AP Biology: Unit 2
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
organelles
membrane-enclosed structures within a eukaryotic cell
eukaryotic cell
Cell with a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
prokaryotic cell
Cell with no nucleus nor membrane bound organelles
nucleoid region
a non-membrane-enclosed region of the cell where prokaryotic DNA is found
cytoplasm
the region in a cell between the cell membrane and nucleus; it contains the cell structures and oganelles
plasma membrane
The selective barrier that surrounds a cell; it controls what enters and leaves the cell
nucleus
chromosome-containing part of a eukaryotic cell
nuclear envelope
encloses the nucleus to separate its contents from the cytoplasm
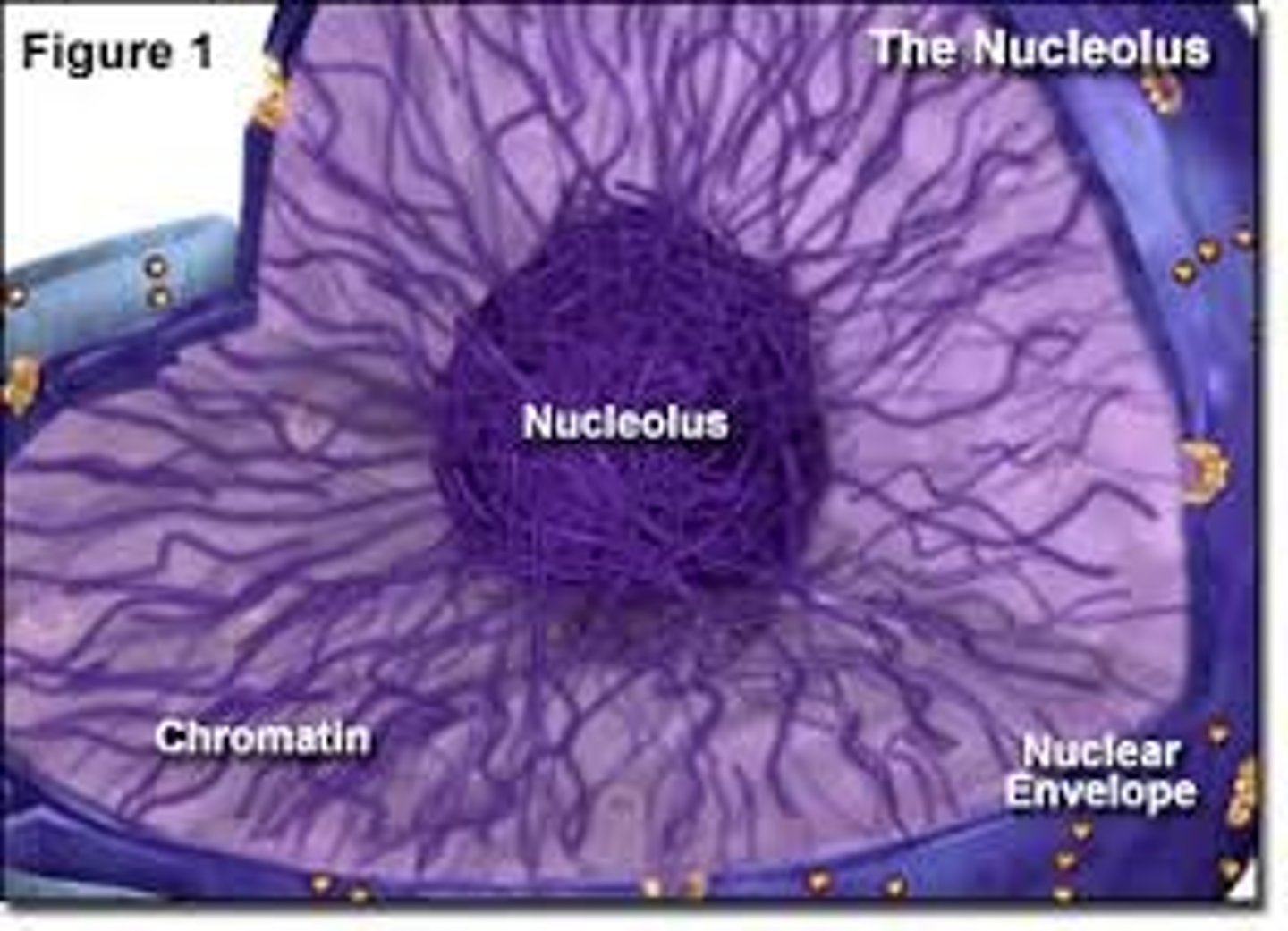
nucleolus
located in the nucleus, makes, synthesizes, and partially assembles ribosomes
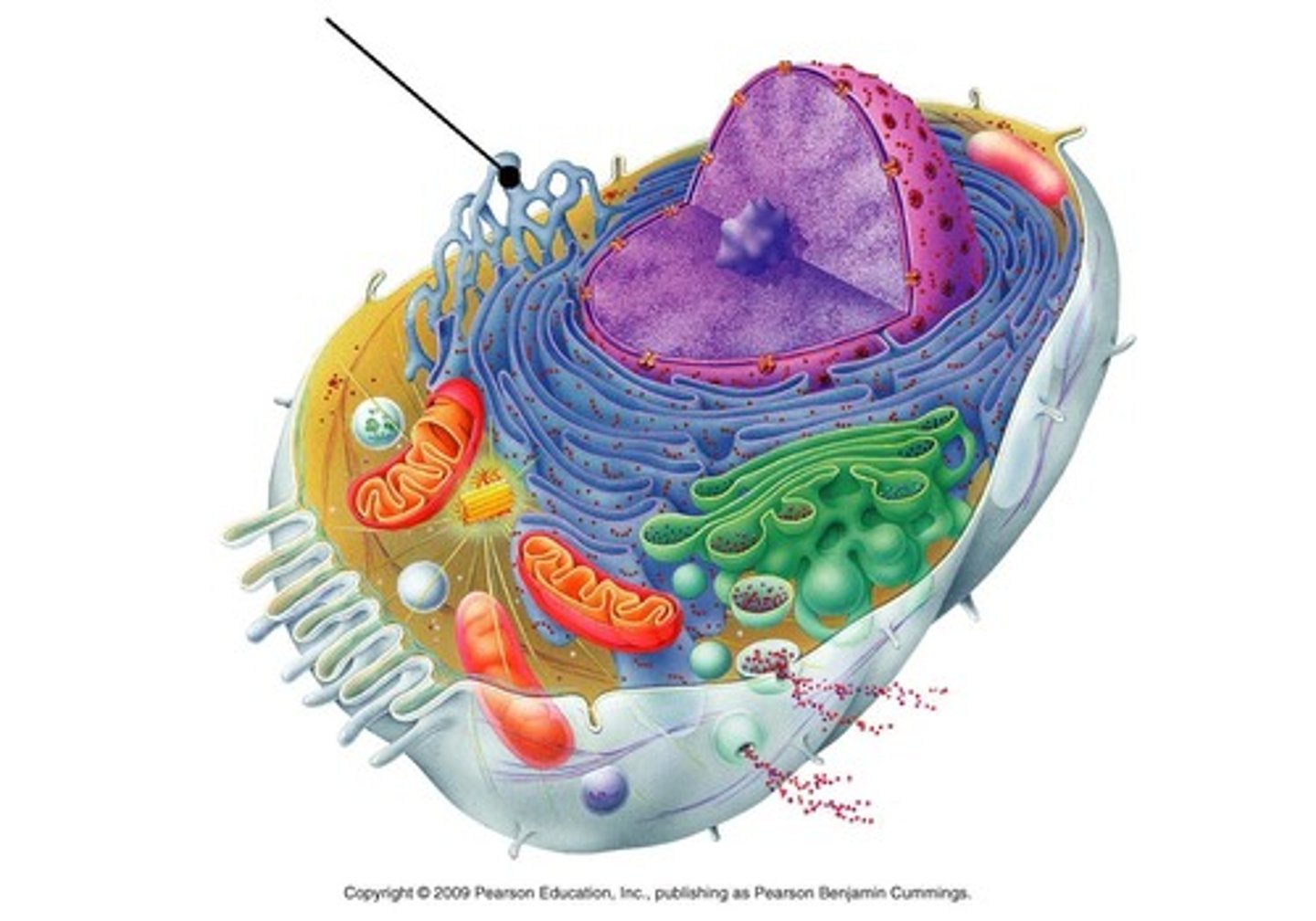
ribosomes
made of ribosomal RNA and protein, synthesize proteins
endomembrane system
organelles that are involved in the production of proteins: includes the nucleus, ribosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, the Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vesicles, and the cell membrane.
