Lecture 2: Earth as a Self-Regulating System
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
Gaia hypothesis
Earth as a self-regulating system through feedback.
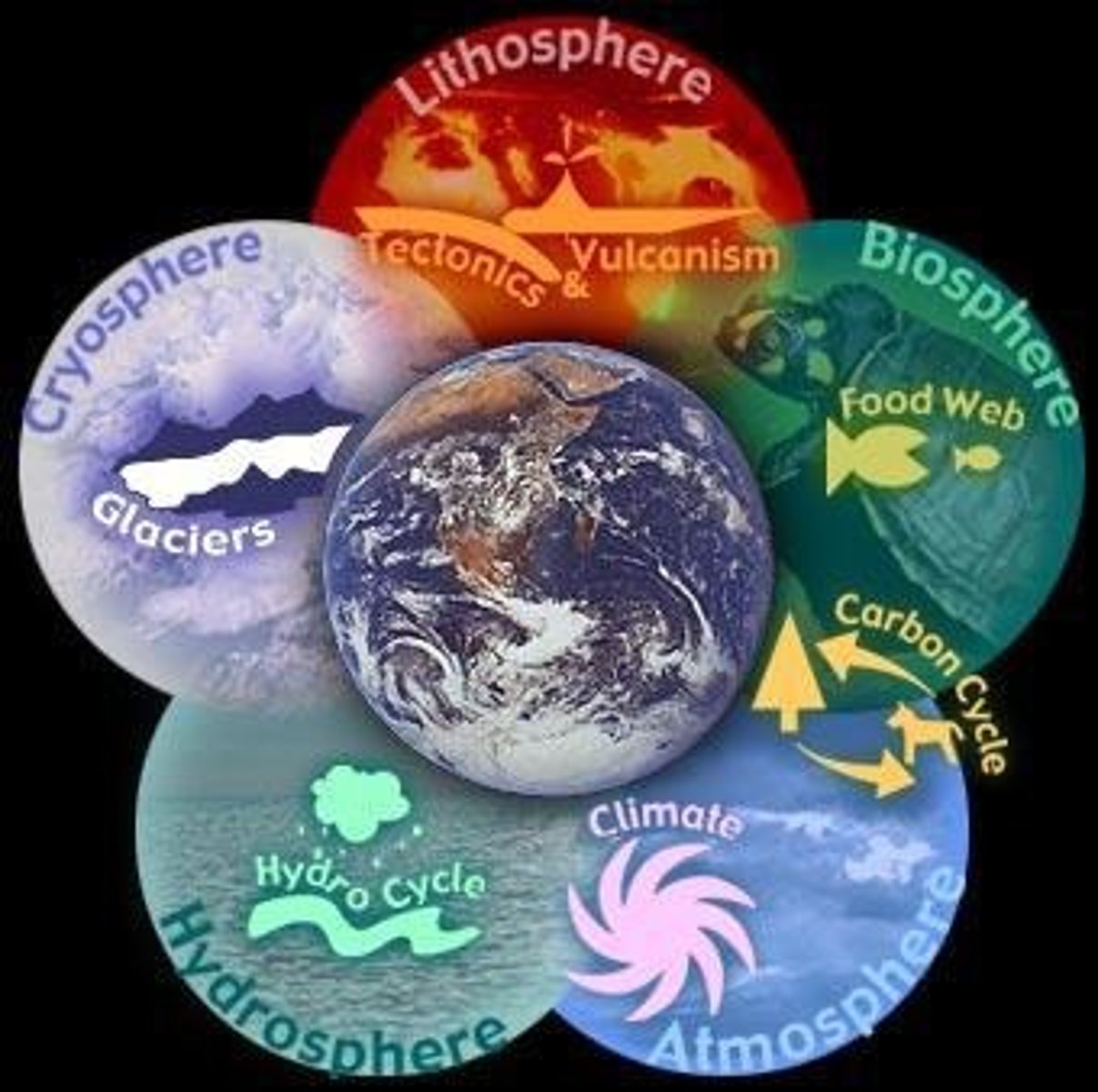

Geosphere
Solid Earth, including rocks and minerals.
Hydrosphere
Water components, including oceans and ice.
Biosphere
All living organisms on Earth.
Atmosphere
Layer of gases surrounding Earth.
Steady state
Condition where system variables remain constant.
Fluxes
Movement of energy and matter between reservoirs.
Residence times
Average time matter spends in a reservoir.
