Bot-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 4: Bryophytes
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
bryophytes
a moss, liverwort, or hornwort; a nonvascular plant that inhabits the land but lacks many of the terrestrial adaptations of vascular plants
gametophyte (haploid)
independent and dominant photosynthetic generation
sporophyte (diploid)
non-photosynthetic and dependent upon the gametophyte
1-3 cm; 15-30 cm
most bryophytes are _-_ cm in height but few species may grow from __-__ cm
thick waxy cuticle
protection of gametophytes of most bryophytes from dessication
dessication
drying out/dehydration
rhizoids
a thin, rootlike, unicellular/multicellular filament structure that anchors bryophytes to the soil
diffusion; capillary action; cytoplasmic streaming
means of substance transport due to lack of vascular tissues
diffusion
the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
capillary action
tendency of water to rise in a thin tube
cytoplasmic streaming
circular flow of cytoplasm, involving myosin and actin filaments, that speeds the distribution of materials within cells
Class Hepaticae (liverworts)
gametophyte may be thallose or leafy; sporophyte is compact with or without seta
thallose
ribbon-like
seta
the stalk supporting the capsule of a moss or liverwort
Marchantia sp.
liverwort; forked thallus; distributed along the thallus are crescent-shaped gemmae that produce the asexual spores
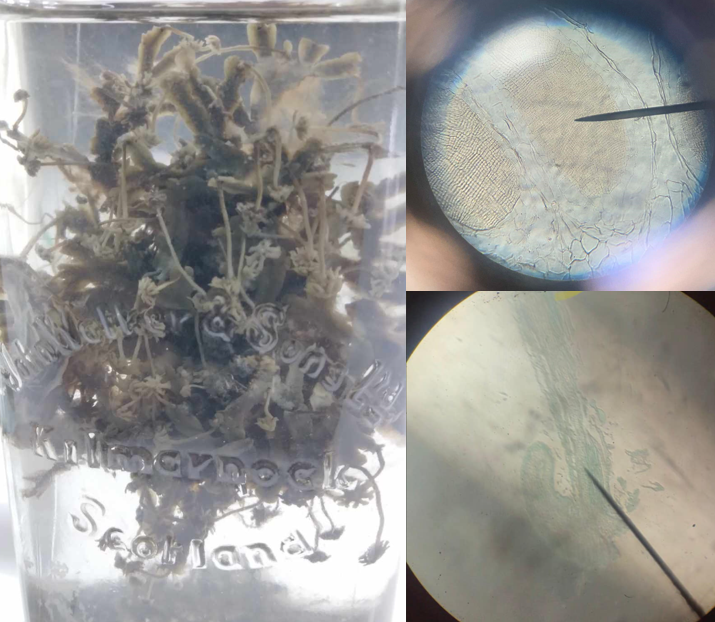
Marchantia sp. (archegonium)
female sex organ of Marchantia sp.; flask-shaped and hang down from the ventral tissue of the disc; the elongated part is the neck and globular base is the venter which contains the egg
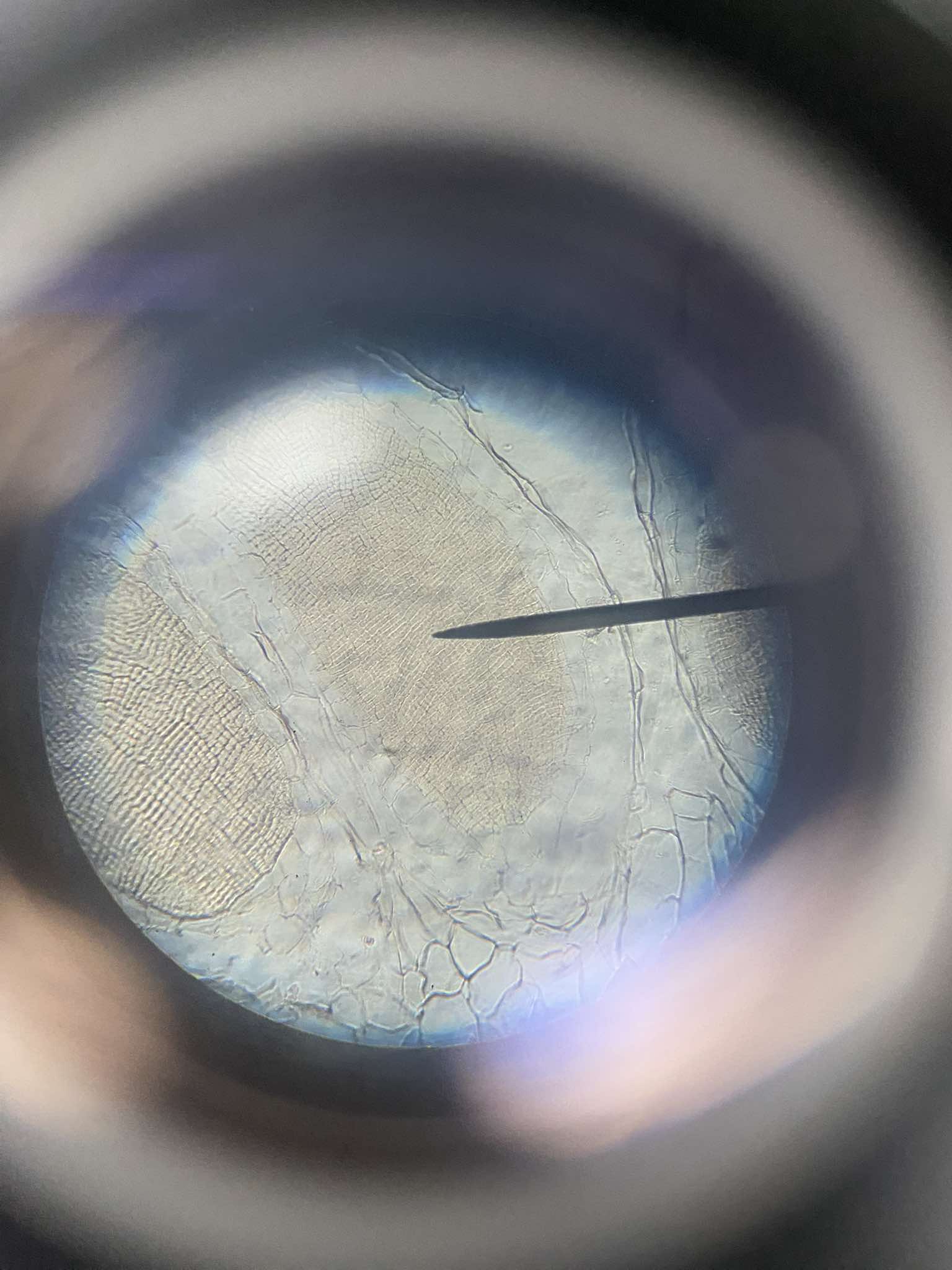
Marchantia sp. (antheridium)
male sex organ of Marchantia sp.; found in the disc and is structurally elongated and covered by a single layered sterile jacket; inside are large numbers of androcytes that produce uninucleate biflagellate antherozoid
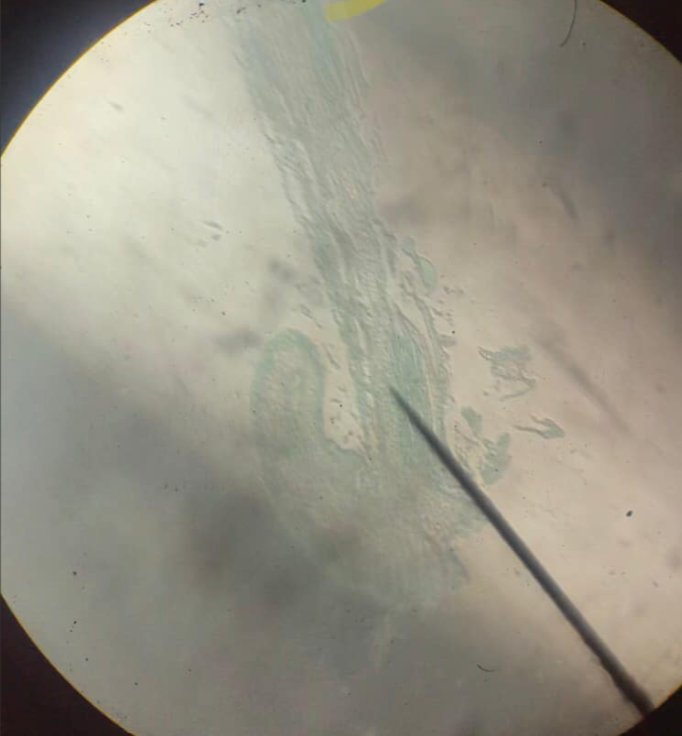
gemmae
small multi-cellular reproductive structure of liverworts
gametangiophores
special stalked umbrella-like structures; has two types: archaegoniophore, which bears the archaegonia, and the antheridiophore, which bears the antheridia
Class Musci (Mosses)
mosses
Mnium sp.
