Biochemistry Exam 3 (Chapters 11-17)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
What are the five classes of lipids
1. Free fatty acids: A common fuel.
2. Triacylglycerols: Storage form of fatty acids.
3. Phospholipids: Membrane lipids.
4. Glycolipids: Membrane lipids composed in part of carbohydrates.
5. Steroids: Polycyclic hydrocarbons with a variety of functions.
How many carbons do typical biological lipids contain (give a range)
14-24 (Most common be 16C and 18C)
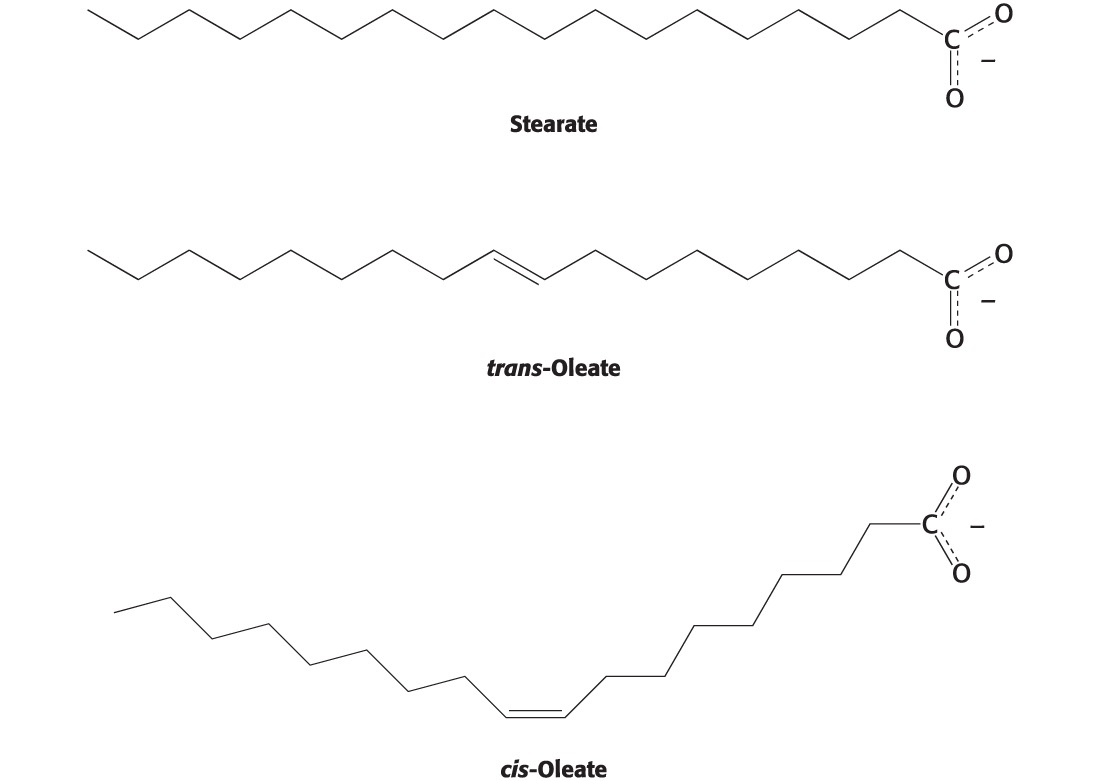
Which of the two fatty acids has a higher melting point and why
Stearate because the tight packing allows for van der waals interactions which raises the MP; whereas in trans-please the lack of tight packing from the double bond (unsaturation) does not and lowers the MP
What is the relationship between MP and fatty acid saturation
The more saturated a fatty acid is the higher the Mp
What is the relationship between MP and unsaturation
The more unsaturated the lower the MP
What properties determine MP for fatty acids
Chain length and saturation
# of cis-double bonds (decreases MP)
Longer chains mean more VDW forces; longer chains mean higher MP
Lipids that contain fatty acids (complex lipids) are found to be/function as
Storage and membrane
Lipids WITHOUT fatty acids
Cholesterol, vitamins, pigments, etc.
Is glycogen better at energy storage or is triglycerol? Why?
Triglycerol is better at energy storage because one triglycerol contains 3 fatty acids which means they can store more energy. Fatty acids are also more reduced and carry less water per gram due to fats being nonpolar
What are the 3 types of membrane lipids
phospholipids
Glycolipids
Cholesterol
What is this
Phospholipid/ phosphoglyceride
What is this
Glycolipid
Some lipid molecules are said to be amphipathic, meaning that they have:
A. asymmetric carbons and can exist in left- and right-handed forms.
B. have a dual nature with part of the molecule being hydrophobic and the other
part being hydrophilic.
C. are capable of moving rapidly from one side of a lipid bilayer to the other.
D. carry a positive charge on one end and a negative charge on the other end.
have a dual nature with part of the molecule being hydrophobic and the other part being hydrophilic
Unsaturated fatty acids have double bonds that are in the cis configuration. One of the consequences of this configuration is:
A. an alteration in the charge of the molecule.
B. an alteration in the number of carbons in the molecule.
C. a bend in the molecule.
D. enhanced flexibility of the molecule.
a bend in the molecule.
In phosphoglycerides, fatty acids are esterified at
A. C-1 and C-2 of glycerol.
B. C-1 and C-3 of glycerol.
C. any two of the three glycerol carbons.
D. a glycerol carbon and the phosphate group
C-1 and C-2 of glycerol.
The fatty acid oleate contains 18 carbons and a cis double bond after C-9. Which designation describes the composition and structure of oleate?
18:1
In biological systems, fatty acids usually contain an even number of carbon atoms.
Which fatty acids are MOST common in biological systems?
