Chemistry - Unit 3: The Periodic Table
5.0(3)
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
Who created the periodic table?
Dimitri Mendeleev
2
New cards
What are some characteristics of metals?
- shiny
- malleable
- ductile
- solid at room temp
- malleable
- ductile
- solid at room temp
3
New cards
Do metals form + or - ions?
Do they gain or lose electrons?
Do they gain or lose electrons?
They form + ions
They lose electrons
They lose electrons
4
New cards
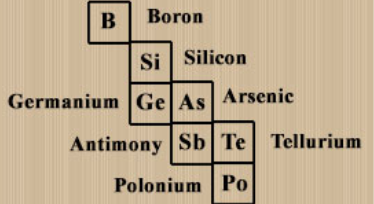
what is the name of the section on the periodic table were metalloids are found
the "staircase"
5
New cards
which side of the periodic table can metals be found?
left side (left of the staircase)
6
New cards
which side of the periodic table can nonmetals be found
right side (right of the staircase)
7
New cards
what are metalloids?
quirky lil elements that showcase features of both metals and nonmetals.
8
New cards
what are characteristics of nonmetals?
- brittle
- dull
- do not conduct electricity
- pretty colors
- typically gases at room temperature
- dull
- do not conduct electricity
- pretty colors
- typically gases at room temperature
9
New cards
do nonmetals form + or - ions?
do they gain or lose electrons?
do they gain or lose electrons?
they form (-) ions
they lose electrons
they lose electrons
10
New cards
What is Group 1 of the Periodic Table called?
Alkali Metals
11
New cards
What kind of ions to alkali metals form?
positive +1 ions, they lose an electron
12
New cards
are alkali metals reactive?
VERY. they react to H2O. one little drop and *boom* (jk idk if they actually go *boom*)
13
New cards
What is the second column of the periodic table called?
alkaline earth metals.
"earth metals"? what are these? elements? oh. haha. they are.
"earth metals"? what are these? elements? oh. haha. they are.
14
New cards
what ion charge do alkaline earth metals form?
+2, they lose 2 electrons
15
New cards
now we're grouping together a big chunk of the periodic table. what are columns 3-12 on the periodic table called?
~transition metals~
16
New cards
yeah, transition metals. good job. now what's up with these guys? gimme some details on the transition metals
- can form ions with different charges :0
- have subgroups lanthanides and actinides (the lil guys underneath
the periodic table)
- have subgroups lanthanides and actinides (the lil guys underneath
the periodic table)
17
New cards
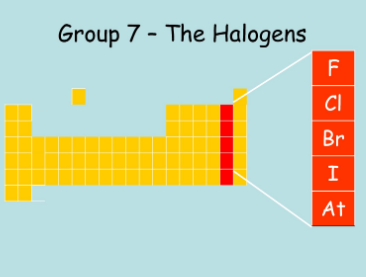
two more groups left. what is the second to last column (group 17/ 7A) of the periodic table called?
ha ha ha haaalogennssss
18
New cards
what's up with halogens?
- very very reactive. they rlly like my jokes.
- i guess that's it for ha ha halogens.
- i guess that's it for ha ha halogens.
19
New cards
what ion charge do halogens form?
-1, gain an electron
20
New cards
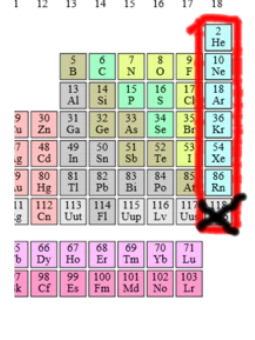
LAST COLUMN OF THE PERIODIC TABLE (Group 18/ 8A)!!! what are these super shnazzy elements called?
the...Noble Gases!!!!!
21
New cards
tell me about these ~noble gases~
- noble gases are the "that girl" of the periodic table
- y'know, unreactive, stable, full valence shell
- these guys don't form ions. why? cuz they don't need them.
- y'know, unreactive, stable, full valence shell
- these guys don't form ions. why? cuz they don't need them.
22
New cards
now it's the moment ya'll have been waiting for. the ~periodic table trends~
don't flip over this card. there's nothing there.
don't flip over this card. there's nothing there.
i said don't flip it over
23
New cards
what is atomic radius?
24
New cards
what is ionization energy?
the energy needed to remove an electron from the atom.
25
New cards
what's the trend for ionization energy like?
-increases across a period because with more protons there is a greater force of attraction
-decreases down a group because larger atoms have a valence shell further from the nucleus
-decreases down a group because larger atoms have a valence shell further from the nucleus
26
New cards
Arrange the following elements in order of their decreasing ionization energy: Rb, Sn, I, Te, Sr
I, Te, Sn, Sr, Rb
27
New cards
now we know ionization energy but what's 2nd ionization energy?
energy needed to remove an electron from a +1 ion
28
New cards
Which family has the highest 2nd ionization energy
Alkali metals
29
New cards
Which family has the lowest 2nd ionization energy
Alkaline earth metals
30
New cards
what's 3rd ionization energy now?
energy needed to remove an electron from a +2 ion
31
New cards
Which family has the highest 3rd ionization energy
Alkaline earth metals
32
New cards
What element has the lowest 3rd ionization energy
ALUMINUM!!
33
New cards
there's another trend called...electronegativity, but what is it?
The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself that it is sharing with another atom
(ofc disregard the noble gases, they're all noble and happy)
(ofc disregard the noble gases, they're all noble and happy)
34
New cards
now tell me about how the trend for electronegativity goes pls
Across a row: electronegativity increases
{Smaller atoms with more protons (such as flourine) will hold electrons best}
Down a column: electronegativity decreases
{Bigger atoms (Fr) have a weaker hold on electrons}
{Smaller atoms with more protons (such as flourine) will hold electrons best}
Down a column: electronegativity decreases
{Bigger atoms (Fr) have a weaker hold on electrons}
35
New cards
don't forget about REACTIVITY, what is it?
The likelihood of an atom to combine with another atom to increase its stability (yess they always want to become more stable)
36
New cards
what do METALS do whey react?
that's right, they LOSE electrons
37
New cards
what do NON-METALS do when they react?
they GAIN electrons when they react
38
New cards
what's the trend like for metals when they react?
Down a family: metal reactivity increases
Across a row: metal reactivity decreases
Across a row: metal reactivity decreases
39
New cards
what's the trend like for non-metals when they react?
Down a family: non-metal reactivity decreases
Across a row: increases reactivity
Across a row: increases reactivity
40
New cards
now moving on to electron affinity, what is that?
How much an element wants to gain an electron
(again disregarding the noble gases)
(again disregarding the noble gases)
41
New cards
Why do HALOGENS have a strong electron affinity?
because if they gain one more electron, they will have a full shell, like the noble gases!
42
New cards
Which groups would have the least electron affinity?
groups 1 and 2 because they don’t want to gain electrons, they would rather lose them
43
New cards
Which is BIGGER? Mg or Mg^+2
Mg, cause its neutral so it has more electrons than a positive ion
44
New cards
Which of the following has the highest electronegativity?
S or F
S or F
F