CHANGING ECONOMIC WORLD
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What is a HIC?
High Income Country (e.g. USA, UK)
What is a LIC?
Low Income Country (e.g. Malawi in Africa)
What is development?
A positive long-term change in people's lives
Name 2 social measures of development
Life Expectancy (Average Years), Literacy Rate (% can read/ write)
Name 2 economic measures of development
GDP per Capita (Income per person per year)
GINI Coefficient (Measures inequality - 0 BEST, 1 WORST)
Name the 3 measures of the Human Development Index
1) Life Expectancy
2) Literacy Rate
3) GDP per Capita
What are 2 disadvantages of a single measure of development?
1) It is an average - Does not show inequality (e.g. most people are poor in Saudi Arabia)
2) Unreliable data - badly measured/ out of date
What word means the growth of manufacturing in a country?
Industrialisation

What word means the loss of manufacturing in a country?
2) De-industrialisation

What does GDP per capita mean?
Income per person per year
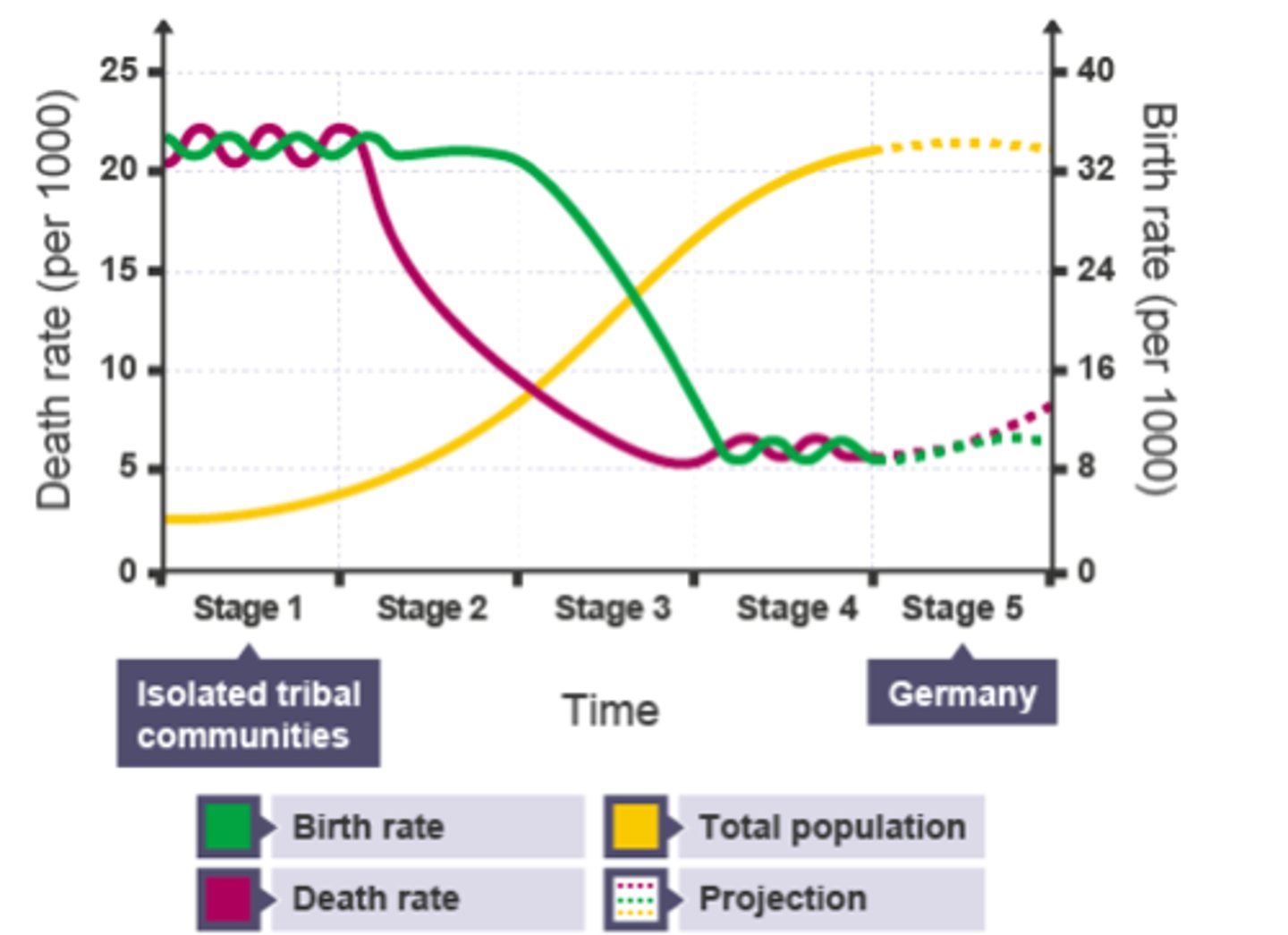
What does the Demographic Transition Model (DTM) show?
