Kaarten: Ch 3: Extrasolar planets | Quizlet
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Explain the radial velocity method for detecting exoplanets and how it utilizes the Doppler effect.
We look at the spectral lines of the star with a high resolution spectrograph and compare this with reference. Star and planet move around a common center of mass and doppler effect moves the spectral lines.
We can use fourier transform to detect multiple planets, only 1 star at the time is observed.
=> Best targets: nearby stars, metal-rich and slowly rotating stars
Describe how the radial velocity technique can reveal the presence of multiple planets in a system.
With the use of a fourier transform
What are the main historical milestones in the discovery of exoplanets using the radial velocity method?
The first exoplanet in 1988, only confirmed in 2002.
The first discovery of a hot jupyter in 1995 exoplanet around main-sequence star: 51 Peg b
What role does the Kepler mission play in the context of exoplanet discovery and characterization?
Kepler was made to search for terrestrial exoplanets and determine occurrence rate of Earth-sized planets using transit method. From Kepler we already got 2778 confirmed exoplanets and 5 potentially habitable planets. 1984 candidates still need to be confirmed.
How does the transit technique allow for the characterization of exoplanets and what recent discoveries have been made using this method?
The flux of stars is monitored and when a planet comes in front of the star, a part of the light is blocked. The bigger the planet and the closer it is to the star, the bigger the dip.
=> Most successful today, good for large planets, close to the star and not suited for nearby stars
=> We need multiple transits to conclude anything
=> The orbit needs to be edge on (two types of eclipses: grazing and full).
=> The radius and flux of the planet is measured
=> challenge: sunspots or other objects could disrupt the transit
Probability of eclipse is
P=Rs/a
Discuss the potential for direct imaging of exoplanets and the challenges associated with it.
Detecting photons from the planets. To separate the light from star and planet coronagraph is used.
- Pupil mask defines the aperture
- Focal mask stops the light in the central region
- Lyot stop blocks the light diffracted by the focal mask
Mostly done in (near-)infrared because then the thermal light from planet is visible and the starlight is less prominent
Shape and phase of pupil changes the PSF and can help detect planets
=> Targets: very bright young (massive) planets far from the star
=> resolution is increased with interferometry (multiple telescopes used)
=> Adaptive optics and post processing is used to minimize optical aberrations
Detection principles, advantages and limitations for astrometry
Looking at the sky in the plane of the star and planet. Star and planet move around a common center of mass, so the star wobbles and the position of the star is measured.
It can be combined with direct imaging to be more precise.
Relative astrometry on multi-planetary systems use another planet as reference.
θ=a/d*mp/ms
=> ancient technique but not effective then because systematic effects
=> measurement needs to be precise, and main source of error on earth is atmospheric turbulence.
=> mostly used for long-period massive planets
Detection principles, advantages and limitations for timing
Delay or advance of periodic signal due to the orbital motion of the source and the finite speed of light. (=measuring time delay of starlight over a period)
∆t= 1/c * aMpsini/Ms
=> Targets: Needs to be a source with a very stable periodic signal. (pulsars, pulsating stars, eclipsing binaries)
=> Very high precision, high enough to detect a big asteroid
Detection principles, advantages and limitations for microlensing
General relativity predicts that light rays are deflected by matter/energy. The brightness of the source is measured and the amplification is studied.
=> Targets: distant objects
=> very accurate, can detect small planets in habitable zone far away, free-floating planets and multi-planetary systems
=> It is insensitive to the activity of the host star
Drawbacks:
=> there needs to be a good allignment between the source and the lens (object).
=> This is a unique detection, no possibility of confirmation of follow-up
=> Distance of system can be hard to constrain if host star is not visible
=> No information on structure and atmosphere of planet
Explain the principle behind transit spectroscopy in the characterization of exoplanet atmospheres.
Measuring the effect the atmosphere has on the starlight.
3 methods:
1) Transit: part of the starlight will go through the atmosphere
Measure the depth of the transit at different wavelength
2) Orbital phase variation: We see different side of planets and cyclical variations in brightness of planet.
3) Secondary eclipse: Thermal radiation and reflected light grom planet disappear and reappear
What does the temperature difference between the day and night sides of an exoplanet tell us about its atmosphere and heat distribution?
It is done using Orbital phase variation which can be both in IR and optical.
It is a way to measure the temperature of the dayside of the planet. We look at the reflected light and thermal emission. It can constrain the day-night heat distribution and the albedo
What is a Lambertian surface?
Fully reflecting surface, with an isotropic emission surface intensity
What is geometrical albedo
Ratio between flux of light reflected by planet as seen from source (star) and flux of light reflected by a Lambertian disk of the same angular size. (value can be bigger than 1)
What is the brightness temperature
Temperature of a black body for which the flux a wavelength lambda would match the measured flux
What does the atmospheric scale height represent in the context of transit transmission spectroscopy?
The altitude at which the pressure drops by a factor of e
How can occultation emission spectrophotometry (Direct imaging) be used to study exoplanet atmospheres?
Looking for bio-signiture in atmosphere of exoplanet in space.
We need both visible/near-infrared (coronagraphy) and mid-infrared spectra (nulling interferometery). (looking at photons)
=> Only reliable in well-characterized environment chemistry to exclude abiotic origin
Explain the importance of eclipsing binaries in the study of exoplanets.
We have both RV and transit measurements, from the RV we have the semi-amplitudes (K) and from that we can get the two masses of the stars. Then from the transit we can get the ratio of radius and semi-major axis.
