IB Economics SL (Macro)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Everything idk
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
List the six macroeconomic objectives
Steady economic growth - income earnt, income spent, output produced are al increasing
low unemployment rate
low and stable rate of inflation
sustainable level of goverment debt
equitable distribution of income
favourable trade balance - export revenue > import expenditure
Define and list factors of production
all resources used in the production process. firms buy the factors of production, and use them to produce goods and services. households own the factors of production, and sell them to firms in exchange for income
land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
Define land as a factor of production
all natural resources used in the production process
Define labour as a factor of production
all human resources used in the production process
Define capital as a factor of production
all man-made resource
Define entrepreneur as a factor of production
the owner who organises the land, labour and capital in order to produce new products
What do firms pay households in exchange for labour, land, capital and entrepreneurship respectively?
wages, rent, interest and profit
Draw the (full) circular flow of income model
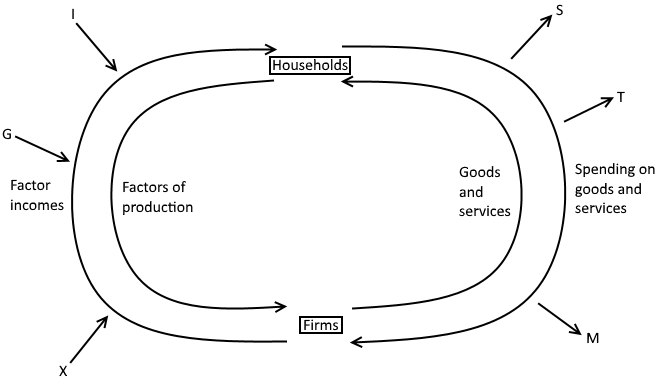
What happens when the circular flow of income is growing (economic growth)
when injections > leakages.
households are earning more income
households spend more money
firms produce more output
firms employ more workers (factors of production
What happens when the circular flow of income is shrinking (recession - two or more consecutive quarters of negative economic growth)
when leakages > injections
households are earning less income
households spend less money
firms produce less output
firms employ fewer workers (factors of production)
Write the equation regarding the circular flow of income model
National Income (earned by factors of production) = National Expenditure (on goods and services) = National Output (value of goods and services produced)
Describe what an injection is with regards to the circular flow of income model, list them
when firms receive income that does not come from domestic household expenditure
investment
exports
government spending
Describe leakages with regards to the circular flow of income model, list them
when households receive income but do not spend it on domestic goods and services
savings
imports
tax
Define GDP
a measure of the total value of all goods and services produced within an economy in a given time period. this is the same as the size of the circular flow of income
Describe the output method as a way of meaasuring GDP
adding the value of all final goods and services produced
sum the value added by all firms in the economy:
value added = value fo final good produced - value of intermediate goods (the resources that are actually factored into the final product)
Describe the income method as a way of measuring GDP
adding up all income earned by the factors of production within a country. this includes all income earned by land, labour, capital and entrepreneurs in the country
GDP = rent (land) + wges (labour) + interest (capital) + profit (entrepreneur)
Descrie the expenditure method as a way of measuring GDP
adding up all spening on final goods and services across all sectors of the economy. this includes all economic agents that can spend money on domestic goods and services
GDP = C + I + G = (X-M) where C is consumption, I is investment, G is government spending , X is exports and M is imports
Define consumption (C)
spending by domestic households on goods and services
Define investment (I)
expenditure by firms on capital stock
Define exports (X)
spendign by foreign households on domestic goods and services
Define imports (M)
spending by domestic households on foreign goods and services
Define GNI, state the equation
the total income earned by a country’s factors of production, regardless of where they are located, within a given time period
GNI = GDP + Net Factor Income
What happens when a country’s GNI > GDP?
it must have a positive net factor income
more is earned abroad by domestic factors of production than is earned here by foreign factors of production
What happens when a country’s GNI < GDP?
it must have a negative net factor income
more is earned here by foreign factors of production than is earned abroad by domestic factors of production
Distinguish between real and nominal GDP
nominal = value of output produced
real = amount of output produced, it is nominal GDP adjusted for inflation. It is a measure of how productive the economy is, rather than its sole value
Define GDP per capita
the GDP per head of population
When must real statisitics be used?
when analysing the performance of an ecoonomy over time
When must per capita statistics be used?
when comparing the national income of two or more different countries
Define aggregate demand, and how to calculate it
the amount of all products (output) that all stakeholders in the economy are willing and able to buy, or the total spending on all goods and services across all sectors of the economy in a given time period
AD = C + I + G + (X-M)
Describe explain, and draw the aggregate demand curve
the curve is a downwards slope, as the average price level increases, people swap domestic output for foreign output, so the output demanded decreases, thus decreasing the net exports
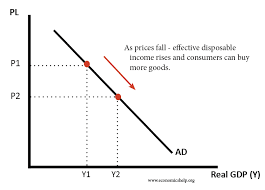
Describe how a movement along the aggregate demand curve arises
When there is a change in the average price level
Describe how a shift in the aggregate demand curve can arise
When there is a change in one of the components of aggregate demand
List and describe things that shift the aggregate demand curve to the right
Consumer confidence - consumers feel less need to save, so can spend more
Wealth - (eg. house prices increase) consumers feel more confident in the value of their assets, thus making them feel richer
Expectation of future price increases - consumers rush to buy products before they become more expensive…this flashcard is not fiished
Define aggregate demand and give the equation
the amount of output that all stakeholders in the economy are willing and able to buy
the total spending on all goods and services across all sectors of the economy in a given time period
AD = C + I + G + (X - M)
Describe how a movement along the AD curve can occur
an increase in the average price level causes people to swap domestic for foreign ouput, meaning the total output demanded within the economy decreases as there is a decrease in net exports
Describe briefly how the AD curve shifts when there is a change in one of the components
a decrease in one of the components shifts AD left
an increase in one of the compon