AP Human Geography Agriculture
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Animal Husbandry
An agricultural activity associated with the raising of domesticated animals, such as cattle, horses, sheep, and goats.
Cash Cropping
Planting large amounts of profitable crops for mass production and sell.
Corporate Agriculture (Agribusiness)
System of food production involving everything from the development of the seeds to the marketing and sale of food products at the market.
Commercial Crops
A crop grown for direct sale rather than for livestock feed.
Domestication of Plants
Domesticating plants for human use, one of the first steps to a full fledged agricultural economy.
Double Cropping
Planting and harvesting a crop on a field more than once a year.
Fallow
When farmers grow crops in a clear field for only a few years until the soil nutrients are depleted. The farmers then have the soil empty for a few years so the nutrients in the soil can be restored; uncropped land.
GMOs
Foods that are mostly products or organisms that have their genes altered in a laboratory for specific purposes, such as disease resistant, increased productivity, or nutrients value; Genetically Modified Organisms.
Intensive Farming
Subsistence agriculture in which farmers must expend a relative large amount of effort to produce the maximum feasible yield from a pared of land.
Labor-intensive Crops
Includes fruits, garden vegetables, herbs, and anything requiring constant tending or wielding.
Labor-intensive Animals
Animals that require constant tending, includes dairy cow and poultry for eggs.
Monoculture
Dependence on a single agricultural commodity.
Mechanization
In agriculture, the replacement of human labor with technology or machines.
Market Gardens
Small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers, Distinguishable by the large diversity of crops grown on a small area of land, during a single growing season. Labor is done manually.
Plantation Agriculture
Raising a large amount of a 'cash crop' for local sale or export.
Suitcase Farmers
A suitcase farm is a farm in which no one reside permanently, they go against the grain of traditional farming. In the US migrant workers provide a cheap, abundant labor source; they work on the farm during the day and leave at night. There is no residence on the site.
Sustainable Yield
Rate of crop production that can be maintained over time.
Transhumance
Movement of animal herd to cooler highland areas in the summer to warmer lowland areas in the winter.
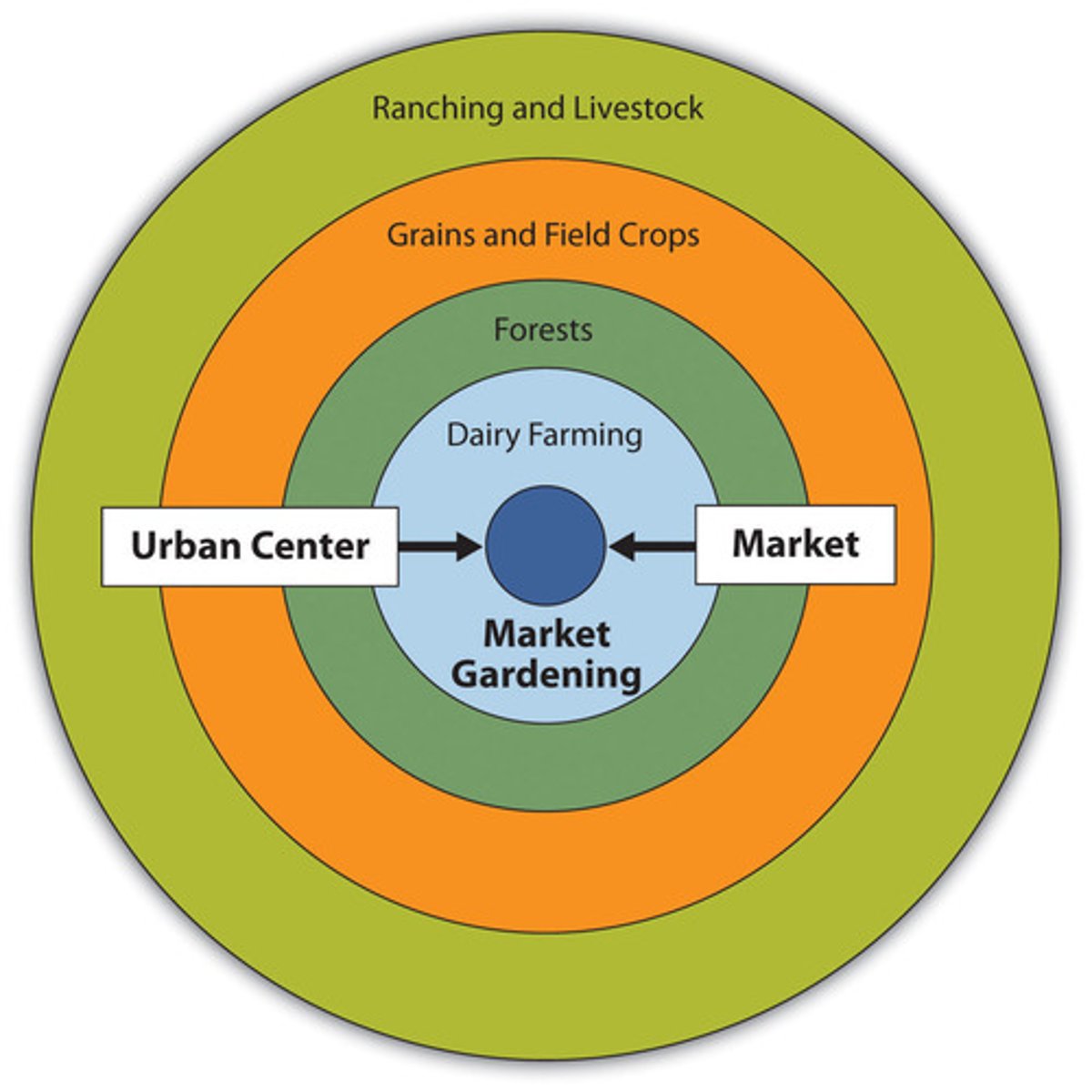
Von Thunen Model
Theory that a commercial farmer wull decide which crops to grow and which livestock to raise depending on the proximity to market.