The change in population in a country as it develops.
Name 2 continents with many HICs
1) North
America
2) Europe
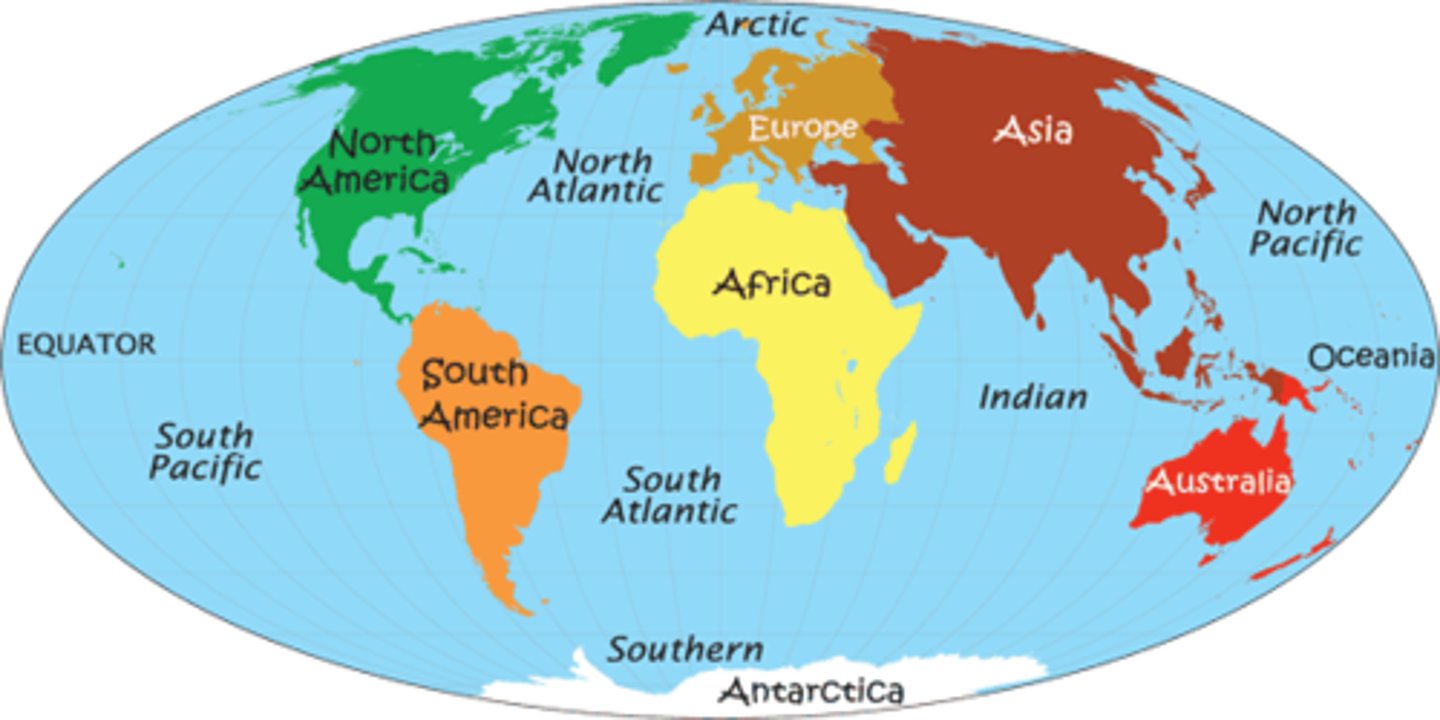
Name a continent with many LICs
Africa
What does NEE stand for? Give an example
Newly Emerging Economy - Nigeria, Brazil, India
Describe how differences in climate cause the development gap
Climate: dry vs. wet climates - difference in ease of farming and availability of food + spread of disease
Describe how natural disasters (e.g. earthquakes) cause the development gap
Natural disasters: cause economic damage and loss of life = smaller workforce and expensive repairs
How do trade barriers widen the development gap?
Trade Barriers - tariffs make selling to HICs more expensive - less income
How does the selling of primary products by LICs widen the development gap?
Primary products (e.g. cocoa beans, bananas) are CHEAP.
Imported manufactured products are expensive. This creates a trade deficit (£Imports > £Exports)
A ________ product is a raw material like bananas, cotton, cocoa beans, coffee beans
Primary
Name 1 historical cause of the development gap
