Visual Pathway
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
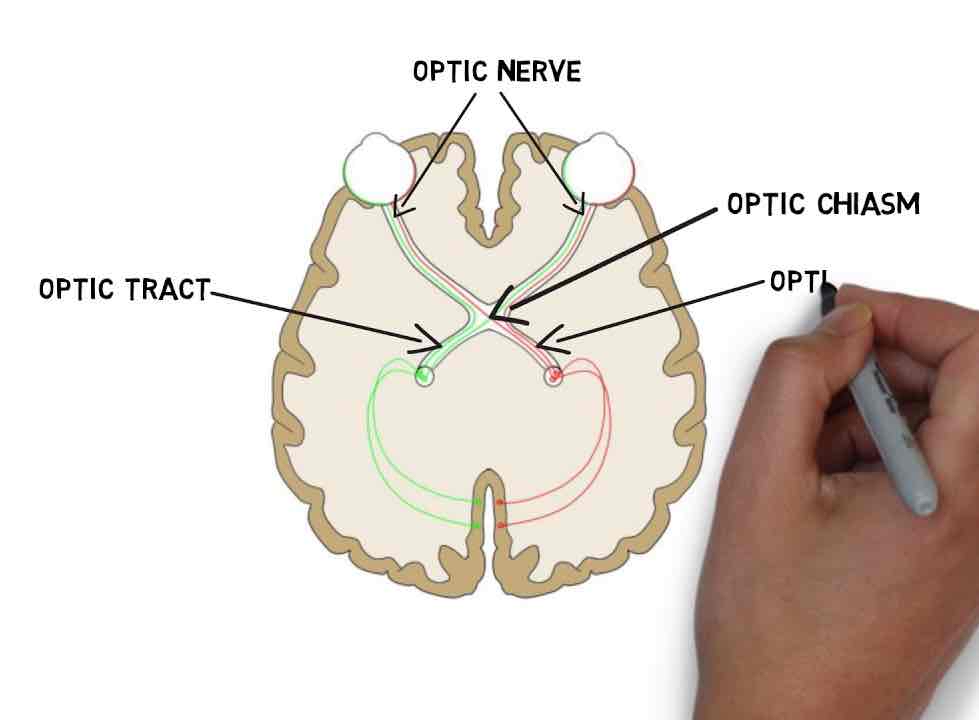
What are optic nerves?
Optic nerves are made up of axons from ganglion cells and help transport visual information to the brain.
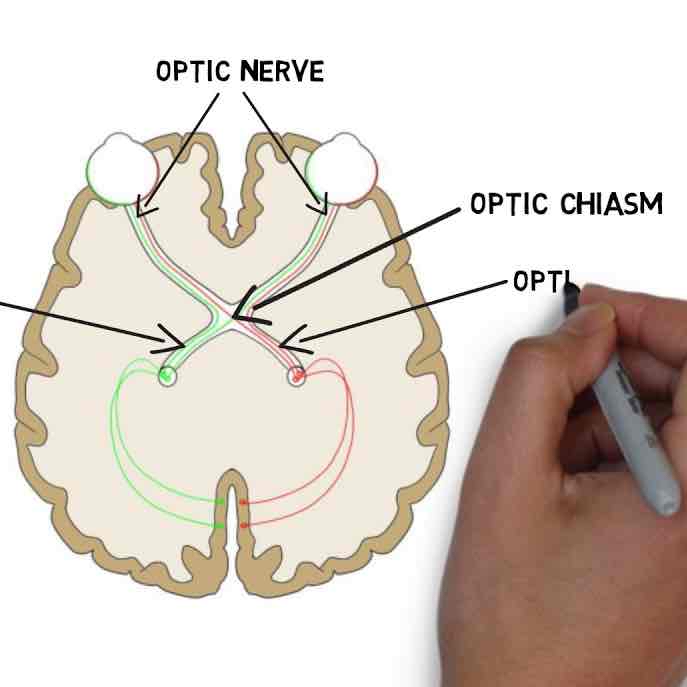
What is an optic chiasma?
A crossover pathway of the visual information.
