BOOOOOOOOO
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
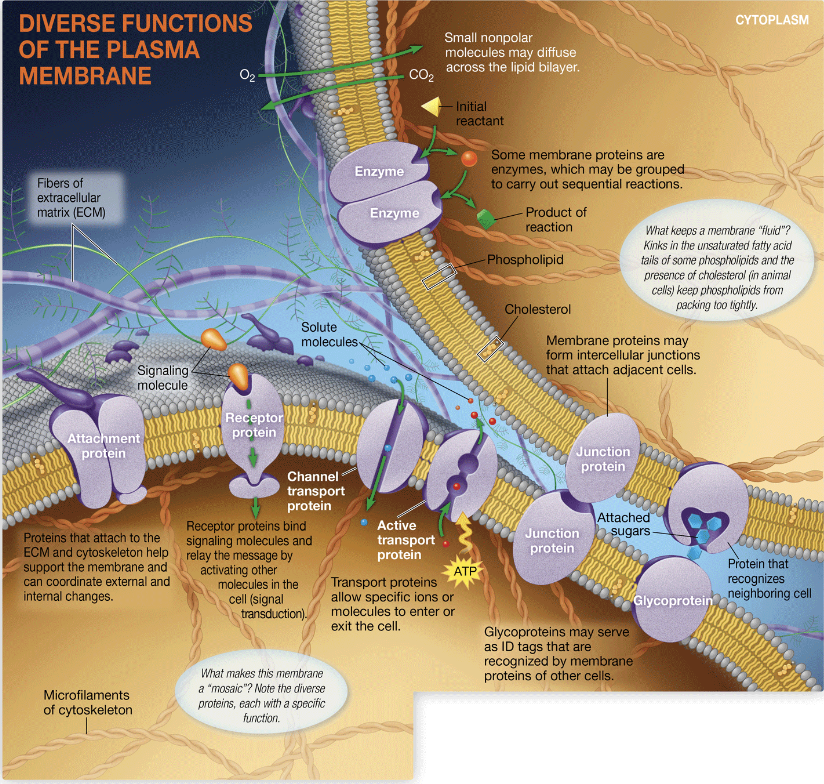
Fluid mosaic model
the model of cell membrane structure, showing the membrane as a mosaic of protein molecules suspended in a fluid bilayer of phospholipid molecules
selective permeability
a property of biological membranes that allows the regulation of passage of substances across them
diffusion
the random movement of particles from a region of more concentration to a region of less concentration
concentration gradient
a region where the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases
dynamic equilibrium
