microbiology lab final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:58 PM on 5/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
1
New cards
What does the O-F test determine?
oxidation and fermentation of organisms.
2
New cards
an O-F test is performed. the results are as follows: green/blue in the sealed tube, yellow in the unsealed tube. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism can perform oxidation only. O
3
New cards
an O-F test is performed. the results are as follows: yellow throughout both sealed and unsealed tubes. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism can perform oxidation and fermentation or fermentation only. O-F or F1
4
New cards
an O-F test is performed. the results are as follows: slightly yellow at the top of both sealed and unsealed tubes. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism can perform slow oxidation and fermentation or slow fermentation only. O-F or F1
5
New cards
an O-F test is performed. the results are as follows: green/blue in both sealed and unsealed tubes. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism is not capable of oxidation or fermentation (no sugar metabolism, nonsaccharolytic). N
6
New cards
what does a Methyl Red (MR) test determine?
whether or not the organism performs mixed acid fermentation
7
New cards
suppose you perform a MR test and the broth turns red. what does this indicate about the organism?
the organism performs mixed acid fermentation
8
New cards
suppose you perform a MR test and the broth turns orange. what does this indicate about the organism?
the organism does not perform mixed acid fermentation
9
New cards
what does the Vogues-Proskauer test identify about microorganisms?
whether or not they ferment glucose, then quickly turn their acid products to acetoin and 2,3-butanediol.
10
New cards
suppose you perform a VP test and the broth turns copper. what does this indicate about the organism?
it does not produce acetoin/2,3-butanediol
11
New cards
suppose you perform a VP test and the broth turns red. what does this indicate about the organism?
it produces acetoin/2,3-butanediol
12
New cards
true or false: results for the VP test should be read immediately after adding reagent
false
13
New cards
what does the catalase test distinguish about an organism?
whether or not it has the enzyme catalase present.
14
New cards
what is the indicator of a catalase-positive test?
bubbling
15
New cards
how old should bacterial cultures being used in the bacterial test be?
24 hours
16
New cards
what does the oxidase test determine in organisms?
the presence or absence of cytochrome c
17
New cards
what is the indicator for an oxidase-positive test?
bacteria culture changing color when presented with oxidase reagent
18
New cards
what does the citrate utilization test indicate about organisms?
the presence of citrate permease and citrate lyase to ferment citrate
19
New cards
true or false: the slant has to be completely blue in order to indicate a citrate positive result.
false
20
New cards
suppose you run a citrate test and only the upper portion of the slant turns blue. what does this indicate about the inoculated organism?
it performs citrate fermentation/utilizes citrate
21
New cards
what is an indicator of a positive citrate test other than the medium turning blue?
growth on the medium
22
New cards
suppose you perform a citrate test and the slant is completely green. what does this indicate about the organism?
it does not utilize/ferment citrate
23
New cards
what does the starch hydrolysis/amylase test differentiate between organisms?
the presence or absence of alpha-amylase or oligo-1,6-glucosidase
24
New cards
what do alpha-amylase and oligo-1,6-glucosidase do?
hydrolyze starch
25
New cards
what is the DNase test an indicator for?
the presence or absence of the enzyme DNase
26
New cards
what kind of enzyme is DNase?
exoenzyme
27
New cards
what is an indicator of a positive DNase test?
clearing around growth
28
New cards
what is the urease test an indicator for?
urea hydrolysis by enzyme urease
29
New cards
suppose you run a urease test and your slant turns all pink within 24 hours. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
it rapidly performs urea hydrolysis and strongly produces urease. +
30
New cards
suppose you run a urease test and your slant turns partially pink within 24 hours and then turns all pink 5 days later. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
it slowly hydrolyzes urea and weakly produces urease. w+
31
New cards
suppose you run a urease test and your slant stays orange/yellow within 24 hours, then turns partially pink 5 days later. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
it slowly hydrolyzes urea and weakly produces urease. w+
32
New cards
suppose you run a urease test and your slant stays orange/yellow for 6 days after incubation. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
it does not hydrolyze urea and urease is absent. -
33
New cards
what is different about urea broth compared to urea slants (2)?