Positive feedback
Amplifies initial changes in a system.
Negative feedback
Dampens or reduces changes in a system.
Reservoirs
Storage locations for matter and energy.
Plate tectonics
Movement of Earth's plates relative to each other.
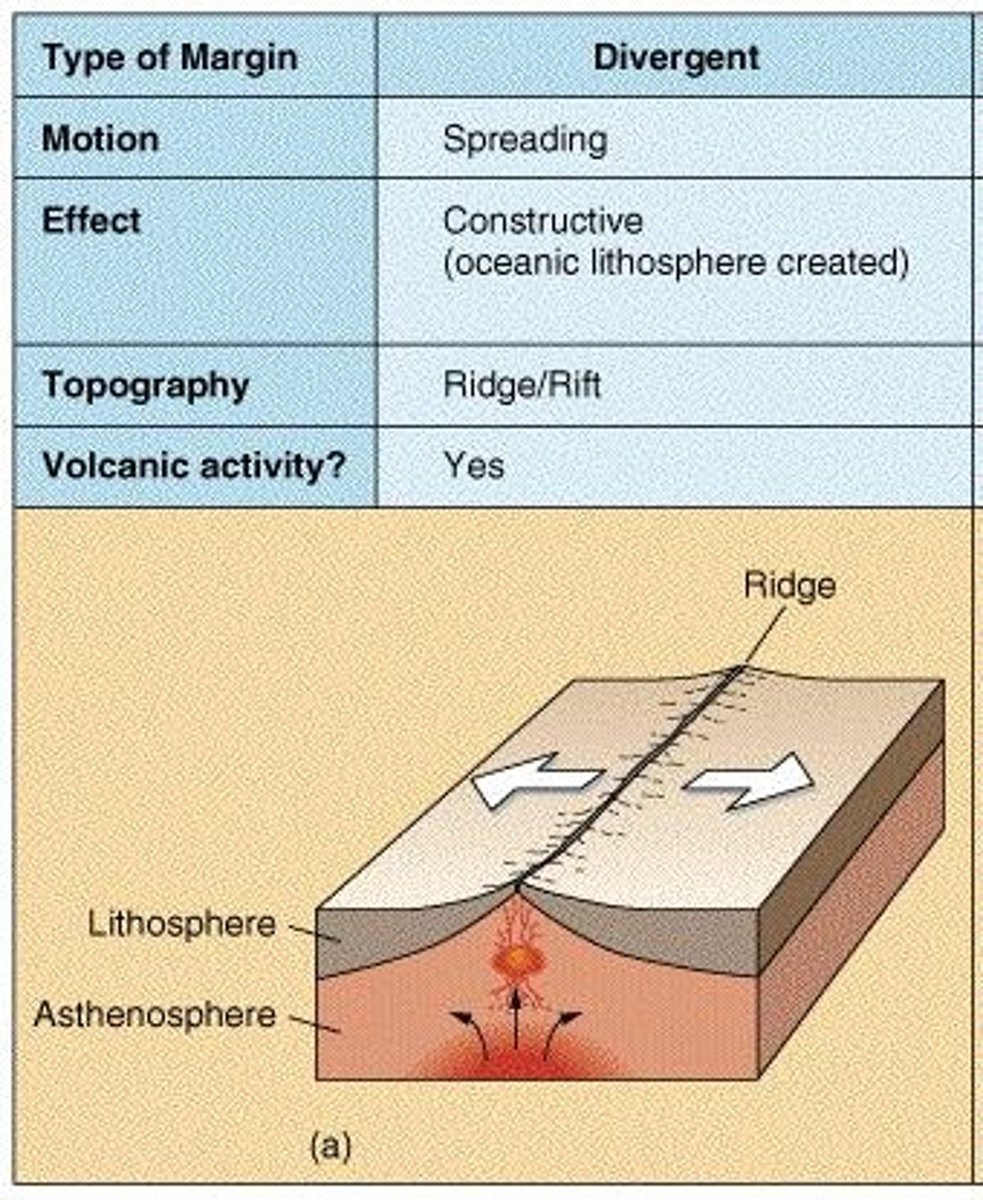
Divergent boundaries
Where tectonic plates move apart.
Convergent boundaries
Where tectonic plates move towards each other.