Green Revolution
An outgrowth of the 3rd agricultural revolution, this effort began in the 1940s and developed new strains of hybrid seeds and fertilizers that dramatically increased the crop output possible from each farm.
SE Asia domesticated what?
Mango, Taro Root, Bananas, palm oil, cattle, sheep, goats
Sub Saharan Africa domesticated what?
Coffee, Cowpeas, Millet
S. Mexico domesticated what?
squash, beans, cotton, Maize(Corn),
SW Asia domesticated what?
Wheat, Barley
1st Agric Revo Change
Nomadic herders to sedentary lifestyle and intentional farming
1st Agric Revo Impact
Birth of civilization
Birth of urban areas
Birth of government
Birth of class structures(social stratified)
Before this egalitarian
Created irrigation
Created farmers,slaves, government officials, merchants
Surplus of food
Led to writing
Began trading which led to system of defense
Towns located on high ground(acropolis) and water
2nd Agric Revo Sustained by...
Mechanical reaper
Combustible engine
Seed drill
Railroad
Refrigeration
Artificial feed
New banking practices
3rd Agric Revo Defintion
new strains with higher yields through genetic manipulation to increase yield through the use of herbicides and fertilizers
How to increase GMOs
1. Purchase artificial fertilizer
Chemicals
2. Irrigation system
3. Purchase herbicides/pesticides
4. Purchase machines to keep up with production
5. Need a receptive environment
6. Need receptive commodity markets
7. Barriers to implementation
Poor, unreceptive environment river water
Shifting Cultivation Location
Subtropics and Tropics
Shifting Cultivation Steps and Characteristics
Steps:
Clear land
Plant land
Fallow(not planting anything so soil can replenish itself)
Come back to land when it is full of nutrients
Characteristics:
Low quality land
Low population density
Nomadism
Dry Areas
Same climate as livestock ranching(commercial farms in MDCs)
Marginalized land
Commercial Farming Positives
Increase yield
Keeps food costs low
Commercial Farming Negatives
Use of chemicals
Human health
Younger age of puberty
Cancer increase
Environment
Rainforest destruction
Desertification
Rise in sustainably sourced farming
Local and organic
Blue zone where business collaborate to show thi
Livestock Ranching
Raising of domesticated animals for food or items like leather
Climate: Dry
Growing industry
As countries develop, meat eating increases
Standard of living increases
Not near market
Bulk-reducing industry
Dairying
Climate: Cold/Warm Mid Latitudes
Perishable
Area surrounding dairying is milk shed
Closer to market
North Latitude
Bulk-gaining
Bottling fluid
Mixed livestock and grain
Raise domesticated animals and growing feed
Commercial Grain Farming
Wheat belt
Bread-basket US
Corn belt
Market Gardening
Items people garden
Near market since items are perishable
Suitcase farms
Rely on migrant labor
Mediterranean
Dry summers
High rainfall needed
France, Spain, Greece, North Africa, Australia, Chile, California
Produce grapes, citrus, etc.
Wine production
Plantation farming
Tropics
In LDCs
Owned by MDCs
Cash crops
Cash Crop Examples
Worldwide Cotton
Rubber
Amazon
Rice
India
Sugar from Caribbean
Coffee
Ethiopian Origin
US #1 consumer
Central America and Africa produce it
Illegal Drugs
Marijuana, Poppy seeds
Core are demanders
Periphery grows them
Takes processing
What two factors influenced Von Thunen model?
Perishability and Transport Costs
Von Thunen ring outside city(1)
Market gardening/dairying/feedlot
Feedlots fatten livestock before slaughter
Skinny before sent near market
Von Thunen ring (2)
Forestry
Von Thunen ring (3)
Food grains and cash crops (Crop Rotation)
Von Thunen ring (4)
Enclosed Field
Von Thunen assumptions
Flat terrain---Similar climate/soil---no barriers to transportation
Von Thunen factors that decrease the model
Refrigeration
Food preservation
Global markets/corporate decision making
New alternatives for fuel
New ways grains are used
Vertical farming
Urban, crowded, squatter areas
Takes up less space
Subsistence crop
Food crops used only by family or local market trading
Organic Farming
o extracts farmers from big corporations
o environmental=reduce synthetic chemicals in soil/water
farming and ranching without the use of herbicides, pesticides, growth hormones, and other synthetic inputs.
o sold in 54% of US grocery store
Truck Farms
Farm where farmers produce fruits for the market
Use mechanization to produce large quantities of fruits and veggies