Science Term 1 Biology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/58
Last updated 4:46 AM on 3/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
1
New cards
Somatic cells
Body cells. These are diploid cells, meaning they have two sets of chromosomes (one from each parent).
2
New cards
Gametes
Sex/reproductive cells located in the gonads (testes and ovaries). Sperm in men and ova in women. These are haploid cells, meaning they have a single set of chromosomes.
3
New cards
Diploid number
2n. The presence of two complete sets of chromosomes (one set from each parent).
4
New cards
Haploid number
N. The presence of one complete set of chromosomes (only in sex cells)
5
New cards
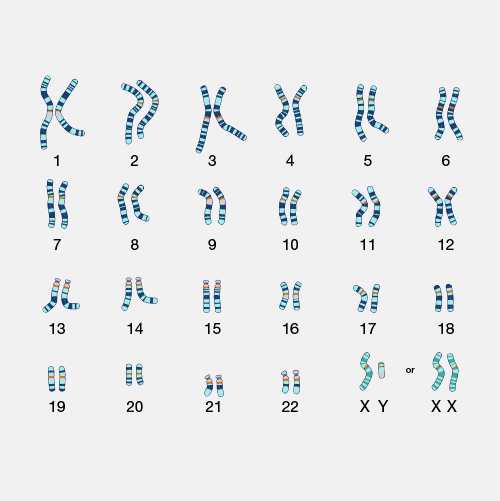
Karyotype
A diagrammatic representation of the chromosomes of an organism.
6
New cards
Autosomes
Chromosomes that control the body characteristics of an organism. In humans, chromosomes 1-22. Autosomes control the inheritance of all an organism's characteristics except the sex-linked ones, which are controlled by the sex chromosomes.
7
New cards
Sex chromosomes
Chromosomes that determine the sex of an organism. In humans, women provide the X chromosome, and men can provide either another X or a Y. If it is XX, it is a female. If it is XY, it is a male.
8
New cards
Homologous chromosomes
A set of one maternal and one paternal chromosome that pair up with each other inside a cell. Chromosome 1 pairs with the other Chromosome 1 etc.
9
New cards
Sexual reproduction
When a gamete with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that develops into an organism composed of cells with two sets of chromosomes. Produced by two parents.
10
New cards
Asexual reproduction
A mode of reproduction in which a new offspring is produced by a single parent
11
New cards
Prokaryotic cell
Single celled organisms that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
12
New cards
Eukaryotic cell
Multi-celled organisms that contain membrane-bound organelles such as a nucleus ( and mitochondria (powerhouse of the cell)
13
New cards
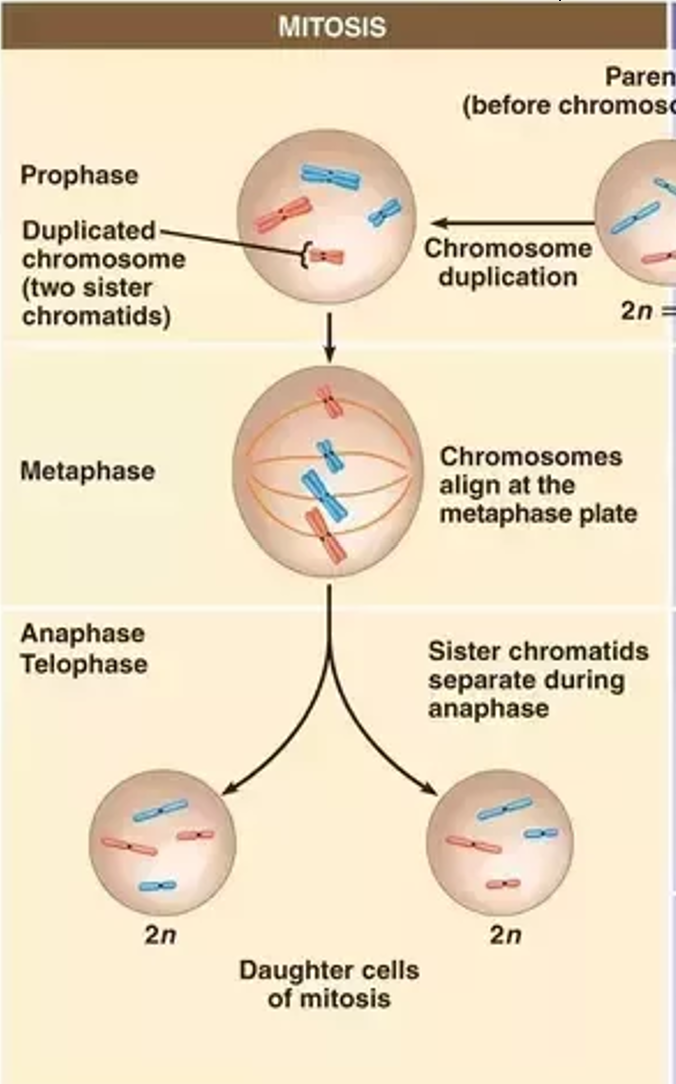
Mitosis
A type of cell division that produces genetically identical daughter cells. Used for asexual reproduction and growth and repair in body cells. The chromosome number of the parent cell is the same as the daughter cell. PMAT x 1 (one division).
