Medical Interventions: Unit 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is the difference between cycle sequencing and PCR?
PCR makes multiple identical copies and CS makes strands of different lengths
CS is diagnostic; PCR just amplifies DNA
What does an ELISA do?
uses antibodies to detect proteins in a patient sample
What is the purpose of a constant region on an antibody?
To distinguish between self and foreign invaders.
What is the purpose of a variable region on an antibody?
To bind with a specific antigen.
Why must antibodies from 2 different organisms be used?
So that they recognize each other as non-self and bind to each other.
B-lactams: mechanism of action
Target transpeptidase which affects cell wall synthesis →makes bacterial defenses weaker
Tetracyclines: mechanism of action
Inhibit protein synthesis by inhibiting the 30s ribosome unit
Fluoroquinolones: mechanism of action
Inhibit topoisomerase (aka DNA gyrase) which inhibits DNA/RNA synthesis
Sulfa antibiotics/sulfonamids": mechanism of action
inhibit folate pathway (folate is a precursor to important nucleotides)
What are methods of antibiotic resistance?
Mutation
Destruction or inactivation: bacteria releases enzymes that degrade the antibiotic before it can do its job
Efflux: the antibiotic enters the bacteria through a porin and is pumped out of the bacteria by an efflux pump
Methods of bacterial genetic transfer?
Conjugation
One-way transfer of DNA (plasmid) through direct cellular contact (bacteria form a pilus (tube) to connect)
Transformation
Uptake and expression of foreign DNA (EX: when one bacteria dies and spills its contents allowing another bacteria to uptake it)
Transduction
Transfer of genetic material through a vector (bacteriophages, bacterial viruses, infect bacteria cells and use the as a host to replicate. Sometimes bacterial DNA is incorporated into the viral DNA and when the virus goes on to infect another bacteria, it takes the bacterial DNA with it)
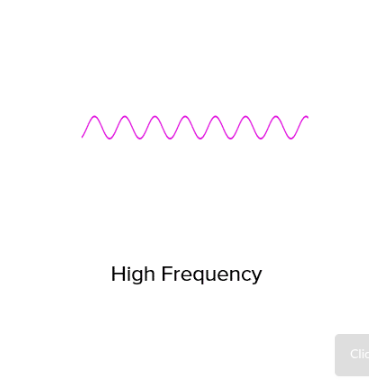
Frequent waves →high pitched sound
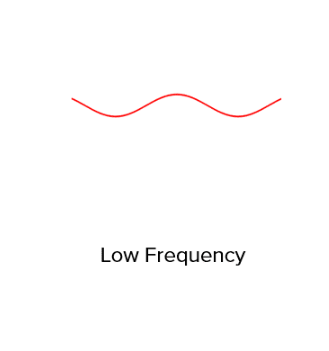
Infrequent waves →low pitched sound
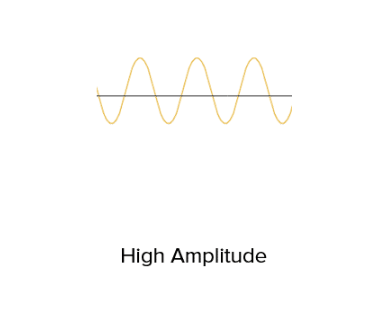
Tall waves →loud sound
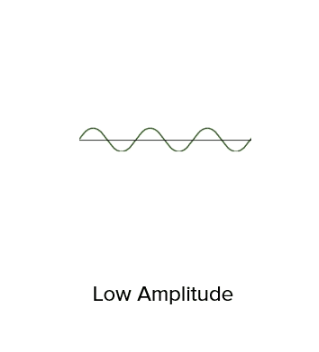
Short waves →quiet sound
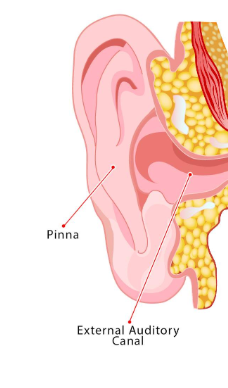
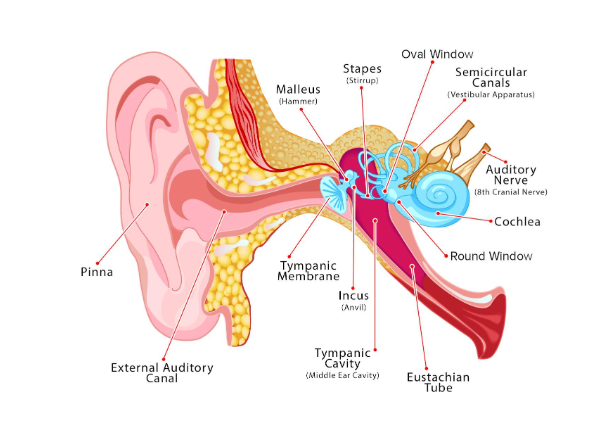
Structures in the outer ear
Pinna: outer, visible part of ear that gathers sound waves
External auditory canal: connects pinna to eardrum
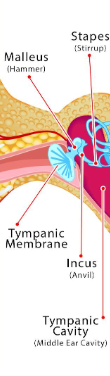
Structures of the middle ear
Tympanic membrane/eardrum
Ossicles (Malleus, incus, stapes): tiny bones that transmit soundwaves
Eustachian tube: connects middle ear to the back of the nose and throat; equalizes pressure in ear
Also contains small muscles and tendons
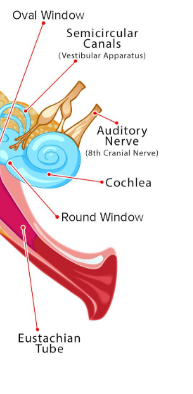
Structures of the inner ear
Cochlea: when sounds enter they vibrate tiny hairs that send signals
Vestibular system
semicircular canals: 3 looped tubes filled with fluid; helps with balance by telling our brain when we move head or change positions
Damage to the inner ear can cause hearing/balance problems
Pathway of sound in the ear
Auditory canal →Tympanic membrane (vibrates) →Ossicles →oval window (in cochlea) →Perilymph (also in cochlea; contain hairs [stereocilia] that send impulse to the brain)
Pathway of sound in ear: explain steps
Sound enters the auditory canal and causes the tympanic membrane to vibrate
Vibration of the eardrum causes the ossicles to move back and forth
The stapes movement against the oval window causes movement in the fluid that fills the cochlea
Movement of the fluid causes the stereocilia to move and send an impulse along the auditory nerve
The brain translates the impulse into sound
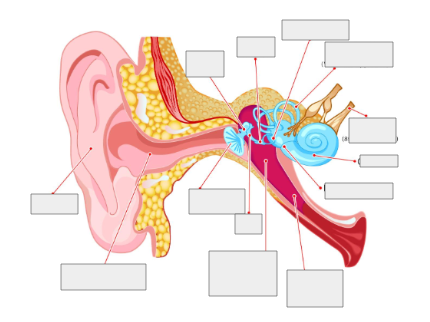
Label
Label
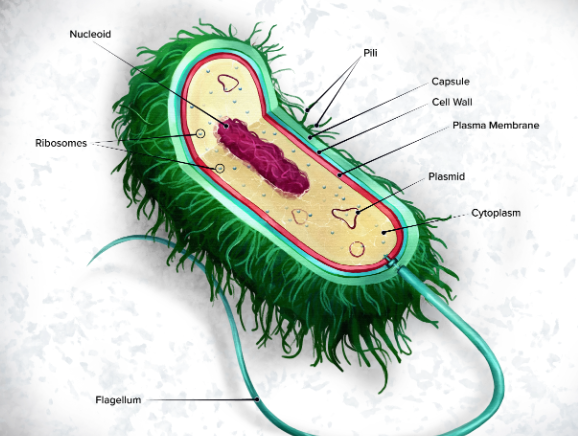
Conductive hearing loss
Mechanical failure
Something isn’t passing vibrations properly
Usually in the middle ear
Sensorineural hearing loss
issue with the inner ear
could be and issue with the auditory nerve or cochlear stimulation
Live attenuated vaccines: Description and example

