Bio 180 - (Prokaryotes, Protists, and Fungi)
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
How are prokaryotes good for you?
Hygiene Hypothesis: proposes that the stimulation of the immune system by microbes protects from the development of inflammatory diseases.
Food
Mutualistic/ Commensals relationships ex.) bacteria living on the roots or leaves of a plant get nutrients from the plant and, in return, produce substances that protect the plant from pathogens.
Nutrient cycling: Recycling CO2
Electricity: harness energy from microbes
Bioremediation: aids in cleaning up environment.
What are endotoxins?
a toxin that is present inside a bacterial cell and is released when the cell disintegrates. (BREAKS APART, then RELEASES TOXIN)
ex.) Salmonella typhi
What are exotoxins?
Secreted by bacteria. (Just RELEASES TOXIN and doesn’t BREAK APART)
ex.) Vibrio cholera, H. Pylori, Streptococcus B
Who is Robert Koch?
Conducted studies on illnesses caused by microorganisms. Found out that microorganisms may be a leading cause of an illnesses within a person. Confirmed the Germ Theory.
What are the 3 domains of prokaryotes?
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
General features of prokaryotes?
basic and small
no nucleus
no membrane bound organelles
Microbiome
Human microbiome (found on/ within humans). If you possess an unhealth microbe on your body, you will become more susceptible to things within the environment. Ex.) asthma
Who is Alexander Fleming?
Creator of penicillin and revolutionized medicine with his discovery of using “bacteria” within medicine.
Common shapes found in bacteria
Coccus: circle
bacillus: Rod
spirillum: Spiral
vibrio: curved rod (check mark)
External autonomy on prokaryotes
Capsule: stick, defend, Biofilm
Pili: Conjunction
Fimbriae: Stick, numerous
Flagella: helps in movement, motor, injects toxins
Cell Wall Plasma membrane
Gram Staining: (+): Purple and think and (-): Pink and thin
Internal autonomy in prokaryotes
Nucleoid: main genetic material found in this region
Plasmids: additional genetic material
Cytoplasm ribosomes: build cytoplasm proteins
Metabolism in prokaryotes
Photoautotroph: cells that capture light energy, and use carbon dioxide as their carbon source.
Chemoautotroph: sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, nitrogen-fixing bacteria and iron-oxidizing bacteria, found in oceans.
Photoheterotroph: organisms that capture light energy to convert to chemical energy in the cells
Chemoheterotroph: down organic wastes and the remains of dead organisms. They play vital roles as decomposers and help recycle carbon and nitrogen.
Aerobic v. anaerobic: (Aero)—> with O2, (anae): without O2
Binary Fission
copying the chromosome and separating one cell into two; making a copy of oneself.
Mutation
Change in genetic code.
Transformation
the prokaryote takes in DNA found in its environment that is shed by other prokaryotes; bacteria get genetic material from environment.
Transduction (virus)
the process by which a virus transfers genetic material from one bacterium to another.
Conjugation (sex pili)
bacteria share the same genetic material as other bacteria.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
the movement of genetic information across normal mating barriers, between more or less distantly related organisms; getting genes from other areas (not just parent cells)
Extremophiles
an organism/bacterium that is able to live in extreme environments.
Halophile/Halobacterium
an organism, especially a microorganism, that grows in or can tolerate saline conditions. Lives in high salt concentrations.
How are prokaryotes different from Eukaryotes?
No Nucleus
No membrane bound organelles.
Different cytoskeleton
Circular DNA
Miasma Theory
The old and inaccurate belief that the air held sickness ; you could get sick by inhaling “bad air”
Germ Theory
Microbes can in fact cause sickness and disease - and can spread from person to person. Specific microbe for each illness.
What is an endospore?
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria. It maintains genetic information and half metabolism until it’s in a proper environment, then it releases spores.
Biofilm
sticky most outer layer built within proteins. Used for defense and helps in moisture.
Fimbriae
long filamentous hair-like protein structures located at the surface of bacterial cells. Help attach to other bacteria.