=> So this is a model-independent determination of stellar mass and radii (without the use of models)
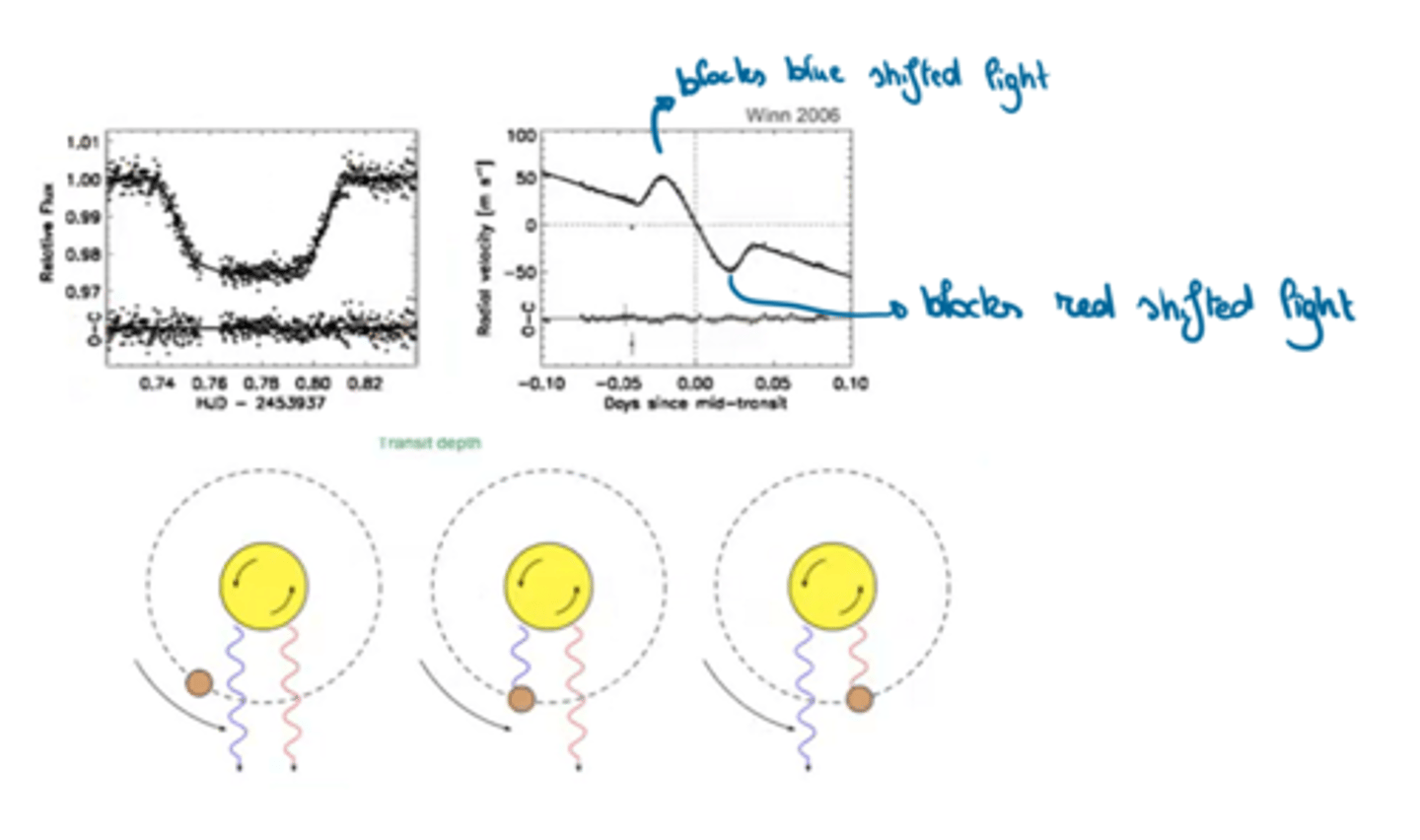
Describe the Rossiter-McLaughlin effect and its relevance to exoplanetary science.
High-cadence RV monitoring shows an "anomaly" during transit.
Geometry depends on angle between the projections on the sky plane of the stellar spin axis and the planet's orbital axis.
This effect gives insight into the spin-orbit misalignment and migration processes.
How is the occurrence rate of giant exoplanets influenced by the semi-major axis of their orbits?
It increases with semi-major axis and peaks near the snow line (~3AU)
How does the metallicity of a host star affect the likelihood of finding giant planets?
The frequency of giant planets increases with the metallicity of host star
What is the relationship between the iceline and the occurrence rate of giant exoplanets
The occurrence rate peaks near the snow line.
Beyond the ice line Neptunes and Super-earths are ~7 times more frequent than Jupiters
What is the 'Fulton gap' and how does it relate to the occurrence rate versus planet size?
There is a gap around 1.8Re in planet size that can't be explained. There are far less planets with that particular size.
Give arguments and statistics as why the solar system is special?
- Less than 5% of solar-type stars have jupiter analogs
- Less than 20% of solar-type stars host a planetary system similar to ours
- We have no sub-neptune
- 30-50% of solar-type stars have one or several planets of a few earth masses in short period orbits (super earths)
Formula transit depth
depth ~ (R2/R1)²
An extrasolar planet passes in front of its star as seen from Earth. The star's diameter is 10 times bigger than the planet's diameter. What do astronomers observe when this happens?
The star's light dim by about 1%
Which color is which?
red= RV
green= transit
purple = microlensing
blue = imaging
yellow = timing variations
orange = orbital brightness modulation
grey = astrometry

Is it possible to discover exoplanets in another galaxy and how?
Yes, through microlensing
While the kepler space telescope has discovered many HZ rocky exoplanets, they are all hardly observable by direct imaging, even with future generation telescope. Explain why.
They are all too far and, hence, very hard to directly detect