when molecules still move back and fourth, but there is no net change in concentration within the membrane
passive transport
the diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane with no expenditure of energy
osmosis
the diffusion of free water across a selectively permeable membrane
tonicity
the ability of a solution surrounding a cell to cause that cell to gain or lose water
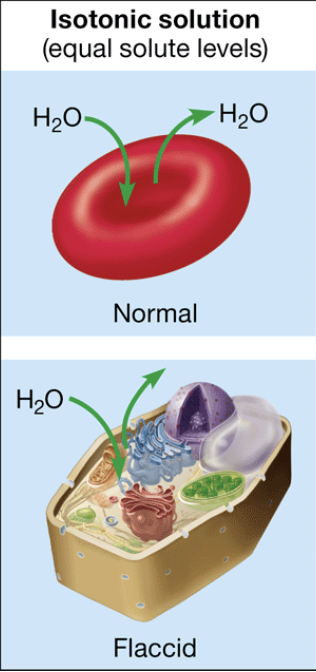
isotonic
solution that causes no net movement of water into or out of the cell
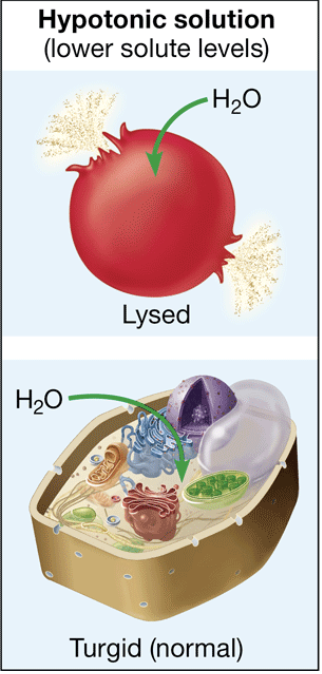
hypotonic
solution that causes the cell to gain water
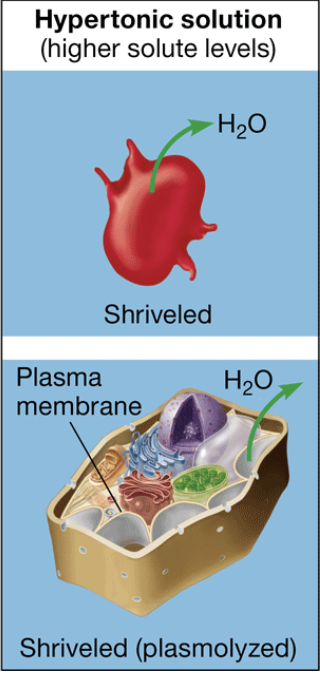
hypertonic