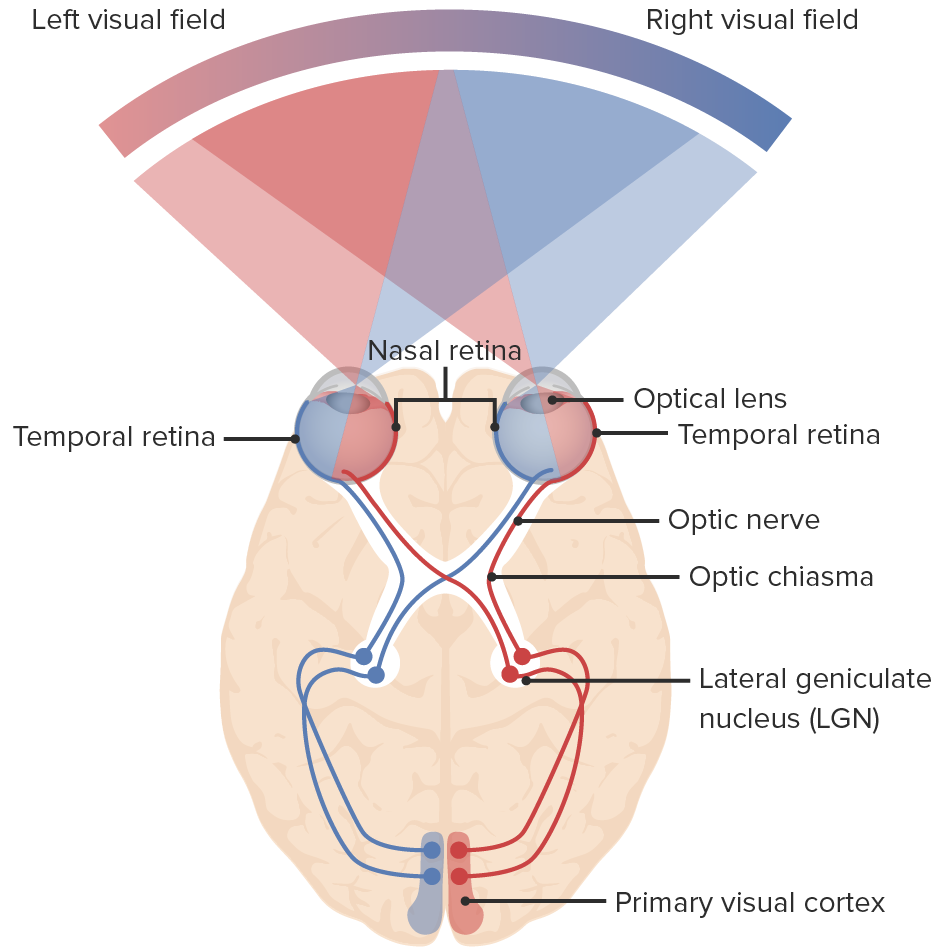
what side of the occipital lobe processes our RIGHT visual field?
LEFT occipital lobe.