* its only nutrient source is a trace of yeast extract
* it contains buffers strong enough to inhibit alkalinization of the medium by all but rapid urease-positive organisms
* it contains buffers strong enough to inhibit alkalinization of the medium by all but rapid urease-positive organisms
34
New cards
what does urea hydrolysis produce? how does that change the color of the medium?
it produces ammonia (NH3), a base. this raises the pH of the medium enough to change its color through phenol red
35
New cards
what do the SIM tests test for?
sulfur reduction, indole production (enzyme tryptophanase), and organism motility
36
New cards
true or false: the SIM medium is semisolid
true
37
New cards
imagine you run a SIM test and your medium darkens with black precipitate. what does this indicate about the organism?
it reduces sulfur
38
New cards
what is the indication for an indole test-positive organism?
reagent layer turning red
39
New cards
suppose you run a SIM test and the medium remains completely clear after incubation, besides where the bacteria was originally inoculated. what does this indicate about the organism?
it is not motile
40
New cards
what does the TSIA medium indicate?
ability of the organism to ferment glucose, lactose, or sucrose as well as its ability to reduce sulfur or produce gas.
41
New cards
suppose you inoculate a bacterium into a TSIA slant. the slant and the butt turn yellow. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
it is capable of glucose and lactose/sucrose fermentation and there is acid accumulation in the butt. A/A
42
New cards
suppose you inoculate a bacterium into a TSIA slant. the slant turns red, while the butt turns yellow. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
it ferments glucose and produces acidic products, proteins are catabolized aerobically with alkaline products. K/A
43
New cards
suppose you inoculate a bacterium into a TSIA slant. the slant and the butt turn red. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism does not ferment and instead catalyzes peptone aerobically and anaerobically with alkaline products. K/K
44
New cards
what group of bacteria is an organism NOT from if it produces no yellow color change?
*Enterobacteriaceae*
45
New cards
suppose you inoculate a bacterium into a TSIA slant. the slant turns red, while the butt does not change colors. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism does not ferment but instead catalyzes peptone aerobically with alkaline products. K/NC
46
New cards
suppose you inoculate a bacterium into a TSIA slant. the slant and the butt do not change colors. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism is growing slowly or not at all and is not from *Enterobacteriaceae*. NC/NC
47
New cards
suppose you inoculate a bacterium into a TSIA medium. the slant of the medium turns red, while the butt of the medium turns black with precipitate. what can we safely assume about the organism?
we can safely assume the organism reduces sulfur, catalyzes peptone aerobically, and ferments glucose. (H2S, K/A)
48
New cards
suppose you run a TSIA test and notice after incubation that the medium has cracks in the agar. what does this indicate about the organism? what is the symbol for this?
the organism produces gas. G
49
New cards
what does BEA test for?
organisms that can and cannot hydrolyze esculin
50
New cards
what is the indicator for an organism that can hydrolyze esculin in a BEA medium?
blackening of the medium around the inoculation
51
New cards
what does MSA indicate about an organism?
members of *Staphylococcus* and whether or not the organism can ferment mannitol
52
New cards
what is the indicator for an organism that can ferment mannitol in MSA?
yellow color change around the inoculation
53
New cards
what Gram type is capable of growing on MacConkey, while the other is not?
Gram (-)
54
New cards
what does MacConkey agar differentiate between?
Gram (+) and Gram (-) organisms. differentiates between Gram (-) coliforms (ferments lactose) and non-coliforms
55
New cards
what is the indicator of a coliform in MacConkey agar?
pinkish coloring of the culture
56
New cards
what groups does HE agar isolate? what does it distinguish?
isolates *Shigella* and *Salmonella* species. distinguishes organisms that can ferment lactose, sucrose, or salicin to acid-end products and reducing sulfur
57
New cards
what is an indication of a coliform in HE agar? sulfur reduction?
coliforms turn the medium orange around them, sulfur reducers turn the medium black around them
58
New cards
which Gram type does HE agar inhibit?
Gram (+)
59
New cards
what is the differential purpose of blood agar?
differentiating between organisms that can produce hemolysins and undergo hemolysis. it also differentiates between the types of hemolysis: alpha-hemolysis, beta-hemolysis, and gamma-hemolysis.
60
New cards
suppose you inoculate a blood agar plate and you notice a clearing around your inoculum after incubation. what type of hemolysis is this and what species is this characteristic of
beta-hemolysis, *Streptococcus pyogenes*
61
New cards
suppose you inoculate a blood agar plate and you notice a greenish zone around the inoculum after incubation. what type of hemolysis is this and what species is this characteristic of?
alpha-hemolysis, *Streptococcus pneumoniae*
62
New cards
suppose you inoculate a blood agar plate and you notice no change in the medium around the inoculum after incubation. what type of hemolysis is this?
gamma-hemolysis/no hemolysis
63
New cards
in the urea hydrolysis test, if the tube is orange throughout the duration of the experiment, the organism is described as demonstrating…
A) rapid urea hydrolysis
B) slow urea hydrolysis
C) no urea hydrolysis
D) no growth
A) rapid urea hydrolysis
B) slow urea hydrolysis
C) no urea hydrolysis
D) no growth
C
64
New cards
the enzymes required for an organism to hydrolyze the glucose polysaccharide starch, are oligo-1,6-glucosidase, and…?