solution that causes the cell to lose water
osmoregulation
the control of water balance in an organism
facilitated diffusion
the passage of a substance through a transport protein across a biological membrane
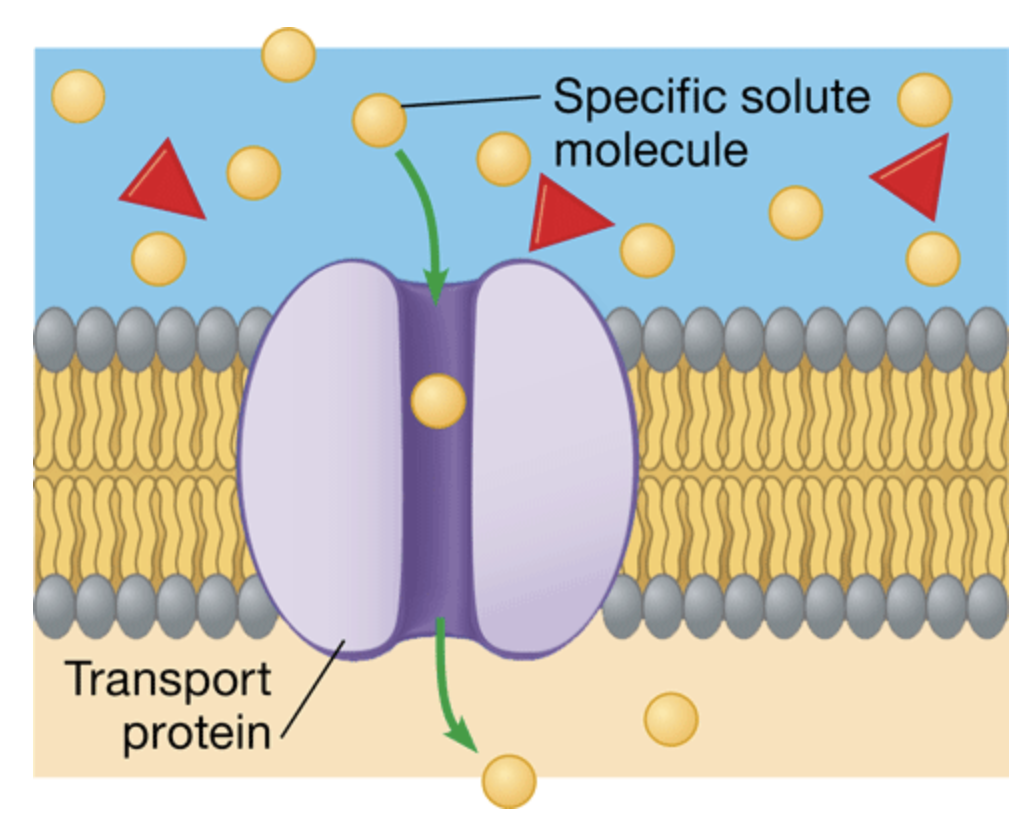
transport protein
a protein that provides a channel that specific molecules can use as passageway through a membrane
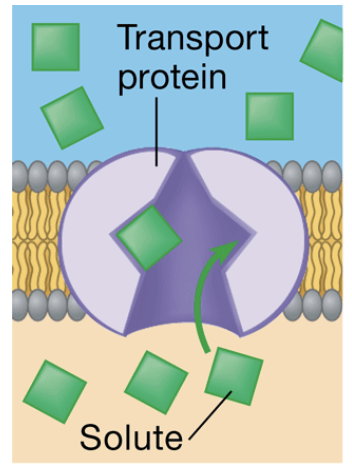
Carrier protein
a transport protein that binds it passenger, changes shape, and releases the molecule on the other side
aquaporin
a transport protein that facilitates the diffusion of water across the membrane
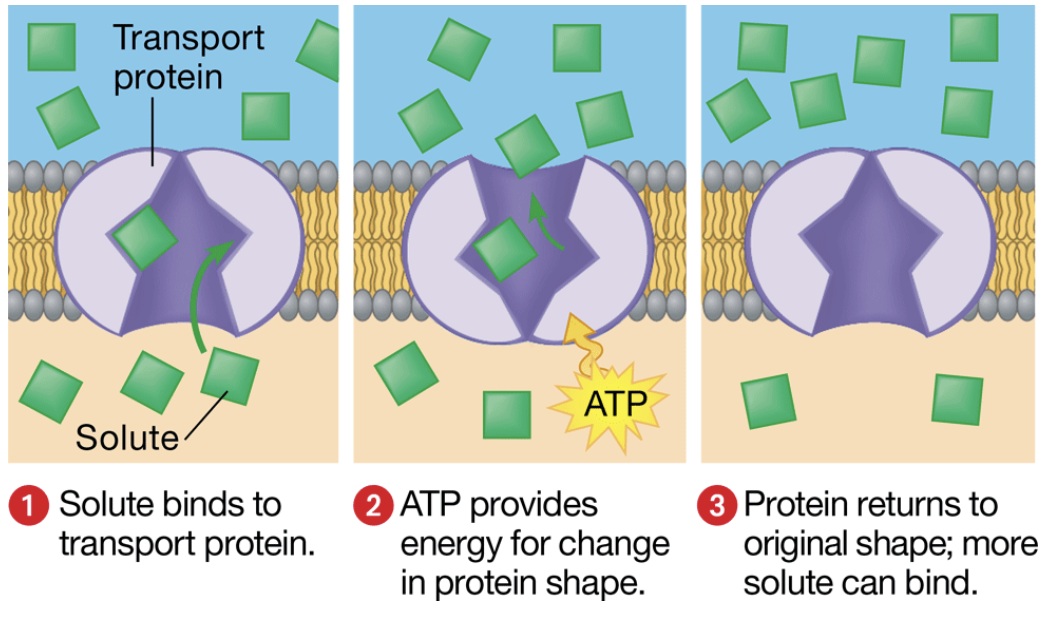
