Muscular System: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder and Elbow Joint
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
muscles crossing the shoulder joint
-primarily originate on the pectoral girdle and insert on the humerus
-act to move the arm at the shoulder joint
-3 largest = powerful prime movers- pectoralis major (flex + add), deltoid (abduction), latissimus dorsi (ext + add)
muscles crossing the shoulder joint anteriorly
-flex the arm
-pectoralis major, deltoid (anterior), coracobrachialis
pectoralis major
-origin: medial half of clavicle (clavicular head), sternum (sternal head), costal cartilages 1-6, external oblique aponeurosis
-insertion: lateral lip of intertubercular groove of humerus
-action: shoulder flexion, shoulder adduction, internal rotation
-innervation: lateral and medial pectoral nerve C5-T1
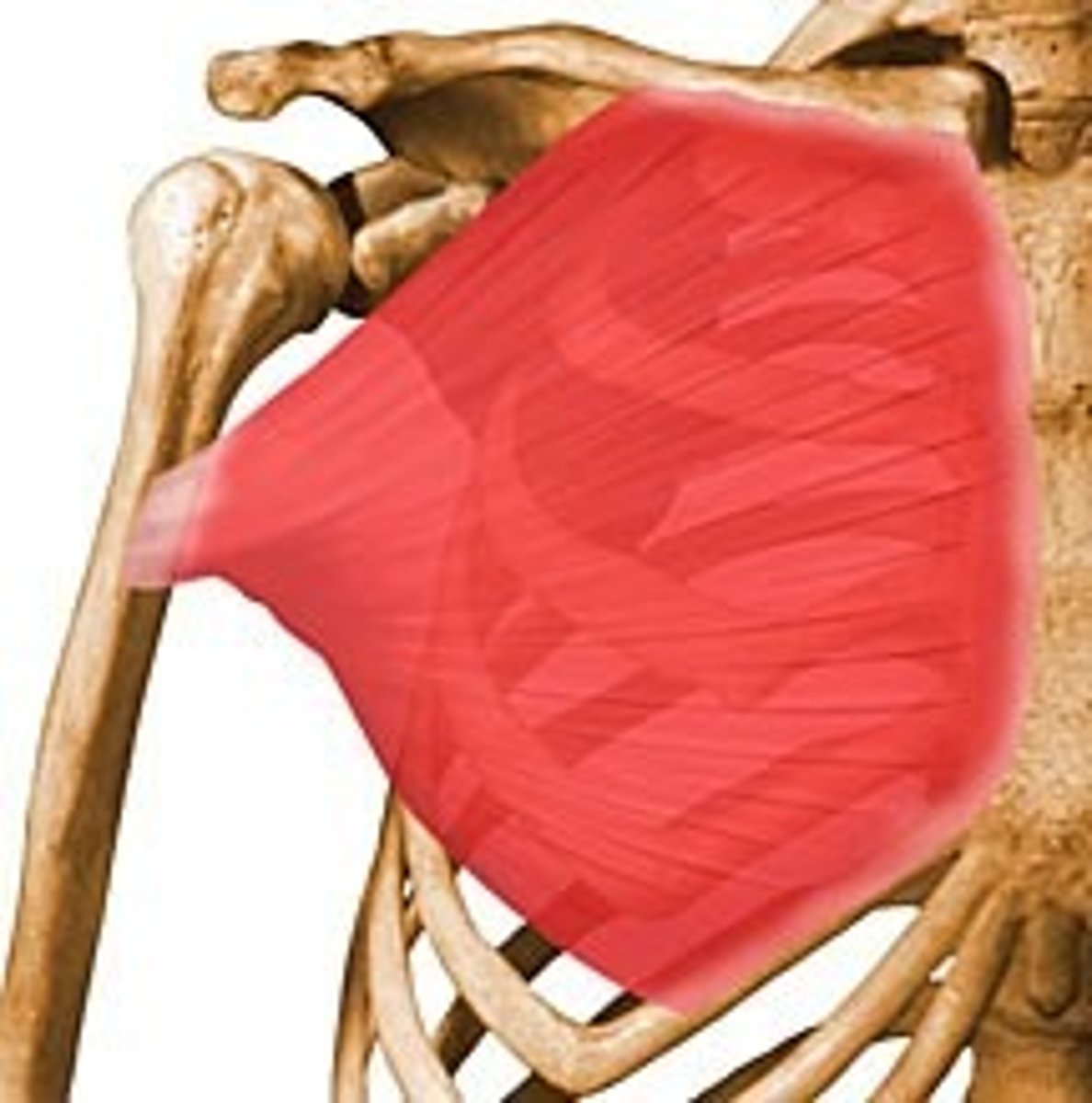
deltoid
-origin: lateral 1/3 of clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula
-insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus
-action: anterior- flexion, internal rotation, middle- abduction (PM), posterior- extension, ER
-innervation: axillary nerve C5-C6
