organic compounds
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Breaking down complex molecules by the addition of water; making monomers
hydrolysis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule; making of polymers
dehydration synthesis
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing
enzyme
Energy needed to get a reaction started
activation energy
When an enzyme binds to its substrate, it forms:
enzyme-substrate complex
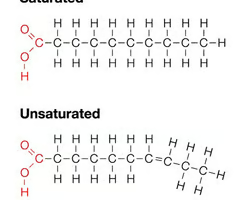
fats that are solid at room temperature; has only single bonds
saturated fats
liquid at room temperature; has at least one double bond
unsaturated fats
loss of normal shape of a protein due to heat or low pH
denaturation
macromolecule made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms; includes fats, oils, and waxes
lipid
lipid structure
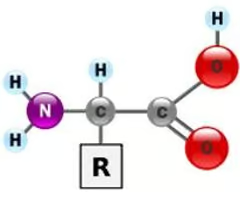
protein structure
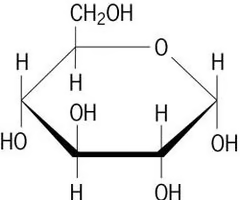
sugar compound made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms; major source of energy for the human body
carbohydrate
carbohydrate structure
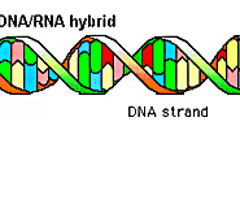
macromolecule that contains genetic information
nucleic acid
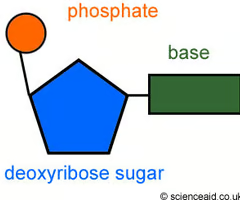
nucleic acid structure
nucleotide
the monomer of nucleic acid
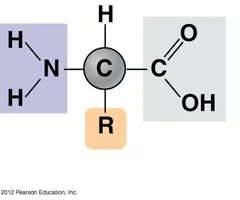
amino acid
monomer of protein
fatty acid
monomer of lipid
monosaccharide (simple sugar)
monomer of a carbnohydrate
simple sugars
monosaccharides
sugar, carbohydrate
words that end in -ose
examples of carbohydrates
Starches, sugars, grains and chitin (bread, pasta, potatoes and rice)
examples of protein
meat, nuts, eggs
example of lipids
butter, oil waxes
long term energy storage and insulation
functions of lipids
Hormones, transport molecules, enzymes, antibodies (immune system)
functions of proteins
quick energy + structure
functions of carbohydrates
store genetic information
function of nucleic acids