Give an example
Colonialism.
The UK colonised Nigeria. It exploited their natural resources and took slaves - became rich. Did not develop schools, hospitals, infrastructure much
__________ means when one country takes control of another to exploit (use) its natural resources and people
Colonialism
Describe the impact of the development gap on global wealth ($) distribution
Wealth Inequality - some rich, others poor.
North America + Europe: 70% of all wealth
Africa: 1.5% of all wealth
Describe the impact of the development gap on people's health
Health - differences in causes of death:
LICs - infectious diseases (e.g. malaria, HIV)
HICs - lifestyle diseases (e.g. obesity, lung cancer from smoking)
What word means the movement of people from LICs to HICs in search of a better standard of living?
Migration
What phrase means when a country buys more than it sells and so loses money?
Trade Deficit
Give 2 reasons birth rate falls in the DTM
1) Women more educated - get better jobs in cities - less time for children
2) Contraception (birth control) - women can choose when to have children
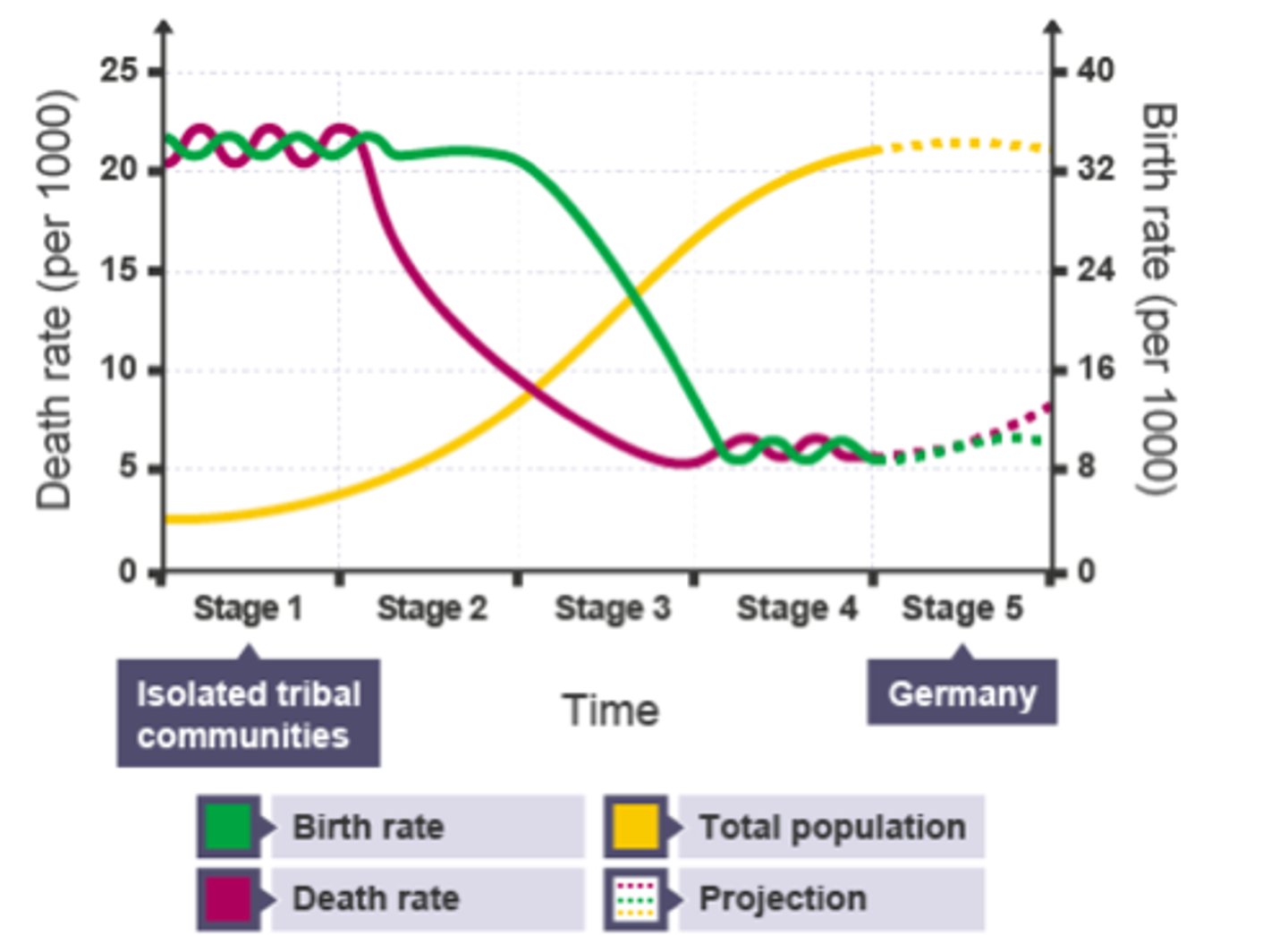
Give 1 reason death rate falls in the DTM
Improved healthcare
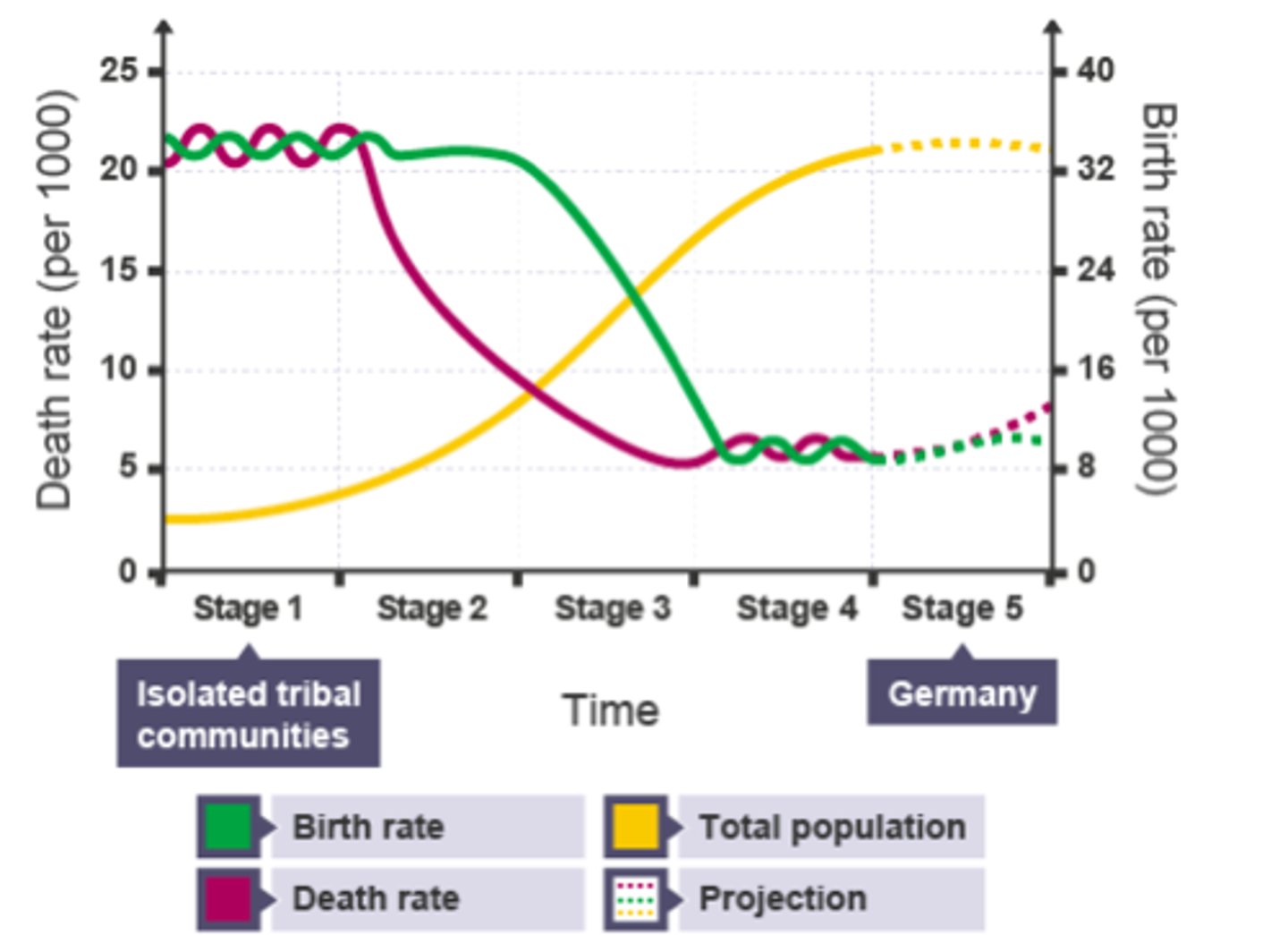
How is the Birth Rate in the DTM affected by urbanisation?
Falling birth rate in Stage 3 - women get better education + high-paid jobs in cities
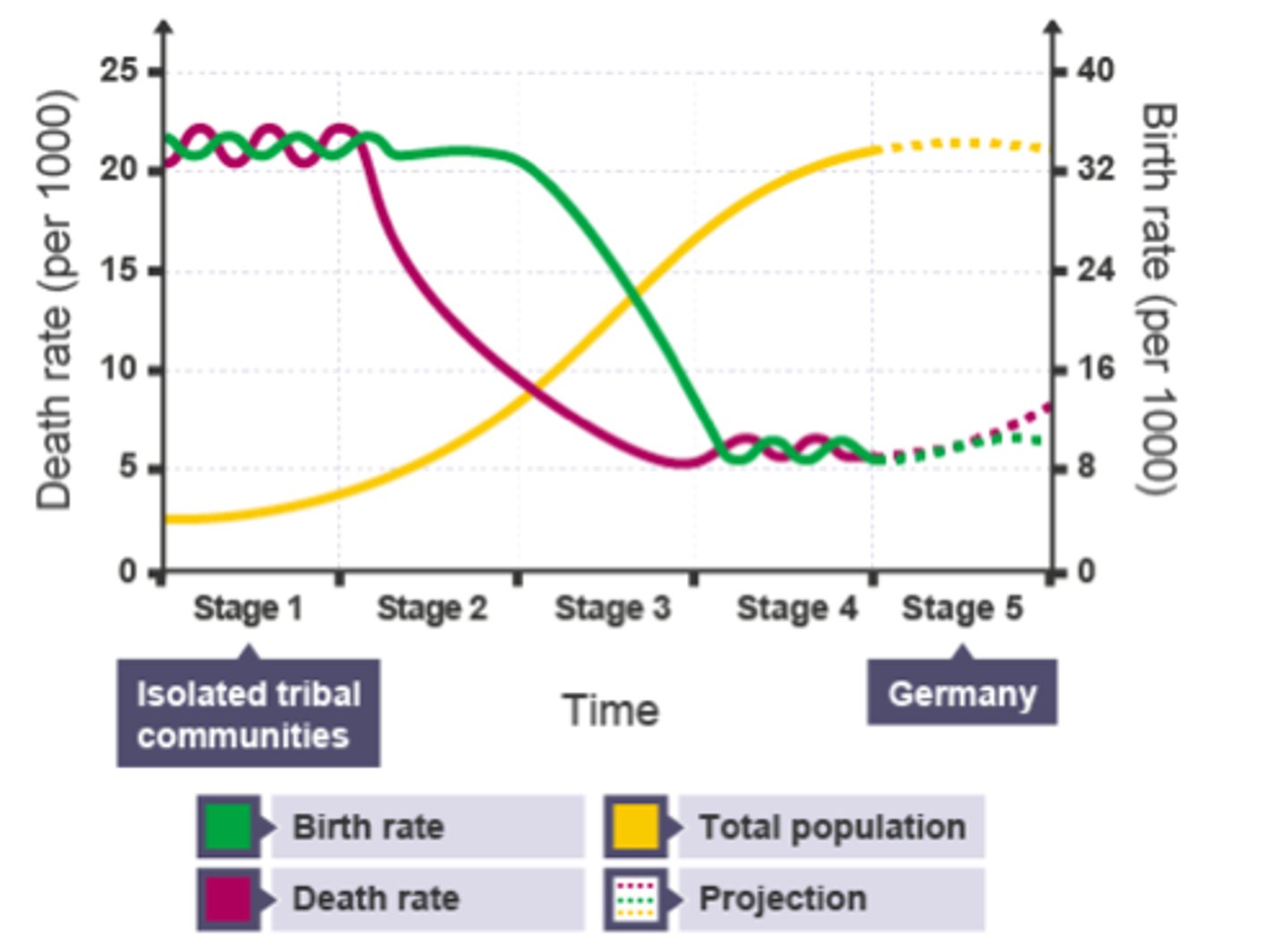
How is the Death Rate in the DTM affected by urbanisation?
Falling death rate in Stage 2/3 - better hospitals/ hygiene/ sanitation in cities = fewer diseases
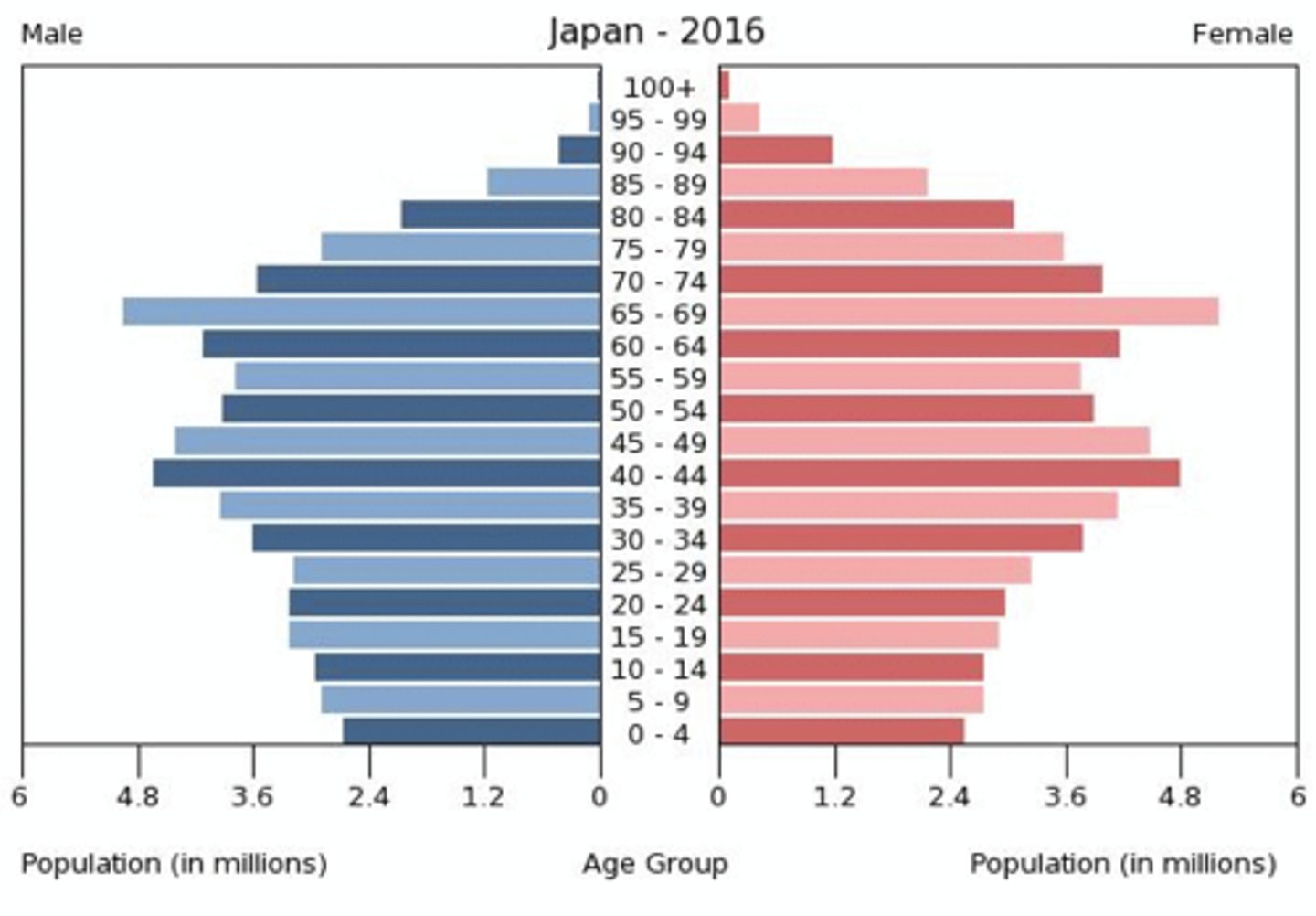
In what stage of the DTM is a top-heavy population pyramid? Give an example
Stage 5:
Japan,
Germany,
Italy
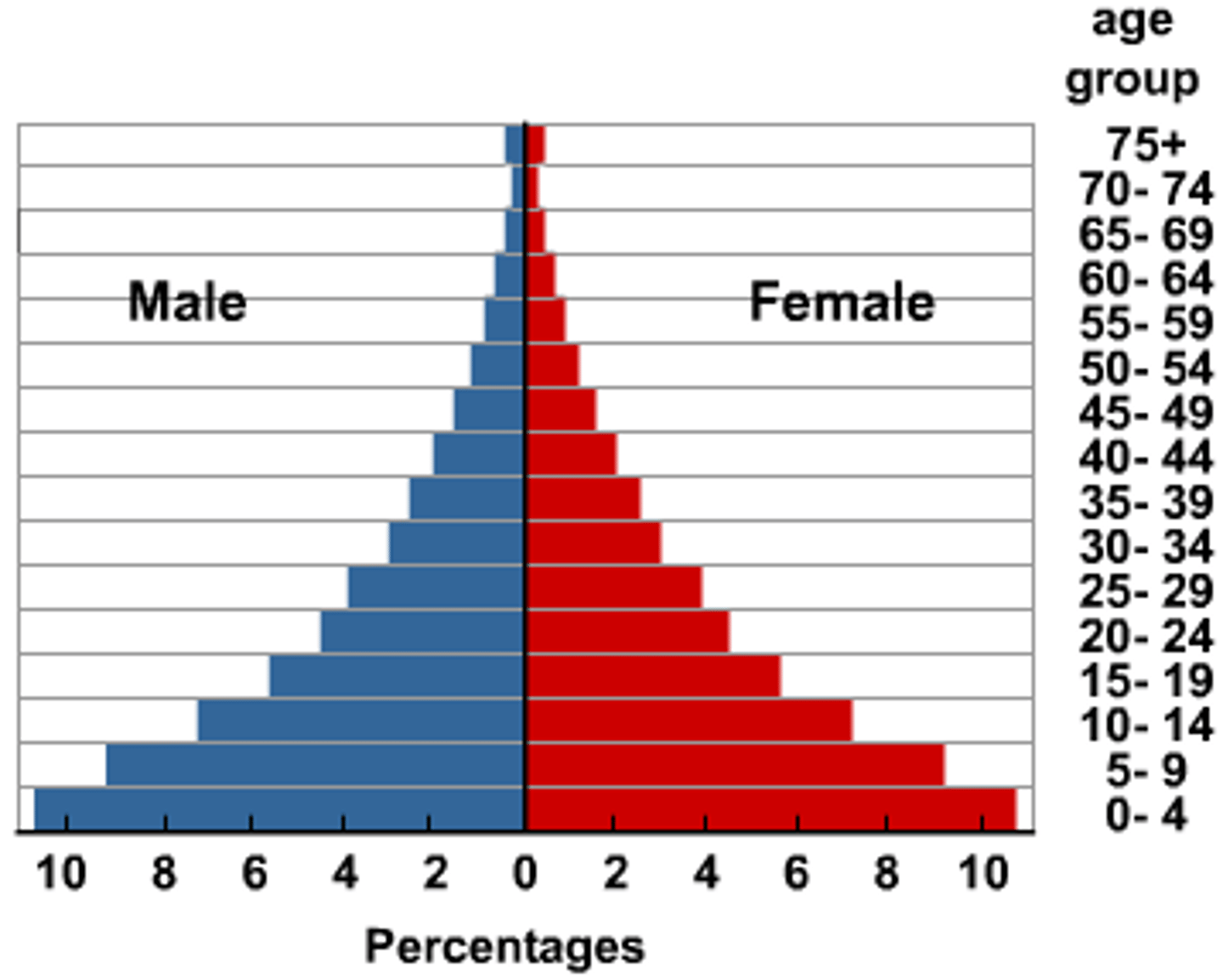
In what stage of the DTM is a country with a population pyramid that is wide at the bottom and narrow in the middle and top? Give 1 reason
Stage 1
Reason: High birth rate = wide bottom
High death rate = narrow top
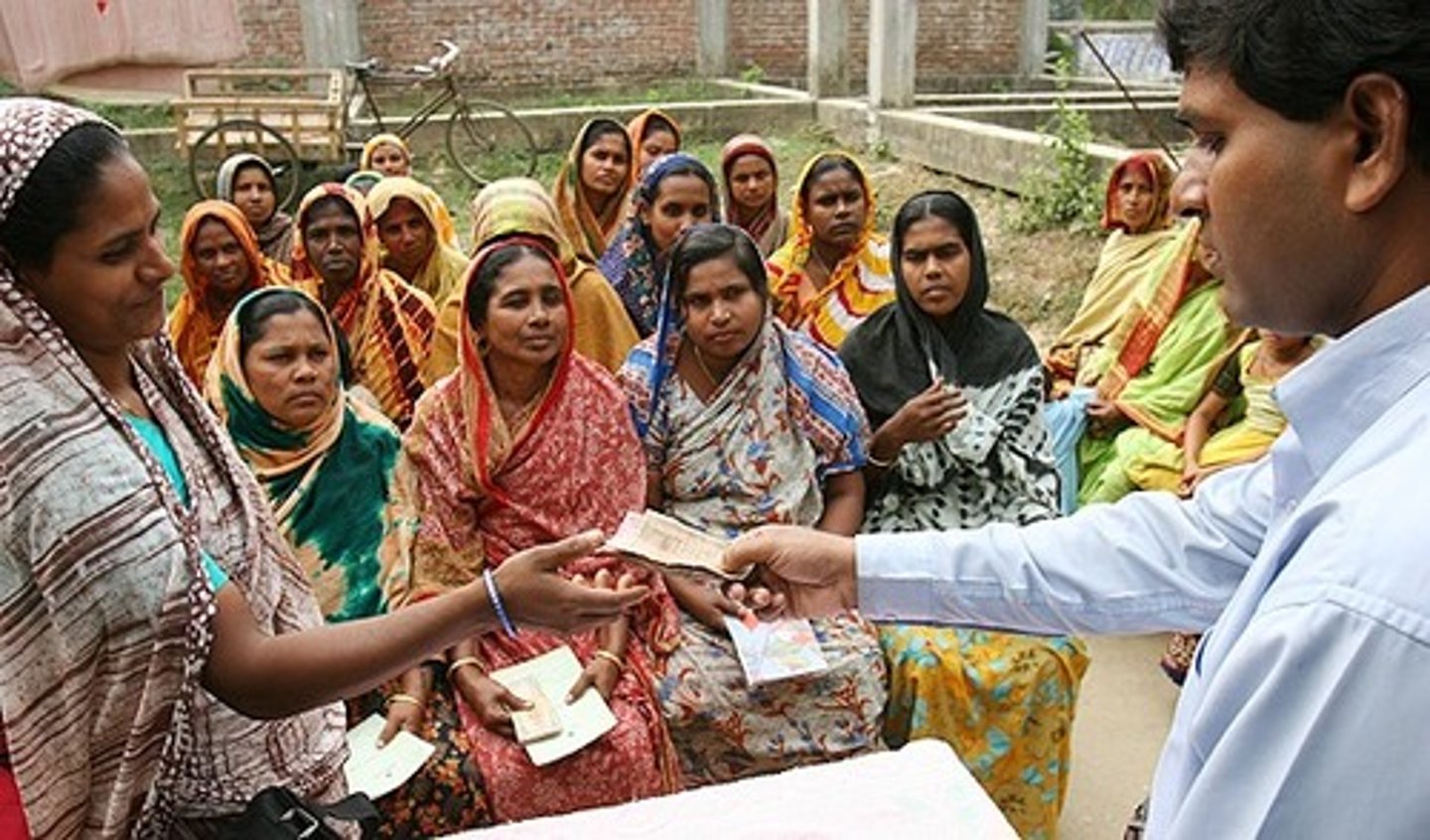
What are micro-finance loans? Give 1 way they help
Small loan given to poor people in LICs to help them start a business.
People are able to pay the loans back - no debt

