presynaptic cytosol
What does the Sec1/Munc18 (SM) do
Not fully understood, Binds to SNARE complex and essential for vesicle fusion.
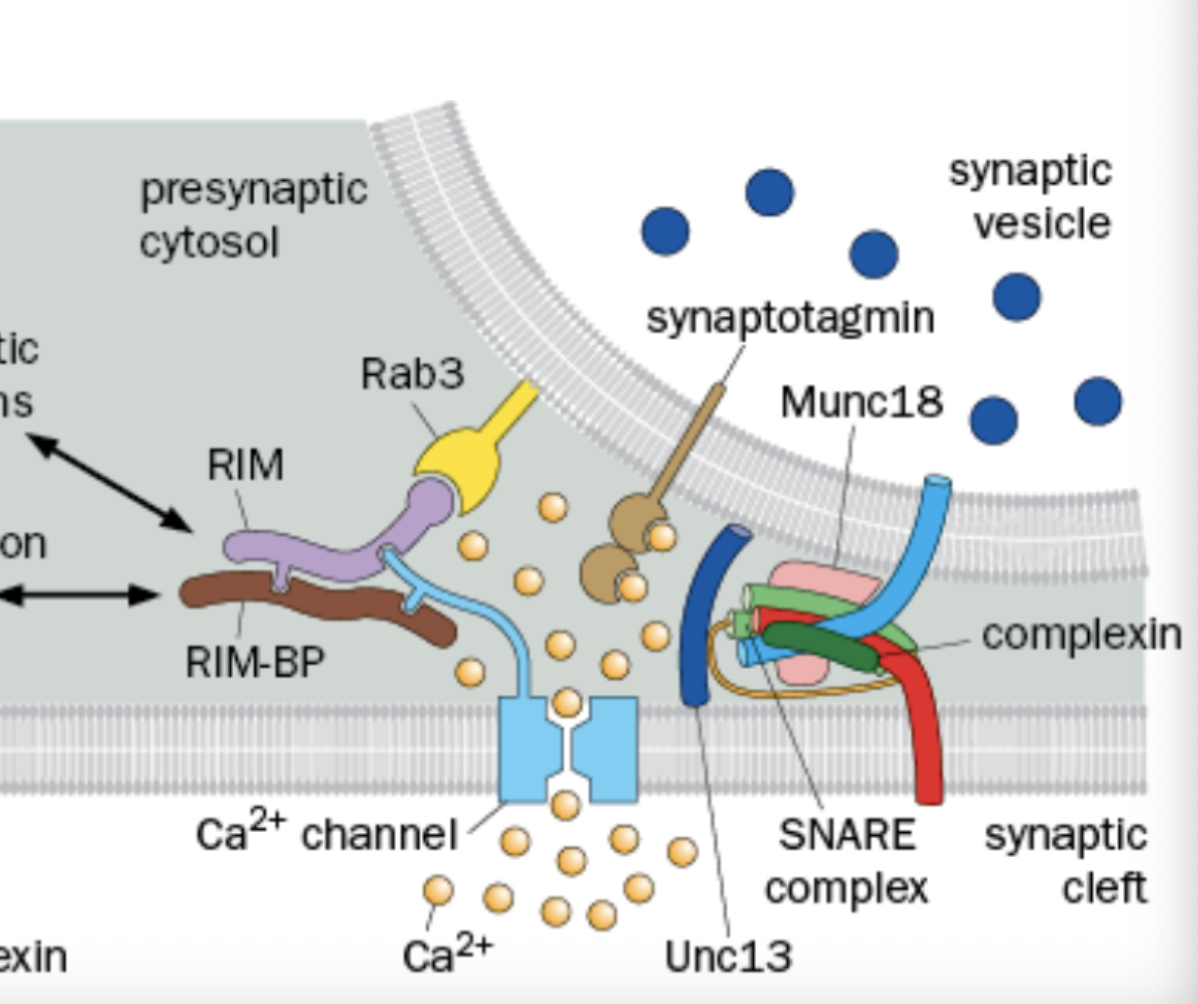
