Class 8- Lipids pt 1
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 5
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
what do lipids include
triglycerides, phospholipids, sterols
why are fats important?
Building blocks for cell membranes
Padding protects your organs
Insulation for extreme temps
Fat reserve for energy in case of starvation situation
Essential Fatty Acids (omega-3 and omega-6)
Raw material for important compounds (hormones and neurons)
Carrier of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E and K)
In foods: satiety, taste, energy dense
where are the 3 lipids found/
1. Triglycerides (or triacylglycerols)
▫ ~95% of all lipids found in food
and the human body
2. Phospholipids
▫ In cell membranes and lecithin
3. Sterols
▫ Cholesterol, phytosterols
What is triglyceride made out of, how many types of fatty acids
1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids
there are : Saturated, unsaturated, monounsaturated, polyunsaturated FATTY ACIDS
what is the run for forming a triglyceride?
3 fatty acids attach to glycerol in condensation rxn
what is form of Fatty Acids (FA)
org, acids
chains of C and H
carboxylic acid @ one end, methyl (CH3) @ other end
what are different lengths of carbon chains in FA? where are they found?
Very long-chain (20–24 C) —> fatty fish
Long-chain (14–18 C) —> most abundant, meat,
fish, vegetable oils
Medium-chain (6–12 C) —> dairy products
Short-chain (4 C or fewer) —> dairy products
Do triglycerides have 3 identical
FA’s or could they have FA’s of
varying length?
Could all be identical or could be varying
Chain lengths most often tend to vary
A long chain triglyceride might have 16C and 18 C and 20C
why do carbon chains tend to have even # of C atoms
Natural fatty acids found in plants and animals
are typically composed of only even numbers of
carbon atoms
BUT Bacteria can synthesize odd-numbered chains
which FA are produced by microbiota and how?
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as butyric
acid/butyrate are the main metabolites produced
by the microbiota in the large intestine through the
anaerobic fermentation of indigestible
polysaccharides such as dietary fiber and resistant
starch.
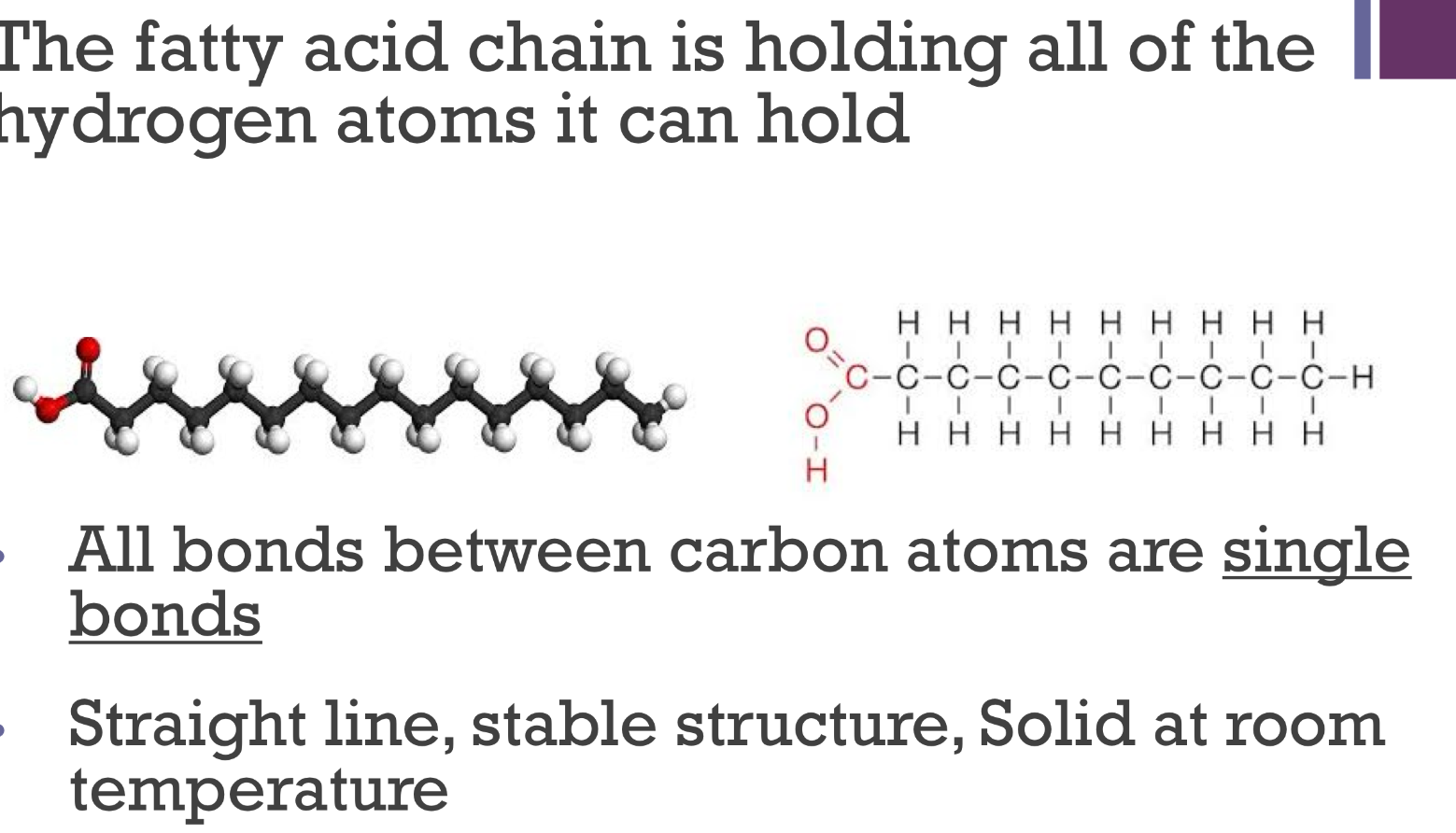
saturated fats are …
