Chapter 1: The Study of Body Function
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Physiology - Hierarchy of living systems - Homeostasis - Primary tissues
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Define: Physiology
The study of biological function, i.e. how
the body works
Living Systems Hierarchy (smallest to largest)
molecular/cellular, tissues,
organs, systems, organism
Cells
the fundamental unit
Tissues
groups of same cell type / collections of cells
Organs
multiple tissues with a common
function / collection of tissues
Organ systems
multiple organs/ collections of organs
Organism
multiple organ systems / all they systems put together
10 Organ Systems
Nervous
Endocrine
Reproductive
Integumentary
Circulatory/Cardiovascular
Respiratory
Digestive/Gastrointestinal
Urinary/Renal
Musculoskeletal
Immune
Musculoskeletal:
muscles, tendons, bones
Urinary/Renal:
kidneys, bladder
Digestive/Gastrointestinal:
digestive tract, glands
Respiratory:
lungs and air passageways
Circulatory/Cardiovascular
heart and vessels
Immune
white blood cells, spleen
Nervous
brain, spinal cord, sensory organs
Endocrine
pituitary gland, thyroid gland, etc.
Reproductive
ovaries, uterus, testes
Integumentary
skin
Define: Homeostasis
State of relative constancy of
the internal environment (a lot of our physical functions, functions to maintain balance in our body )
How is Homeostasis maintained?
Through Negative feedback loops (ex) body temp, sodium, glucose, pH, oxygen)
physiological Variables are maintained by homeostasis
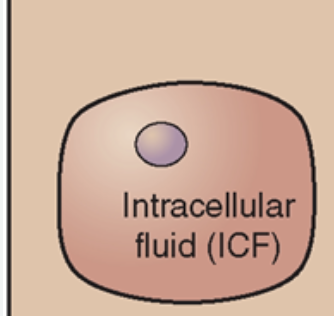
ICF
Intracellular Fluid
fluid within the cell
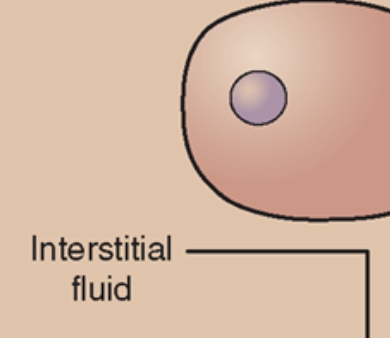
ISF
Interstitial Fluid
fluid around the cell (within tissue)