active transport
the movement of a solute against the concentration gradient of a cell that requires energy (ATP)
exocytosis
the movement of materials out of a cell by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane
Endocytosis
cellular uptake of particles via formation of new vesicles from the plasma membrane
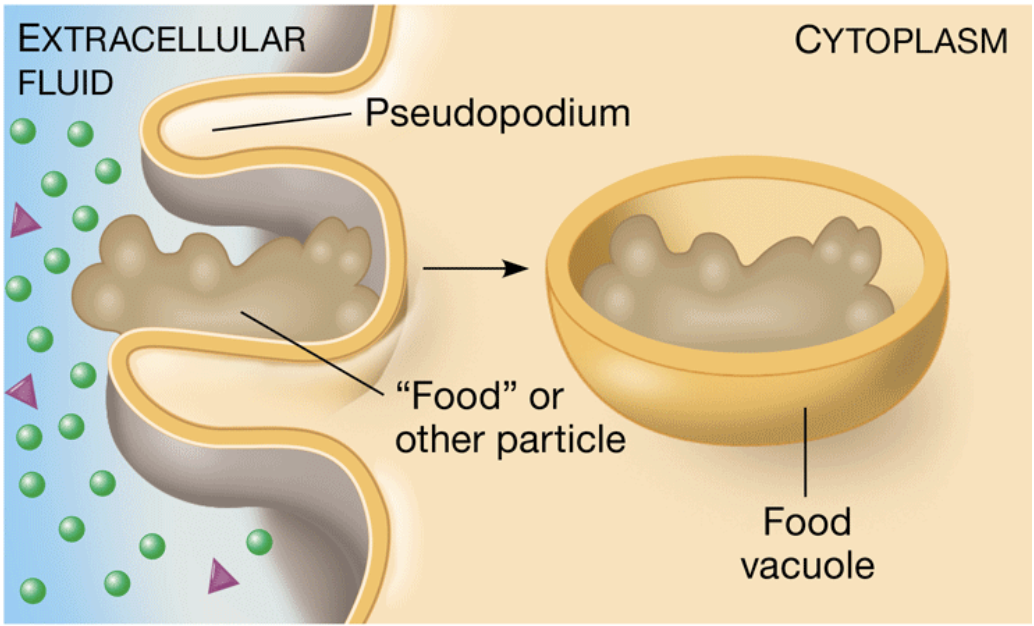
Phagocytosis
Cellular eating, a type of endocytosis where a cell engulfs macromolecules into its cytoplasm
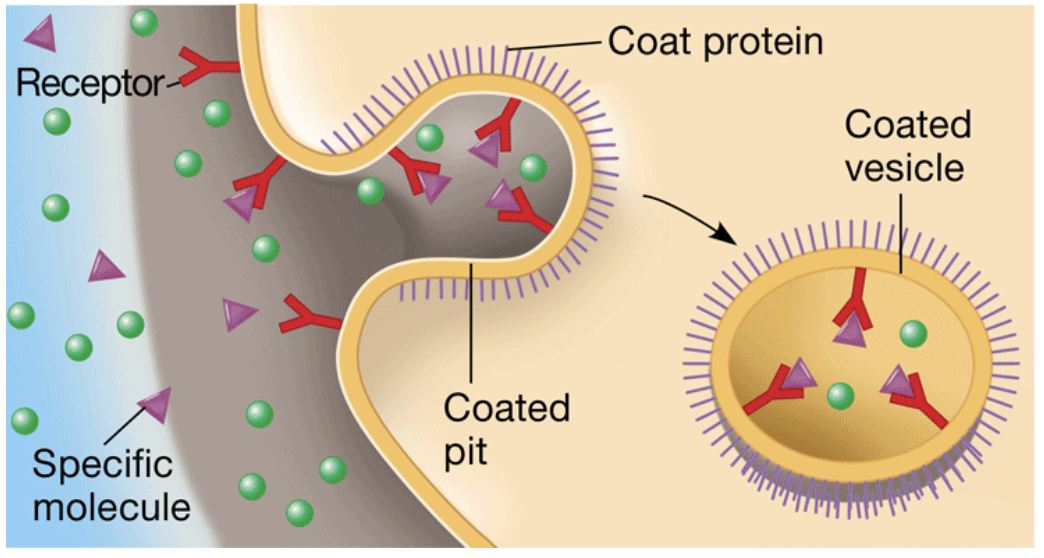
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
the movement of specific molecules into a cell by the infolding of vesicles containing proteins with receptor sites specific to the molecules being taken in