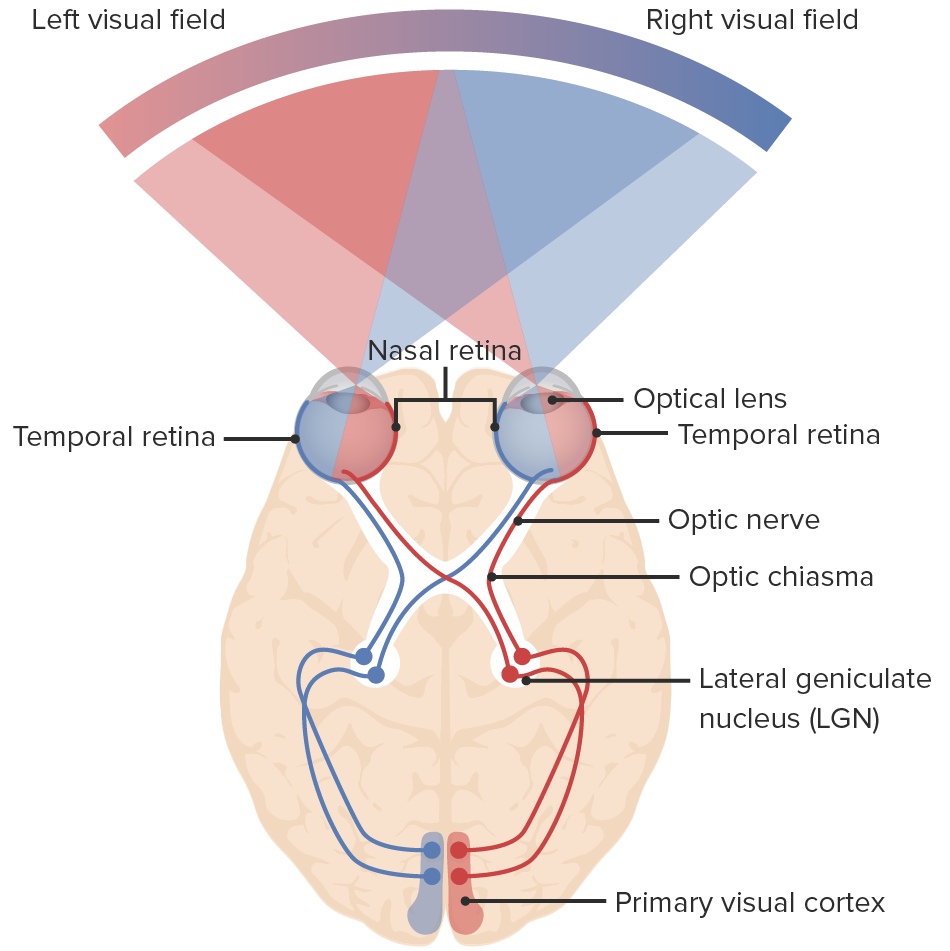
Which side of the occipital lobe processes our LEFT visual field?
The RIGHT occipital lobe.
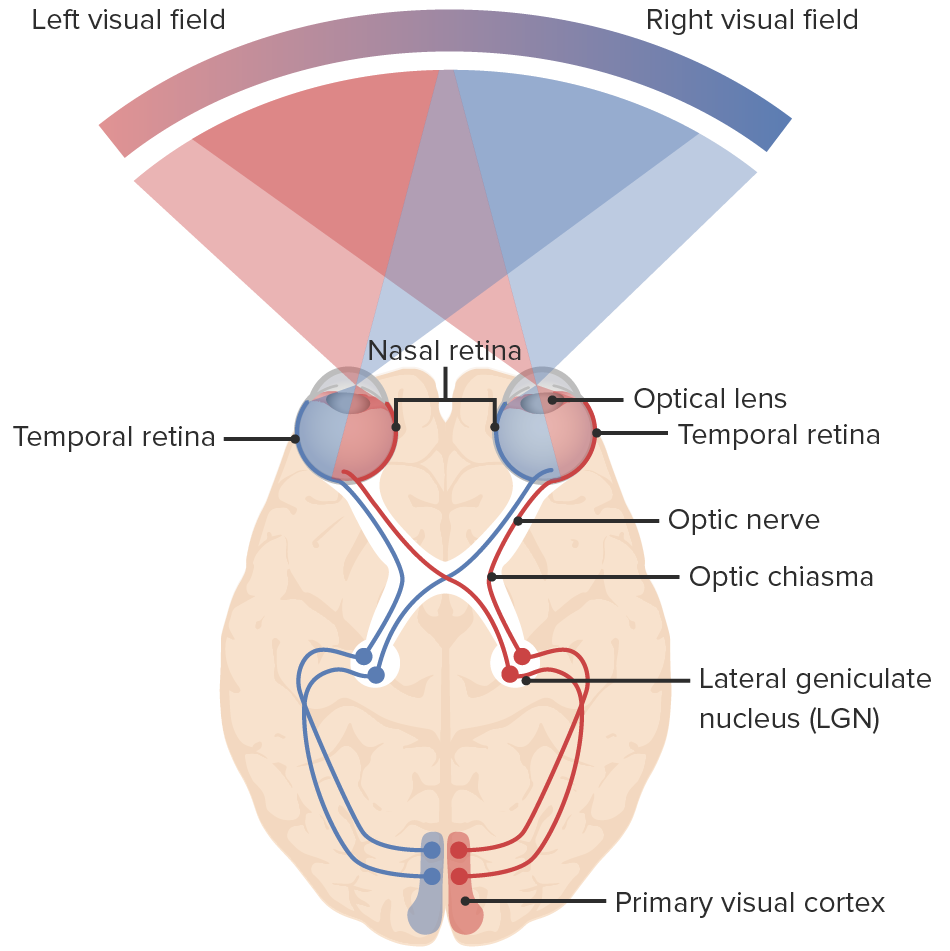
What happens if one of the optic nerves stopped working?