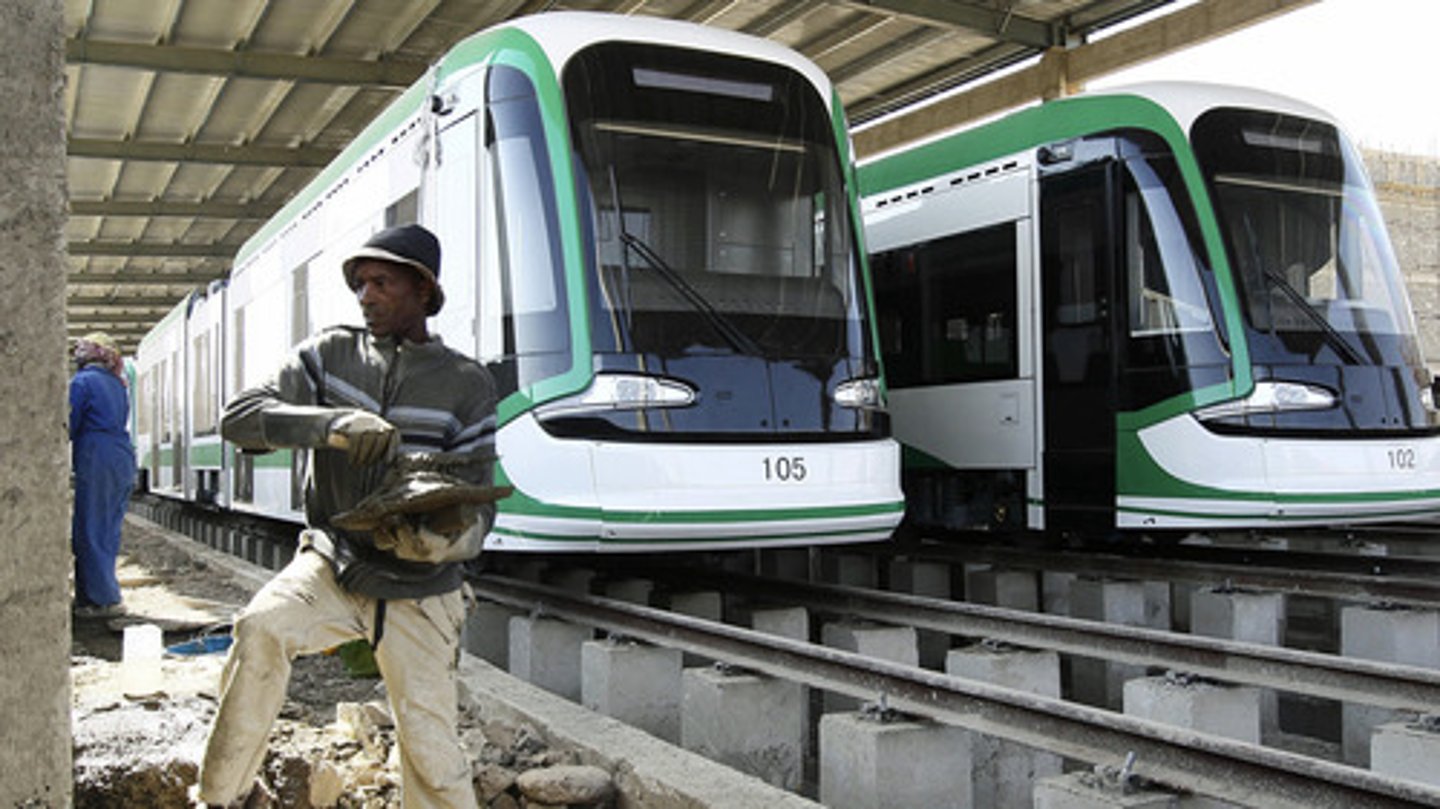
What is Foreign Direct Investment? Give an example
Money spent by one country in another on a project for profit. E.g. China invests in infrastructure in Ethiopia (Africa) as part of a deal to extract resources

