NEUR305: Social Cognition
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the regions involved in pre-frontal cortex?
Pre-frontal cortex
lateral regions (dlPFC, vlPFC, etc.)
medial regions (orbitofrontal cortex and vmPFC)
What regions are involved in self-referential processing?
dlPFC, vmPFC, posterior cingulate cortex, medial/lateral parietal cortex
What is the orbitofrontal cortex associated with?
visual and olfactory processing
assessing values
What is the insula involved in?
pain pathways
Which develops first? The prefrontal cortex or the limbic system?
The limbic system (explains risky behavior in teenage years)
What can affect the development of the PFC?
Adverse social environments (ex. chronic stress)
What are perceptions of isolation correlated with?
Higher morbidity, morality rates, increased vascular resistance, higher blood pressure, fragmented sleep, sedentary lifestyles, decreased immunity, decreased impulse control.
What was the case of Phineas Gage?
A metal spike shot into his head but did NOT kill him.
Suffered personality changes (PFC damaged)!
Disorders affecting social cognition?
ASPD
Schizophrenia and ASD
What is ASPD (anti-social personality disorder)?
Aware of social norms, but may disregard them
May lack empathy
Low impulse control, increased aggression
May not care for the welfare of others
What is schizophrenia and ASD?
Both heterogenous disorders that lie on a spectrum
Deficit in social perception
Difficulties understanding mental states
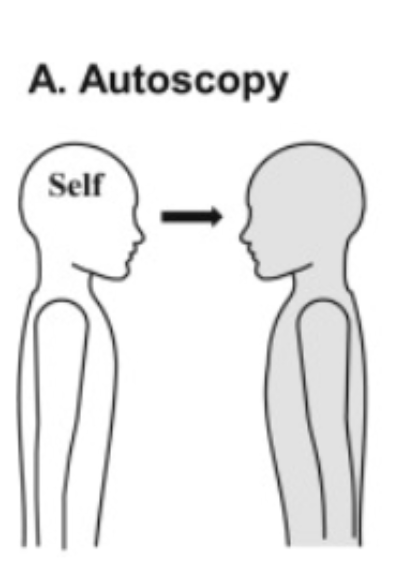
What is autoscopic phenomena?
The person seems to be awake yet sees their body and the world from a location outside the body!
What is autoscopy?
Not residing in your body (view that you’re looking as yourself)
Right parieto-occipital cortex
Right temporo-occipital cortex
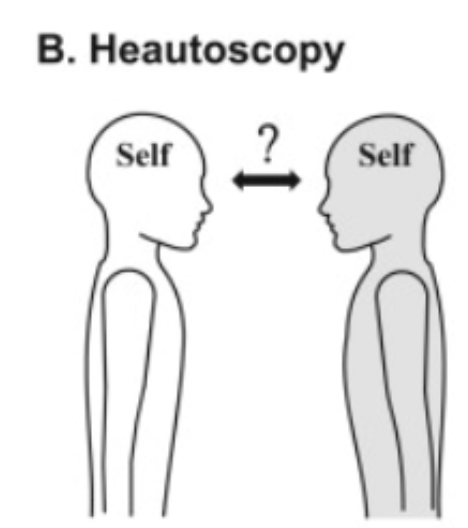
What is heautoscopy?
Inhabiting another body (not sure of which is self)
Left temporoparietal cortex
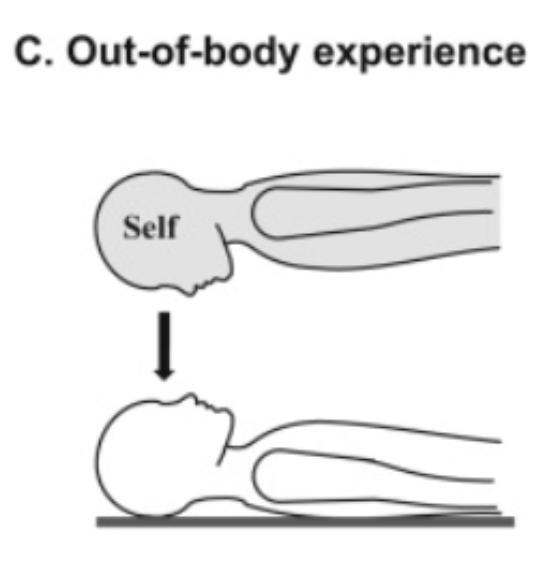
What is out-of-body experience?
See your own body a view of the world from that location (hoovering above self)
Right temporoparietal cortex
What area of the brain is most involved in body ownership.