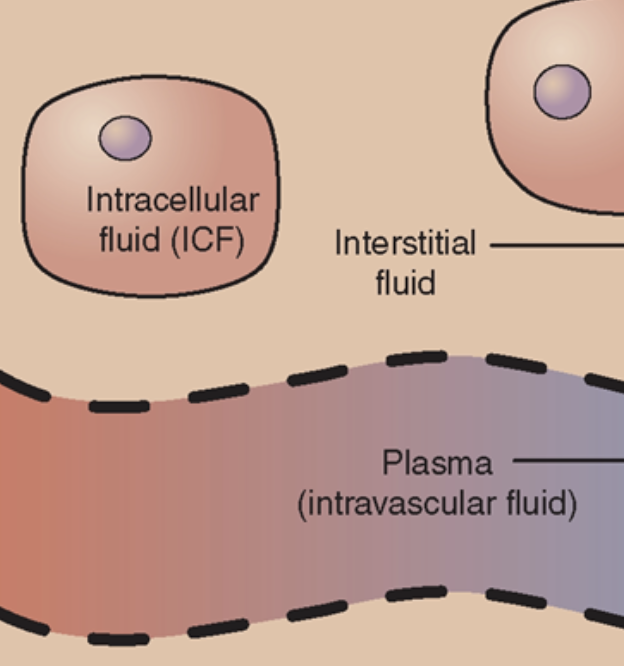
Plasma
Fluid Component of blood (within blood vessels)
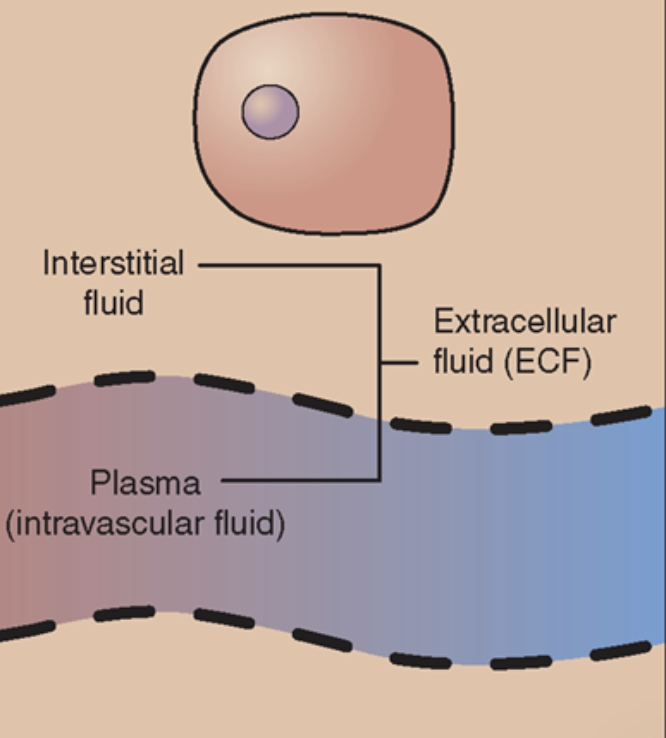
ECF
Extracellular Fluid
Fluid outside of the cell
(includes ISF and Plasma)
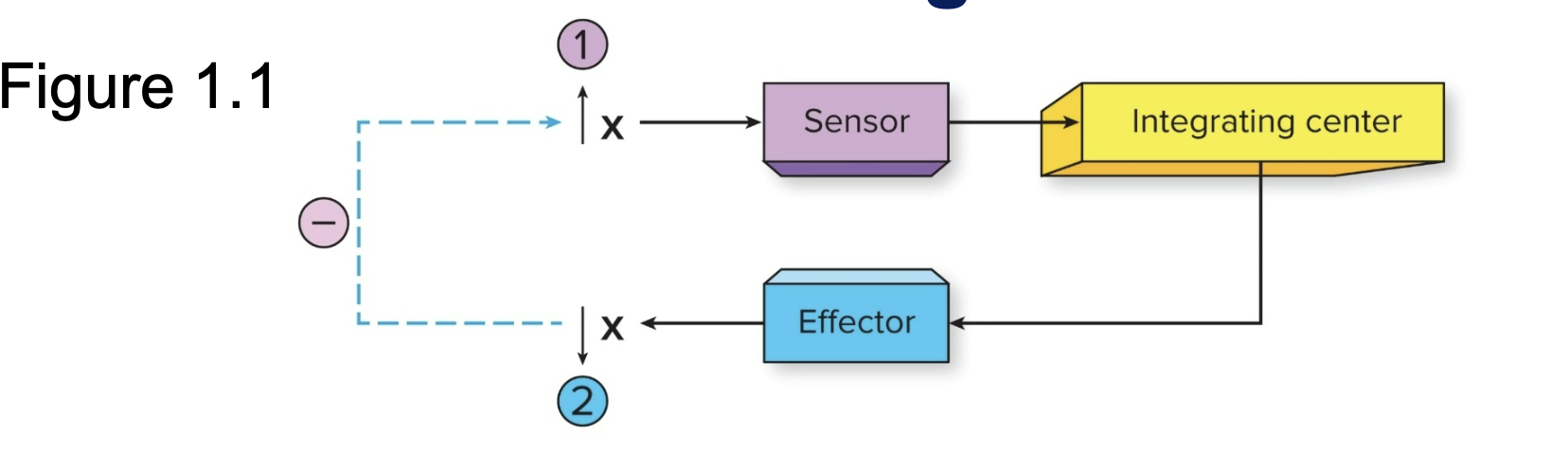
Homeostasis & Negative Feedback: Sensors
Where changes in physiological Variables are detected (sense the changes )
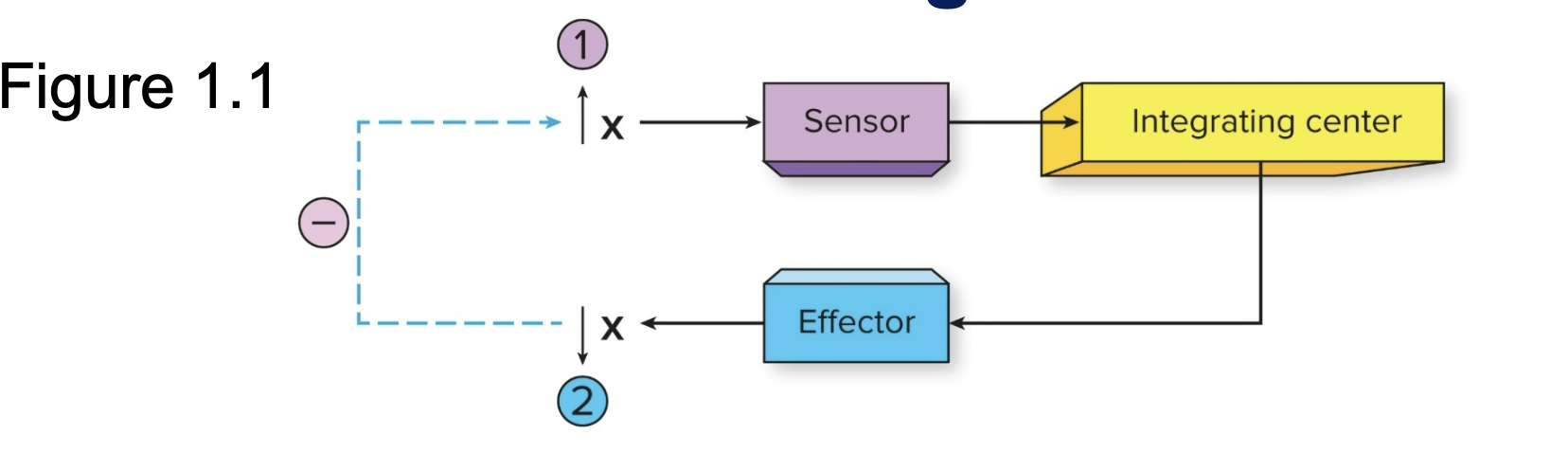
Homeostasis & Negative Feedback: Integrating Centers
Where information is sent (coordinates output)
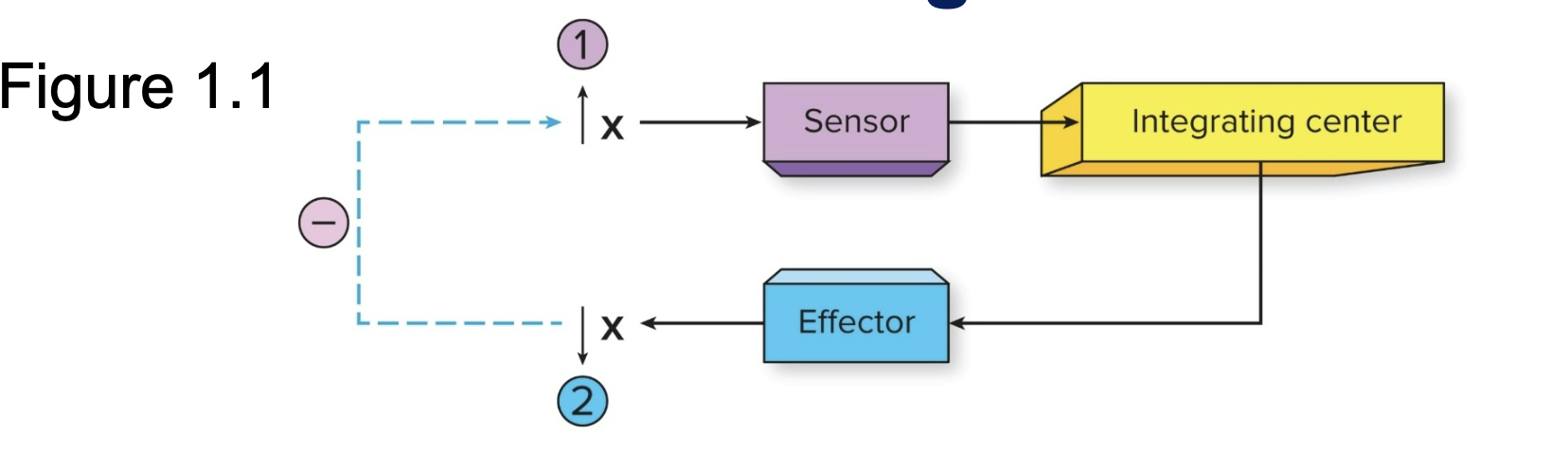
Homeostasis & Negative Feedback: Effector
Information from the integrating center causes the effector to produce change in the opposite direction. (Produces a reversal of initial change)
Define: Negative Feedback
An increase or decrease in a variable causes a
response to move the variable in the direction opposite the original change.