Give 1 advantage and 1 disadvantage of international aid
Adv: Can provide emergency supplies after a natural disaster - e.g. Nepal, 2015
Disadv: Can be stolen/ wasted by corrupt governments
What is Fair Trade? What is 1 disadvantage?
When producers (farmers) in poor countries are given a fair price for their products.

Give 1 disadvantage of Fair Trade
Not enough money is given to people for a LIC to become a HIC - most profits still go to HICs
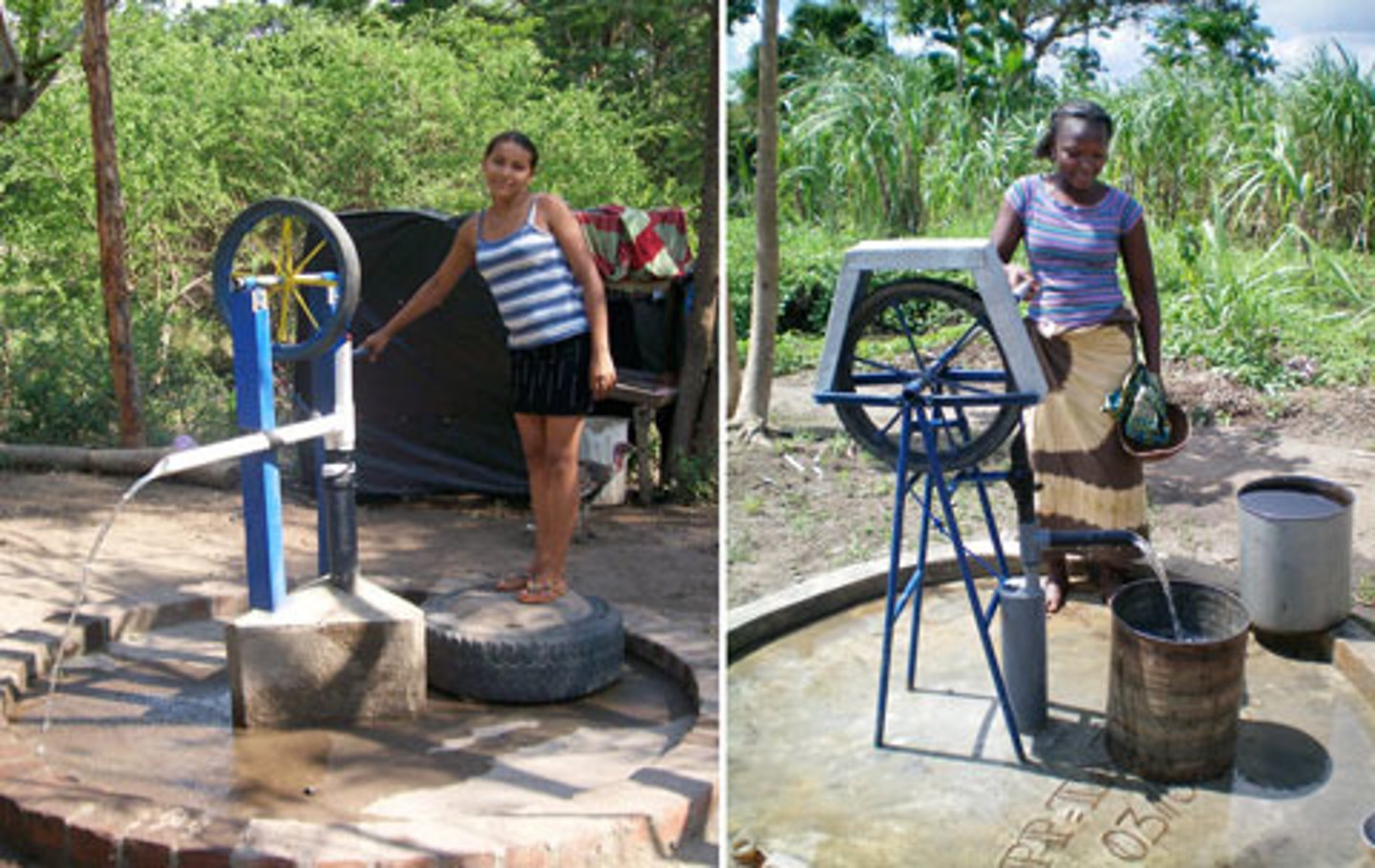
What is appropriate technology? Give an example.
Technology that is:
1) Cheap
2) Easy to build/ repair
3) Built using local materials/ labour
Bicycle water pump in Malawi, Africa