amylase
65
New cards
the methyl green dye in the DNase test agar plate functions…
A) to allow visualization of pH changes
B) to stabilize the DNA
C) to allow visualization of where the bacterial growth is occurring
D) to allow visualization of DNA hydrolysis
A) to allow visualization of pH changes
B) to stabilize the DNA
C) to allow visualization of where the bacterial growth is occurring
D) to allow visualization of DNA hydrolysis
D
66
New cards
in the addition of Kovac’s reagent produces a floating red layer on a SIM medium culture, this indicates what about the organism?
it possesses tryptophanase
67
New cards
catalase is an enzyme that functions to…
convert hydrogen peroxide into water and gaseous oxygen
68
New cards
the enzyme necessary to hydrolyze urea into ammonia and carbon dioxide is…?
urease
69
New cards
in the urea hydrolysis assay, the phenol red indicator will turn pink when…
A) the media has become alkaline
B) the media has become neutral
C) the media has become acidic
D) the media has become anaerobic
A) the media has become alkaline
B) the media has become neutral
C) the media has become acidic
D) the media has become anaerobic
A
70
New cards
if you were to check on the Kligler iron agar tube of an organism that ferments glucose but not lactose at about 10 hours of incubation, what would you expect to see?
the media would be all yellow
71
New cards
a positive result for a starch hydrolysis test performed on a starch agar plate will appear…
as a clear halo
72
New cards
upon completion of an OF test, you observe that your organism had produced an acid result in the aerobic tube and a neutral result in the anaerobic tube. you can reasonably conclude that the organism exhibits ________________ metabolism of carbohydrates.
no
73
New cards
why would an organism that carries out oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates, but not fermentation of the carbohydrates, not cause an acid reaction throughout the entire tube in a stab inoculation of an OF medium?
autoclaving drives oxygen out of the media during preparation and it often does not diffuse back into the depths of the tube during incubation
74
New cards
the methyl red tests is intended to detect organisms that are capable of…?
performing mixed acid fermentation of glucose
75
New cards
a positive result in DNA hydrolysis will produce…
a zone of clearing on the plate
76
New cards
the Vogues-Proskauer test is intended to detect organisms that are capable of…?
converting acid products of fermentation into acetoin and 2,3-butanediol
77
New cards
a positive result in the oxidase test will appear as…?
purple on the bacterial cells
78
New cards
the ferrous ammonium sulfate in the SIM medium functions to…
produce a visible result when hydrogen sulfide is produced
79
New cards
why do organisms that have the capacity to utilize citrate as the sole carbon source tend to produce an alkaline reaction in Simmons citrate agar?
A) the metabolism of citrate always produces alkaline waste products
B) the organism will also utilize ammonium phosphate as a nitrogen source, resulting in alkaline waste
C) the conversion of citrate into pyruvate produces carbon dioxide as alkaline waste
A) the metabolism of citrate always produces alkaline waste products
B) the organism will also utilize ammonium phosphate as a nitrogen source, resulting in alkaline waste
C) the conversion of citrate into pyruvate produces carbon dioxide as alkaline waste
B
80
New cards
the oxidase test will yield positive results for organisms that...
utilize cytochrome c oxidase
81
New cards
why is it important to use a light inoculum when preparing a Simmons citrate gar slant?
a heavy inoculum of inactive cells can be mistaken for new growth past incubation
82
New cards
a positive result in the catalase test is indicated by…
bubbles upon addition of hydrogen peroxide
83
New cards
a positive result for esculin hydrolysis on BEA appears as…
a darkening around the growth
84
New cards
on a blood agar plate, the complete destruction of red blood cells and hemoglobin, resulting in a clearing of the medium around the colonies, is…
A) alpha hemolysis
B) beta hemolysis
C) gamma hemolysis
D) non hemolytic
A) alpha hemolysis
B) beta hemolysis
C) gamma hemolysis
D) non hemolytic
A
85
New cards
when a mannitol salt agar plate turns yellow, this indicates…
A) a neutral pH
B) a basic pH
C) an acidic pH
D) a change in salinity
A) a neutral pH
B) a basic pH
C) an acidic pH
D) a change in salinity
C
86
New cards
if an organism that is grown on a blood agar plate does not cause any visible change to the blood in the agar, the pattern is called
A) alpha hemolysis
B) beta hemolysis
C) gamma hemolysis
D) hemolytic
A) alpha hemolysis
B) beta hemolysis
C) gamma hemolysis
D) hemolytic
C
87
New cards
Hektoen enteric agar is used to isolate what two genera?