Temporoparietal cortex
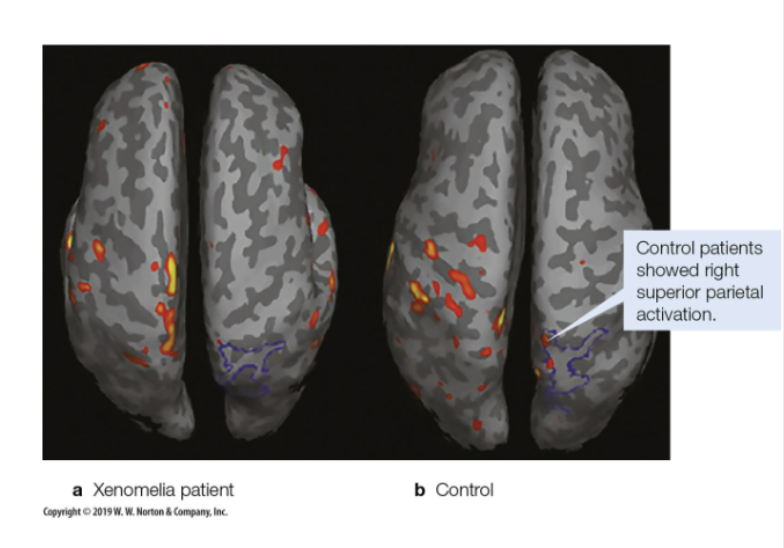
Xenomelia?
Lifelong desire to amputate a limb
Usually a left limb, so right hemisphere is affected
Problem in superior parietal lobule (somatosensory, visual, and vestibular information converge)
delays in information or limb info not being integrated properly
Self-reference effect?
More likely to recall information if you can relate to yourself!
mPFC more active!
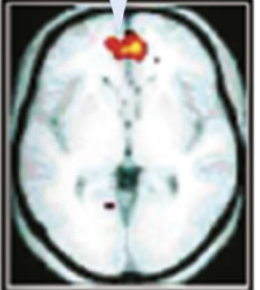
Self-descriptive personality traits
Self-judgement
Autobiographical
Definition
What is the default mode network?
Areas active when NOT actively thinking about a tasks (resting state): mPFC, left TP, right TP
Self-referential processing (think about past)
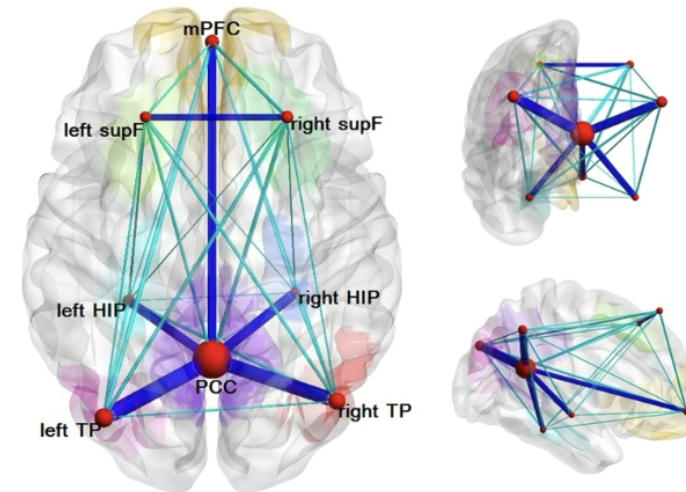
What is the sentinel hypothesis?
The default mode network is there to ensure we always have some idea of what is going on around us
What is the social geometry dyads and triads?
dyads are groups of two!
triads are groups of three!
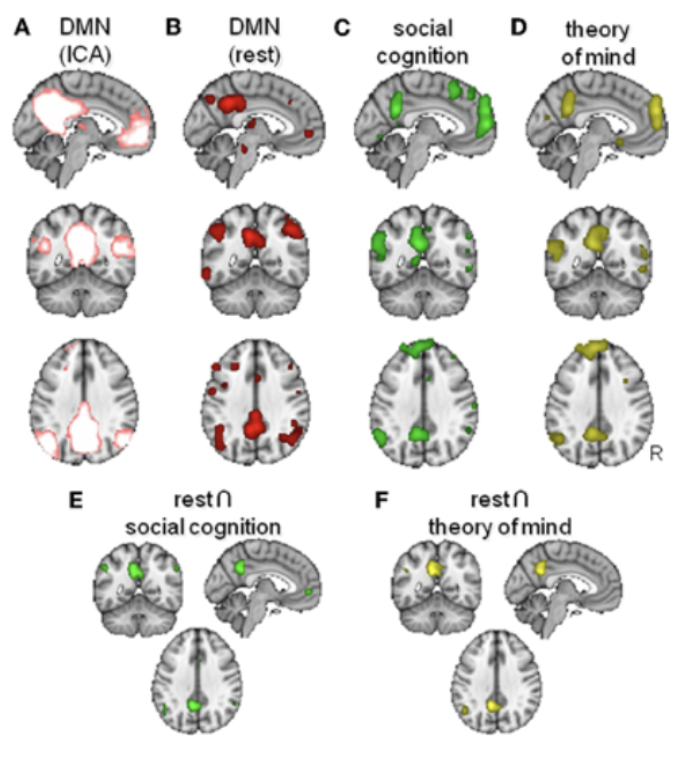
Certain areas of the DMN are activated by specific social tasks!
Strong overlap between network of areas activated in social cognition and the DMN
What does the orbitofrontal cortex help us do?
Take things into context!
What is the vmPFC important for?
Social decision-making!
Lesions to this area encounter difficulties with reversal learning.
We rely specific behaviors when deciding whether an adjective describes…
someone else