Name 1 type of aid that is effective in helping Nigeria. Give an example
Voluntary Aid (money given to charities).
It can improve healthcare in rural areas: ActionAid built rural medical clinic in Aduwan village - gave vaccines + education for women

Name 1 type of aid that is not effective in helping Nigeria. Give an examples
Bilateral aid - from one government to Nigeria's government.
UKAid spent by Nigerian government to improve navy, not on poorest people.
Give 2 advantages of tourism for Jamaica
1) More jobs - 200,000
2) Multiplier Effect - food for hotels grown by farmers - income used to improve farms, educate children, pay more taxes
Give 2 disadvantages of tourism for Jamaica
1) Inequality - only some parts of Jamaica receive government investment in services
2) Dependence - during hurricanes, unemployment rises due to lack of tourism - no income

What is the multiplier effect?
Happens when money/ resources put into something lead to a larger benefit for other people - e.g. government spending on factories = more jobs = better education/ health = more taxes = more government investment
Where is Nigeria? What is the largest city?
What type of country is Nigeria?
Where: West Africa
City: Lagos (South West)
Type: NEE
Name 2 ways the UK is improving transport infrastructure
1) Roads - Smart Motorways - less congestion
2) Ports - Liverpool2 - more international trade/ jobs
3) Airports - Heathrow 3rd runway - more tourism/trade
4) Railways - High Speed 2, Crossrail (underground) - better access to jobs
Describe an environmental disadvantage of TNCs in Nigeria
Environmental - Shell oil spills (600,000 barrels in 2008-9) - cause cancer + loss of crops and income in Ogoniland (South East)

Describe an economic disadvantage of TNCs in Nigeria
Economic - most of the profits leave Nigeria and go to TNC headquarters
Describe how DEPENDENCE on oil worsens corruption in Nigeria
1) Nigeria needs oil for income
2) Shell (TNC) extracts oil
3) Government DEPENDS on Shell for income
4) Shell can pollute/ take profits from oil without harsh consequences
Describe an economic advantage of TNCs in Nigeria
Economic - Shell creates 60,000 jobs. Unilever creates 1,600 jobs.

Describe a social advantage of TNCs in Nigeria
Social: Health - Unilever sells Knorr food supplement - gives iron - reduces anaemia (causes tiredness) among women