Inactivated or killed vaccines: Description and example

Toxoid vaccines: Description and example

Subunit vaccines: Description and example

Conjugate vaccines: Description and example

Qualities of a vaccine

Intradermal vs subcutaneous
Intradermal
superficial/shallow
injection into the dermis (first layer of skin)
Subcutaneous
Deep
injection under all layers of skin
Live attenuated: steps
Grow virus strain in a tissue culture (must be colder than human body)
Fill syringe
Killed vaccine: steps
Grow new viruses
Isolate viruses
Kill viruses (heat, radiation, chemicals)
Fill syringe
Toxoid vaccines: steps
Copy virus in a growth medium
Isolate toxin with a purifier
Neutralize toxins (aluminum salts, formaldehyde)
Add an adjuvant to help it produce an immune response
Subunit vaccines: steps
pull out a segment of viral dna
Add to the DNA of a yeast cell
Use purifier to isolated the antigen produced by the yeast cells
Naked DNA vaccine: steps
copy viral gene with PCR
combine viral gene with vectors
Add bacteria to vectors so the bacteria can replicate
use the purifier to separate the altered vectors and bacteria
Similar pathogen vaccine: steps
collect a similar virus and isolate with purifier
Fill syringe
Recombinant DNA
a DNA molecule with segments from different sources
B-cells function
create antibodies
T-cells function
activated by antibodies, destroy pathogens
Helper-T function
can activate B-cells, macrophages, and others
how can you determine conductive hearing loss from a graph?
The bone conduction is at least 10db higher than air.