Fatty acids with 16 and 18 carbons
A triacylglycerol consists of fatty acids attached to:
A. three cholesterols.
B. one glycerol phosphate.
C. two glycerol phosphates.
D. one glycerol.
One Glycerol
What is the make up of a triacylglycerols ( compounds and bonds)
3 fatty acids + Glycerol; linked by ester linkages
If a lipid has a sphingosine backbone it is referred to as
Sphingolipid
What type of backbone do glycolipids use
Sphingosine
Why is it necessary to break down food in smaller pieces?
The body cannot directly absorb and utilize the large, complex molecules found in food
Why are enzymes packaged as zymogens?
To prevent premature/uncontrolled enzymatic activity that could damage cells (regulation)
Proteins are digested into small fragments. What are these fragments called?
Oligopeptides
Oligopeptides are broken down by peptidases into…
Amino acids, dipeptides, and tripeptides
alpha-amylase cleaves what type of bonds
1,4 glycosidic bonds
What other enzymes can digest carbs
Alpha- dextrinase, alpha-glucosidase, lactase (lactose), sucrase (sucrose)
Lipases hydrolyze lipids. What are the products of a broken triacylglycerol
Two fatty acids and a monocylglycerol
Enzymes that are activated by specific proteolytic cleavage are called
Zymogens
The process of digestion in the stomach is carried out in two main ways. One way involves the environment that exists in the stomach. What environmental condition within the stomach promotes digestion?
Low pH (acidity)
Increased levels of cholecystokinin (CCK) lead to a feeling of satiety. CCK is a family of peptide hormones released from the
Small intestine
Saliva is an aqueous solution of which ion?
HCO3− (Bicarbonate ion)
Chylomicrons are
A. micelles.
B. lipoprotein transport particles.
C. comprised of disaccharides and protein.
D. transported from the intestinal lumen to mucosal cells.
lipoprotein transport particles.
Bile salts, which aid in lipid adsorption, are synthesized from cholesterol in the liver and released into the small intestine from the
Gallbladder
What do micelles and chylomicrons have in common?
They both contain fatty acids
What are Cholymicrons composed of
Triacylglycerol and lipoprotein
All digestive molecules (proteases, amylases, and lipases) are hydrolases. This means that they break down substrate using
Water
What transporter does fructose use
GLUT 5
What cotransporter does glucose and galactose use. (Bonus if you name the ion they cotransport with)
SGLT (sodium)
Catabolism/ Catabolic Rxns
Degrade molecules to produce energy
Anabolism/ Anabolic Rxns
Synthesize molecules and requires energy
Amphibolic
Pathways that can function anabolically or catabolically
How many phosphoanhdride bonds in ATP, ADP and AMP?
ATP: 2
ADP: 1
AMP: 0
Why does ATP have a high phosphoryl-transfer potential
Charge Repulsion/ Charges
Resonance Stabilization
Entropy (Increase)
Stabilization by hydration
How many negative charges on ATP?
4 negative charges
Why are Phosphate and its esters are especially prominent in biology
Phosphate esters are thermodynamically unstable, yet they are kinetically stable. ( Dumb terms: stable bc the negative charge prevent them from getting broken down by hydrolysis, can be regulated by enzymes)
Metabolic Processes Are Regulated in Three Principal Ways
1. The amount of enzymes present
2. The catalytic activity of enzymes
3. The accessibility of substrates
Which statement correctly describes metabolic reactions?
A. Anabolic processes break down material and transform fuels into cellular energy, whereas catabolic processes require energy for biosynthesis.
B. Catabolic processes break down material and transforms fuels into cellular energy, whereas anabolic processes require energy for biosynthesis.
C. Intermediary metabolism breaks down material and transforms fuels into cellular energy, whereas metabolism requires energy for biosynthesis.
D. Metabolism breaks down material and transform fuels into cellular energy, whereas intermediary metabolism requires energy for biosynthesis.
Catabolic processes break down material and transforms fuels into cellular energy, whereas anabolic processes require energy for biosynthesis.
In a metabolic pathway,
A. a reaction with a positive Δ𝐺 can occur if it is coupled to a reaction with a more negative Δ𝐺.
B. a reaction with a positive Δ𝐺 cannot occur.
C. it is Δ𝐺°, not Δ𝐺, that determines whether a reaction can occur.
D. a reaction with a positive Δ𝐺 can occur if there is an increase in the concentration of the reaction's products.
A. a reaction with a positive Δ𝐺 can occur if it is coupled to a reaction with a more negative Δ𝐺.
Which factor does NOT contribute to the high phosphoryl-transfer potential of ATP?
A. resonance stabilization
B. the adenine ring structure
C. charge repulsion
D. the ability of water to interact more favorably with the products of ATP hydrolysis than with ATP itself
the adenine ring structure
The hydrolysis of ATP drives metabolism by
A. shifting the equilibrium of coupled reactions.
B. providing part of the activation energy for a key reaction.
C. providing energy in the form of heat.
D. altering the conformation of metabolic reactants.
shifting the equilibrium of coupled reactions.
What material in vertebrate muscle serves as a reservoir for high-energy
phosphate groups?
A. glycogen
B. phosphoenolpyruvate
C. creatine phosphate
D. glucose 6-phosphate
creatine phosphate
During catabolic processes, the oxidation of energy-rich molecules often results in
the reduction of NAD+ to NADH.
What comparable molecule is the most commonly used reductant for reductive steps in anabolic processes?
A. FAD
B. NADPH
C. coenzyme A
D. FMNH2
E. ATP
B. NADPH
Acyl groups generated during metabolic processes involving carbohydrates and fatty acids are activated by attachment to
A. glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
B. pyruvate.
C. coenzyme A.
D. biotin
C. coenzyme A.
NADPH is commonly found in
Reductive bioSYNTHESIS