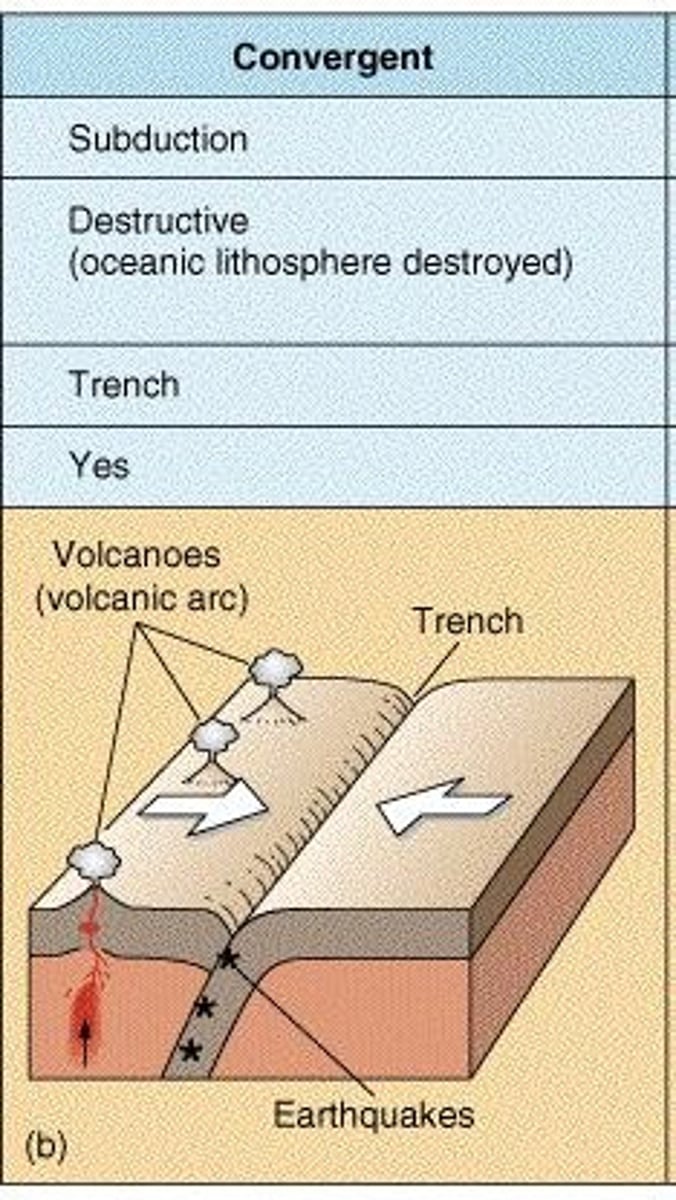
Subduction zones
Areas where oceanic crust is destroyed.
Volcanic eruptions
Release of gases like CO2 into atmosphere.
Chemical weathering
Process removing CO2 from the atmosphere.
Cryosphere
Frozen water components of the Earth.
Stromatolites
Fossilized evidence of early life, 3.5 Ga.
Feedback mechanisms
Processes that regulate Earth's systems.
Earth's interior
Includes magmas and gases beneath the surface.
Abiotic oxygen generation
Oxygen produced by non-living processes.
Weak Young Sun
Early Earth CO2 source compensating for solar output.
Divergent Plate Boundaries
Locations where tectonic plates pull apart.
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Example of divergent plate boundary formation.