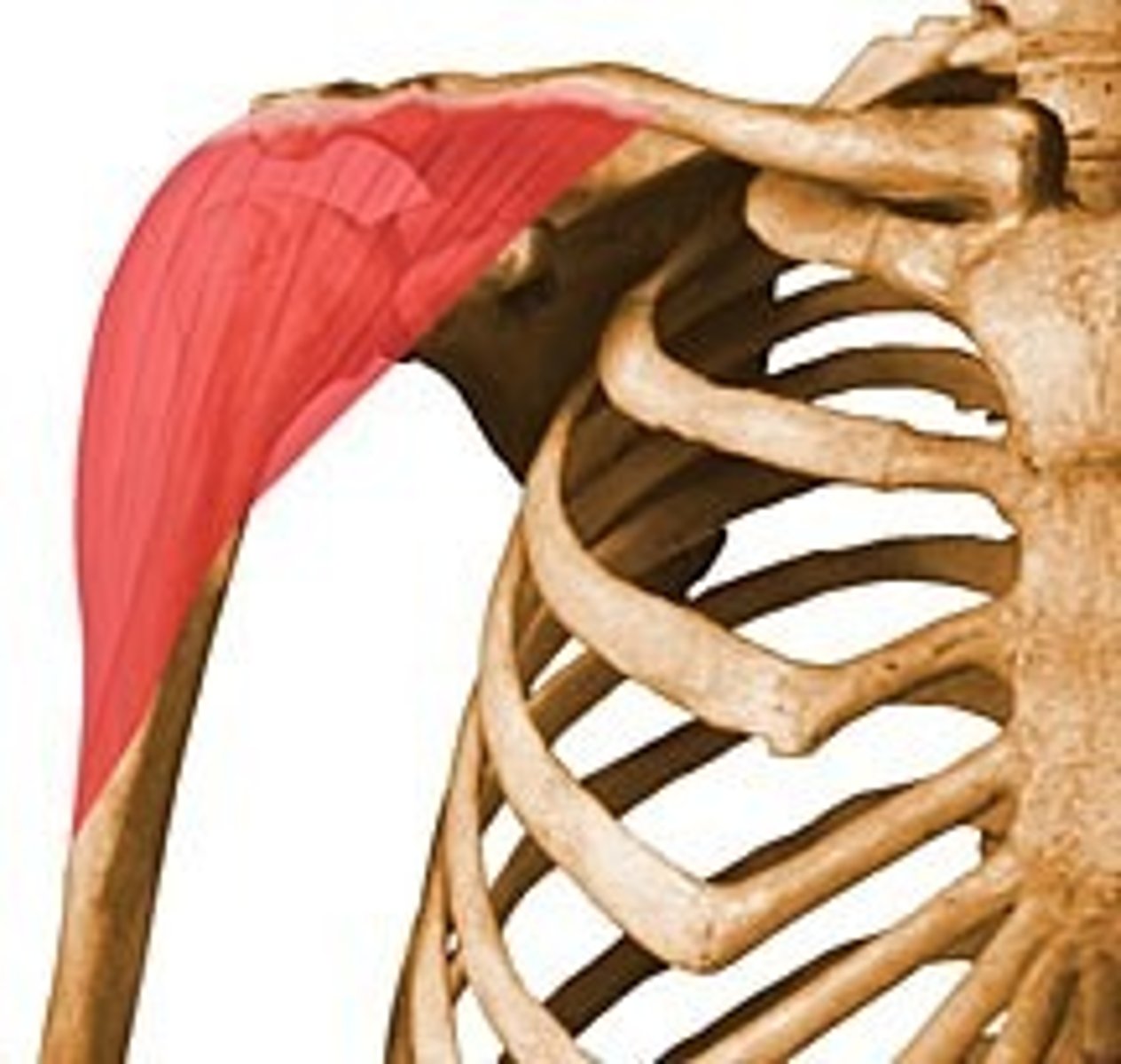
coracobrachialis
-muscle included in the anterior compartment of the arm that acts at the shoulder
-origin: coracoid process of scapula
-insertion: medial surface of humeral shaft
-action: shoulder flexion and adduction
-innervation: musculocutaneous nerve, C5-C7
muscles that originate posterior to the shoulder joint
-extend the arm
-latissimus dorsi, teres major, posterior deltoid
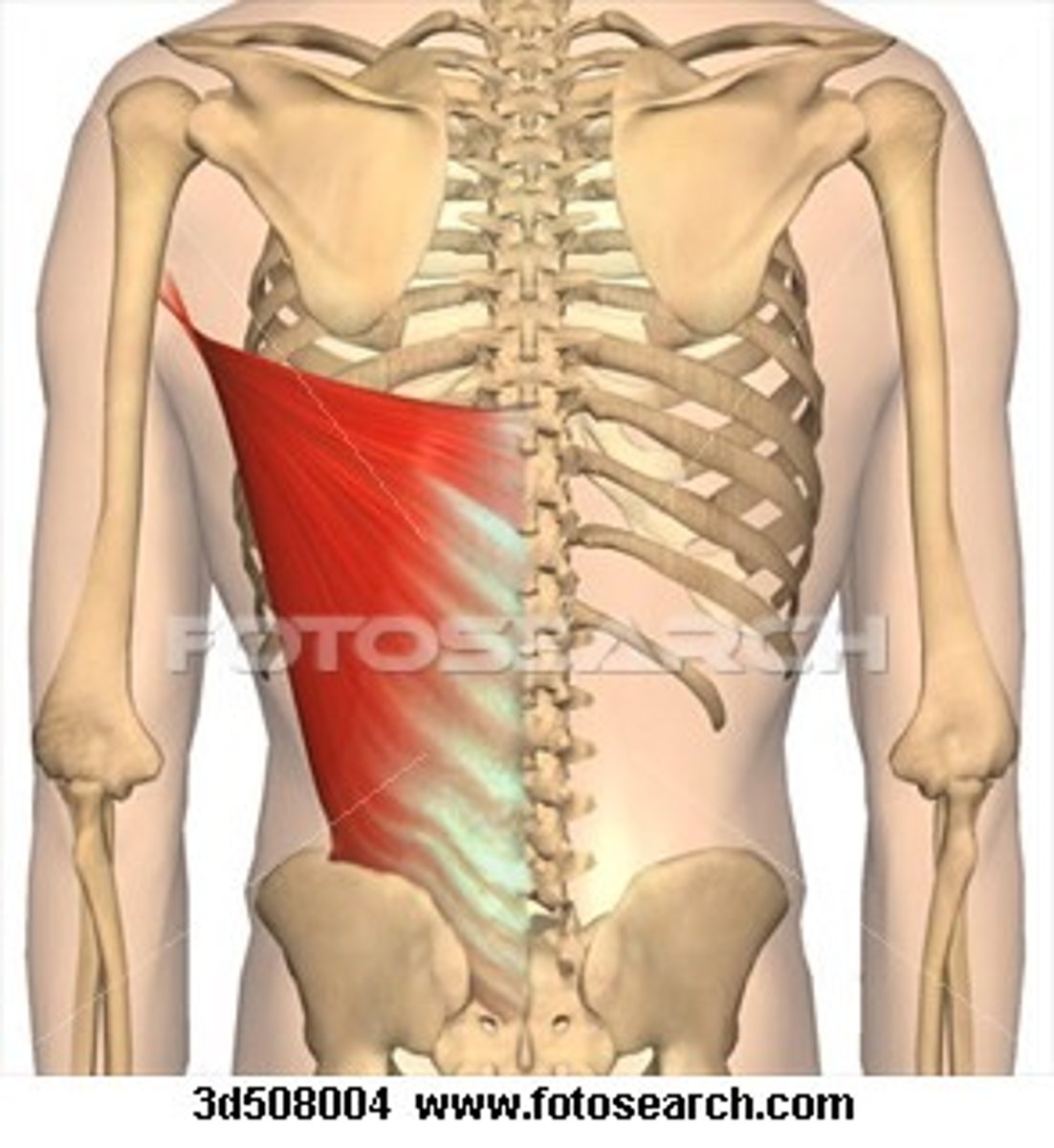
latissimus dorsi
convergent muscle
-origin: indirect by thoracolumbar fascia (spinous processes T7-L5, iliac crest, ribs 9-12), inferior angle of scapula