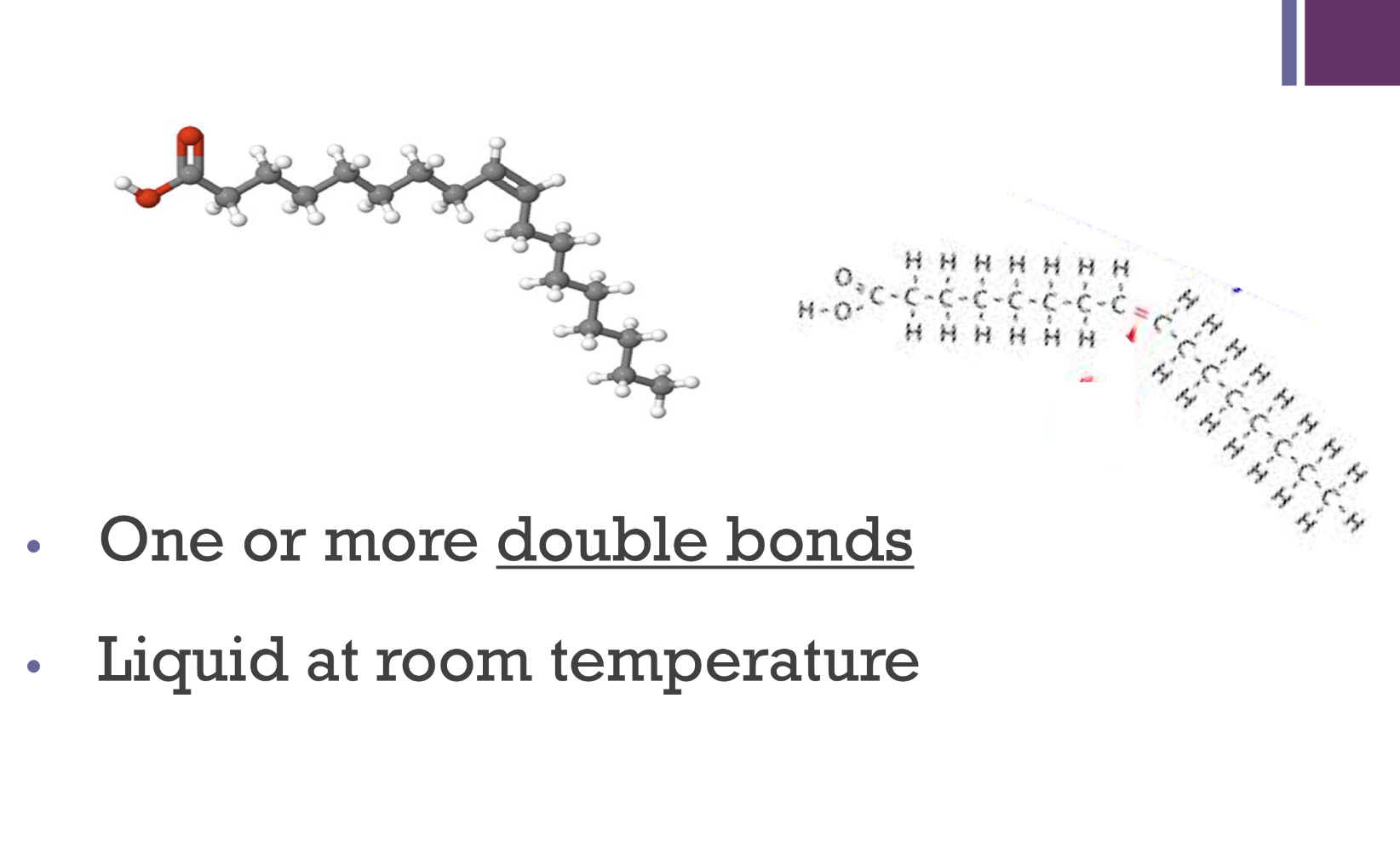
unsaturated fats are…
what are the three ways FA can differ?
Length (from 4 to 22 carbon atoms)
Degree of saturation of carbon atoms
Location of double bond between carbon atom
saturated
monounsaturated (1 DB)
polyunsaturated ( 2+ DBs)
what are the 4 18-Carbon FA?
steric acid (sat), oleic acid (monounsat), linoleic acid (polyunsat), linolenic acid (polyunsat)
what are the 2 essential FA?
Linoleic acid (LA) —> omega 6
alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) —> omega 3
essential bc they can’t be synthesized by body
what are some functions of essential FA
Both LINOLEIC and LINOLENIC can:
Provide raw material for eicosanoids.
Serve as structural and functional parts of cell membranes.Contribute lipids to the brain and nerves.
Promote normal growth and vision.
Assist in gene regulation.
Maintain outer structures of the skin, thus protecting against water loss.
Help regulate genetic activities affecting metabolism.
Support immune cell functions.
what are the two families of essential FA?
omega 3 and omega 6
what are the two important acids coming from omega 6 pathway vs omega 3 pathway?