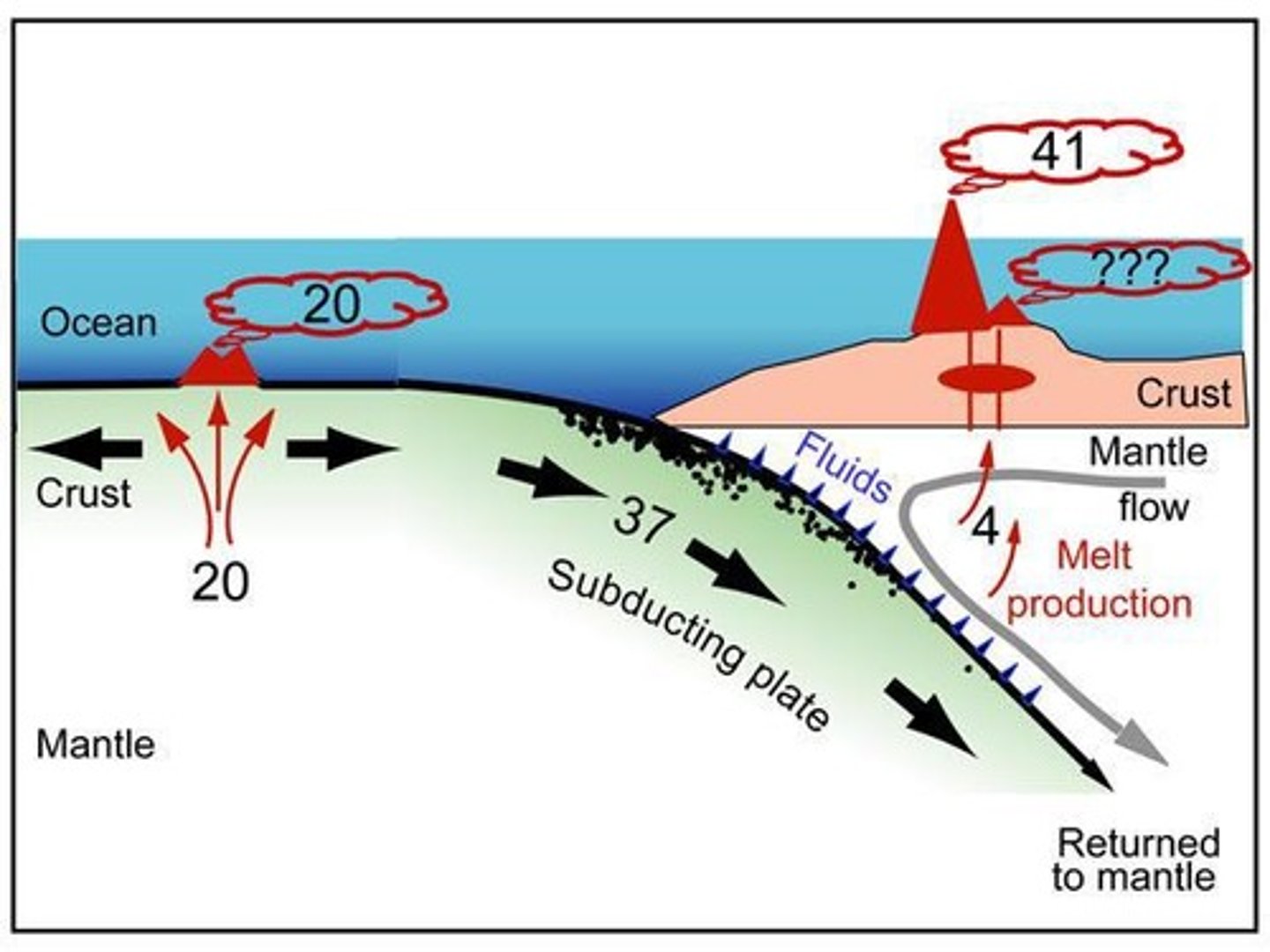
Carbon Degassing
Release of CO2 from Earth's reservoirs.
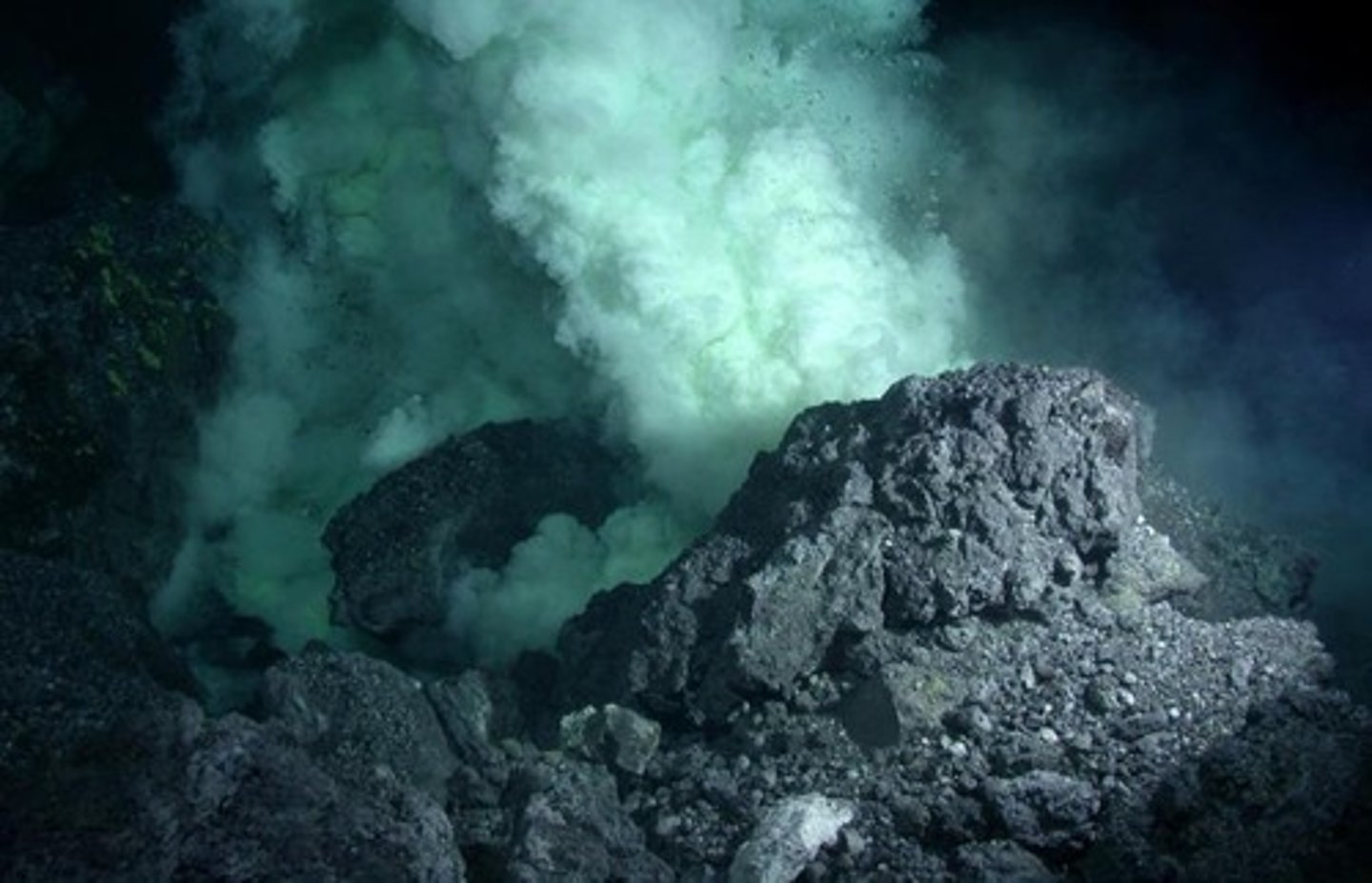
Submarine Volcanoes
Underwater volcanoes contributing to CO2 emissions.

Anthropogenic Emissions
Human-induced CO2 from fossil fuels and cement.
GtCO2
Gigatonne of CO2, equals one billion tonnes.
Natural Emissions
CO2 released from natural processes like volcanism.
Mount Pinatubo
Volcano in the Philippines, significant eruption in 1991.

Flux
Mass transfer rate, measured in kg/year.
Reservoir
Storage of mass, measured in M units.
Steady State
Condition where input equals output flux.
Perturbation
Change in system affecting concentration over time.
Input Flux (Jin)
Mass entering the reservoir per unit time.
Output Flux (Jout)
Mass leaving the reservoir per unit time.
Unbalanced Fluxes
Condition where Jin exceeds Jout, not steady state.
Hydrosphere Interaction
Seawater alters rock composition at mid-ocean ridges.
Black Smokers
Hydrothermal vents releasing hot metal-rich fluids.
White Smokers
Hydrothermal vents with different mineral compositions.
Geosphere
Earth's solid outer layer interacting with hydrosphere.
Carbon Reservoirs
Natural storage locations for carbon in Earth.
Residence Time
Average time a particle stays in a system.
Steady State
Input equals output in a system.
Global CO2 Emissions
CO2 released from fossil fuels and cement.
Atmospheric CO2 Reservoir
Atmosphere holds 750 Mt of CO2.
Photosynthesis
Process plants use to absorb CO2.
Food Chain
Pathway through which energy and nutrients flow.
Chemical Weathering
Natural process releasing CO2 into the atmosphere.
Carbonic Acid
CO2 dissolved in water forms this acid.
Marine Organisms
Organisms that incorporate salts like CaCO3.
Ocean CO2 Absorption
One-third of human-emitted CO2 absorbed by oceans.
Ocean Acidification
Decreasing pH due to rising CO2 levels.
Positive Feedback
Reinforces initial changes in a system.
Negative Feedback
Counters or dampens initial changes in a system.
Albedo Effect
Reflectivity of Earth's surface affecting temperature.
Global Thermostat
Chemical weathering regulates atmospheric CO2 levels.