-insertion: floor of intertubercular groove of humerus (from medial aspect)
-action: scapular depression, shoulder extension (PM), shoulder adduction (co-PM), IR "chopping muscle"
-innervation: thoracodorsal nerve C6-C8
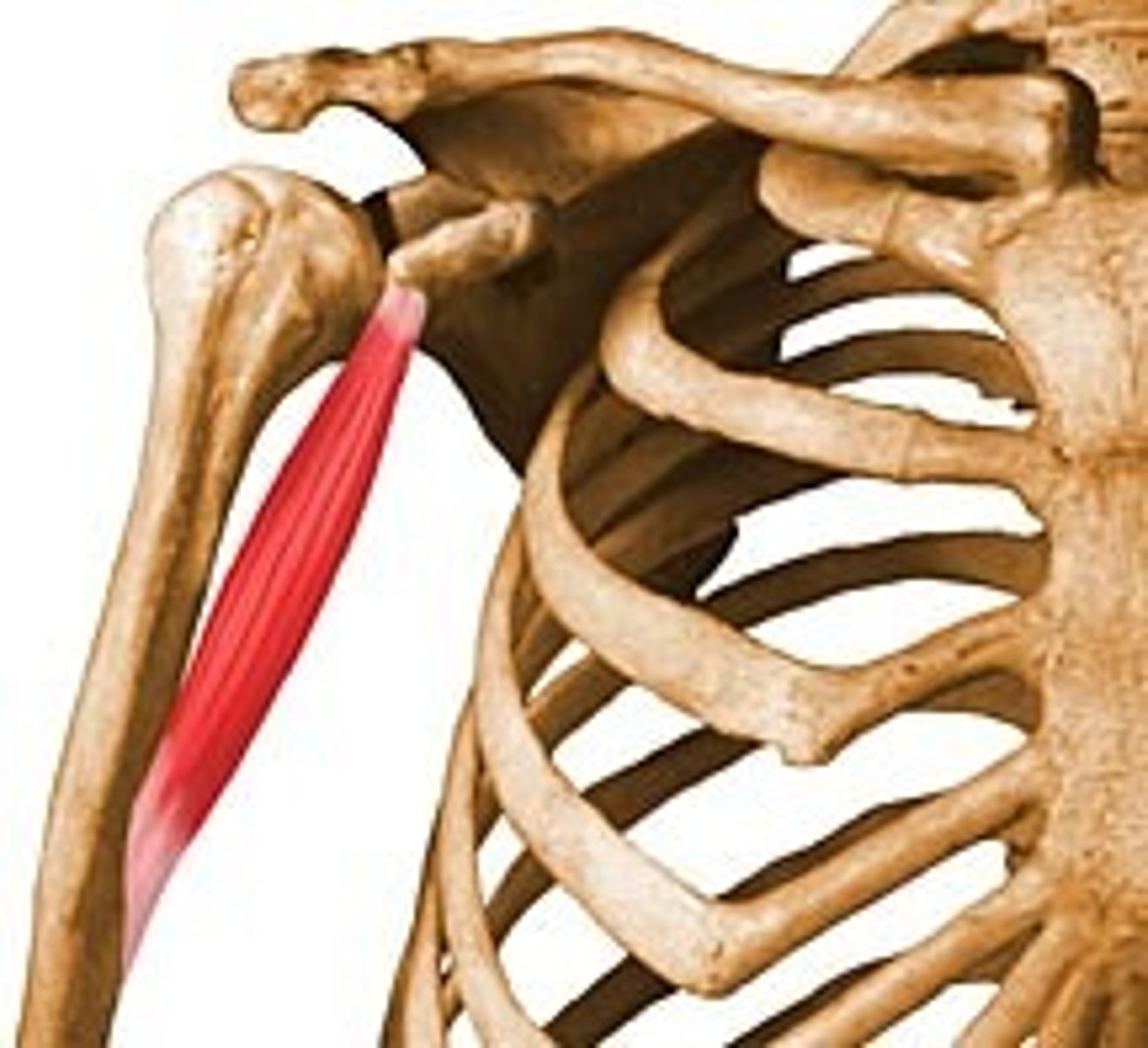
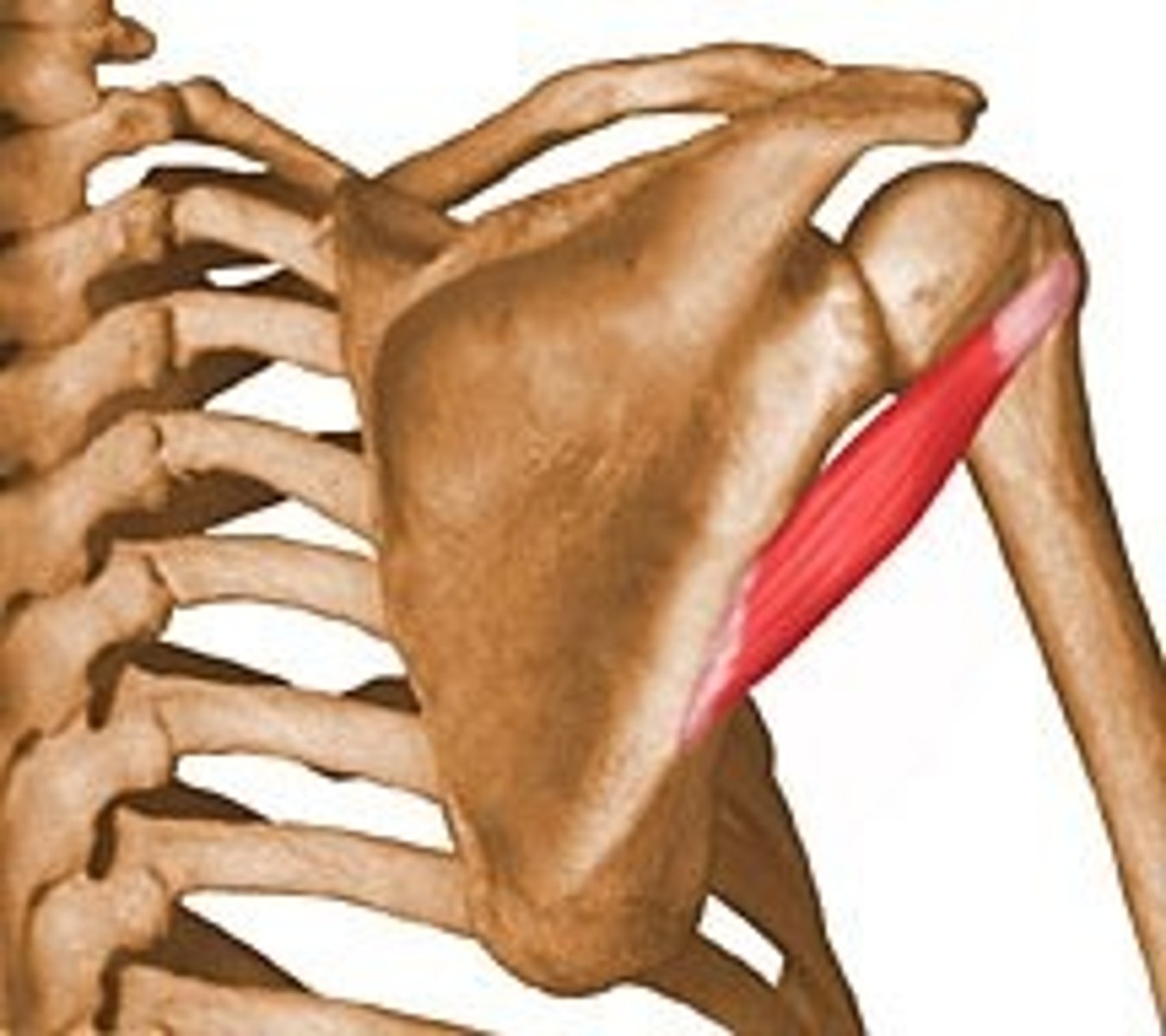
teres major
-origin: posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula
-insertion: medial lip of intertubercular groove, may fuse with tendon of latissimus dorsi
-action: lats synergist- shoulder extension, adduction, IR