Define: Dynamic Constancy
physiological parameters are not constant, but fluctuate around a set point
levels:
change over short amount of time
remains relatively consistent over long period of time
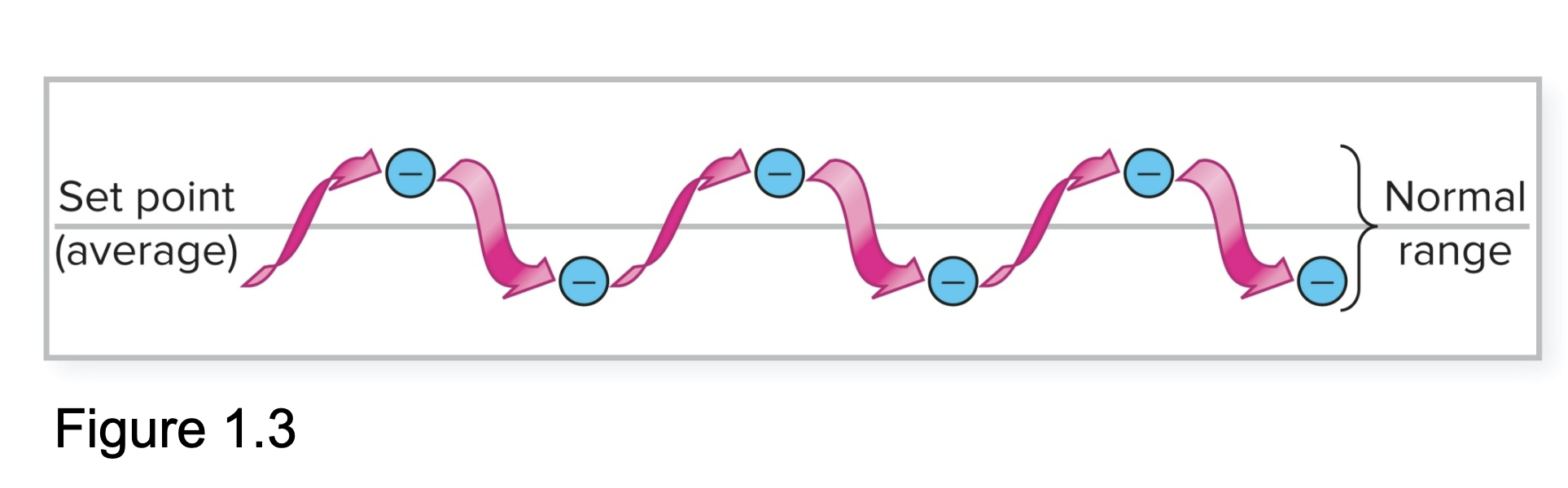
A physiological Variable
is a variable that changes
A set point
is a variable that doesn’t change
An Afferent Pathway
carry to (away from sensor)
An Efferent Pathway