You would still have FULL visual field
your brain won’t be able to process information from one of the eyes.
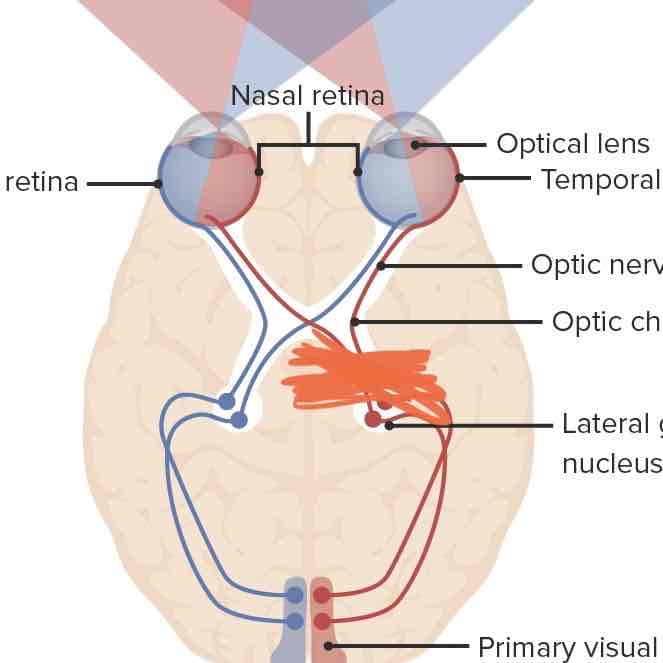
What would happen if one of your optic tracts were to be destroyed?
We would lose EITHER visual fields.
What is the thalamus responsible for?
The thalamus is responsible for being a big operator that guides sensory information to corresponding parts of the brain for processing and coding.
What is the thalamus made up of?
The thalamus is made up of the lateral geniculate body.
What is the lateral geniculate body responsible for?
Responsible for making our visual information go to the primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe.
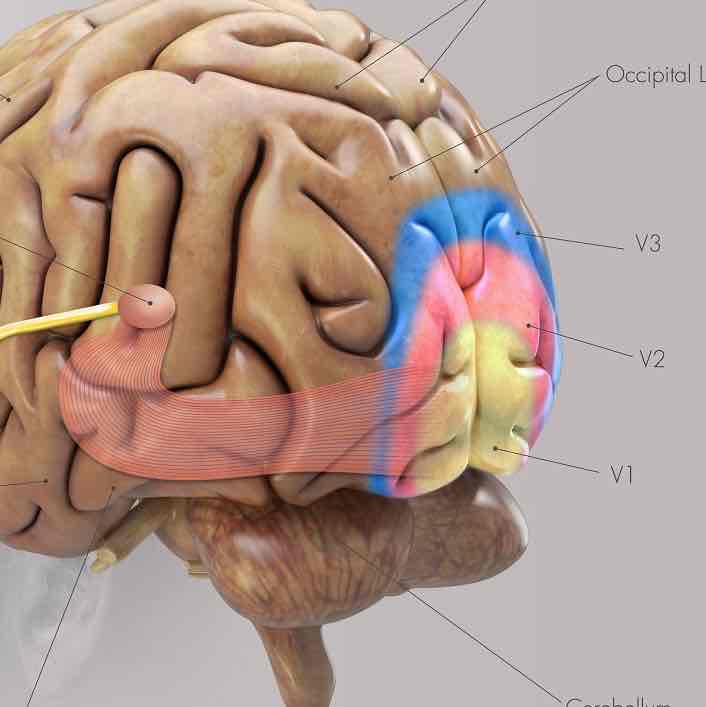
What is the primary visual cortex (V1)?
