UNIT 4 BIOLOGY TEST
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
energy
the ability to do work
kinetic energy
energy of motion used for cellular work
potential energy
stored energy in the bonds of molecules
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is not created nor destroyed, but it can change form
Second Law of Thermodynamics
With every conversion of energy, there is an increase in entropy (less usable energy available)
Car and Cell Analogy of First Law
chemical energy in gasoline is converted into mechanical energy that moves the wheels and chemical energy in glucose is converted into energy used for cellular work
Car and Cell Analogy of Second Law
only 25% of the energy stored in the bonds of gasoline are converted into the kinetic energy of the car’s movement and much of the energy stored in the bonds of glucose is released as waste (heat+ carbon dioxide)
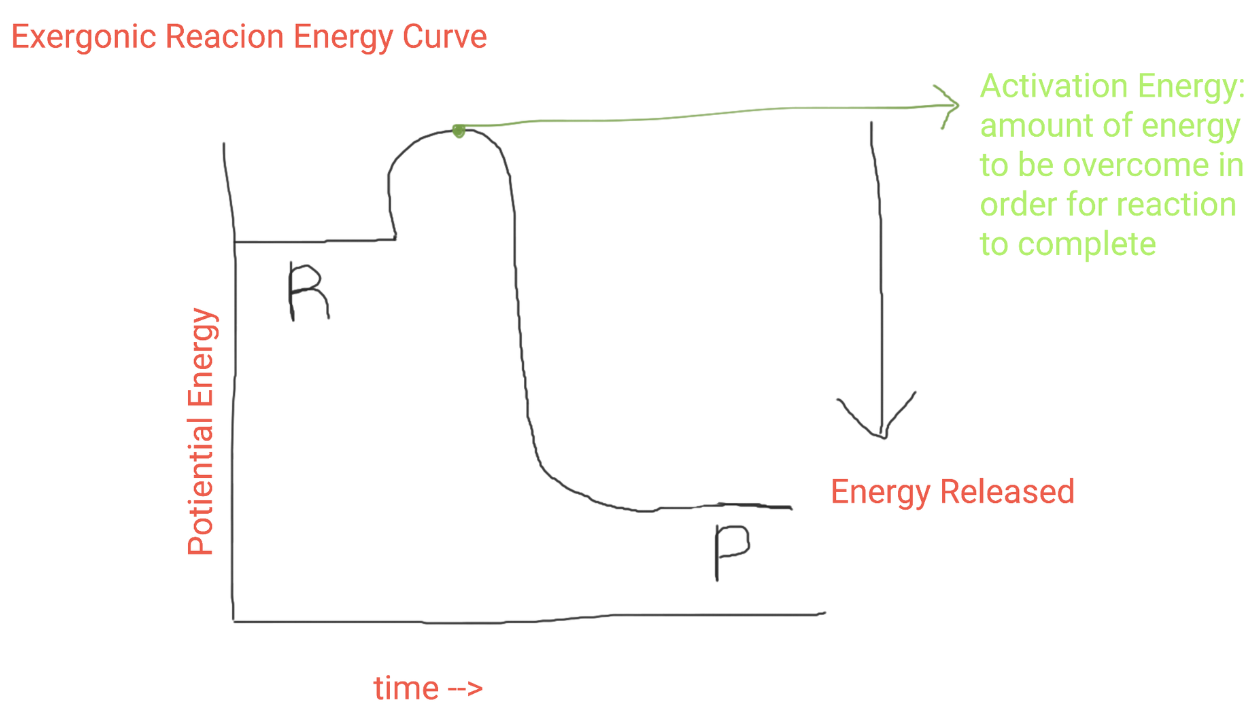
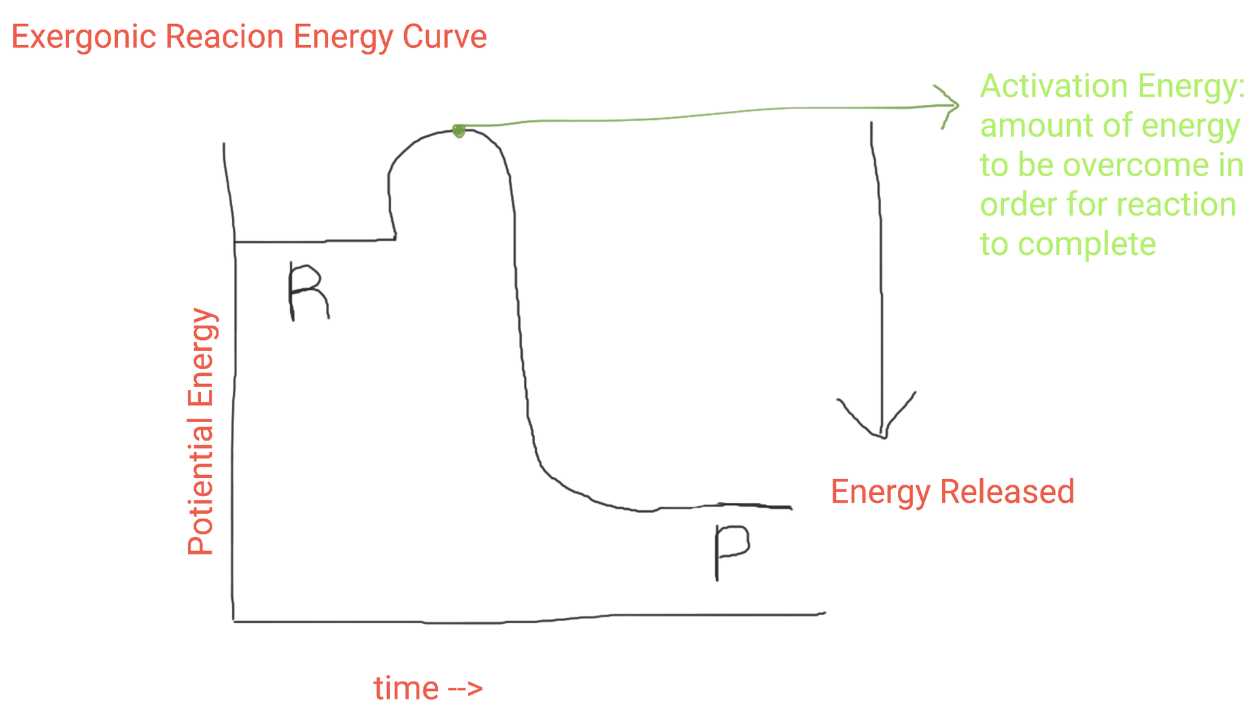
Exergonic Reactions
reactions where reactants have more total energy than the products resulting in broken bonds and a net release of energy (less reactants than products)
Endergonic Reactions
products of a reaction have more total energy than the reactant resulting in an input of energy and the form of bonds (more reactants than products)
Exergonic Reaction Graph
Endergonic Reaction Graph
competitive inhibition
when a substrate molecule is prevented from binding to the active site of an enzyme
Non-competitive (allosteric) Inhibition
something else that changes the enzyme so the active site doesn’t work
Purpose of non-competitive inhibition
To prevent an overabundance of molecules in the cell to maintain homeostasis
Feedback Loops
pathway for building or breaking molecules that can involve many steps, which may require several enzymes
How do enzymes denature
Change in temperature, pH, and ion concentration
Reactions will happen faster with
More substrates, more enzymes, and higher temperatures
co-enzyme
organic molecule which helps the enzyme react
examples of co-enzymes
Vitamins
cofactor
irons which helps the enzyme react
examples of cofactors
Magnesium, Iron, Zinc
metabolism
all of the chemical processes that occur within a living organism in order to maintain life
catabolic reaction
chemical reaction that results in the breakdown of large molecules into smaller-sized molecules (exergonic)
anabolic reaction
chemical reaction that absorb energy and build bigger molecules from smaller ones (endergonic)
denaturation
loss of shape and function
aerobic respiration steps
glycolysis, Krebs cycle, electron transport chain
glycolysis
the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy, and two molecules of pyruvate, ATP, NADH and water