\
1. The DNA replicates in interphase. That means there are still the same amount of chromosomes but double the amount of chromatids.
2. In metaphase, the chromosomes align at in the middle
3. In anaphase, the sister chromatids are ‘ripped’ apart or seperated into two cells.
\
1. The DNA replicates in interphase. That means there are still the same amount of chromosomes but double the amount of chromatids.
2. In metaphase, the chromosomes align at in the middle
3. In anaphase, the sister chromatids are ‘ripped’ apart or seperated into two cells.
14
New cards
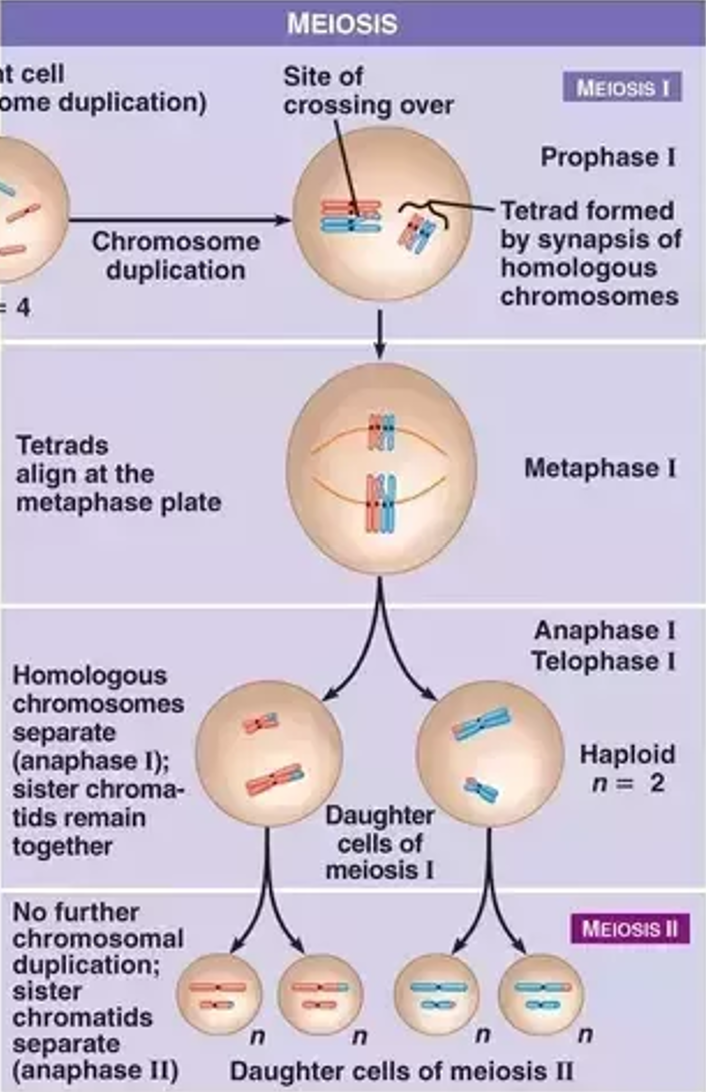
Meiosis
A type of cell division that occurs in gonads (testes and ovaries) that produces gametes (sex cells: sperm and egg). The four daughter cells produced contain half the chromosome number (haploid) of the original parent cell). Used for sexual reproduction and produces non-identical cells. PMAT x2 (two divisions).