Where is Synaptotagmin
In the Synaptic Vesicle
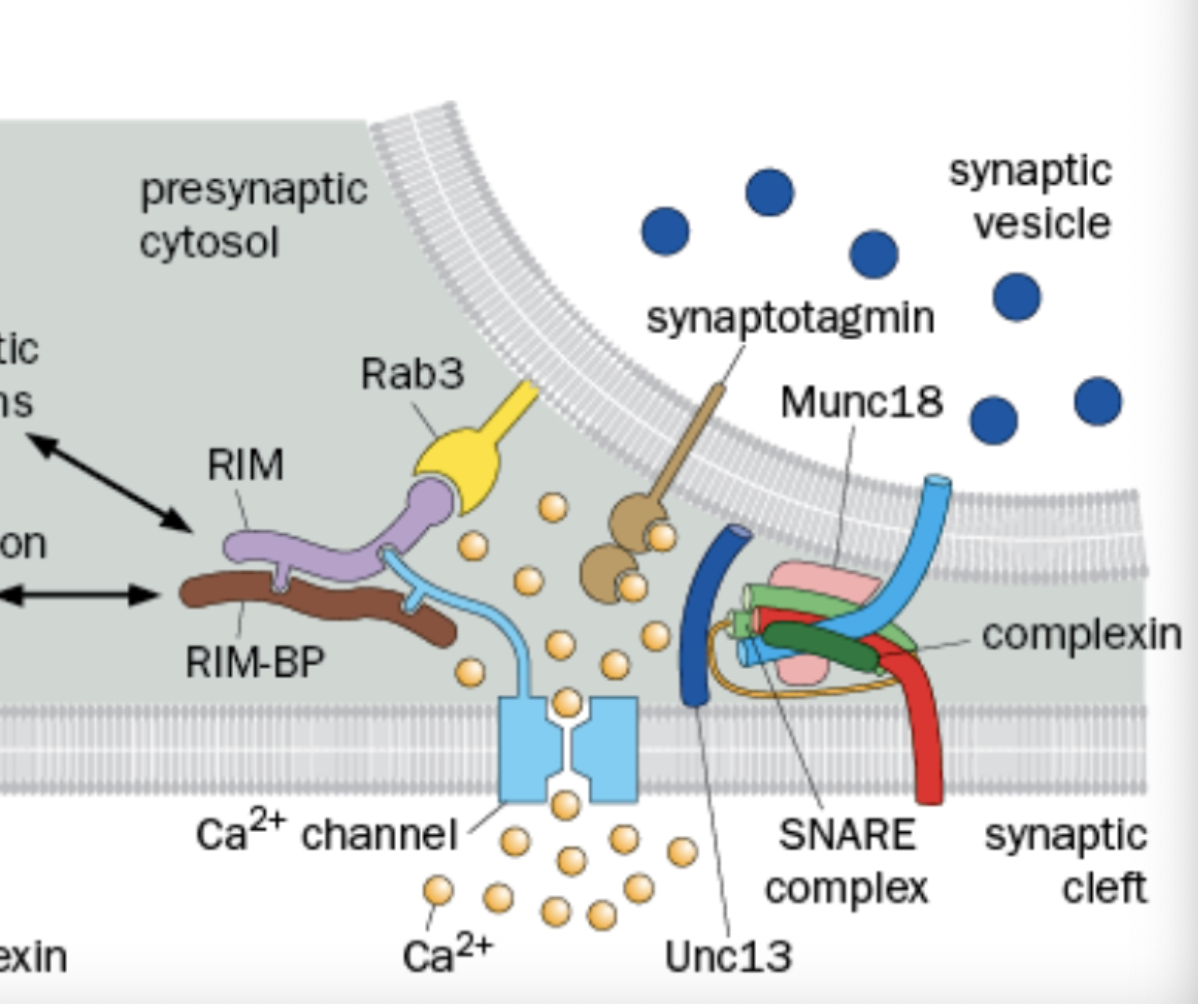
what does the Synaptotagmin do
Senses Ca2+ to trigger vesicle fusion.