smooth ER
synthesize lipids, detoxifies the cell, and regulates calcium levels; portion of the endoplasmic reticulum free of ribosomes,
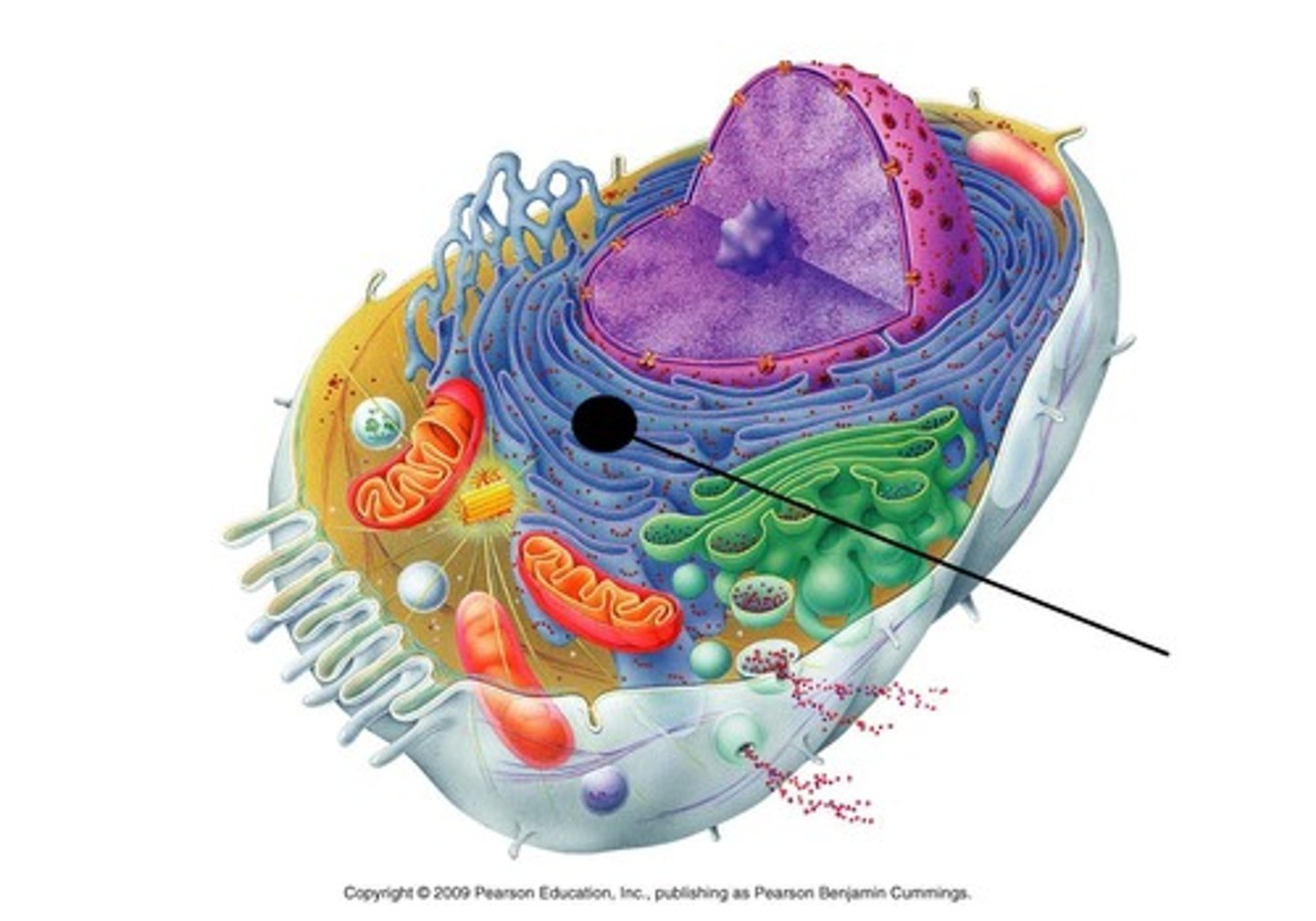
rough ER
organelle studded with ribosomes; produces and transports membrane and secretory proteins; partially attached to the nuclear envelope
glycoproteins
proteins with covalently-bonded carbohydrates that play a role in cell to cell interaction
vesicles
plasma membrane that moves molecules, secretes substances, digests materials, and regulates pressure of cells
Golgi apparatus
stack of membranes that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum
lysosome
digestive system of cell: degrade material outside of cell & digest obsolete components of cell using hydrolytic enzymes
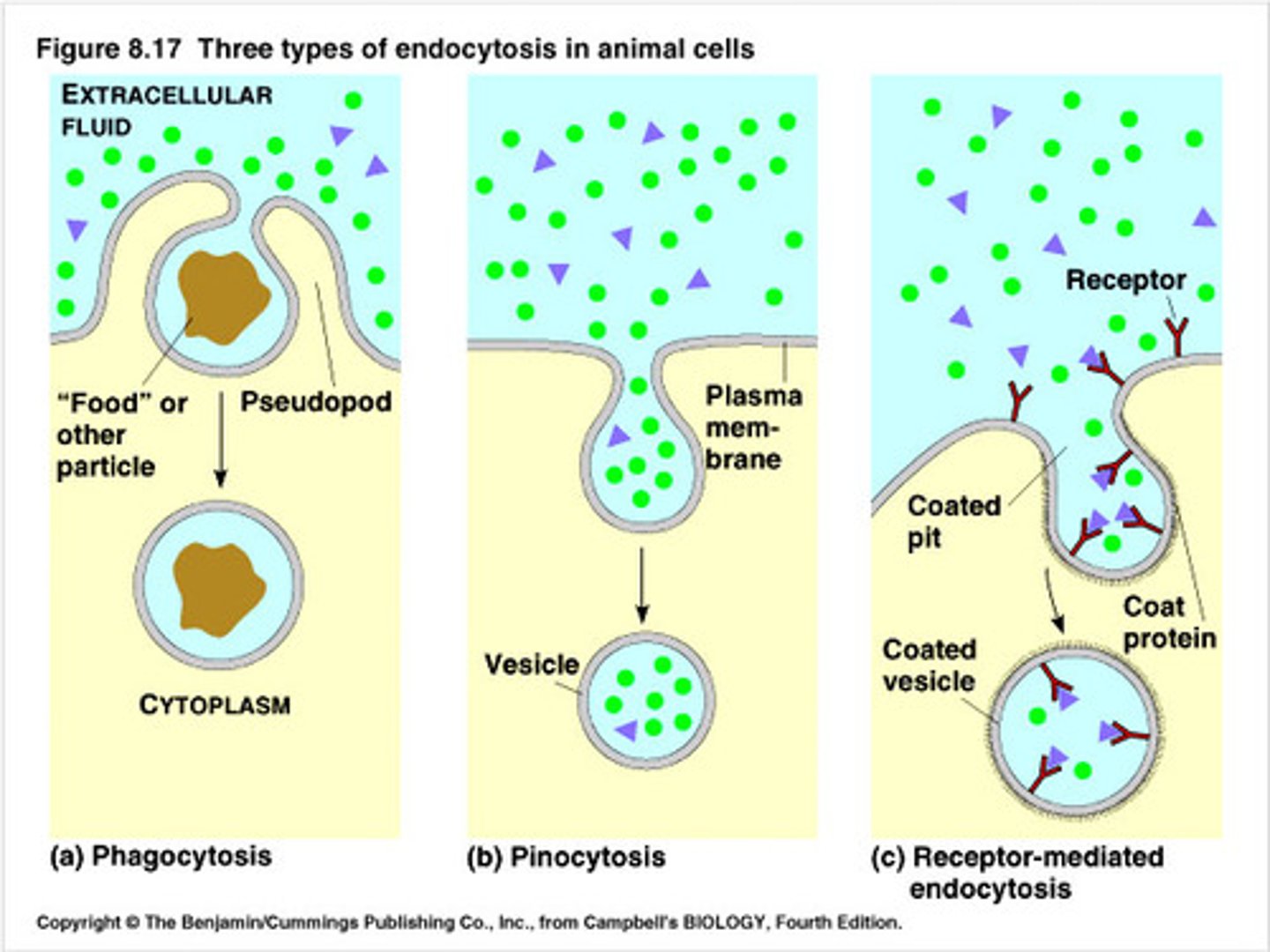
phagocytosis
the process by which a cell engulfs a solid particle
central vacuole
the largest organelle in a plant cell. It is surrounded by the tonoplast and functions to hold materials and wastes. It also functions to maintain the proper pressure within plant cells
mitochondria
chemically convert chemical (food) energy into usable ATP energy through cellular respiration
chloroplasts