*Salmonella* and *Shigella*
88
New cards
colonies that produce hydrogen sulfide on Hektoen enteric agar will turn…
black
89
New cards
the mannitol in the mannitol salt agar plate serves as…
A) a pH indicator
B) a carbohydrate food source
C) a selective agent
D) a preservative
A) a pH indicator
B) a carbohydrate food source
C) a selective agent
D) a preservative
B
90
New cards
growth of an organism on mannitol salt agar plates indicates that the organism…
tolerates salt up to 7.5%
91
New cards
the Bile Esculin test is commonly used to identify
A) enterococci
B) staphylococci
C) enterics
D) coliforms
A) enterococci
B) staphylococci
C) enterics
D) coliforms
A
92
New cards
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential medium. it selects for _______________ while differentiating between those that can and cannot ______________.
Gram-negatives, ferment lactose
93
New cards
when using radiation, such as UV light, to control microbial growth
A) shorter wavelengths are more effective
B) longer wavelengths are more effective
C) wavelength is not a factor for UV radiation
D) all wavelengths are equally effective
A) shorter wavelengths are more effective
B) longer wavelengths are more effective
C) wavelength is not a factor for UV radiation
D) all wavelengths are equally effective
A
94
New cards
why is an autoclave more effective at sterilizing objects and solutions than boiling would be?
an autoclave produces steam at a higher temperature than boiling
95
New cards

What is the name of this medium? What are the results for *S. pyogenes* and *E. faecalis* (positive or negative)? What does this indicate about these organisms?
bile esculin agar (BEA), *S. pyogenes* is negative and *E. faecalis* is positive. *S. pyogenes* does not hydrolyze esculin/possess esculinase in the presence of bile while *E. faecalis* does.
96
New cards
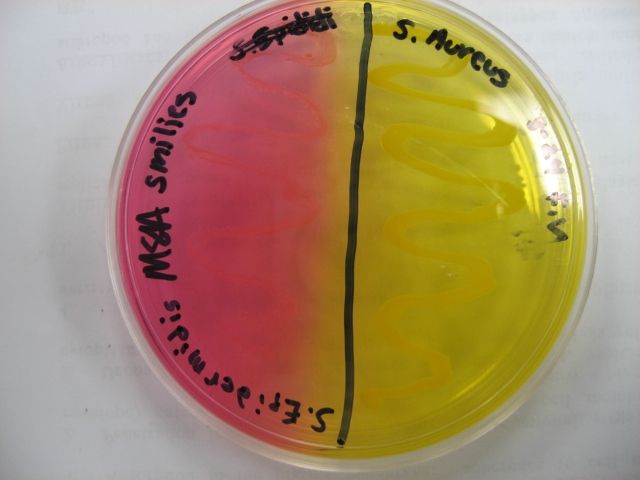
What is the name of this medium? What are the results for *S. epidermidis* (left) and *S. aureus* (right) (positive or negative)? What does this indicate about these organisms?
mannitol salt agar (MSA), *S. epidermidis* is negative and *S. aureus* is positive. *S. epidermidis* can survive in salt content \~7.5% but cannot ferment mannitol, while *S. aureus* can both survive in \~7.5% salt as well as ferment mannitol.
97
New cards
does mannitol fermentation raise or lower pH?