carry away (exiting the integrating center)
Maintaining Body Temp
Shivering : response to decrease in body temp
Sweating: response to increase body temp
Primary Tissues
Muscle, Nervous, Epithelial, Connective
Function of : Muscle Tissue
for contraction
Function of: Nervous Tissue
generating & conduction of electrical events, and related support functions
Function of: Epithelial Tissue
forms membranes coving & lining body surfaces, or glands comprising of these membranes
Connective Tissue
characterize by large amount of extracelluar material
ex) blood, bone, and cartilage
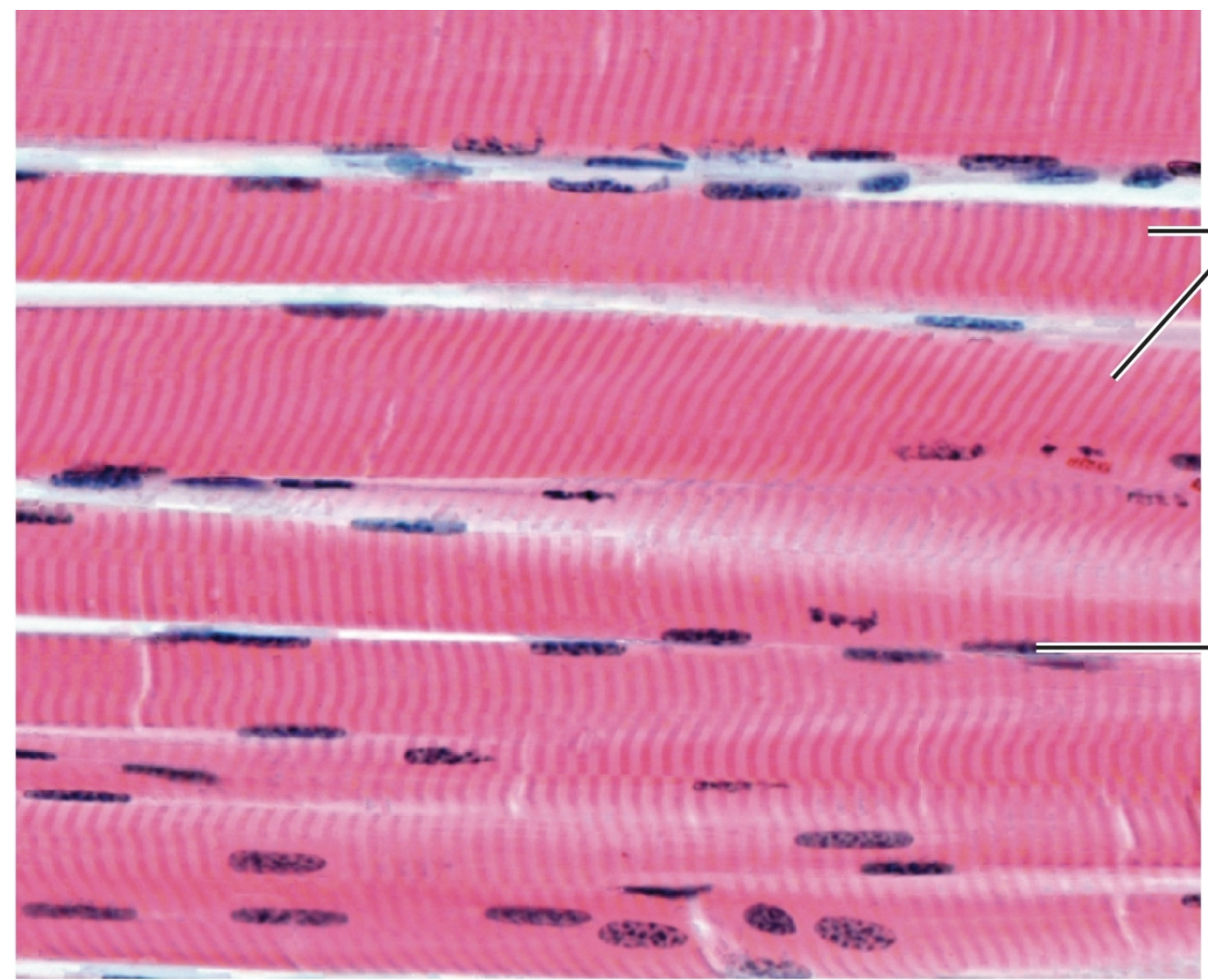
What tissue is this?
Muscle tissue: skeletal muscle fibers
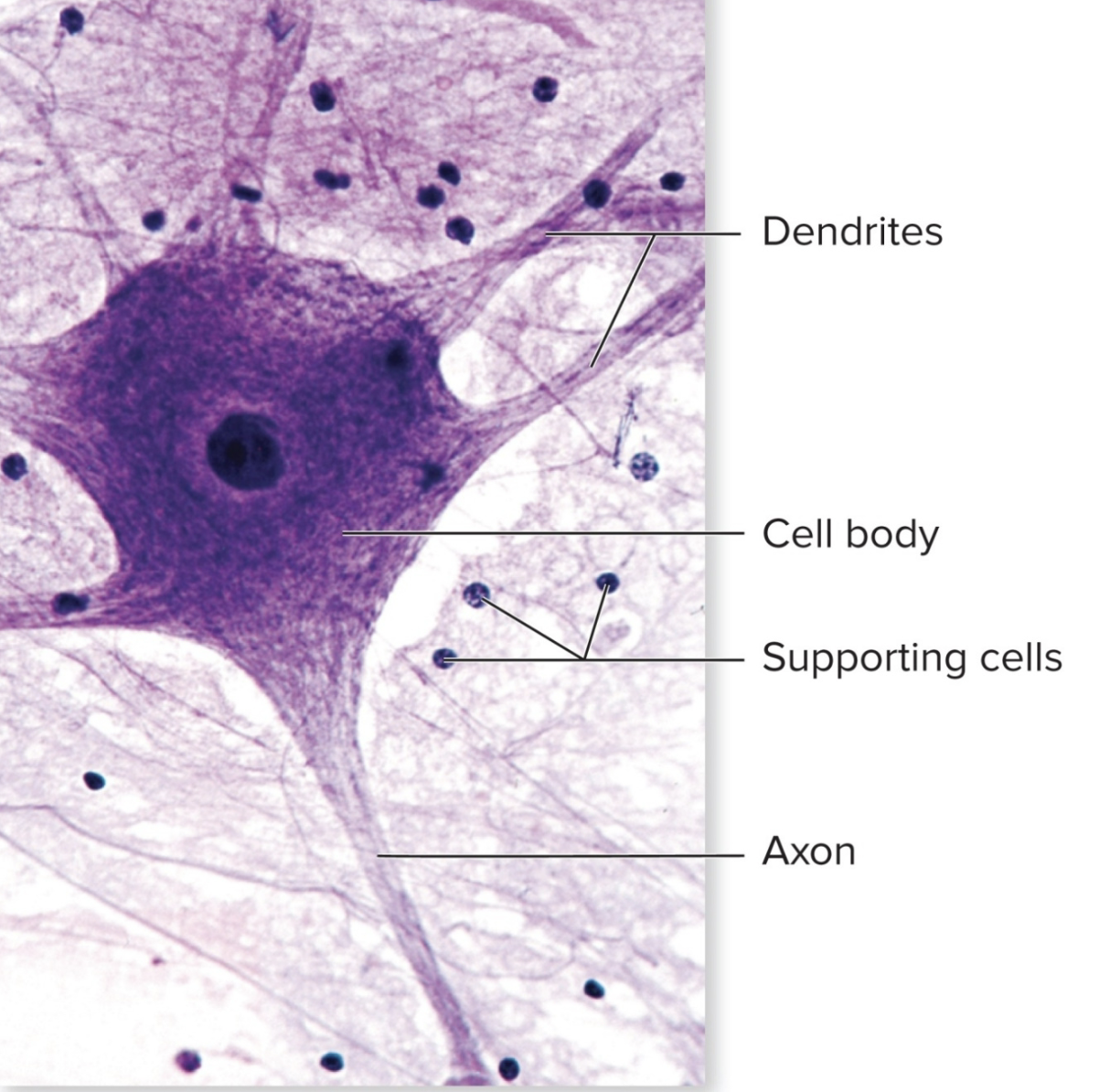
What tissue is this?
Nervous Tissue: Neuron & Supporting Cells
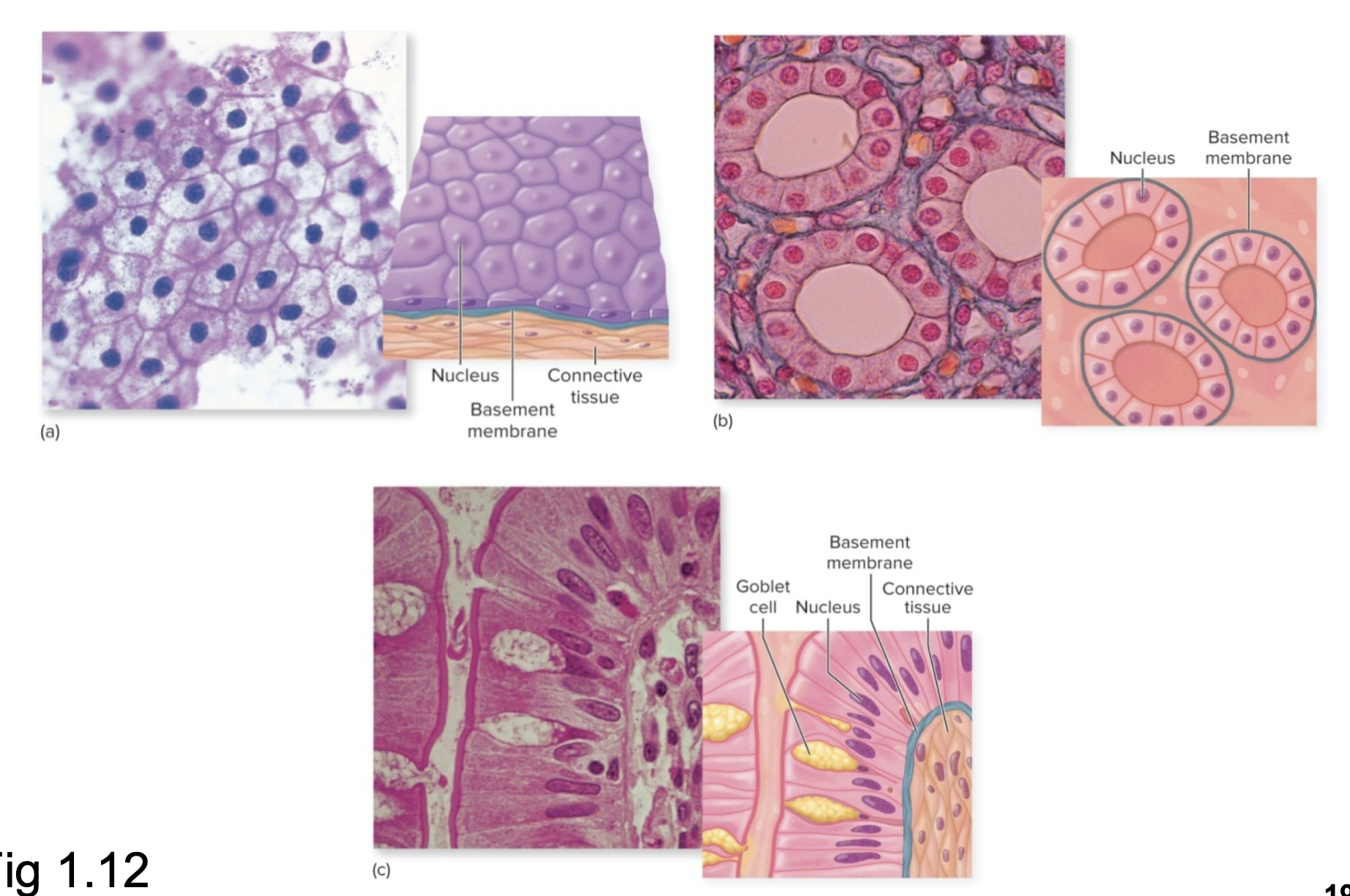
What type of tissue is this?
