L2 Membrane Transport I
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
define macrotransfer
large scale movement of molecules
define endocytosis
membrane wraps around stuff and brings it into the cell
define exocytosis
vesicle fuses with membrane to release substances
define microtransfer
smaller scale movement (cell membrane transport of small molecules and ions)
what is vesicular transport involved in
the movement of proteins into and out of the cell
what hydrophobic molecules have high plasma membrane permeability
O2, CO2, N2 and steroid hormones
what small uncharged polar molecules have some plasma membrane permeability
H2O, Urea, Glycerol
what large polar molecules have little plasma membrane permeability
glucose, sucrose
what ions have low plasma membrane permeability
H+, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl-, Mg2+
what is the relative plasma membrane permeability of hydrophobic molecules
high
what is the relative plasma membrane permeability of small uncharged polar molecules
relatively high
what is the relative plasma membrane permeability of large polar molecules
relatively low
what is the relative plasma membrane permeability of ions
low
what is the resting membrane potential determined by
the distribution of ions across the membrane
what is the resting membrane potential of ions mostly due to
Na+ and K+
what is the resting membrane potential related to
equilibrium potential (determined by the Nernst equation)
what do ions need for transport across the membrane
membrane proteins
what is the artificial semi-permeable membrane only permeable to
K+
what does the artificial semi-permeable membrane measure charge across
the membrane
what does 3+ve and 3-ve ions on each side of an artificial semi-permeable membrane suggest
no charge difference across the membrane (and no concentration difference)
what is the Nernst equation
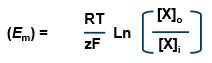
what is Em
membrane potential
what is z
number of charges on ion
what is F
Faraday’s number (96485.3 C.mol-1)
what is [X]o
conc of ion outside
what is [X]i
conc of ion inside
what is the ICF of Na+ in the Skeletal muscle
12mM
what is the ICF of K+ in the Skeletal muscle
155mM
what is the ICF of Cl- in the Skeletal muscle
4.2mM
what is the ECF of Na+ in skeletal muscle
145mM
what is the ECF of K+ in skeletal muscle
4.5mM
what is the ECF of Cl- in skeletal muscle
116mM
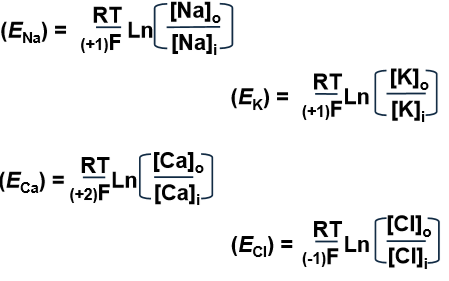
what is the ENa in skeletal muscle
+67mV
what is the EK in the skeletal muscle
-95 mV
what is the ECl in the skeletal muscle
-89 mV
what does the Nernst equation predict
equilibrium membrane potential based on concentration of that ion across the membrane
what is concentration of that ion across the membrane
Nernst potential
what is the concentration gradient maintained by
Na+/K+ -ATPase
what is the membrane permeable to
multiple ions
how can the membrane potential of multiple ions be calculated
the GHK equation
what is the GHK equation
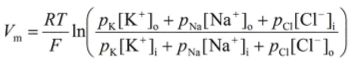
what does the GHK membrane take into account
all ions and their retrospective permeabilities
what is the resting membrane potential generated from
the asymmetrical distribution of ions
what ions is the resting membrane potential generated from
Na+ and K+
what if permeability of the membrane is higher for K+ than Na+?