having a microphyllous feature and spiral arrangement of leaves

moss protonema
a thread-like chain of cells that forms the earliest stage of development of the gametophyte in the life cycle of mosses
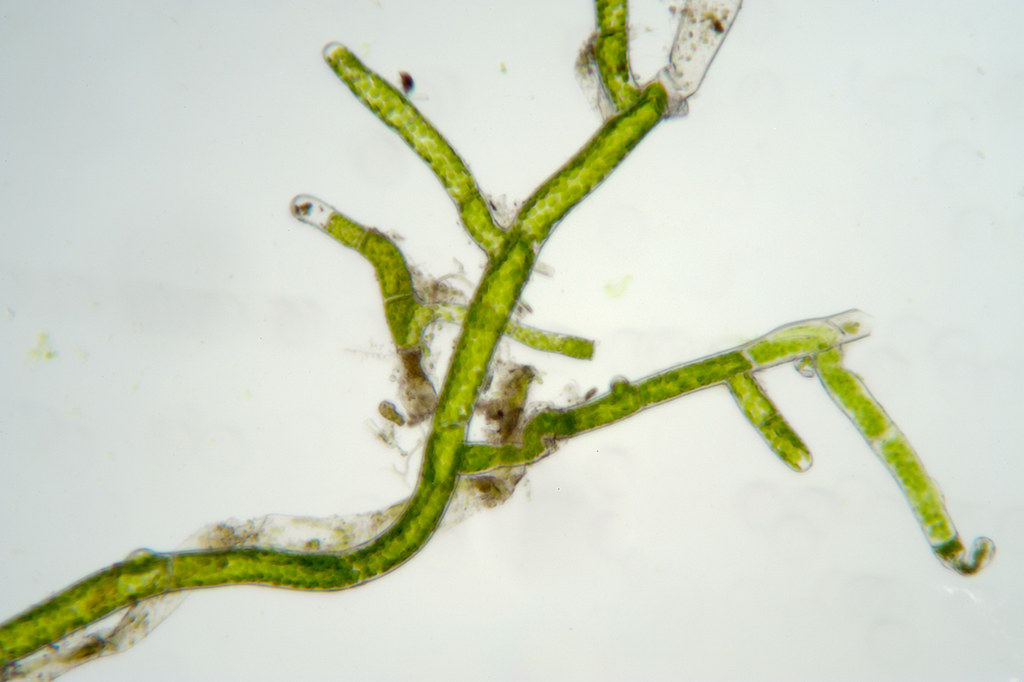

moss gametophyte
leafy portion; leaves are sessile and spirally-arranged along a stem-like structure in three rows; leaf may have costa (midrib)
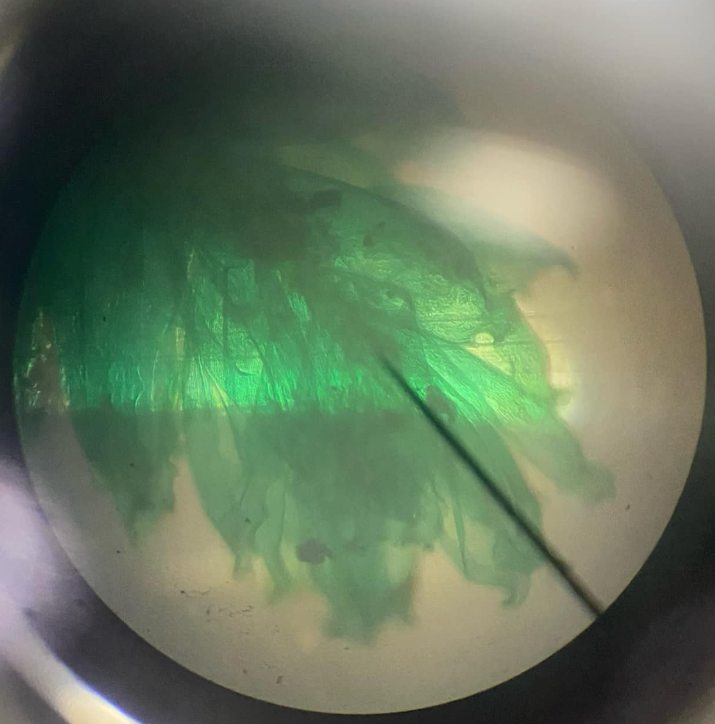
moss sporophyte
typically made of a stalk (seta) which bears at its apex, the capsule; capsule contains the sporangium that prodcues the spores; at the mouth of the capsule are teeth-like structures known as the peristome, which functions for the release of the spores; calyptra serves as covering of the mouth
peristome
teeth-like structures which function for the release of the spores
calyptra
serves as covering of the mouth of the capsule of a moss sporophyte
Class Anthocerotae (Hornwort)
a group of non-vascular Embryophytes constituting the division Anthocerotophyta; the common name refers to the elongated horn-like structure, which is the sporophyte.