\
1. The DNA replicates in interphase.
2. The homologous chromosomes pair up and align at the metaphase middle.
3. The DNA crosses over, causing genetic variation)
4. The homologous chromosomes separate in anaphase 1 (the sister chromatids stay together)
5. This means that it goes from 2N to N. For example, there are 4 chromosomes after DNA replication. When these homologous chromosomes split, each cell (there are 2 cells now) has 2 chromosomes.
6. Then, the sister chromatids separate into 4 cells.
\
1. The DNA replicates in interphase.
2. The homologous chromosomes pair up and align at the metaphase middle.
3. The DNA crosses over, causing genetic variation)
4. The homologous chromosomes separate in anaphase 1 (the sister chromatids stay together)
5. This means that it goes from 2N to N. For example, there are 4 chromosomes after DNA replication. When these homologous chromosomes split, each cell (there are 2 cells now) has 2 chromosomes.
6. Then, the sister chromatids separate into 4 cells.
15
New cards
Chromosome
A thread-like structure of tightly wound DNA located inside the nucleus of cells. Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
16
New cards
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated DNA) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an organism. DNA is a double-stranded molecule that forms a ‘double helix’ shape, like a twisted ladder. DNA is a polymer (poly means ‘many’) as it is made up of numerous subunits called nucleotides.
17
New cards
Gene
Segments of your DNA. A length of chromosome. Genes code for proteins.
18
New cards
Nucleotide
The basic building block of nucleic acids (RNA and DNA).
A nucleotide of DNA has three major components: • a five-carbon deoxyribose sugar • a nitrogenous base – one of adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) or thymine (T), which pair up (AT, GC) • a negatively charged phosphate group.
A nucleotide of DNA has three major components: • a five-carbon deoxyribose sugar • a nitrogenous base – one of adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) or thymine (T), which pair up (AT, GC) • a negatively charged phosphate group.
19
New cards
Chargaff’s Rule
Chargaff's rules state that in the DNA of any species and any organism, the amount of guanine should be equal to the amount of cytosine and the amount of adenine should be equal to the amount of thymine.
20
New cards
Alleles
Different versions of the same gene (which in itself is a segment of DNA).
21
New cards
Proteins
Molecules made up of amino acids. They all have different functions and play a critical part in the body
22
New cards
Amino acids
Molecules that combine to form proteins.
23
New cards
Codons
A codon is a DNA sequence of three nucleotides that codes for a particular amino acid or signalling the termination of protein synthesis (stop signals). There are 64 different codons: 61 specify amino acids and 3 are used as stop signals.
24
New cards
mRNA
mRNA produces proteins. It is a single-stranded RNA that codes for protein production. The coding strand, being double stranded, is unzipped. It then makes mRNA, which is single-stranded, in accordance to how it pairs up with the original DNA base. The mRNA then moves out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasm, then into the ribosomes. The ribosomes then read the mRNA and produce the proteins accordingly.
25
New cards
Mutation
Alterations in the DNA of an organism.
26
New cards
Gene mutation
A small change where the DNA base sequence in a gene is altered.
27
New cards
Chromosome mutation
A large change where all or part of a chromosome is deleted or duplicated. This changes the structure of the chromosome.
28
New cards
Spontaneous mutation
Natural, random changes in the base sequence of DNA that arise due to errors in DNA synthesis when DNA is being replicated before cell division.
29
New cards
Induced mutation
Accidental or deliberate exposure to environmental factors that cause a change in the DNA. Agents that induce mutations are called mutagens. These may be radiation, carcinogens, viruses etc.
30
New cards
Neutral (silent) mutations
Mutations that are hard to detect since they produce little or no change and little or no effect on the survival capacity of an organism.
31
New cards
Same sense mutation
Where a change in the 3rd base of a codon still codes for the same amino acid.
32
New cards
Germline mutations
A change in the DNA of a germ cell (gamete) that may be passed onto offspring.
