B9: Respiration
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What do organisms need energy for?
Movement
Keeping warm
Chemical reactions to build larger molecules
How is the energy we need supplied?
Cellular respiration
What type of reaction is respiration and why?
Exothermic
Releases energy
When does respiration take place?
Continually in all living cells
Cellular respiration
An exothermic reaction which is continuously occurring in living cells
What does the energy transferred from respiration supply energy for?
Living processes
What does respiration do?
Transfer energy
2 types of respiration
Aerobic
Anaerobic
Word equation for aerobic respiration
Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water

How much energy does aerobic respiration release and why?
Lots
Glucose molecule fully oxidised
Symbol equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
When do cells carry out aerobic respiration
When there is O2
When does anaerobic respiration occur?
When there isn’t enough O2
Where does anaerobic respiration occur?
In muscles
In plant + yeast cells
What do muscle cells need lots of energy for?
Contraction
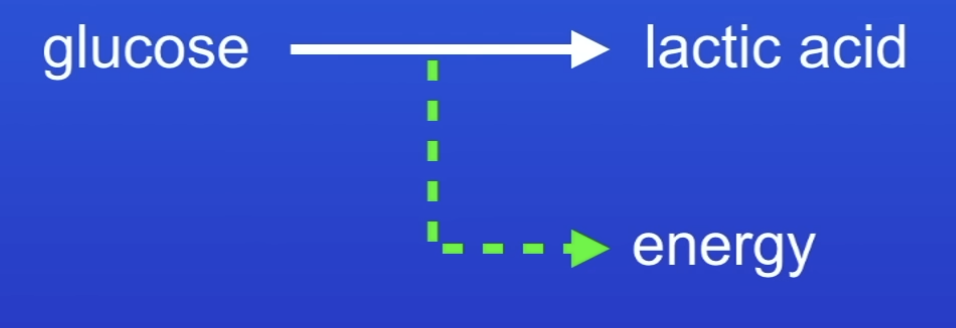
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in muscles
Glucose → lactic acid
How much energy does anaerobic respiration release and why?
Much less than aerobic
Oxidation of glucose in incomplete
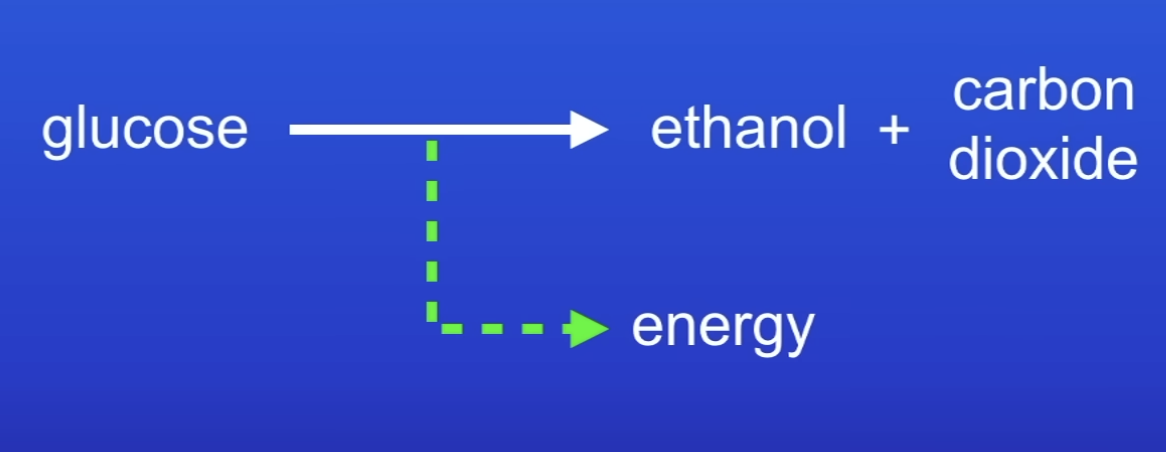
Word equation for anaerobic respiration in plant + yeast cells
glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide
Fermentation
Anaerobic respiration in yeast cells
What is anaerobic respiration of yeast (fermentation) economically important for?