-innervation: lower subscapular nerve C5-C6
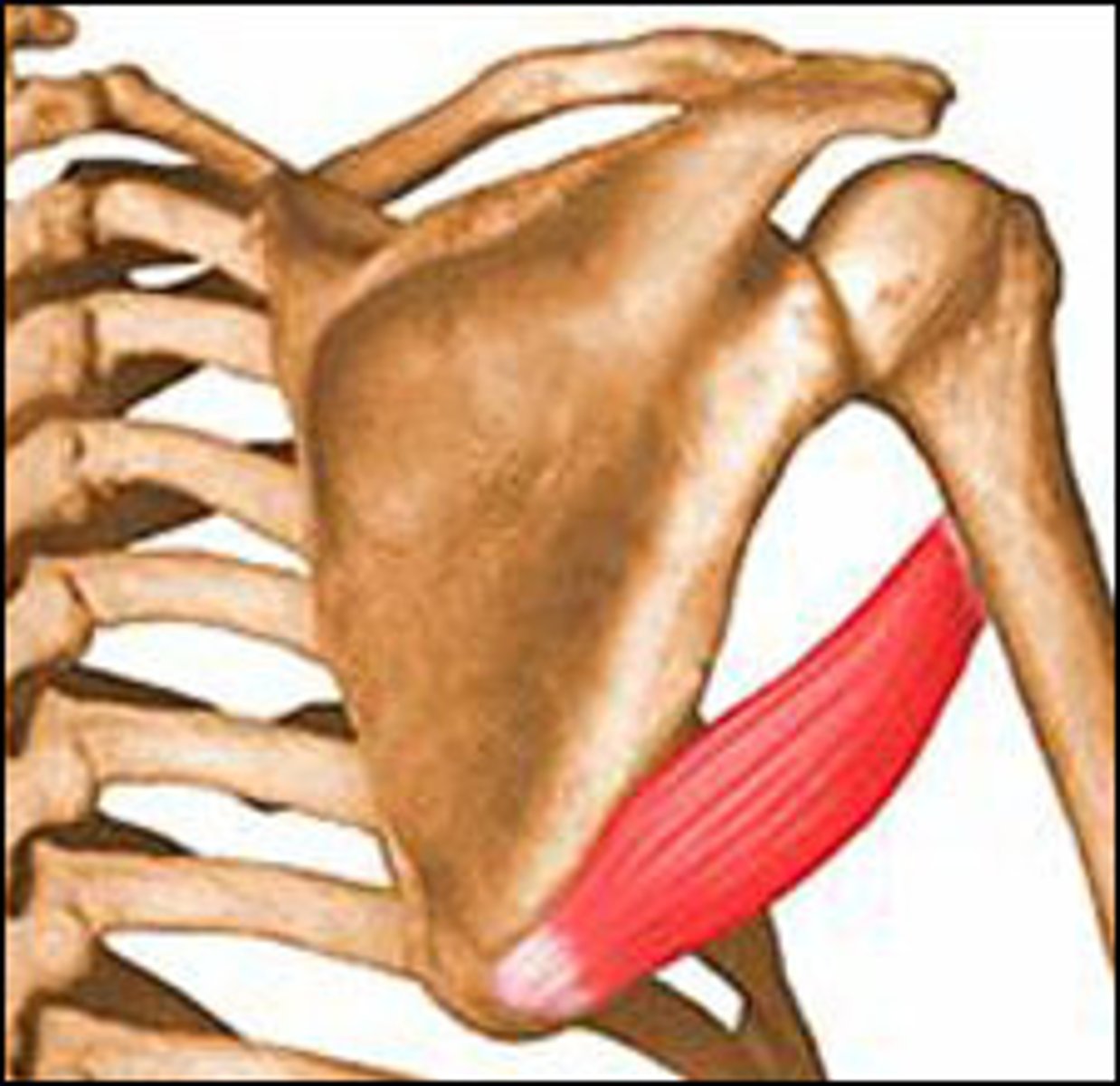
rotator cuff muscles
important for stabilization of shoulder joint
-supraspinatus, infrapsinatus, teres minor, subscapularis
supraspinatus
-origin: supraspinous fossa of scapula
-insertion: superior facet of greater tubercle of humerus
-action: initiates abduction (30 deg)
-innervation: suprascapular nerve C5-C6
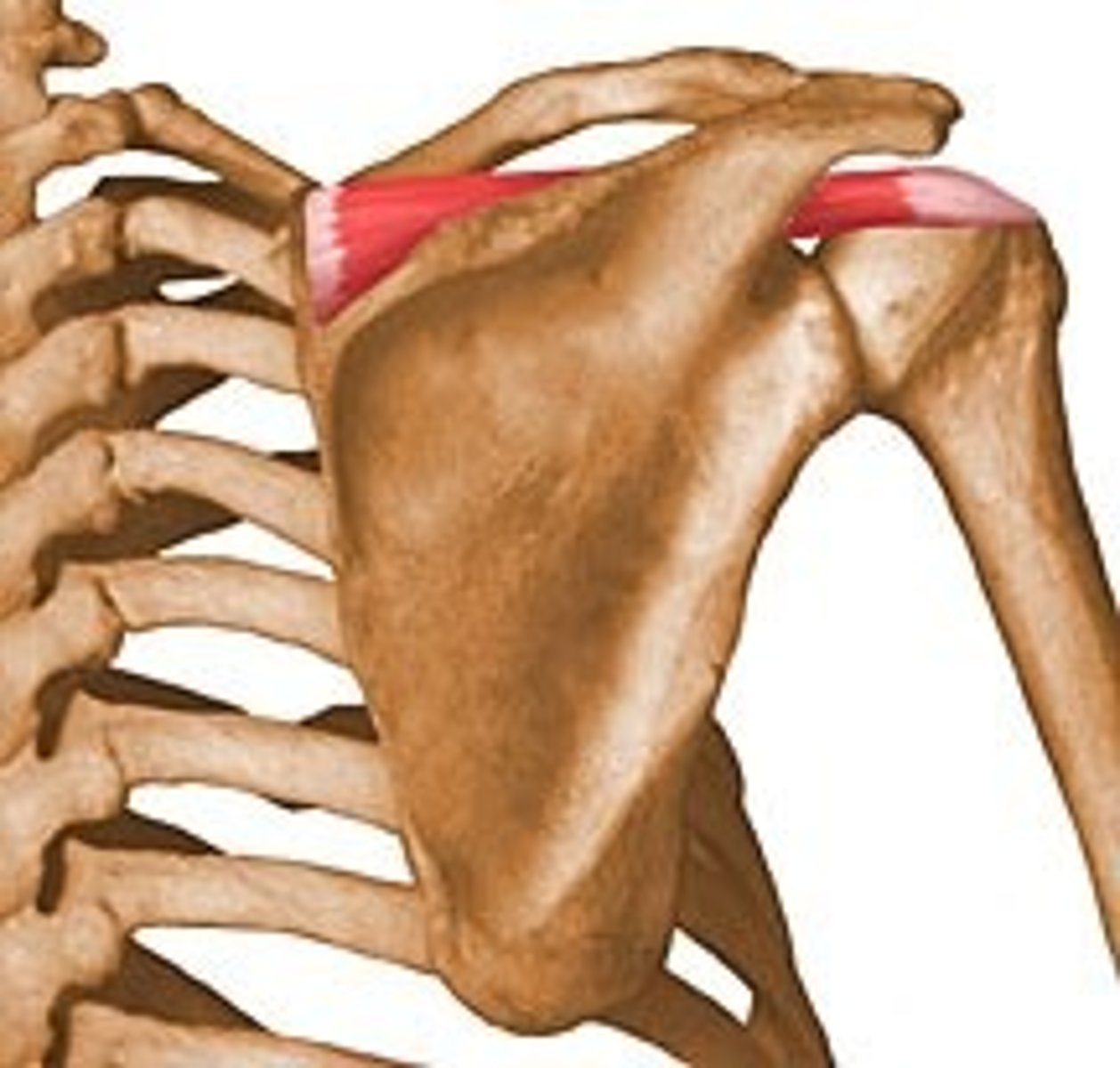
infraspinatus
-origin: infraspinous fossa of scapula
-insertion: middle facet of greater tubercle of humerus
-action: external rotation (co-PM)