an organelle in plant cells that contain chlorophyll which help absorb solar energy in order to convert carbon dioxide and water into sugars during photosynthesis
cytoskeleton
a network of fibers embracing the cytoplasm
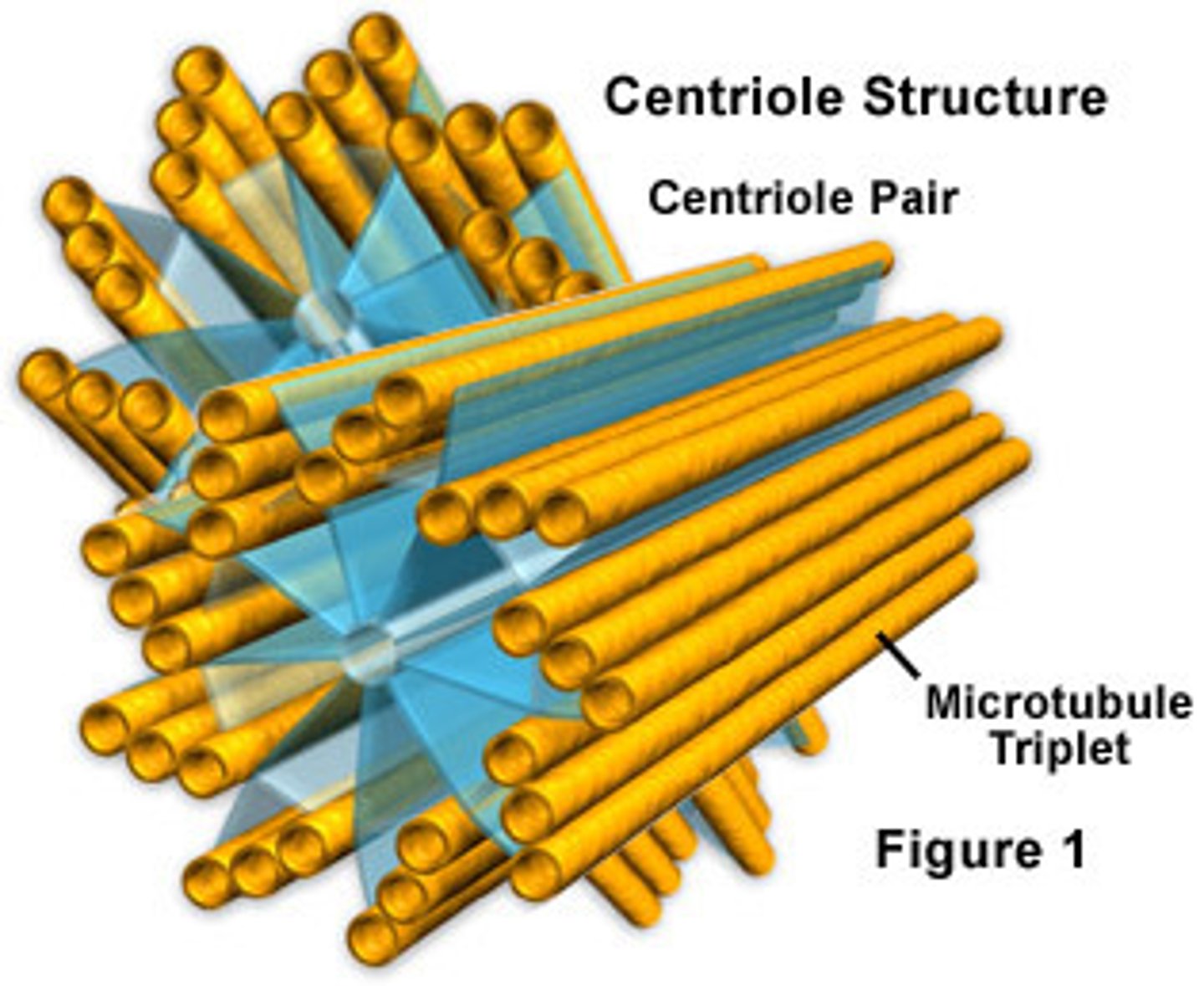
centrioles
cylindrical organelle near the nucleus in animal cells, occurring in pairs and involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division
flagella
a long tail-like structure that aids in cell movement
cilia
a short hair-like structures that enable movement of cells or movement of materials outside a cell, utilizes a back-and-forth motion
cell wall
extracellular structure specific to plant, bacterial, and fungal cells. protects the cell, maintains its shape, and prevents excessive water uptake
peptidoglycan
the polysaccharide in bacteria cell walls
cellulose
the polysaccharide in plant cell walls
archae
the domain of life composed of prokaryotic extremophiles
eukarya
Domain of all organisms made up of eukaryotic cells
Plasmid
A small ring of DNA that carries accessory genes separate from those of the bacterial chromosome
capsule
A sticky layer that surrounds the cell walls of some bacteria, protecting the cell surface and sometimes helping to glue the cell to surfaces.