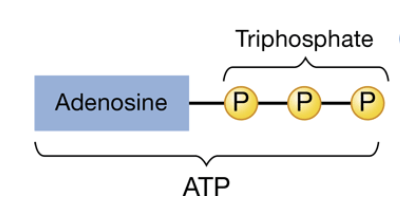
ATP (adenosine triposphate)
the main energy source for cells
phosphorylation
the transfer of a phosphate group to a molecule
activation energy
the amount of energy that reactants need before a chemical reaction starts
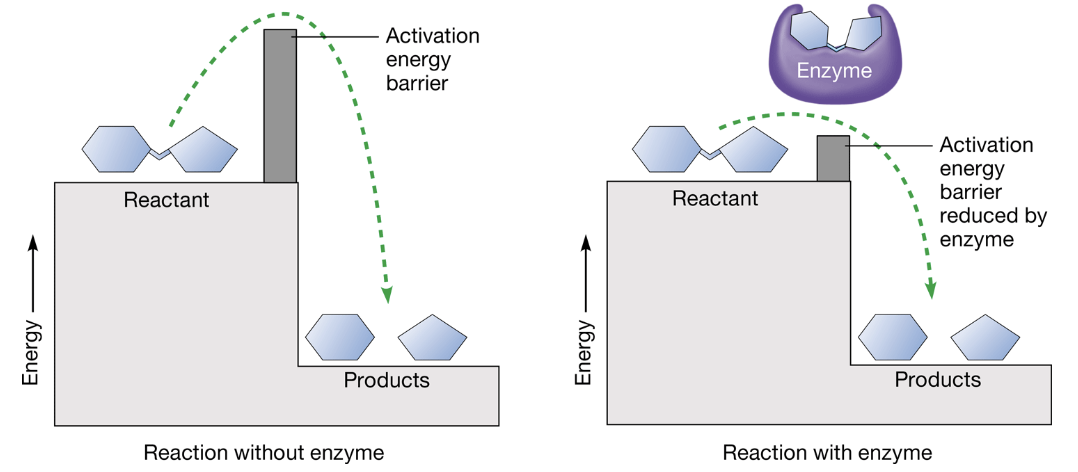
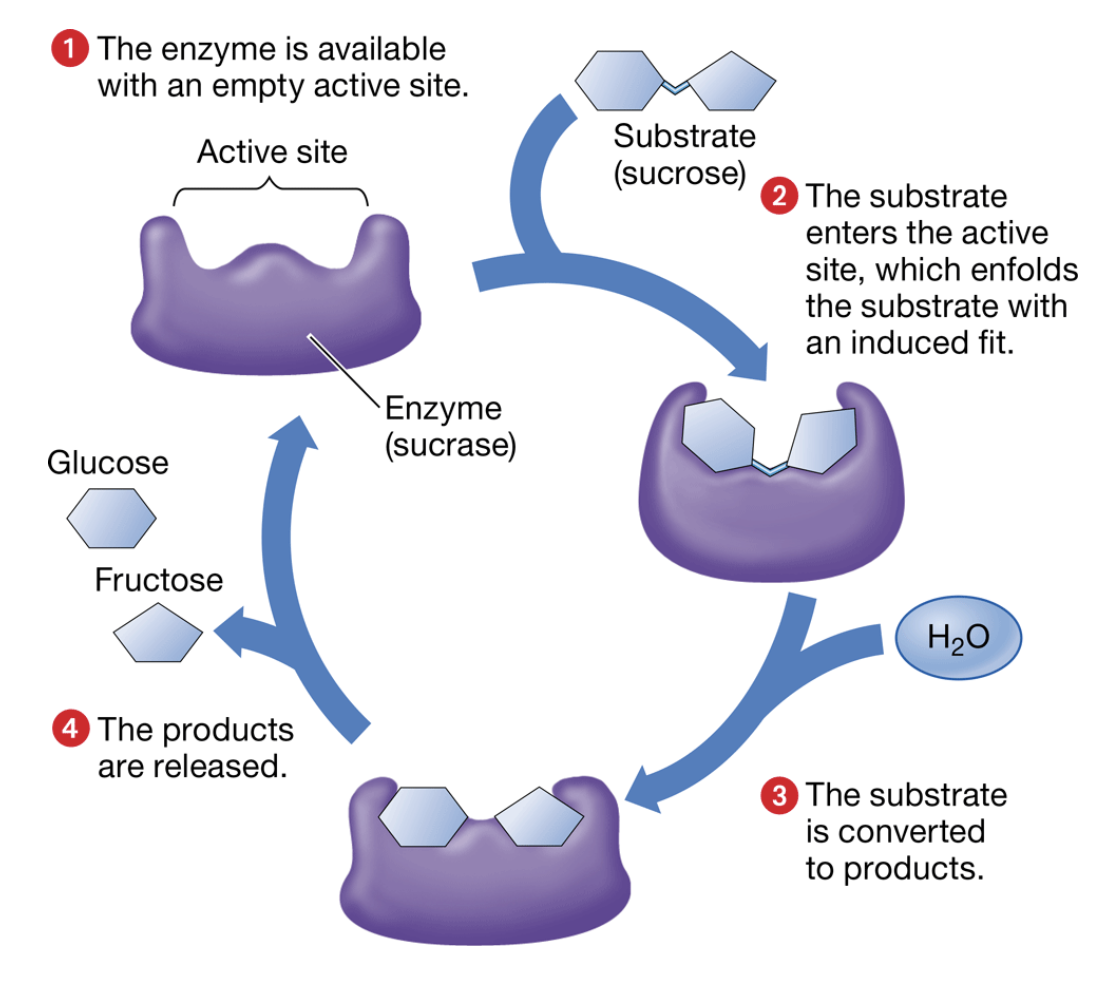
enzymes
a macromolecule (proteins) that changes the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed by it
substrate
a specific substance that goes into an enzyme
active site
the part of an enzyme where a substrate molecule attaches