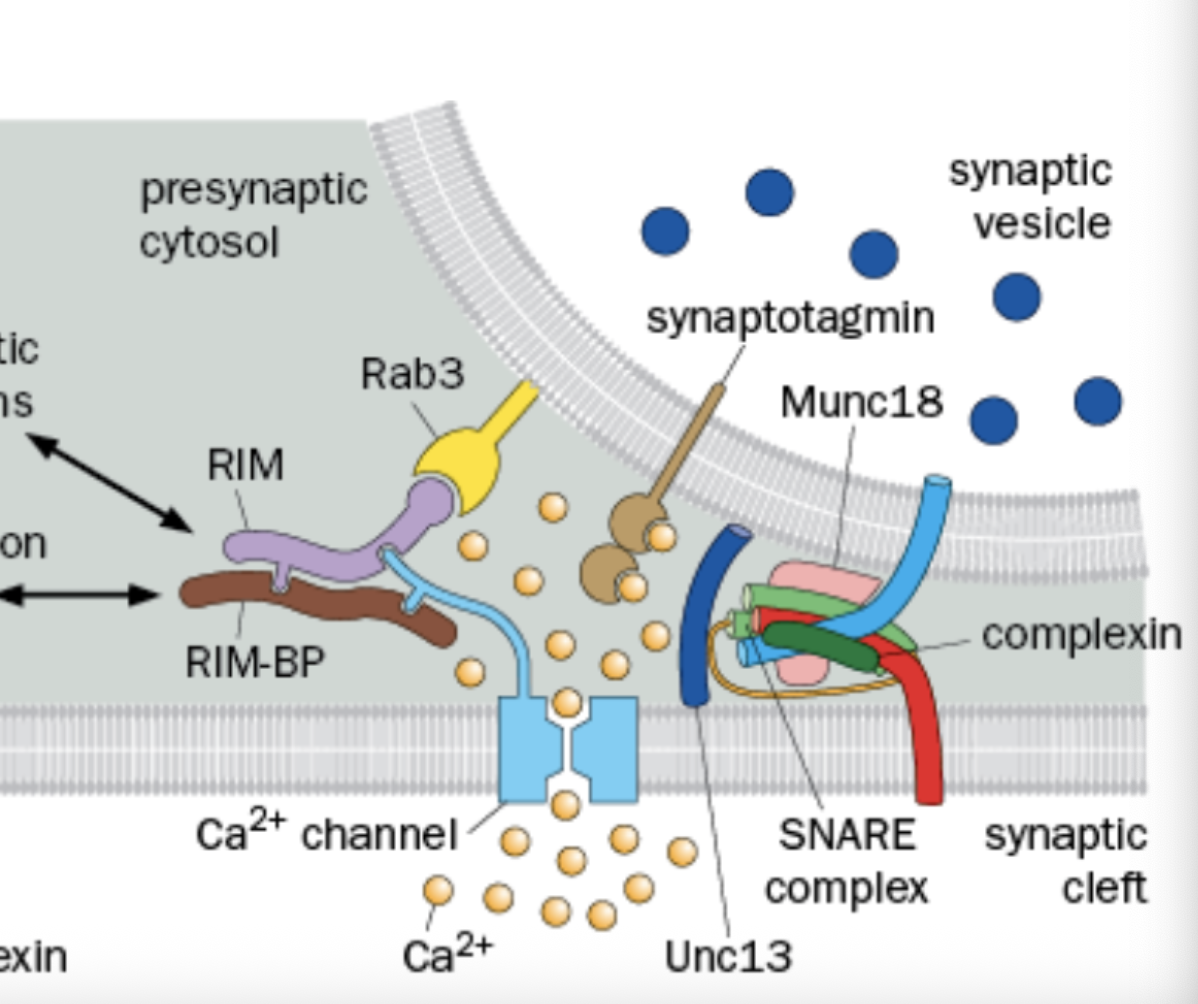
Where is Complexin
Found in the Presynaptic Cytosol
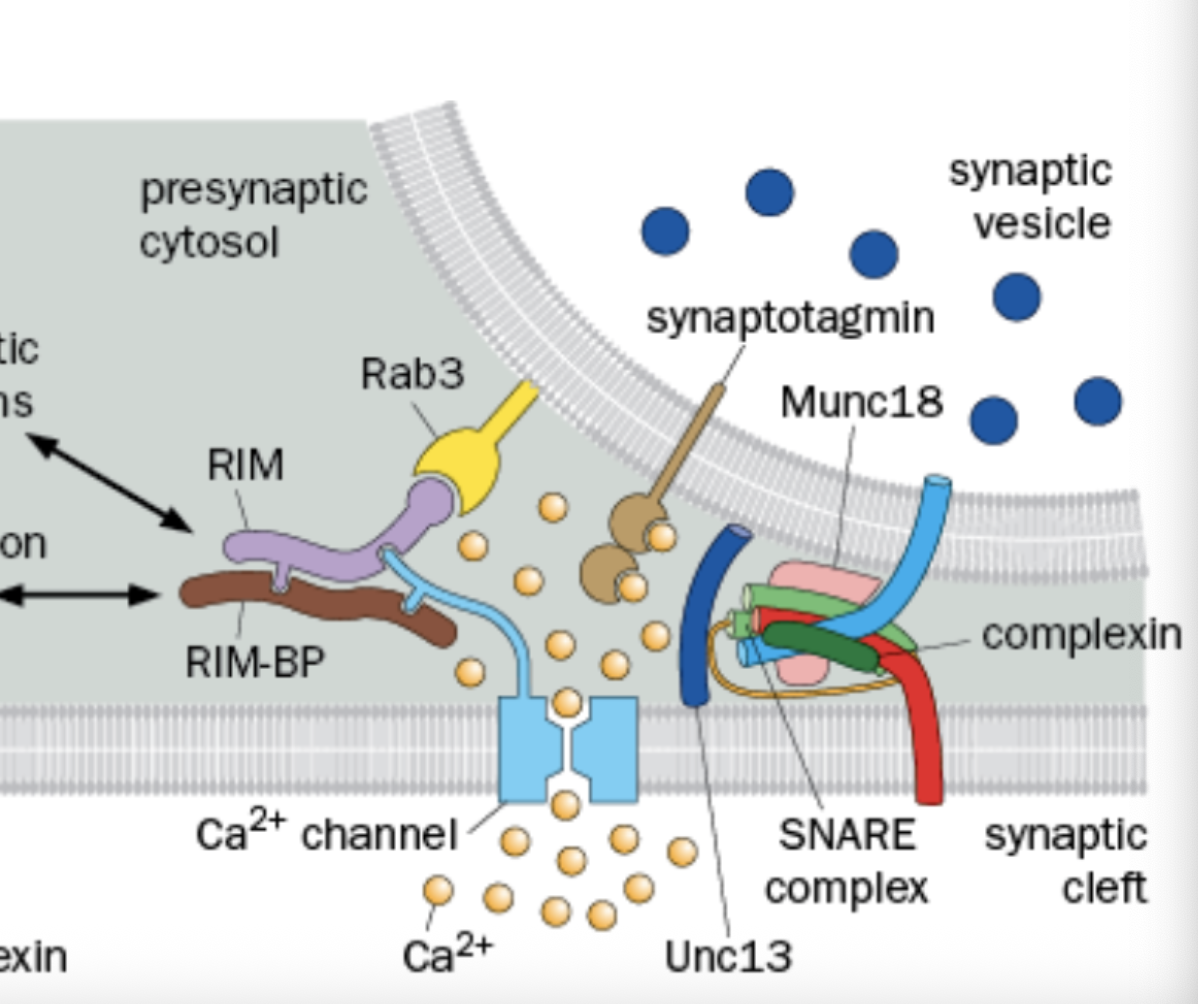
what does Complexin do?
Binds and regulates the SNARE-meditated vesicle fusion
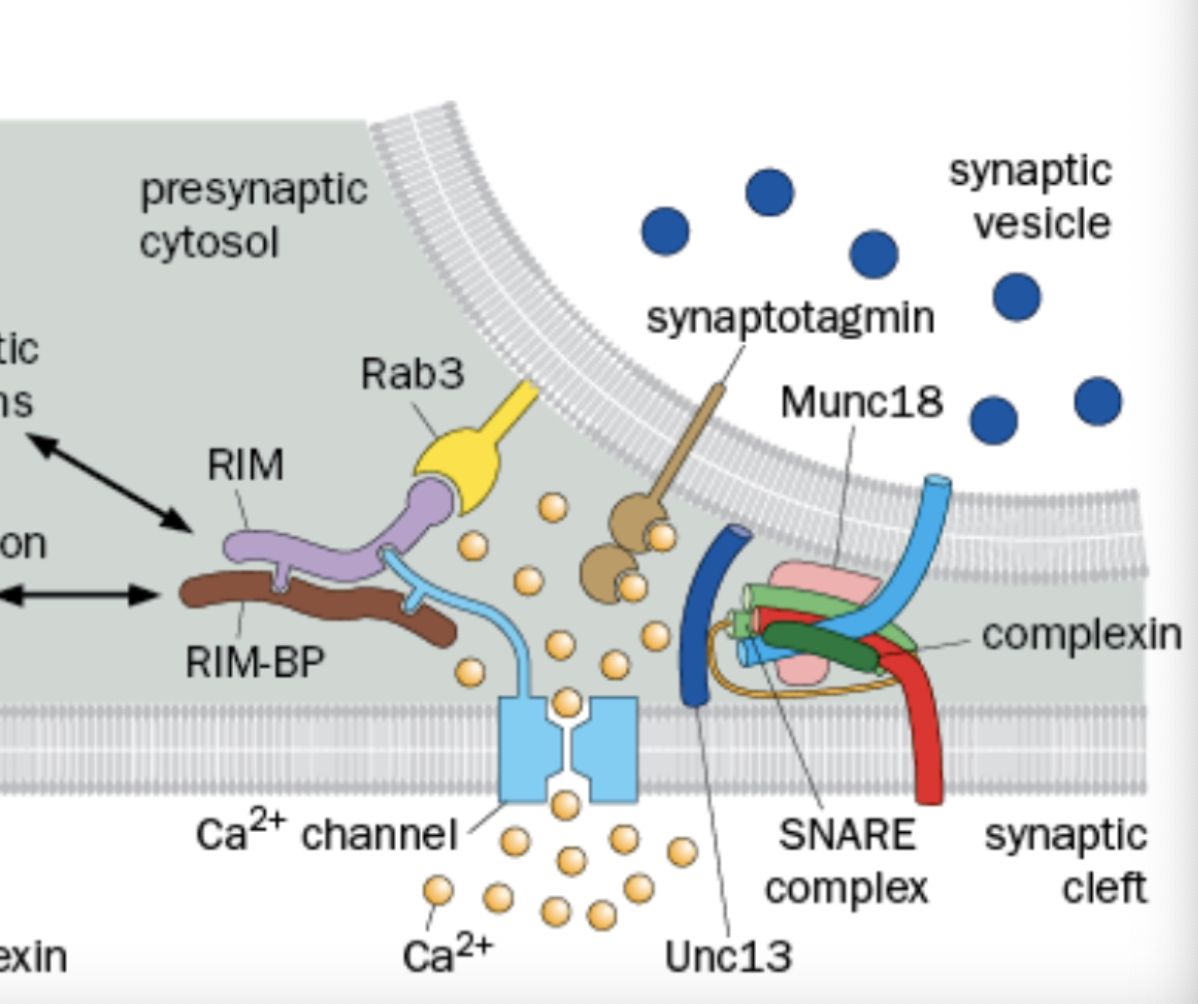
Where is RIM and RAB3 found
Found in the active zone
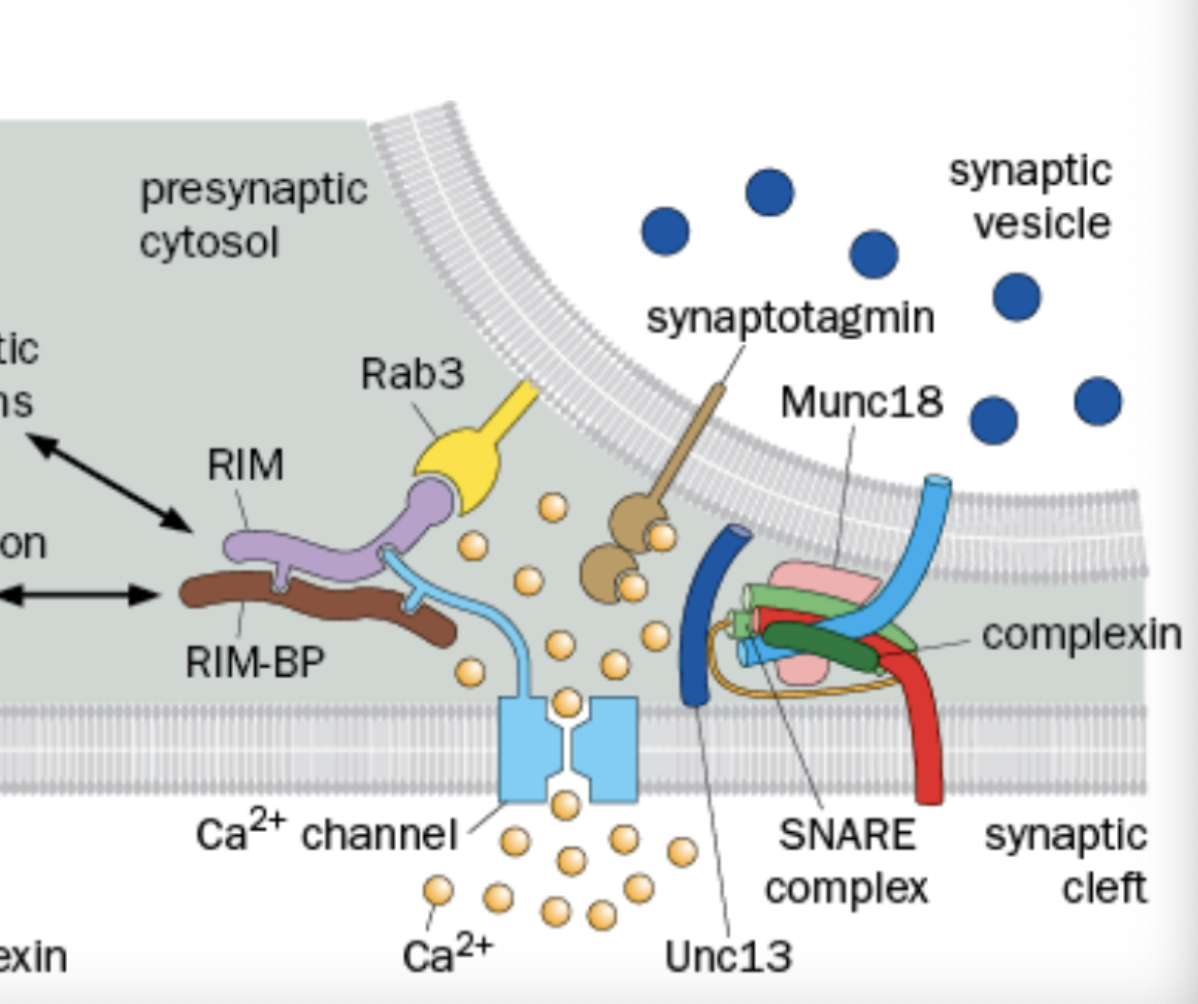
What does Rim do
Organized the presynaptic scaffold, Cytoplasmic