apoptosis
programmed cell death initiated using lysosomes
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
hypertonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater than that of the cell that resides in the solution
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution
passive transport
Requires NO energy, Movement of molecules from high to low concentration, Moves with the concentration gradient
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels or carrier proteins
integral proteins
proteins that penetrate the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
peripheral proteins
The proteins of a membrane that are not embedded in the lipid bilayer; they are appendages loosely bound to the surface of the membrane.
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
fluid mosaic model
model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane
Plasmolysis
This happens when a cell shrinks inside a plant cell wall while the cell wall remains intact.
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
water potential
The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow, governed by solute concentration and applied pressure; mostly used for plant cells
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
organelle compartmentalization
the ability of eukaryotic cells to have specialized functions because they have separated compartments
Secondary active transport
Combination of active transport and passive transport
membrane potential
Difference in electric potential between interior and exterior of cell
electrochemical gradient
a gradient of electrochemical potential, usually for an ion that can move across a membrane.
Exocytosis
Molecules secreted by a vesicle that is fused with plasma membrane
Endocytosis
Molecules taken in, vesicle created by plasma membrane
Types of endocytosis
Receptor mediated & pino
Phagocytosis
bacteria (phages) taken in & broken down by lysosomes
Examples of phagocytosis
white blood cells
Bulk transport
Usually protein transported by vesicles in bulk out of cell
antiport
One substrate at a time, transport of opposite directions
Symport
Two substrates at a time, both sides of membrane
Animal Cell Vacuoles
plasma membrane that helps sequester waste products
Peroxisomes
carries out oxidative reactions using molecular oxygen, generates hydrogen peroxide
Microtubules
form part of internal skeleton of cell, serve as transportation routes for vesicles