-innervation: suprascapular nerve C5-C6
teres minor
-origin: lateral border of scapula, posterior surface
-insertion: inferior facet of greater tubercle of humerus
-action: external rotation (co-PM)
-innervation: axillary nerve C5-C6
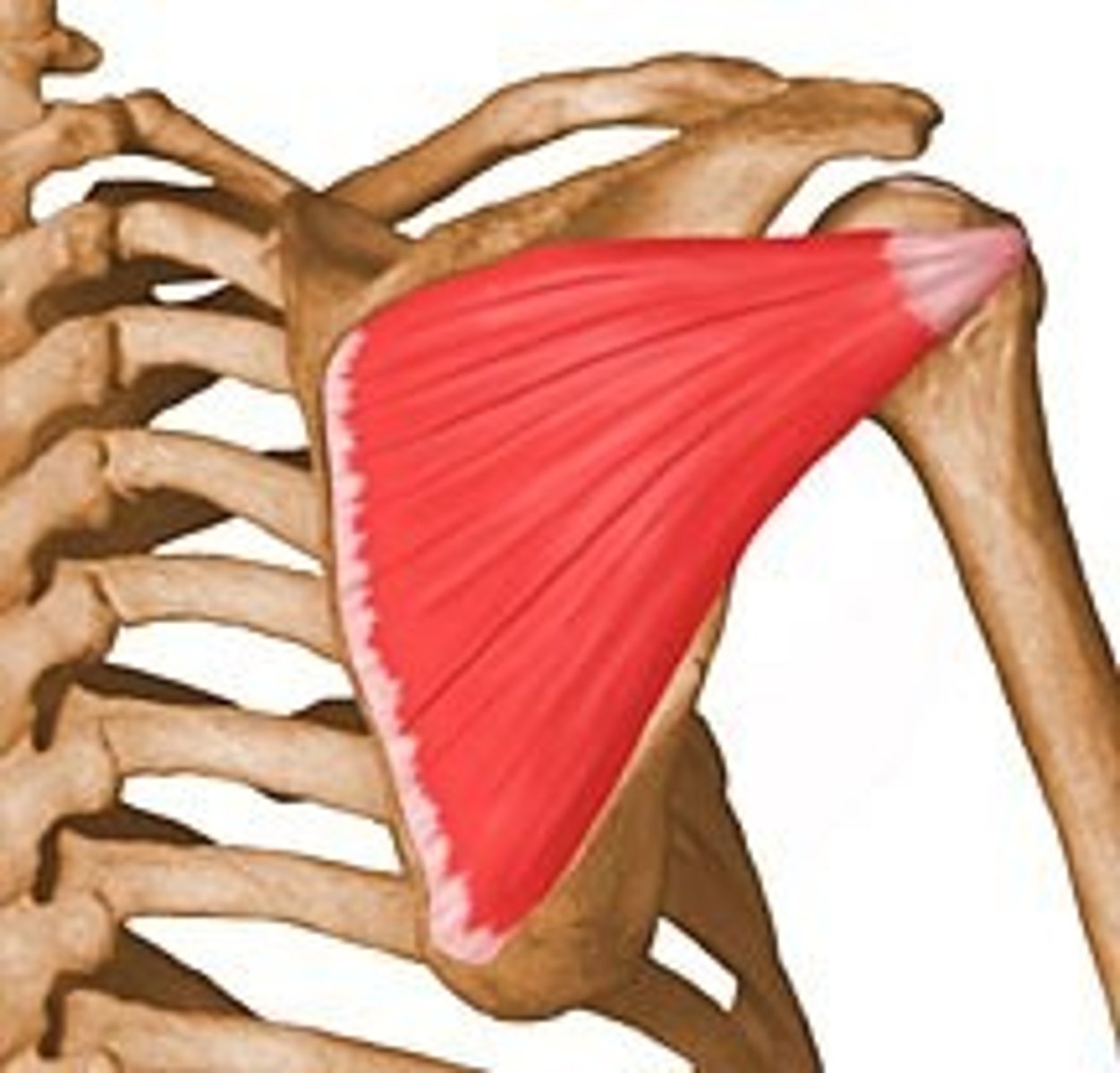
subscapularis
-origin: subscapular fossa
-insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus
-action: internal rotation (PM)
-innervation: upper and lower subscapular nerve C5-C6
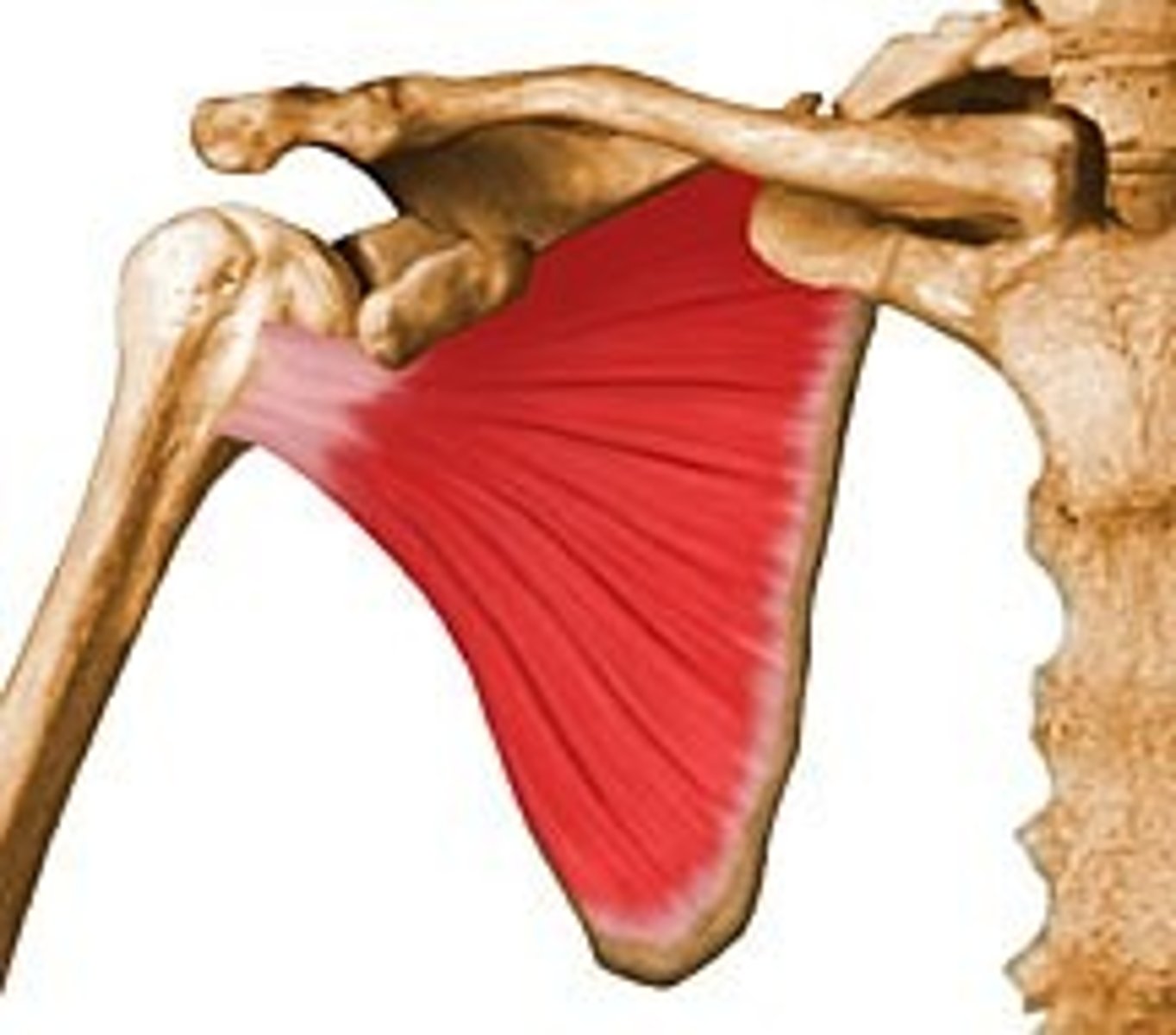
how would you "turn off" the deltoid to utilize only the rotator cuff muscles for IR and ER?