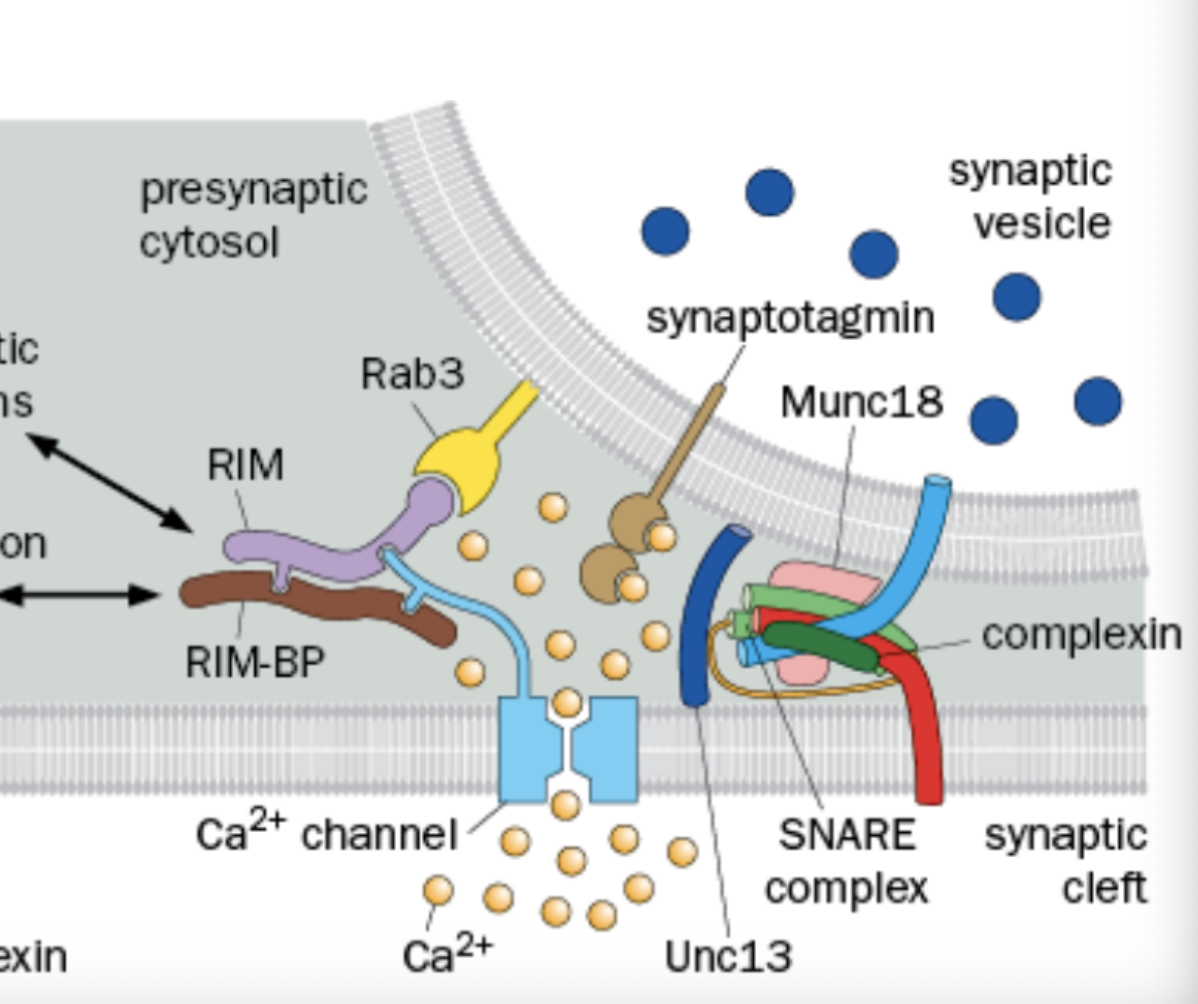
What does RAB3 do
Interacts with the acitve zone components (Synaptic Vesicle Associated)
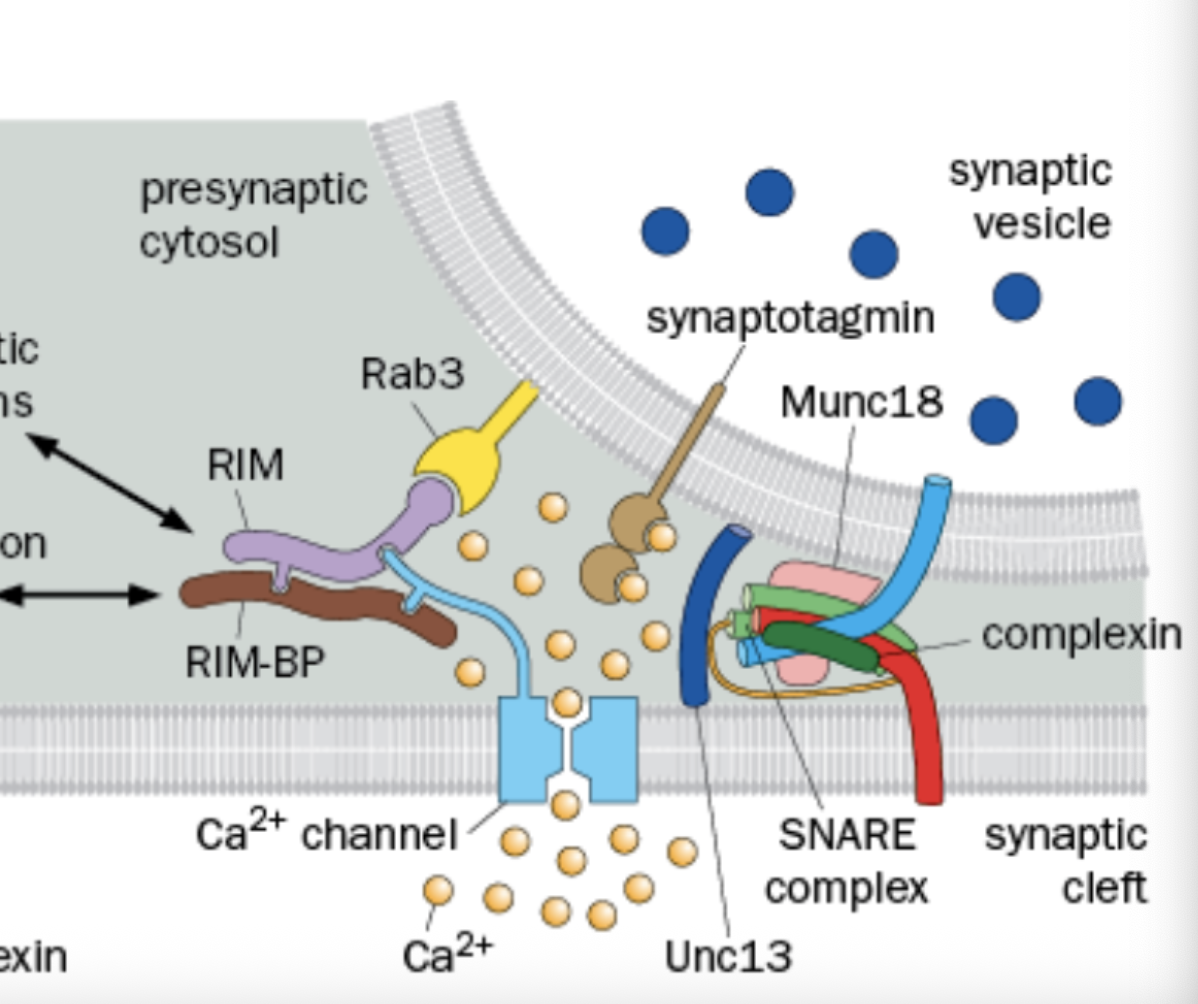
What does Rim and Rab3 do together
tethter voltage gated Ca2+ channels to synatotaxin
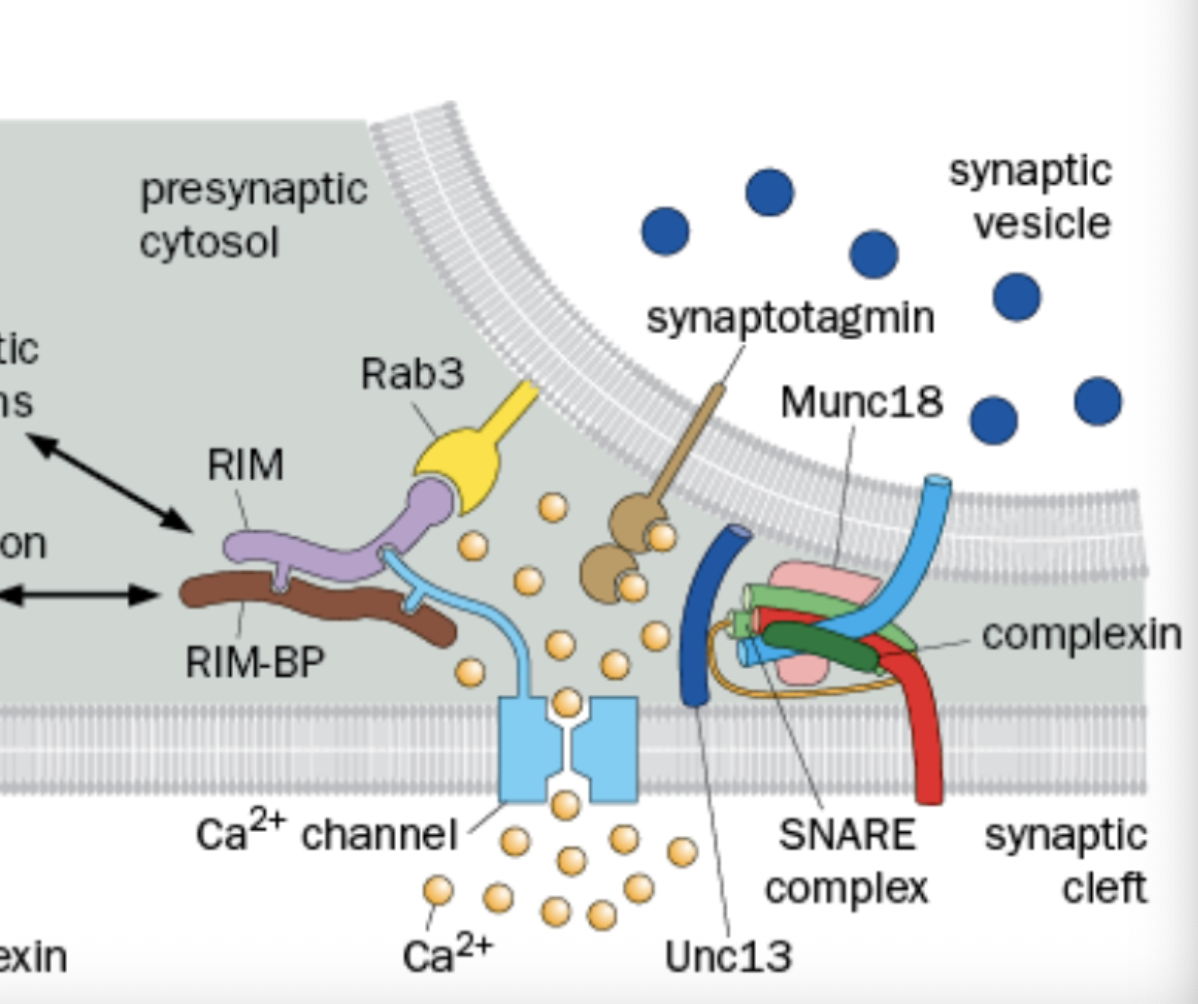
What does Synapsin do?
Maintains vesicles in the vicinity of the active zone and regulates the size of reserve