The manufacture of:
Bread
Alcoholic drinks
Type in alcohol produced from the fermentation of yeast
Ethanol
What product of fermentation is used to make bread and how?
CO2 creates bubbles in dough → causes bread to rise
Does anaerobic or aerobic respiration transfer more energy?
Aerobic
When we are relaxing do we need lots of energy- why or why not?
No, need little- we aren’t moving
Does our body need lots or little energy during exercise?
Lots- for muscle contraction
When the body needs lots of energy eg for exercise / muscle contraction, what increases?
Aerobic respiration
When aerobic respiration increases, what do body cells need?
More O2
During exercise what does the human body react to?
The increased demand for energy
To provide extra O2 for contraction, what happens?
Breathing rate increases
Breathing volume increases
Heart rate increases
Why does breathing rate + breathing volume increase during exercise?
To supply muscles with more oxygenated blood
More oxygen enters BS
Why does heart rate increase during exercise?
To pump oxygenated blood around th ebody
When exercising hard, what happens if insufficient oxygen is supplied to muscles?
Anaerobic respiration takes place in muscles
What does the incomplete oxidation of glucose in anaerobic respiration lead to?
Build up of lactic acid
Creates O2 debt
What does lactic acid cause during long periods of vigorous activity?
Muscles become fatigued
What does muscle fatigue cause?
Muscles stop contracting efficiently
How does the body recover from muscle fatigue?
By removing lactic acid from muscles
Oxygen debt
The amount of extra O2 the body needs after exercise to react with the accumulated lactic acid + remove it from cells
How does the body deal with the accumulated lactic acid?
Blood flowing thru the muscles transports the lactic acid to the liver
In liver, it’s converted back into glucose in a series of chemical reactions
What does reacting with accumulated lactic acid + removing it from cells need?
O2
Why do people continue breathing rapidly for sometime after finishing exercise
To supply the extra oxygen needed to pay off the oxygen debt
During exercise, your cells need more energy for respiration.
True or false?
False
During exercise, your cells need more energy FROM respiration
Causes of muscle fatigue
Anaerobic respiration
Build up of lactic acid → oxygen debt
What creates the oxygen debt?
Removing lactic acid from muscles requires oxygen → oxygen debt
Oxygen debt repayment equation
Lactic acid + oxygen → Carbon dioxide + water
How is the energy released by respiration in cells used in an organism?
Continual enzyme-controlled processes of metabolism that synthesise new molecules
Metabolism
Sum of all the reactions in a cell or the body
How is glucose used in plants?
Converted to cellulose → strengthens plant cell wall
Converted to starch → storage form of glucose
Reacted with nitrate ions → makes AA → used to synthesise proteins
How is glucose used in humans?
Converted to glycogen → storage form of glucose
How is a lipid made and where is it found?
1 glycerol molecule + 3 fatty acid molecules → lipid
Cell membrane
Where are lipids found in cells?
Cell membranes
What happens to excess proteins?
Broken down into urea
What is urea excreted by?
Kidneys
5 metabolic reactions
Conversion of glucose to starch, glycogen + cellulose
Formation of lipid molecules from 1 molecule of glycerol + 3 molecules of fatty acids
Glucose + nitrate ions to make amino acids to synthesise proteins
Respiration
Breakdown of excess proteins to form urea for excretion
Role of liver
Detoxify poisonous substances
Pass down breakdown products into blood so they can be excreted in urine via kidneys
Breaking down old, worn out blood cells + storing the iron unit it is needed to synthesise more blood cells
Dealing with lactic acid
What does blood flowing thru muscles do?
Transport lactic acid to liver
What is lactic acid converted to in the liver?
Glucose