keep it adducted
muscle compartments of the limbs
-dense connective tissue divides muscles of the limbs into compartments
-in general muscles in the same compartments act as synergists and have common innervation
-muscles in opposing compartments = antagonists
muscles crossing the elbow joint
-insert on forearm bones
-allow movements at the elbow (flex/ext) and radioulnar joint (sup)
-2 muscle compartments: anterior = flexors, posterior = extensors
anterior flexors of the elbow joint
-biceps brachii
-brachialis
-brachioradialis (flexor, but majority in posterior compartment)
-coracobrachialis (in anterior compartment but acts at the shoulder)
common innervation = musculocutaneous nerve
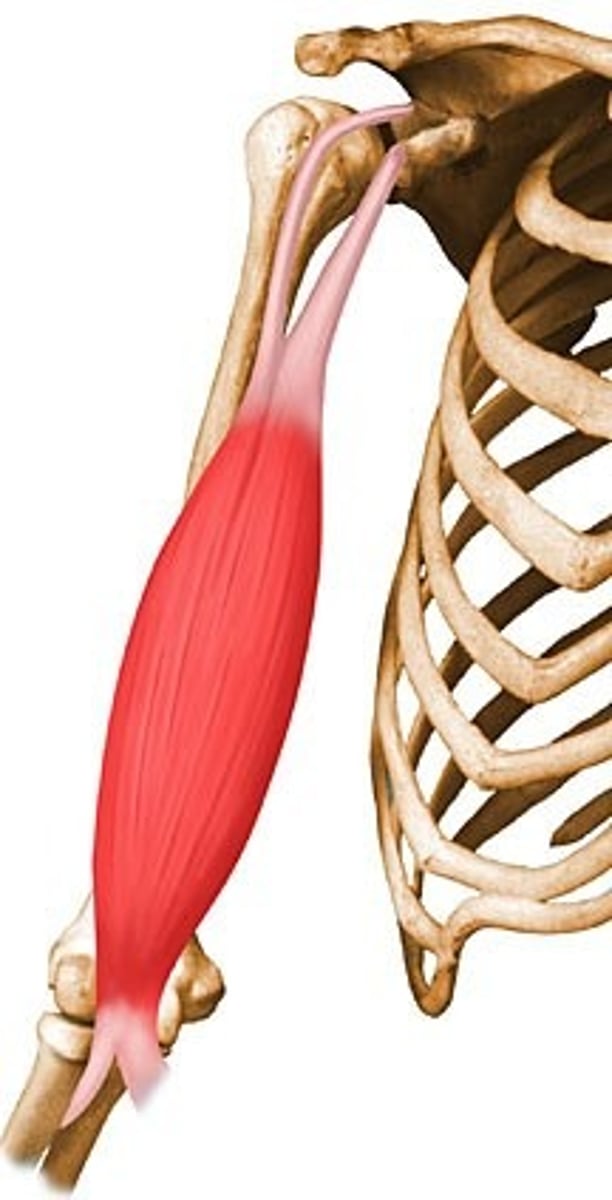
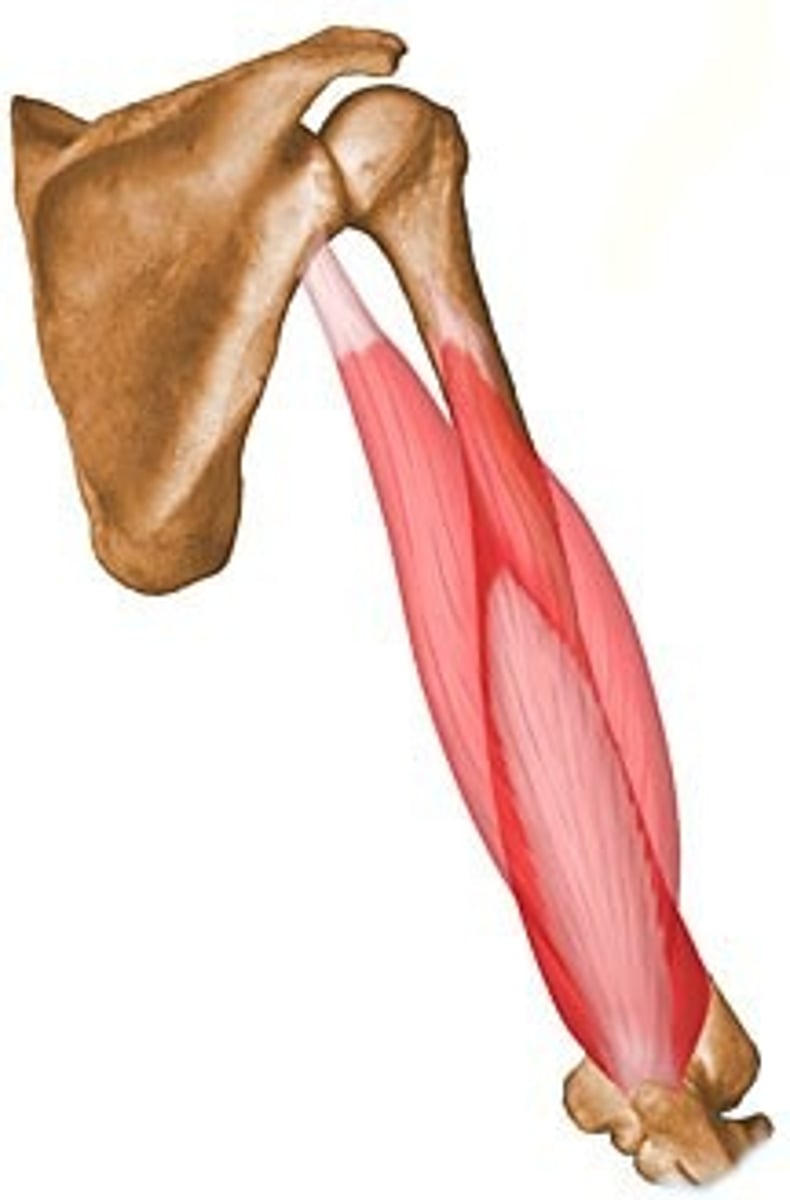
biceps brachii
-origin: long- supraglenoid tubercle, short- coracoid process
-insertion: radial tuberosity of radius, bicipital aponeurosis
-action: elbow flexion, supination