33
New cards
Somatic mutations
A change in the DNA of a somatic cell that cannot be passed onto offspring
34
New cards
Point (gene) mutations
When there is a change in the sequence of bases of a single gene that may produce a new allele of the gene. These mutations involve 1 nucleotide. The new DNA sequence may or may not result in a new sequence of amino acids. There are 3 types: substitution of a base (results in a silent, missense or nonsense mutation), insertion of a base (results in a reading frameshift), or deletion of a base (results in a reading frameshift.
35
New cards
Missense substitution
When a single base is substituted for another, usually resulting in coding for a new amino acid. It may end up as a same sense mutation, meaning it still codes for the same amino acid.
36
New cards
Nonsense substitution
When a single base is substituted for another, but results in a triplet that does not code for an amino acids (eg. a STOP or START codon).
37
New cards
Reading frameshift
When a single base is inserted or deleted, meaning the triplet sequence will be shifted and therefore completely different.
38
New cards
Dominant
When an allele completely masks the effect of the recessive gene (there are 2 of the same gene in a pair of homologous chromosomes, one from the maternal parent and one from the fraternal parent). Represented by a capital (eg. Gg, GG). In a pair of homologous chromosomes that have one recessive and one dominant allele, the dominant allele will mask the effects of the recessive allele.
39
New cards
Recessive
When an allele can be masked by the dominant gene. The dominance of one allele over the other decides the characteristics of an organism
40
New cards
Genotype
The type of alleles an organism has for a particular trait (the person’s unique sequence of DNA).
41
New cards
Phenotype
The physical appearance of an organism, the observed result of its alleles for a gene.
42
New cards
Homozygous
2 alleles that are the same (eg. GG, or gg)
43
New cards
Heterozygous
2 alleles that are different (eg. Gg)
44
New cards
Homozygous dominant
Two dominant alleles (eg. GG).
45
New cards
Homozygous recessive
Two recessive alleles (eg. gg)
46
New cards
Heterozygous
2 different alleles (eg. Gg). In this case, the dominant masks the effects of the recessive allele.
47
New cards
Sex-linked inheritance
When a gene is linked to one sex chromosome only (like, if it’s linked to the X chromosome). This means that it will be more common in males because for it to be present in females they would need the gene on both chromosomes, whereas the male would only need one.
48
New cards
Evolution
The cumulative changes in the characteristics of living organisms from generation to generation, resulting in the development of new types of organisms over long periods of time.
49
New cards
Mechanisms of evolution
Sexual reproduction (crossing over), mutation, gene flow (certain alleles migrating to certain places), gene drift (a chance event completely changing the makeup of phenotypes in a place, for example a natural disaster), and natural selection (survival of the fittest: variation comes to occur due to crossing over, some of these variations mean that some are better suited to survive in that environment than others, then these organisms are more likely to reproduce, and ‘take over’).
50
New cards
Chiasma
The point of contact between chromosomes during meiosis where two chromatids interchange corresponding segments.
51
New cards
Speciation
When a group within a species separates from other members of its species and develops its own unique characteristics.
52
New cards
Independent assortment
The law that the allele a cell receives is completely random (it’s completely random which gene goes into which cell)
53
New cards
Recombination
Another word for ‘crossing over’. When the homologous chromosomes meet up and exchange genetic information
54
New cards
Selection pressures
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population.
55
New cards
Adaptations
Heritable traits that allow an organism to survive in its habitat better.
56
New cards
Structural adaptations
Adaptations that affect the physicality of an organism, the body structure, anatomy (more outside than inside processes). For example, colours, size, shape, body parts (like dolphin fins)
57
New cards
Functional adaptations
Adaptations that affect how the organism works inside (how it operates). For example, how it digests, how it reproduces.
58
New cards
Behavioural adaptations
Adaptations that affect how the organism behaves. For example, nocturnal behaviour, migration in cold weather. Can be instinctive or learnt.
59
New cards
4 steps of natural selection
1. Genetic variation exists in the population due to sexual reproduction (crossing over and independent assortment) and mutation.
2. These genetic variations positions the organism at a high chance/ability to survive to reproduce.
3. They reproduce and pass on traits to some offspring.
4. Eventually this trait becomes more common in the population.