The very end of your occipital lobe
what is activated when we imagine seeing things?
The primary visual cortex
What happens if our primary visual cortex was destroyed?
We wouldn’t be able to visually imagine.
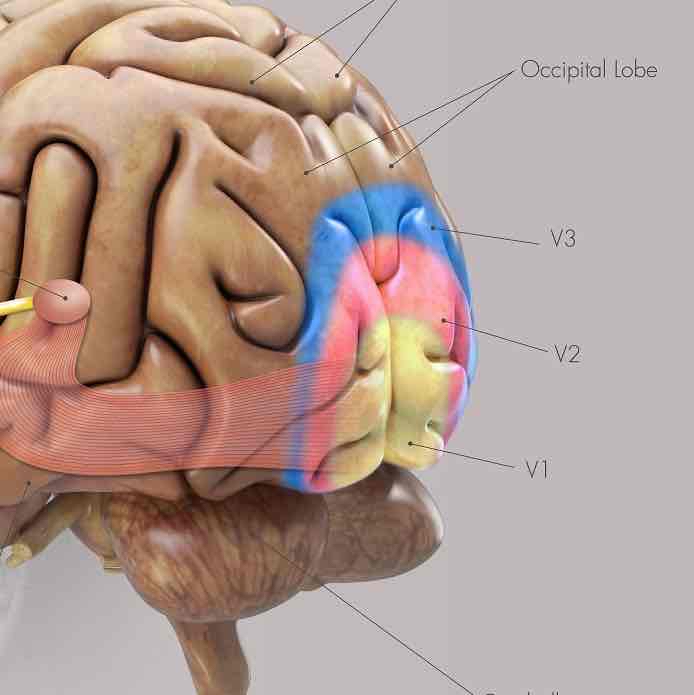
What is the secondary visual cortex (V2) responsible for?
Responsible for helping to process visual information EVEN FURTHER.
Helps add CONTOUR and BORDERS to what we see
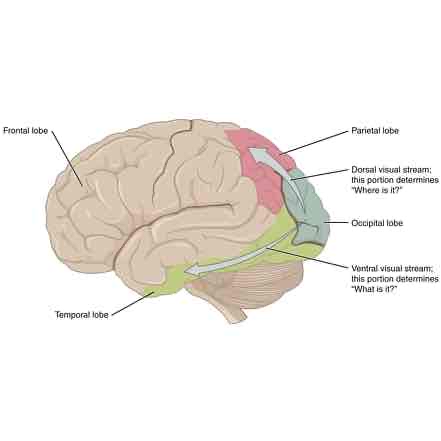
What is the DORSAL stream (V4)?
The dorsal stream is a pathway that visual information takes to go to the PARIETAL CORTEX to determine WHERE an object we see is.
What happens if your PARIETAL lobe was damaged?
If the parietal lobe was damaged, we can’t locate WHERE an object is or code color vision properly.
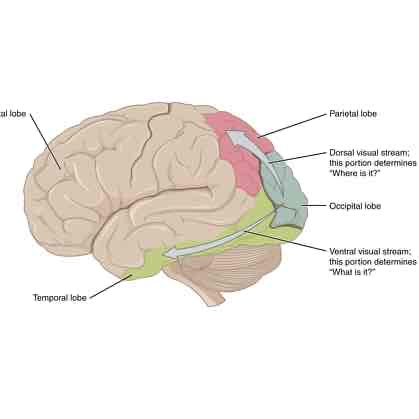
What is the VENTRAL stream (V5) for?
The ventral stream is a pathway visual information take to go to the TEMPORAL lobe to determine WHAT the object we’re seeing is: shape, size, color.
What happens if your temporal lobe was damaged?
You would have VISUAL AGNOSIA where you wouldn’t be able to properly describe WHAT an object is: shape, color, size.
What is the fusiform gyrus responsible for?
Responsible for recognizing faces.
What happens if it is damaged?
You would have PROSOPAGNOSIA where you would be unable to recognize faces.
What did the survey on baby’s face preference tell us?
Babies have a poor recognition to faces.