Where is the Synapsin found
in the Synaptic Vesicle
Where is Clathrin found
It is found in the Presynaptic Cytosol
What does the Clathrin do?
Shapes recyled vesicles from presynaptic plasma membrane or endosome membrane during endocytosis.
Shibire/Dyamin is found where
Presynaptic Cytosol
What does the Shibire/Dyamin do?
Cytoplasmic protien for final pinshing off of endocytosis.
NSF found in
Presynaptic Cytosol
what does the NSF do
Disassembles SNARE complex after fusion
Spacial Submation
2 separate pulses, that meet each other and stack.
temporal submation
2 pulses from the same location, one after the other
dendrites length constant
distance of the dendrite
dentrites time constant
the sharp peaks dull over time
amplitude decreases, duration increases
Diameter imposes ________ _______
But ______ ______ does not change Diameter
Internal Resistance
“Alpha s “is what
Activates AC
From Epinephrine
“Alpha I” is what
Inhibits AC Ca2+ Channel
Activates GRIK,
From ACh
“Alpha q” is what
Activates PLC
Capacitor is what of the cell
Plasma Membrane
Facilitation
Releasing more Neurotransmiteasters as time goes on makes it larger
Depression
Leaving less neurotransmitters
Activates G protein-coupled Receptors
lower voltage gates Na+ channels
Activating K+ channels
TARP
regulate AMPA receptor function and placement at synapses
Regulate decay kinetics \
Why do you need Glycine for NMDAR
it is a co-agonist with glutamate for the NMDAR channel can open
Sodium Gates
Fast voltage gate
Slow, inactivation gate (closed if above threshold)
Ohms Law
I=V/R