lowers pH
98
New cards
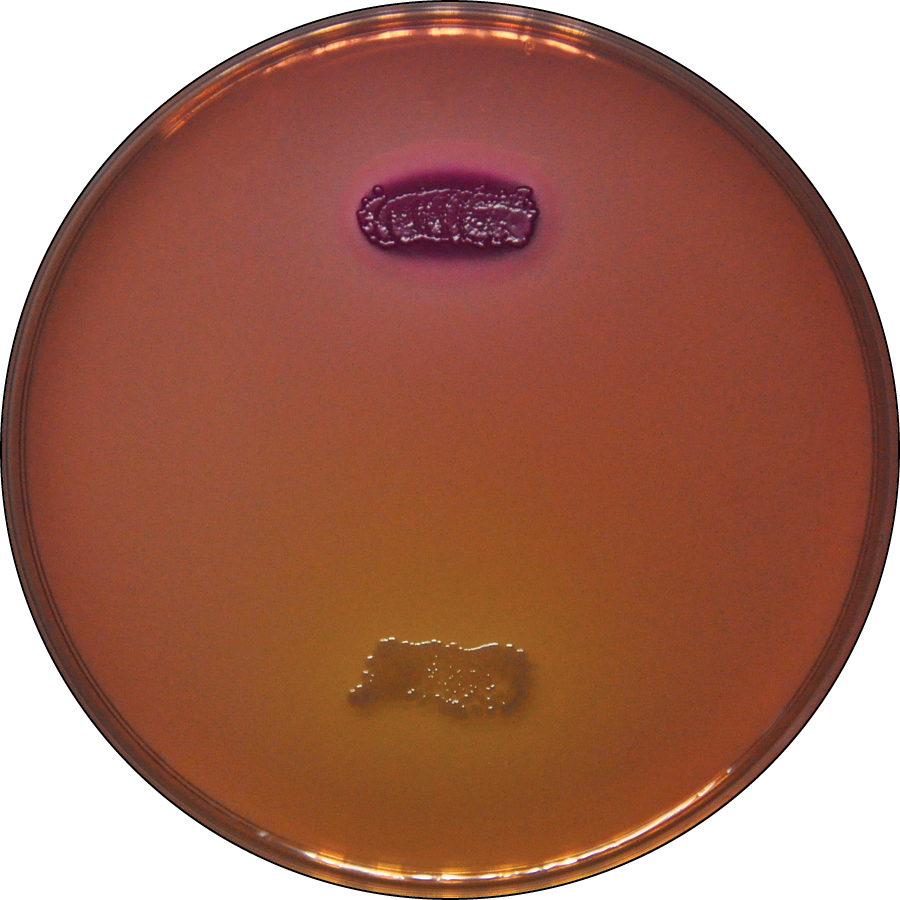

What is the name of this medium? What are the results for the organisms on the top and bottom (positive or negative)? What does this indicate about these organisms?
MacConkey agar, top is positive and bottom is negative. They are both Gram-negative, but top is a coliform (ferments lactose) and bottom is not.
99
New cards
does lactose fermentation on MacConkey agar raise or lower pH?
lowers pH
100
New cards
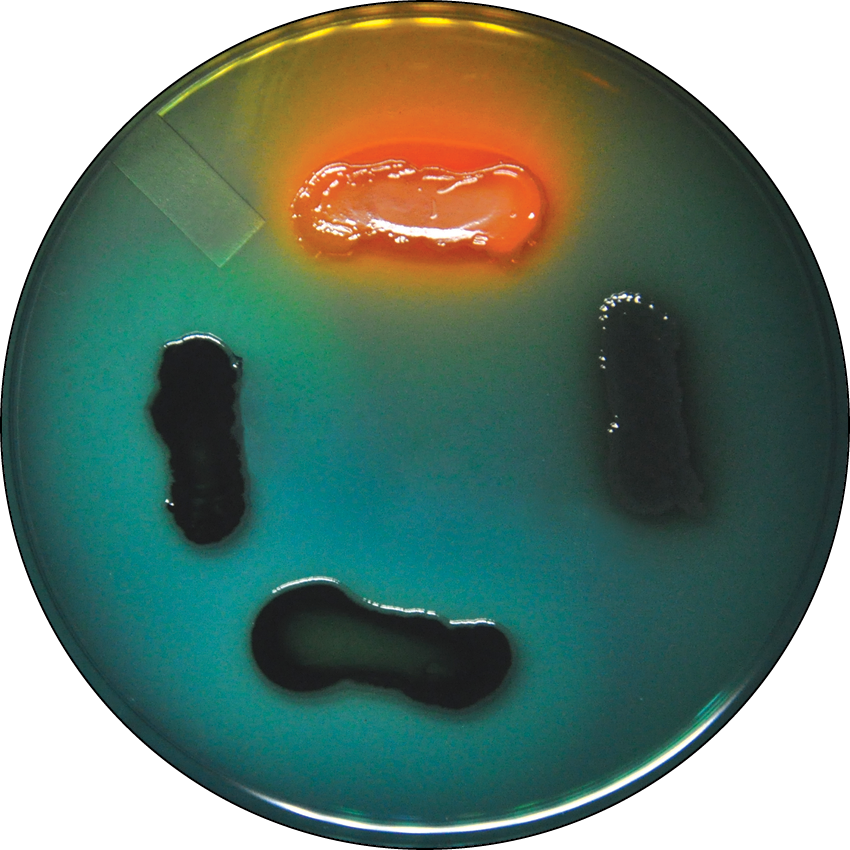
What is the name of this medium? What is indicated about each organism featured?
hektoen enteric agar (HEA), the top organism is a coliform/enteric and not *Shigella* or *Salmonella*, the organisms on the left and bottom are noncoliforms and non-sulfur reducing, the organism on the right reduces sulfur