omega 6:
LINOLEIC (LA)
ARANCHIDONIC (AA)
omega 3:
EICOSAPENTAENOIC (EPA)
DOCOSAHEXANOIC (DHA)
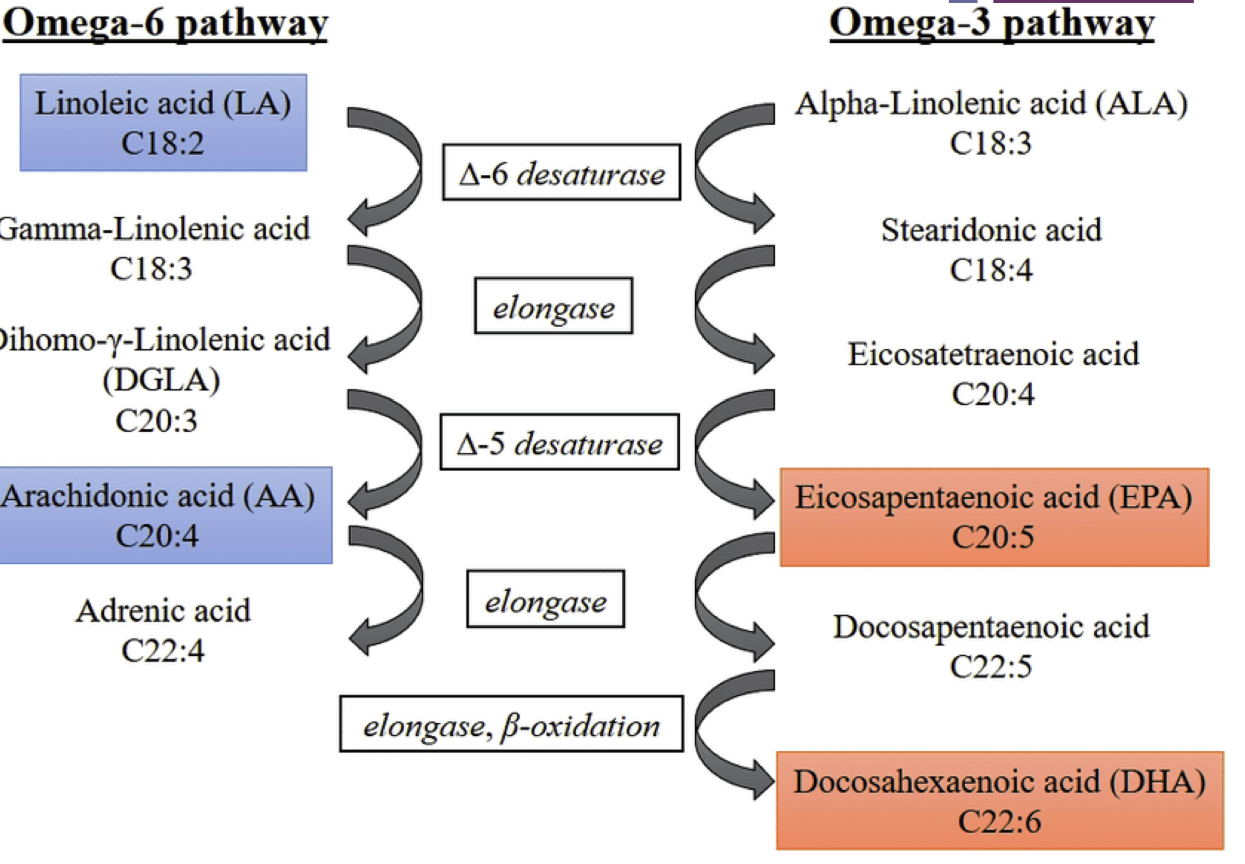
why is it recommended to consume foods rich in EPA and DHA?
eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA)
and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) CAN be synthesized from ALA, but due to low conversion efficiency eating enough/supplementation is recommended
what are omega 3 eicosanoids cardiovascular benefits , how many grams of fish per week is recommended?
Anti-inflammatory
Lower blood pressure through vaso-dilation
(vessels are more relaxed and wider—> better blood flow)
Reduce or prevent unwanted blood clot formation
Protect against irregular heartbeat
Reduce inflammation in small vessels and
capillaries
350-425 g /fish per week
what are risks of fish oil supplements?
Often made from fish skins & liver and may
have accumulated toxic conc. of:
Pesticides
Heavy metals, such as mercury
Other industrial contaminants
why is it recommended to eat mono/poly unsaturated fat?
Unsaturated fats:
may lower the “bad” LDL
cholesterol and reduce risk of cardiovascular
disease
keep “good” HDL cholesterol high
what were the healthy dietary fats provided in the mediterranean diet study?
In the Prevención con Dieta Mediterránea
(PREDIMED) trial, 7447 ppl consumed Mediterranean diet supplemented with
extra-virgin olive oil (56 ml/day), a Mediterranean
diet supplemented with mixed nuts (30 g/day; 15gof walnuts and 7.5 g of almonds and 7.5 g of
hazelnuts) or a control diet reduced in dietary fat.
