Lecture 26 - Therapeutic Approaches to Tumor Hypoxia
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 335 - Radiobiology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
three reasons why hypoxia is a problem for radiation therapy
it leads to less indirect DNA damage
hypoxia induces HIF-1a, aids stem cell renewal
enhances plasticity of cancer cells to undergo EMT
are most measurs of tumor hypoxia direct or indirect
indirect
We try to use uptake of compounds that prefer to get uptaken in hypoxic cells and then use PET imaging
what is the only direct way to measure tumor hypoxia
Only direct way is to stick probes into tumor and measure O2
not possible for all tumors
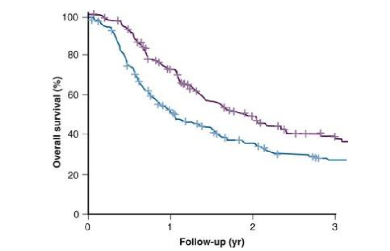
what does this graph tell us?
the more hypoxic the tumor, the lower the patient survival after 3 years
patient responds less to radiation
two ways to reduce tumor hypoxia
increase partial oxygen pressure in blood
target vasculature surrounding the tumor
two ways of increasing partial oxygen pressure in blood
HBO therapy
increase Hg levels
what is hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy
put cancer patients into a hyperbaric chamber and increase the partial pressure of oxygen so lungs take up more oxygen
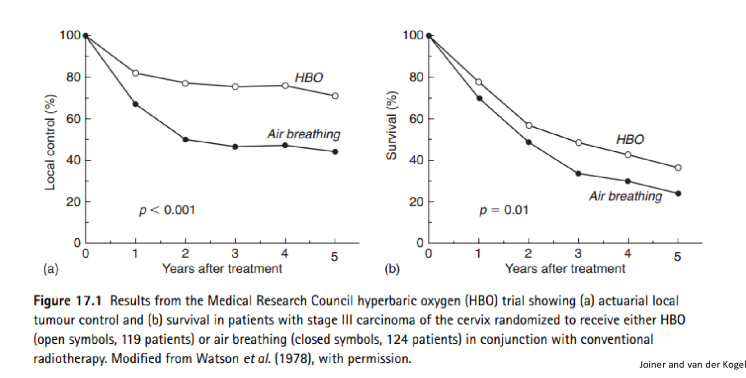
does HBO therapy work?
yes, there are clear improvements for patients who underwent HBO before radaition therapy
with exception ot bladder cancer patients
although HBO therapy works, why is not commonly used
it is very uncomfortable and claustrophobic for patients
what is HBO therapy used commonly to rtreat
osteoradionecrosis
what is osteoradionecrosis
radiation damaging the blood vessels to bone, causing bone death
why are people told to get their teeth cleaned before radiotherapy
cleaner teeth decreases chance of osteoradionecrosis in H+N patients
theoretically, why would increasing EPO levels increase RT efficacy
there is a correlation between tumor control and the amount of RBCs carrying oxygen to tumor
why does smoking lead to decrease radiation efficacy
smoking decreases the ability of the lungs to transfer oxygen to red blood cells, thus their tumors may be more hypoxic
did giving EPO to radiation patients work?
EPO increased hemoglobin concentrations but had no effect or even worse effect for patients
what is ARCON
Accelerated Radiotherapy with Carbogen and Nicotinamide
what is carbogen
a mixture of oxygen and carbon dioxide
helps regulate pH levels better than straight O2 for patients
What does nicotinamide do ?
enhances blood glow and inhibits PARP
how does ARCON affect radiotherapy tx time
it decreases radiotherapy time by delivering several fractions per fay
how do tumor blood vessels compare to regular blood vessels
very sporadic and chaotic
results in the ability to leak or collapse = hypoxia
what are two classes of drugs that were tested to target tumor vasculature
Angiogenesis Inhibiting Agents (AIAs)
Vascular Disrupting Agents (VDAs)
How do Angiogenesis inhibiting agents (AIAs) work?
inhibit VEGF, helping the tumor blood vessels become more regular and lead to more oxygen entering the tumor
how did tumors respond do radiation therapy after AIAs
there didn’t seem to be a benefit unfortunately
but many questions still remain, like what would happen if it was used with SBRT
how do vascular disrupting agents (VDAs) work?