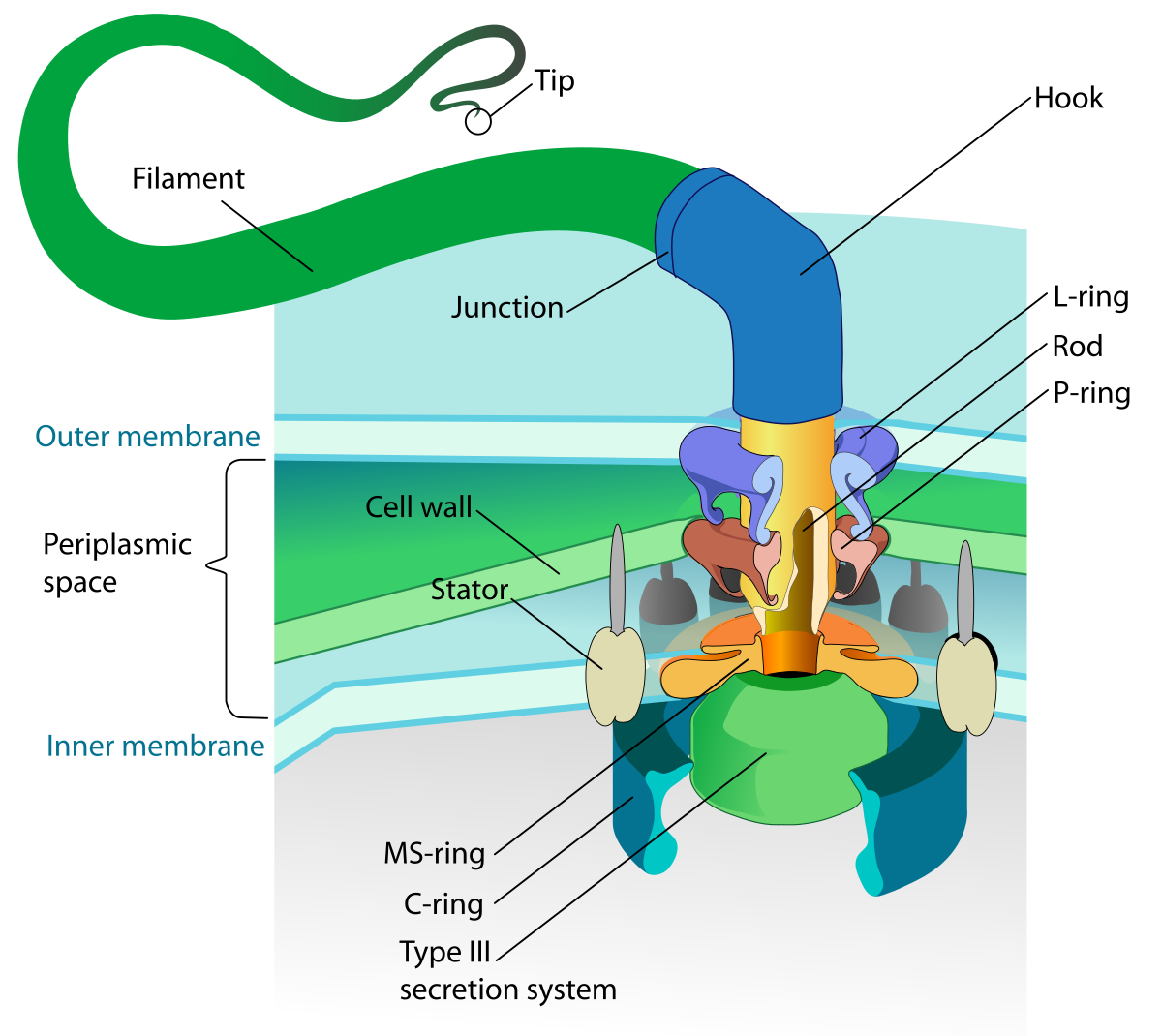
Flagella
a slender threadlike structure, especially a microscopic appendage that enables many bacteria to swim and move. Microtubes are used within the flagella. The flagella has 3 parts.
3 parts of the flagella
Motor
Hook
Tail
who is Hans Christian Gram?
discovers staining bacteria. Depending on how thick or thin the layer is, the cell will be dyed purple (+, thick) or pink (-, thin).
Endosymbiotic Theory
Lynn marriese founded the theory. The theory suggests that ancient bacteria evolved into the bacteria of today.
Reasons backing the Endosymbiotic Theory
Ancient DNA in mitochondria and chloroplasts are similar.
The membrane is similar to the ancient protist.
What is a protist?
The first eukaryotes, they are very diverse.
Reproduction in Protists
Asexual reproduction and binary fission
Relationships w/other organisms
(mutualistic) coral need dinoflagellate to survive (Primary Producers) in photosynthesis carbon sinks and protist absorb carbon.
(Algae blooms) kill fish.
(Disease) Protists may cause disease.
Excavata
modified mitochondria, feeding groove, cytoskeleton
Diplomonads: Giardia (causes stomach pain)
Parabasalids: Trichorrias (causes vaginalis)
Euglenozoa: Trypanosoma (african sleeping disease)
SAR- Stramenopiles
straw like structures
Diatoms: sillica
Golden Algae
Brown Algae: Blade, stipe, holdfast
SAR - Alveolates
tiny sac under membrane
Ciliophora: Paramecium
Dinoflagellates: Zoomanthellae
Apicomplexans: Malaria
SAR - Rhizarians
hard outershells photosynthetic and moves with amoeboid projection.
Radiolarians
Forams/Formaniferans
Cercozoans
Archaeplastida
Red algae
green algae
How old are fungi?
1.3 trillion
Hyphae
Underground roots of network. 2 types of hyphae :septate hyphae and coenocytic hyphae.
septate hyphae
have walls between cells that allow for the passing of nutrients.
coenocytic hyphae
no walls or membrane between cells
Mycelium
mass network of hyphae
Cells walls in fungi
made of chitin
Mycorhizzae
symbiotic relationship with the roots of plants. The fungi share water with the plants and the fungi in return get the products from photosynthesis.