Fluxes
Flows between or within Earth's reservoirs.
Interconnected Reservoirs
Solid Earth, hydrosphere, biosphere, atmosphere are linked.
Anthropogenic CO2 Increase
Human activities significantly raise atmospheric CO2.
Research on Feedback Mechanisms
Active study of climate system interactions.
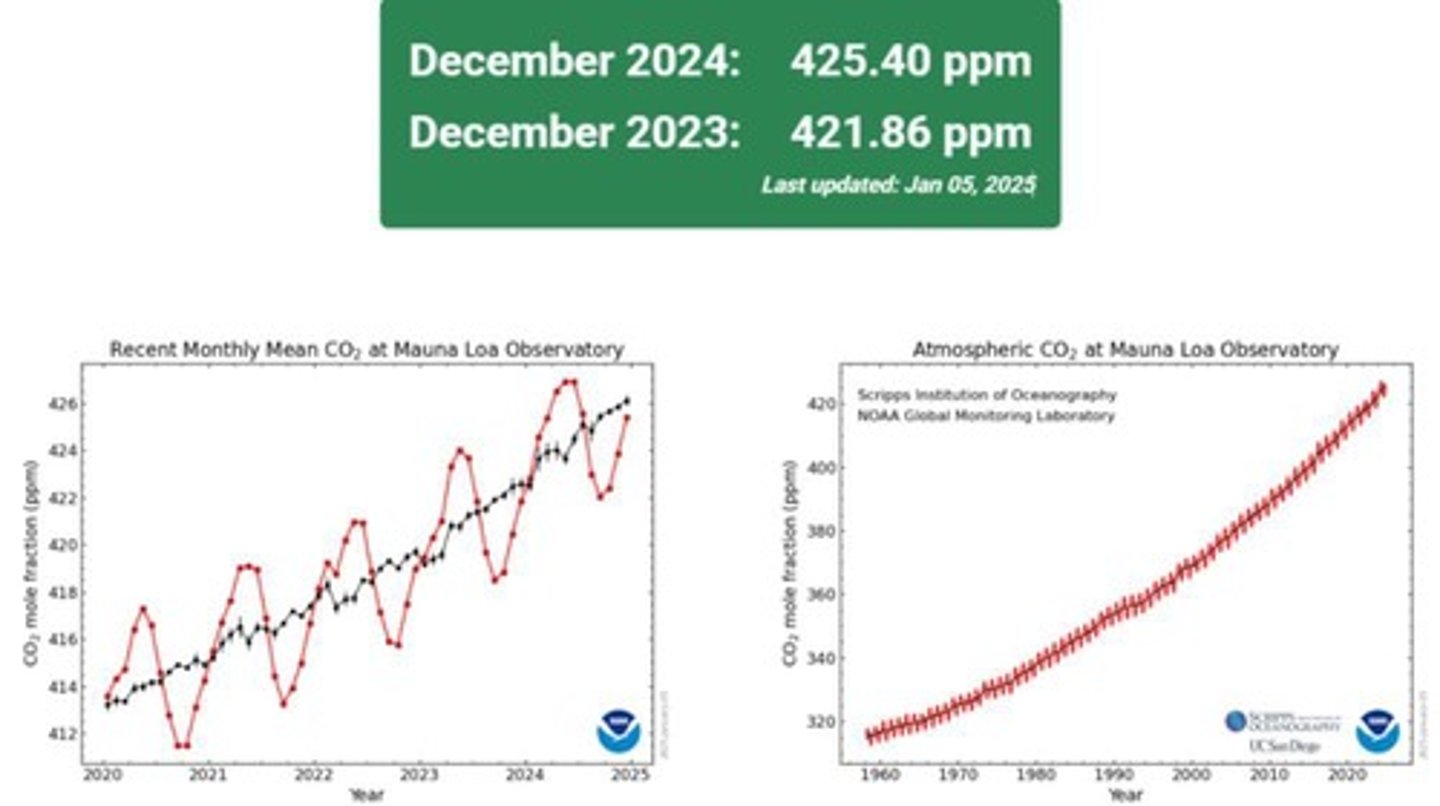
Mauna Loa Observatory
Location for monitoring atmospheric CO2 levels.
Carbon Cycle Processes
Includes photosynthesis, respiration, decay, and weathering.
Terrestrial Ecosystems
Land-based systems that absorb CO2.
Oceanic CO2 Sink
Oceans absorb CO2, slowing atmospheric increase.