Epithelial Tissue: Epithelial Membranes
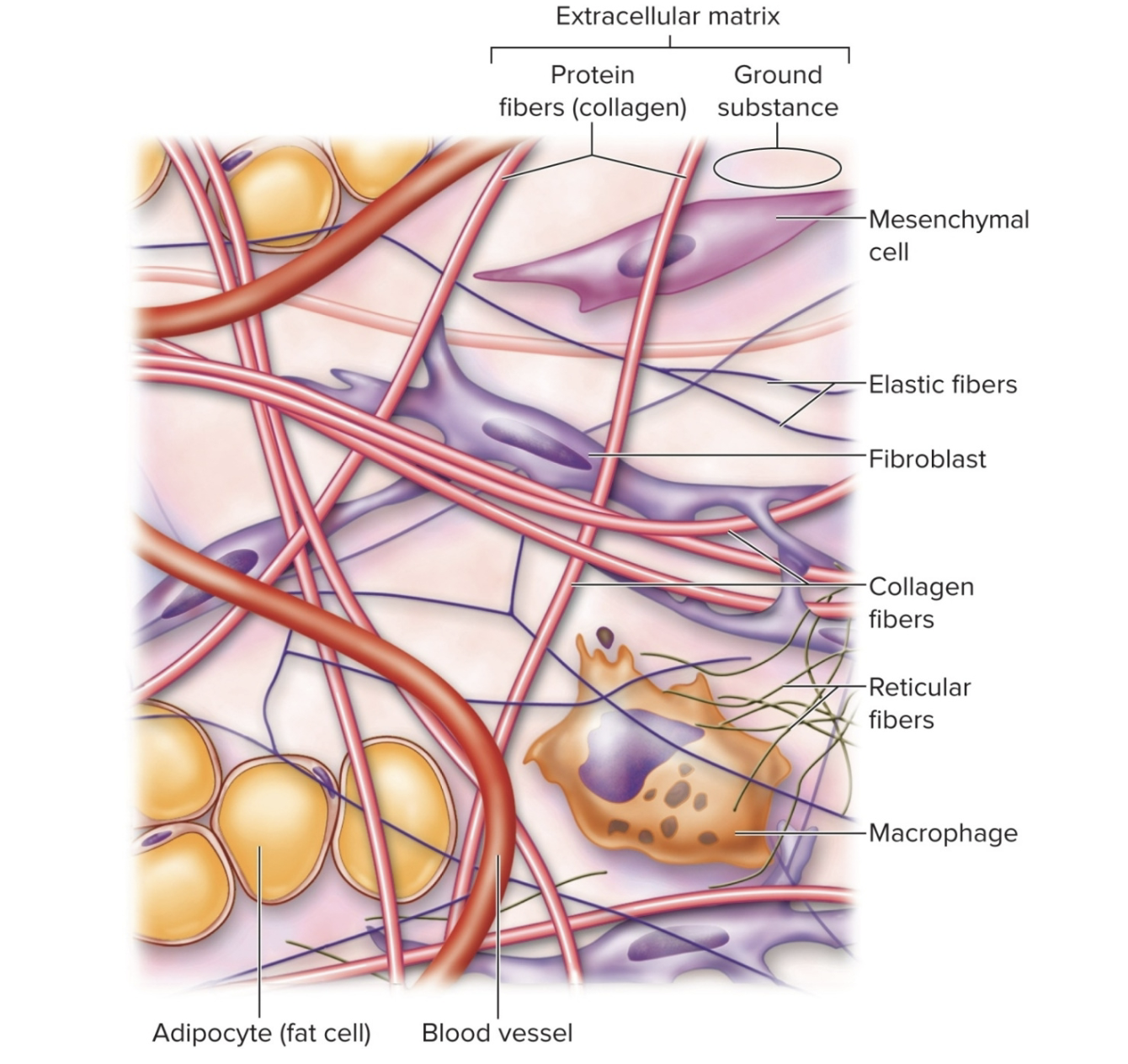
What tissue is this?