What is Nigeria's main export?
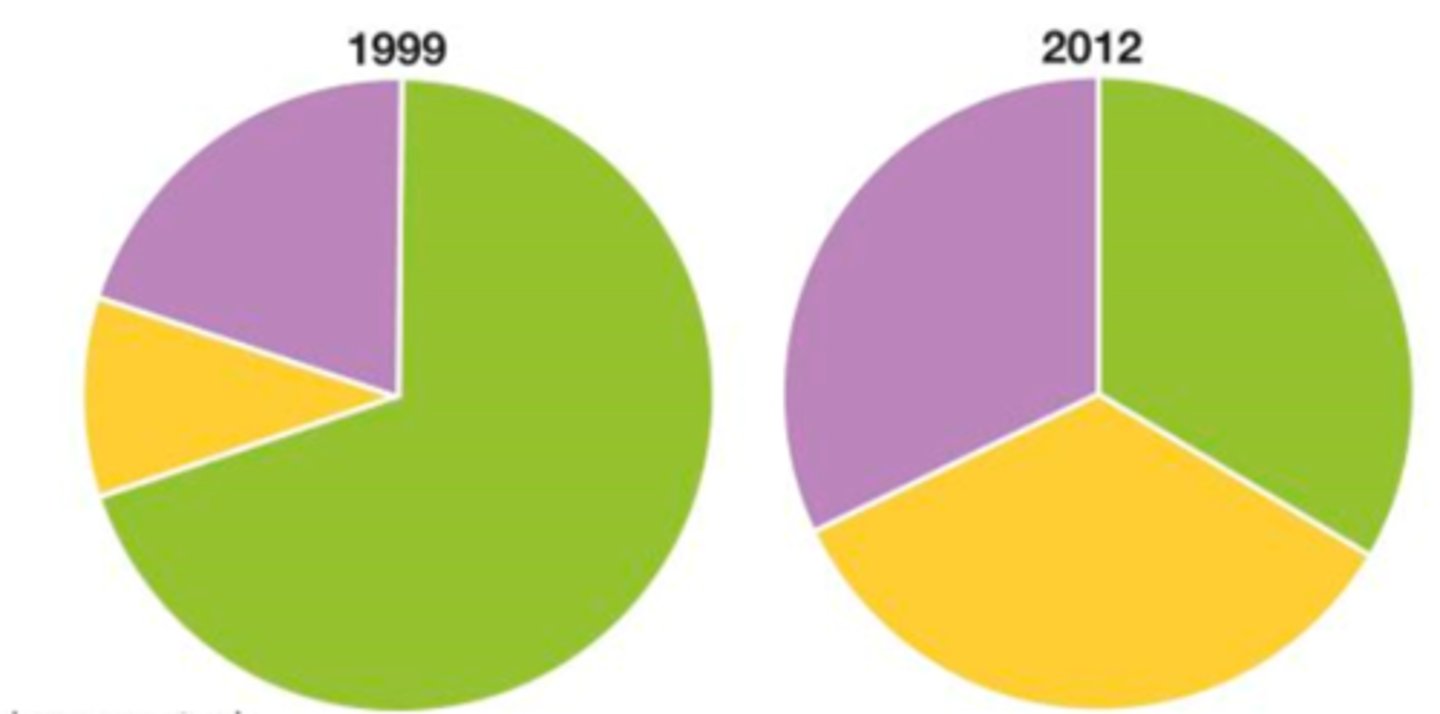
How has Nigeria's industrial structure changed?
Export: Oil
Change: From mostly primary to more secondary + tertiary jobs - almost balanced economy
Name 1 environmental impact of development in Nigeria
Deforestation: 75% of Nigeria's forest loss for farmland, housing, and cities
Name 1 positive effect of development on quality of life in Nigeria
Education: completion rate of secondary school DOUBLED from 25% to 50% since 1990
Describe how globalisation caused de-industrialisation in the UK
Globalisation: Competition from foreign companies (e.g. Volkswagen) = less profit for UK companies = loss of manufacturing jobs
Describe how privatisation caused de-industrialisation in the UK
Privatisation: Government sold manufacturing companies so if they were not profitable, they went bankrupt
Give 3 features of the UK's post-industrial economy
1) Research: £3 bn per year (universities)
2) Finance: banks - £600 bn per year
3) IT: 1.5 million computer-based jobs

Name 2 reasons Science Parks are successful in the UK
1) Increased demand for high-tech products
2) Location: outskirts of university cities + near transport links

Name 1 environmental impact of industry in the UK and 1 solution
Impact: Increased air pollution from factories, transport.
Solution: Clean Air Act (1993) - bans release of harmful gases + vehicles must be modern/ clean
Describe one way manufacturing companies in the UK have reduced:
a) air pollution
b) waste pollution
a) Jaguar factory invested in solar panels = 30% of its electricity
b) Jaguar recycles 90% of its waste
Outline how de-industrialisation caused the North/South Divide in the UK
1) North was mostly mining (coal) and manufacturing (cars/ ships). South mostly services.
2) De-industrialisation LED TO rise of unemployment in north. TERTIARY sector INCOMES rose in the south
State 2 effects of the North/South Divide
1) Health Inequality: Life expectancy 5 years higher in the south
2) Economic Inequality: Unemployment lower in south than north
Describe how the Lancashire Enterprise Partnership can reduce the North/South Divide
The Lancashire Enterprise Partnership means investment in 3 things:
1) reduced business tax = more profit
2) improve education = more skills
3) infrastructure = easier trade
Describe how devolution can reduce the North/South Divide
It gives cities in the North more power to solve problems like lack of education or poor infrastructure
Name 1 advantage of Fair Trade
Producers (farmers in LICs) are given a good income to improve quality of life

Name 2 TNCs in Nigeria
Shell: extracts and refines oil
Unilever: manufactures domestic (home) products
How many people pass through Heathrow Airport every year?
80 million

What is the UK's largest trade partner?
Germany
Name 2 companies in Cambridge Science Park
AstraZeneca - medicines
ARM - computer chips

Give 1 way industrialisation helps a country develop
Higher incomes = more taxes = more government
investment in education and healthcare

By how much has the % of people with access to clean water in Nigeria increased since 1990?
46% (1990) - 64% (2018)

Give 1 reason aid can be ineffective in Nigeria
Bilateral Aid (to government)
Money can be stolen/ wasted by corrupt governments - e.g. Nigeria spent it on navy ships
Name 3 laws created by the EU that affect the UK
1) Justice: Human Rights Act, 1990. Freedom from discrimination
2) Economy: Common Agricultural Policy - subsidy (extra money) given by EU to UK farmers
3) Environment: 20-20-20 Climate Change Law. 20% less CO2 by 2020.
Name 2 ways the UK benefits from the Commonwealth (former colonies)
1) Increased trade - common language so trade 20% cheaper
2) Business investments during Commonwealth Games business meetings
Name an example of the UK's communication and transport links with the world
1) Comm: Arctic Fibre - undersea data cable to transfer internet with Japan
2) Transport: Eurotunnel - trade, migration, tourism with EU - 30 million passengers, 55 million tonnes of goods per year
Name an example of the UK's cultural and trade links with the world
1) Culture: UK EXPORTS £1.5 billion worth of TV and films every year (e.g. Doctor Who).
2) Trade: UK EXPORTS £7.4 bn of cars per year. Imports £4.5 bn of aeroplanes from USA.