Innate and adaptive immunity
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What are the different forms of first line of defence
Mechanical
Molecular and cellular
Microbiological and environmental
What are the different mechanical first line of defences
Body surface
Cilia in respiratory tract
Air movement in respiratory tract
Flushing by liquids
Mucus as barrier
What are the different physiological first line of defences
pH changes and extremes
Pyrexia kills some infectious agents
What are the different cellular innate defences
Macrophages - function by ingesting and killing microorganisms
Neutrophils - also phagocytic and degranulate
Mast cells, basophils and eosinophils - have receptors for antibodies and increase vascular permeability
Which one is a monocyte
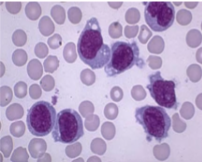
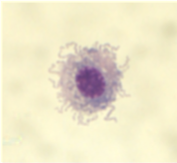
Which one is a macrophage
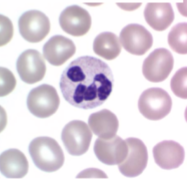
Which one is a neutrophil
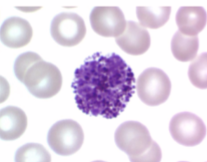
Which one is a basophil
Which one is an eosinophil
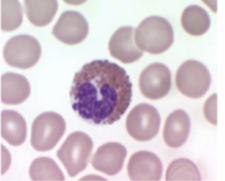
What are the different molecular defences
Defensins
Lysozyme and sweat gland secretions
Myeloperoxidase system
Acute phase proteins
Complement systems
Interferons
What are defensins
Small 15-20 aa proteins
Where are defensins found
In many tissues and cells, especially phagocytes and epithelial cells
What are defensins active against
Bacteria
Fungi
Viruses
What are defensins important in
Skin barrier to infections
What are lysozymes
Family of enzymes which attach peptidoglycan cell walls of bacteria
What are the sites of action of lysozymes
Cellular
Secreted from epithelial cells
Sebum
How do lysozymes act on cells
In cytoplasmic granules of macrophages
How are lysozymes secreted from epithelial cells
Tears
Saliva
Mucus
How do lysozymes act in sebum
From sebaceous glands
Waxy fatty acids stop bacterial attachment to skin
Hydrates and lubricates skin
What is myeloperoxidase
An enzyme found mainly in lysosomes in granulocytes and macrophages
What do myeloperoxidases do
Kill bacteria and other pathogens by production of toxic hypochlorite and singlet oxygen
How do commensal bacteria work
Inhabit mucosal surfaces, especially in GI and respiratory tracts and skin
Prevent attachment of pathogenic bacteria and hence block their invasion and infection
What husbandry factors effect innate immunity
Diet
Temperature
Humidity
What are the defining features of adaptive immunity
T and B cells
Specificity
Self and non self discrimination
Memory
What is an antigen
Any molecule that can bind specifically to an antibody or antigen receptor
What is an epitope
A site on an antigen recognized by an antibody or an antigen receptor
What is an antibody
A protein that binds specifically to a particular substance
What are the stages of action of defending against microbial invasion
Invading microorganism passes physical barriers
Innate immunity such as inflammation, defensins and lysozymes
Specific immunity such as antibody production and cell mediated immunity