The catalytic cycle of an enzyme
cofactors
a molecule or ion that binds the active site of an enzyme and function in catalysis
coenzyme
an organic molecule serving as a cofactor
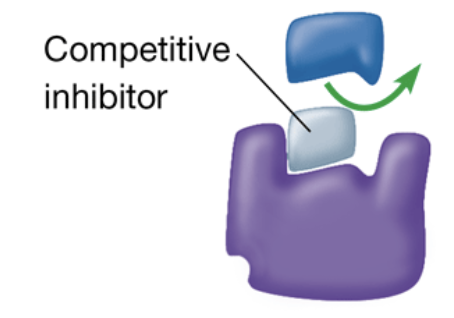
competitive inhibitor
a substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of substrate
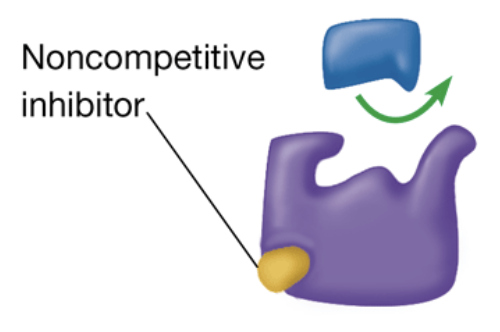
noncompetitive inhibitor
a substance that is a competitive inhibitor, but instead of entering the active site, it changes the shape of the enzyme
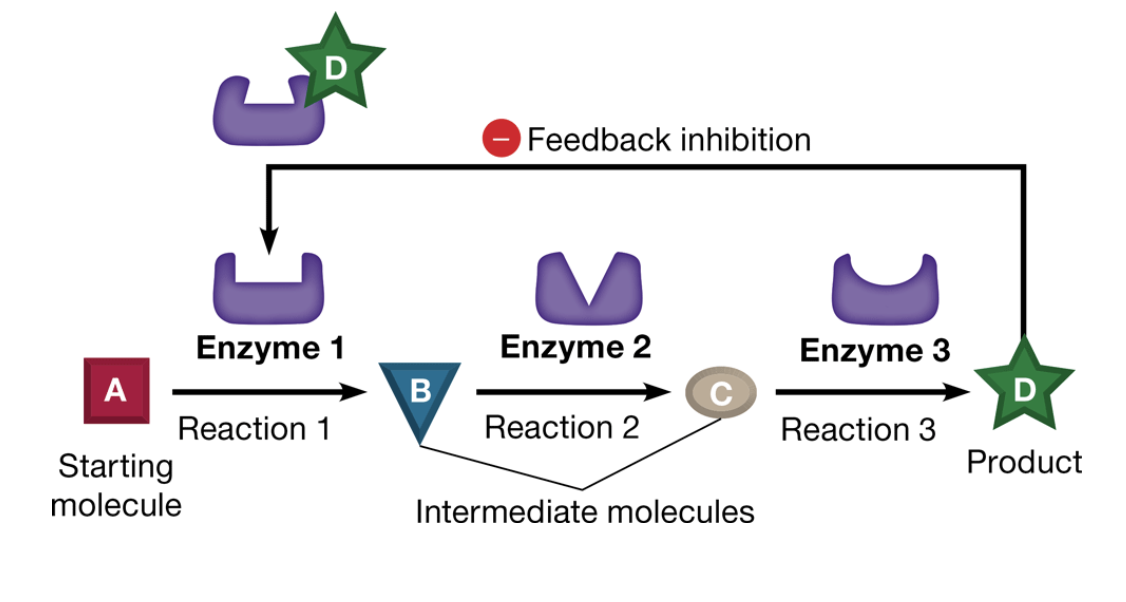
feedback inhibition
a method of metabolic control where a product acts as an inhibitor of an enzyme