membrane potential will be closer to the equilibrium potential for K+
what will the membrane potential be if the permeability of the membrane is higher for K+ than Na+
about -70mV
EK= -95mV
what do non-excitable cells have a K:Na permeability ratio of
2:1
what do nerve/muscle cells have a K:Na permeability ratio of
25:1
what is the Nernst-Goldman calculator
what is the voltage clamp
most powerful electrophysiological method for basic research
what does the voltage clamp allow
detailed measurement and analysis of electrical activity across a tissue, cell or artificial membrane that is mediated by specialised ion channels and electrogenic carriers
what can the voltage clamp, combined with molecular biology provide
fundamental information on structure, function and regulation of transport proteins
what is voltage controlled by
an electronic feedback circuit
how is the voltage clamp set up
voltage is stepped (in a preset pattern) and current is required to hold voltage as each step is measured
current is equivalent to the total ionic current flowing across the membrane
what does the current clamp circuit control
amplitude of injected current via a microelectrode and allows the voltage to vary
what does the amplifier in a current clamp record
voltage generated by the cell
what is the current clamp used to study
how a cell responds when electric current enters a cell
give an example of how a cell responds when electric current enters a cell
how a neuron responds to neurotransmitters that act by opening ion channels
what is the method of the voltage clamp
investigator sets holding voltage (command potential)
voltage clamp uses negative feedback to maintain the cell at this command potential
ion channels open/close as normal, but apparatus compensates for changes in current to maintain a constant membrane potential
who was the voltage clamp first developed by
Cole and Marmont in 1930s/40s
who was the voltage clamp further developed by
Alan Hodgkin and Andrew Huxley in the 1950s
what was the voltage clamp first used in
a squid giant axon
how long is the squid giant axon
1mm
in the patch clamp, what does the recording pipette physically isolate
a patch of membrane on the cell surface
what can the patch clamp electrically ‘clamp’
the potential across the ‘patch’ to measure current flow through a single ion channel
who was the patch clamp invented by
Neher and Sakmann in 1976
who further refined the patch clamp
Hamill et al. in 1981
what can the patch clamp record the activity of
single ion channels
measure whole-cell currents
what does the patch clamp form
a high resistance seal (giga-seal > 10Gomega) between membrane and micropipette
what does the giga-seal of the patch clamp mean
there is current flowing through ion channel in the patch that can be recorded with minimal noise
why is it important for there not to be noise in the patch clamp
single-channel currents are tiny (pA or less) so can easily be swamped by background electrical noise
what is movement across the membrane directly through the lipid bilayer through
passive (simple) diffusion
what does passive (simple) diffusion obey
Fick’s law of diffusion
give an example of passive (simple) diffusion obeying Fick’s law of diffusion
O2 from alveoli to pulmonary capillaries
what is movement across the membrane via integral membrane proteins through
facilitated diffusion
active transport
secondary active transport
describe facilitated diffusion (via integral membrane proteins)
through pores, channels and carriers (uniports)
describe active transport (via integral membrane proteins)
energy (ATP) is required to transport across the membrane
what are co-transporters (symporters) as an example of secondary active transport (via integral membrane proteins)
movement of a solute coupled to the movement of another down its concentration gradient
what are counter-transporters (antiporters) as an example of secondary active transport (via integral membrane proteins)
coupled movement of two or more solutes in opposite directions
what is another word for symporter
co-transporter
what is another word for antiporter
counter-transporter
what is passive (non-coupled) transport of
solute/gas passes down conc gradient
what happens at finish of passive (non-coupled) transport
inward flux = outward flux
net flux = 0
if a substance can pass through a membrane, that membrane is said to be…
permeable
the substance is ‘permeant’
what is the driving force in passive (simple) diffusion
the electrochemical gradient = sum of chemical energy differences as well as charge differences
what is J
flux
how do we calculate flux
permeability x concentration difference
how do we calculate permeability (P)
diffusion coefficient (D)K (partition coefficient)/X (distance)
what is the diffusion coefficient (D) a measure of
the size of the diffusion area at a given timepoint
what is the partition coefficient (K)
how easily a substance crosses a membrane
what are the three types of transporters that facilitate diffusion
channels (non-gated)
gated channels
uniporters
what do transporters all facilitate
uncoupled transport of a solute down a concentration gradient
what are non-gated channels
integral membrane proteins that allow direct access to the cell
give examples of non-gated channels
porins in bacteria, mitochondria, nuclear pore complex
aquaporins
what is ENaC
epithelial sodium channel
give examples of gated channels
ENaC
K+ channels
Ca2+ channels
almost all ion channels
what are the functional components of gated channels
gate
sensor (detects signal to open gates)
selectivity filter (stops other substances)
what are gated channels modulated by
voltage
mechanical stimuli
ligand binding
what does carrier-mediated (uniport) facilitated diffusion include
GLUT1
GLUT2
GLUT4
where is GLUT 1 in carrier-mediated (uniport) facilitated diffusion
Red blood cells