RESULTS= after 4.8 years, consumption of
a Mediterranean diet supplemented with either
extra-virgin olive oil or nuts resulted in a 30%
reduction in risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death.
why are nuts so healthy?
Fibre, protein
Phytochemicals that act as antioxidants
Plant sterols
milk contains sat. fat. why is it still deemed good?
dairy is Source of Short chain FA’s and medium chain FA’swhich are beneficial.
due to the complex nature of dairy
fats, the presence of beneficial nutrients like
calcium, potassium and conjugated linoleic acid
(CLA) is good
difference between cis/trans fats
cis= H on same plan, usually unsat. fats comes from plants and contain cis unsaturated fatty acids
the cis DB causes kink which prevents FA from packing tightly —> causing liquid @ room temp
trans= H on app sides at a certain point on chain, used to improve shelf life and texture
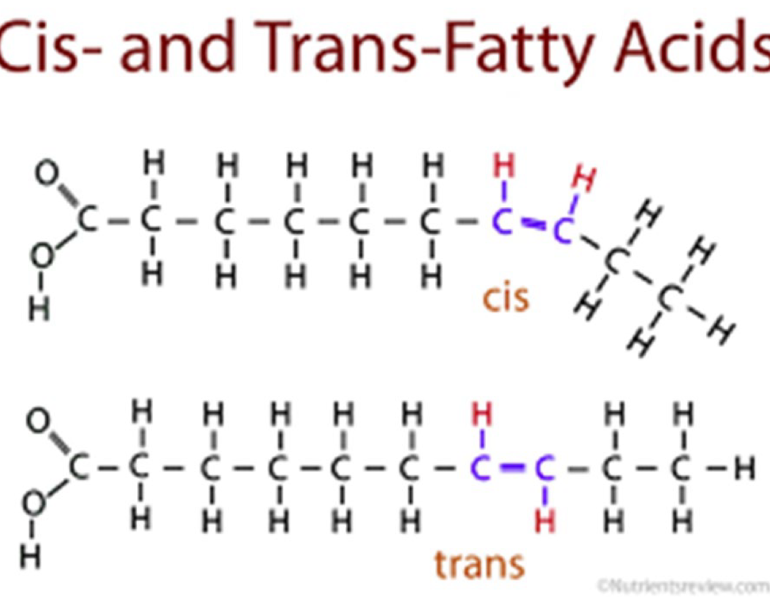
why are trans fats banned? why was hydrogenation even a thing?
Mainly found in highly processed foods
Pose risks to heart health: Raise “bad” LDL cholesterol and Lower “good” HDL cholesterol :(
Produces inflammation in the body
hydrogenation adds H to unsaturated fats, makes liquid more solid @ room temp, increases shelf life
what FA have lowest oxidative stability (and what does this mean?)
PUFA bc of DBs, saturated fats are most stable
all fats will spoil when exposed to O2
oxidation = process of combining with oxygen and losing e-
what does ‘refined’ vs ‘unrefined’ mean. what is EVOO?
after extraction, oils can be either packaged right away or refines/processed
Extra virgin” olive oil (EVOO): most natural
version from first press of olive, cold-pressed (not
heated)
what are phospholipids? are they essential ?
a glycerol + 2 FA + Phosphorus contains molecule
form cell membranes
are considered non-essential
phospholipid vs triglyceride form
phospholipids are similar to a triglyceride BUT contains only two fatty acids.Third position is occupied by a phosphate group and sometimes a functional group attached to the phosphate
what are sterols? what are some functions?
large lipid consisting of interconnected rings of
carbon atoms, + side chains of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
Functions=
• Naturally found in plants (phytosterols) and animal based products (cholesterol)
• Subgroup of steroids -Sex hormones (estrogen,
testosterone)
what is cholesterol? what 3 common synthesis pathways is it involved with?
structural component of cell membrane
precursor for:
1.making bile in gallbladder
2. steroid hormone biosynthesis (test, estrogen, progesterone)
3. vit. d syntheis