Connective Tissue: Loose Conective Tissue
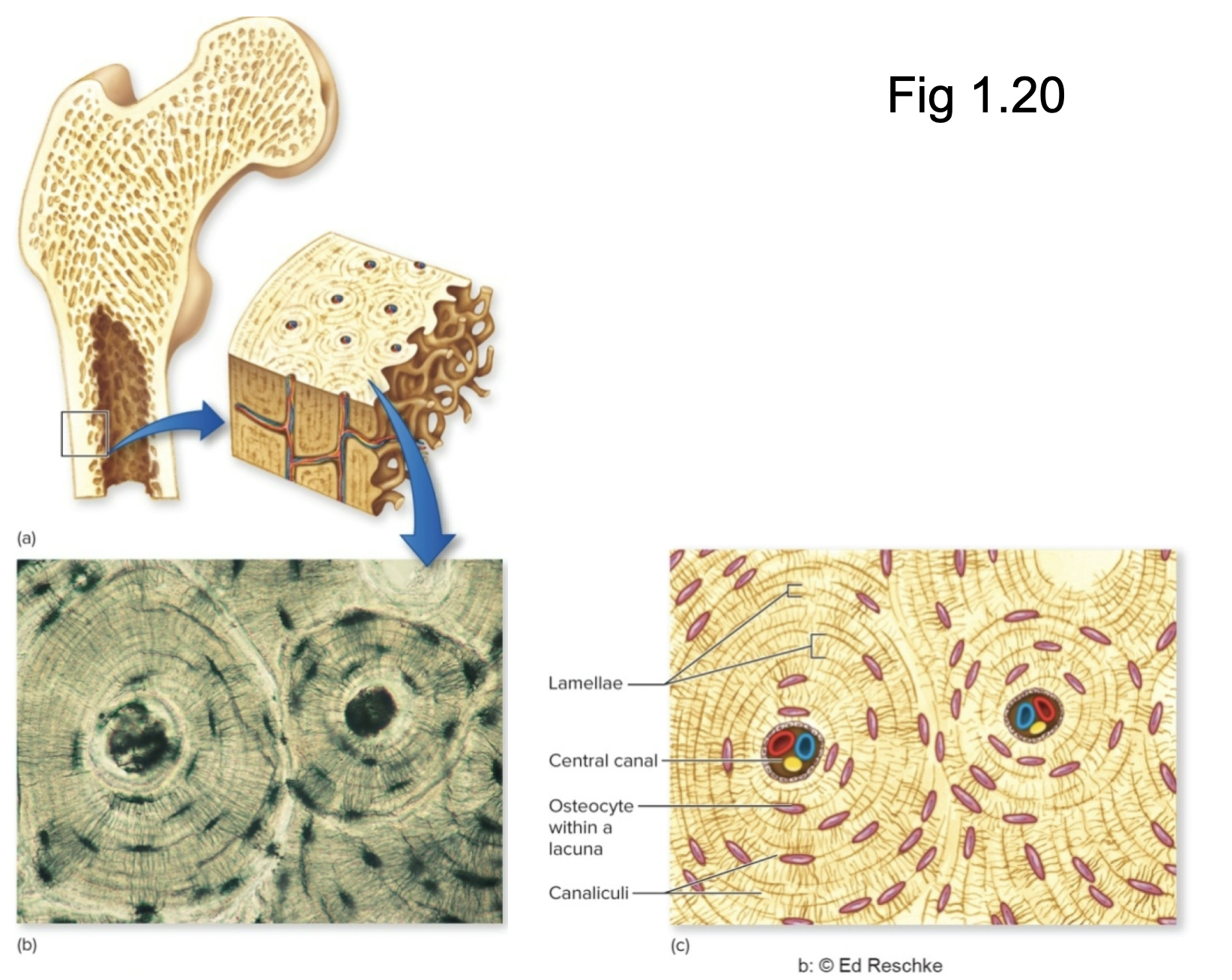
What tissue is this?
Connective Tissue: Bone