VDAs lead to the destruction of endothelial of cells, resulting in starving the tumors of more oxygen
- Work opposite to AIAs
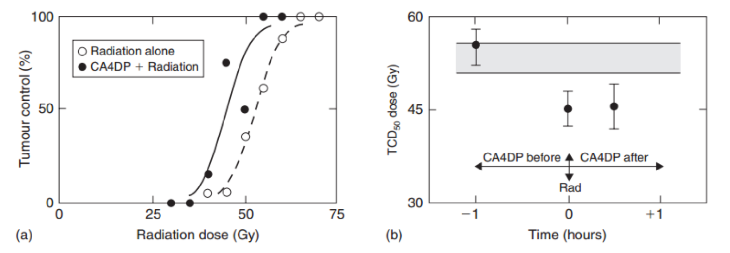
how did VDAs work in animals
worked well animals, particulary if you gave it to them before treatment
how did VDAs work in humans
no success in human trials
what are hypoxic cell radiosensitizers
chemicals that can mimic oxygen that would travel to hypoxic sites and make them more radiosensitive
would not affect well oxygenated normal healthy tissue
what kind of compounds are needed for hypoxic cell radiosensitizers
conpounds with high electron affinities to fix indirect damage in place to tumor cells
why can hypoxic cell radiosensitizers penetrate deeper into hypoxic tumors than oxygen can
drugs are not metabolized/used by the tumor cells!
what class of drugs have been studied as hypoxic cell radiosensitizers
nitromidazole
example of a nitromidazole hypoxic cell radiosensitizer
Misonidazole
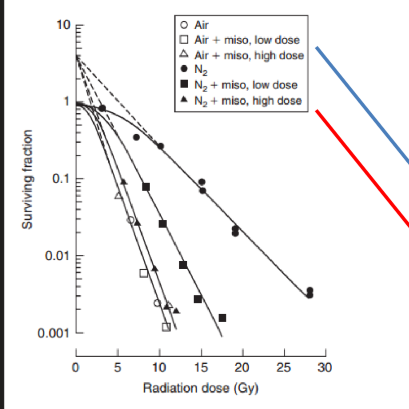
what does this graph tell us about misonidazole
no effect on normal oxygen cells
strong effect on hypoxic tumor cells!
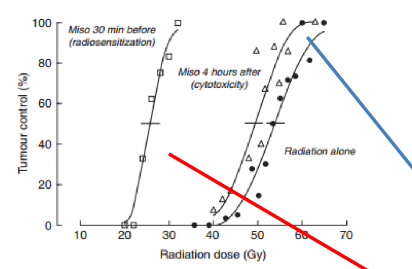
what does this graph tell us about misonidazole
giving the drug before radiation therapy works better than giving it after!
why is misonidazole not used in humans very often
because it is toxic to the CNS
what hypoxic cell radiosensitizer is used in head and neck cancers for patients
nimorazole
control is better than placebo when given before treatment
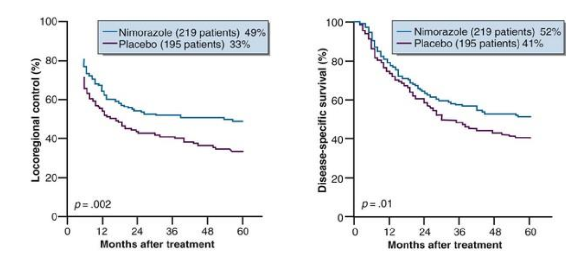
does nimorazole work for all cancers
no, only head and neck cancers have seen benefit
what are bioreductive drugs
compounds that undergo reduction reactions to become activated in low oxygen tensions
drugs will become activated in hypoxic regions
three groups of bioreductive drugs
quinones
nitroimidazole (derived from misonidazole)
N-oxides
did bioreductive drugs work in clinical trials
they had promising phase I trials but didnt work in later clinical trials
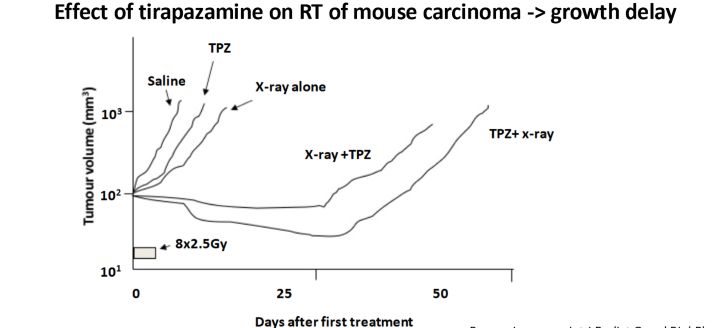
why did bioreductive drugs work better in mice than humans?
Drugs were getting broken down with the reductase enzymes in mice which worked well
Humans have different levels of reducatase, lowering the efficacy
what is the major side effect of bioreductive drugs
can cause blindness since the retina of the eye is hypoxic
what is thermoradiotherapy
heating of tumors/patients above normal body temperatures causes enlarged blood vessels to increase oxygen
combined with radiotherapy
essentially give the patient a fever before treatment