-innervation: musculocutaneous nerve, C5-C7
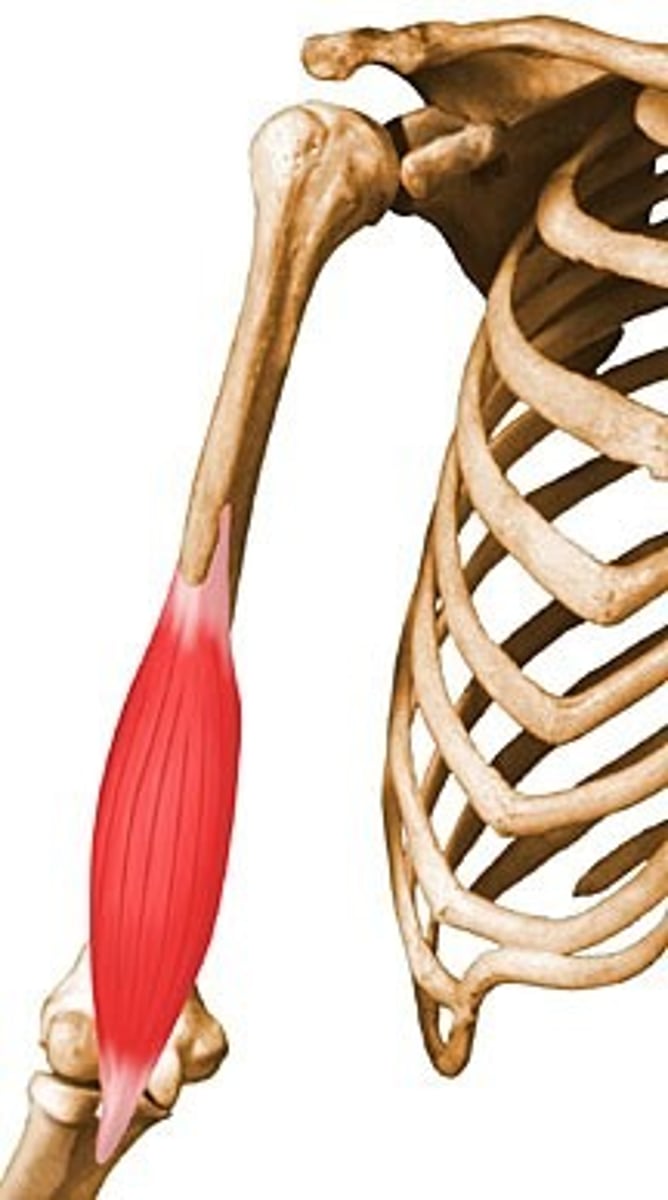
brachialis
-origin: anterior shaft of humerus- distal to deltoid tuberosity
-insertion: coronoid process of ulna, elbow joint capsule
-action: elbow flexion (PM)
-innervation: musculocutaneous nerve, C5-C6
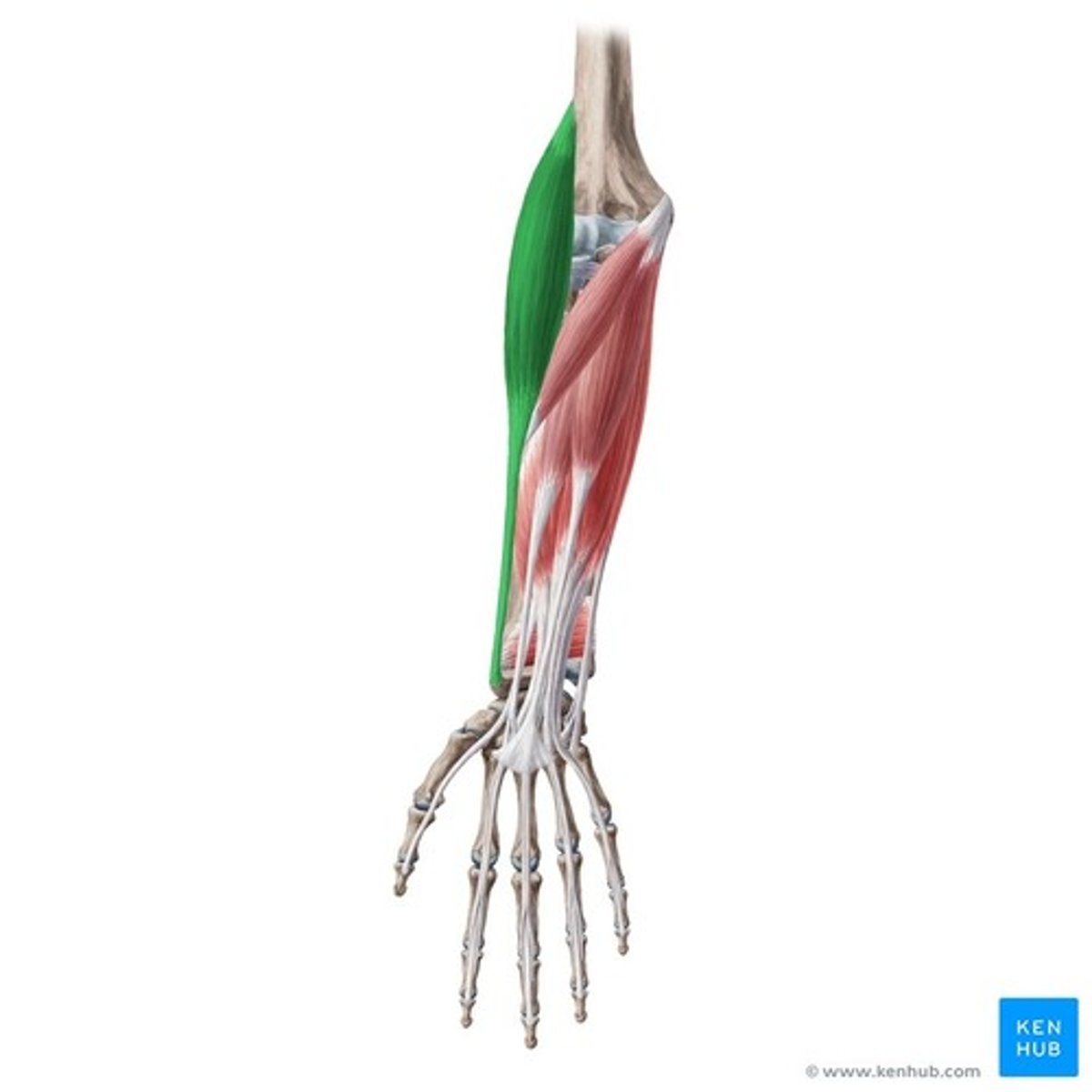
brachioradialis
primarily located in posterior compartment of arm
-origin: lateral supracondylar ridge of humerus
-insertion: styloid process of radius
-action: flexion in slight forearm pronation
-innervation: radial nerve C5-C7
posterior extensors of the elbow joint
-triceps brachii
-anconeus
common innervation: radial nerve
triceps brachii
-origin: long- infraglenoid tubercle, lateral- posterior shaft of humerus, medial- posterior shaft of humerus, distal to radial groove
-insertion: olecranon process of ulna
-action: elbow extension (PM), long- shoulder adduction
-innervation: radial nerve C6-C8
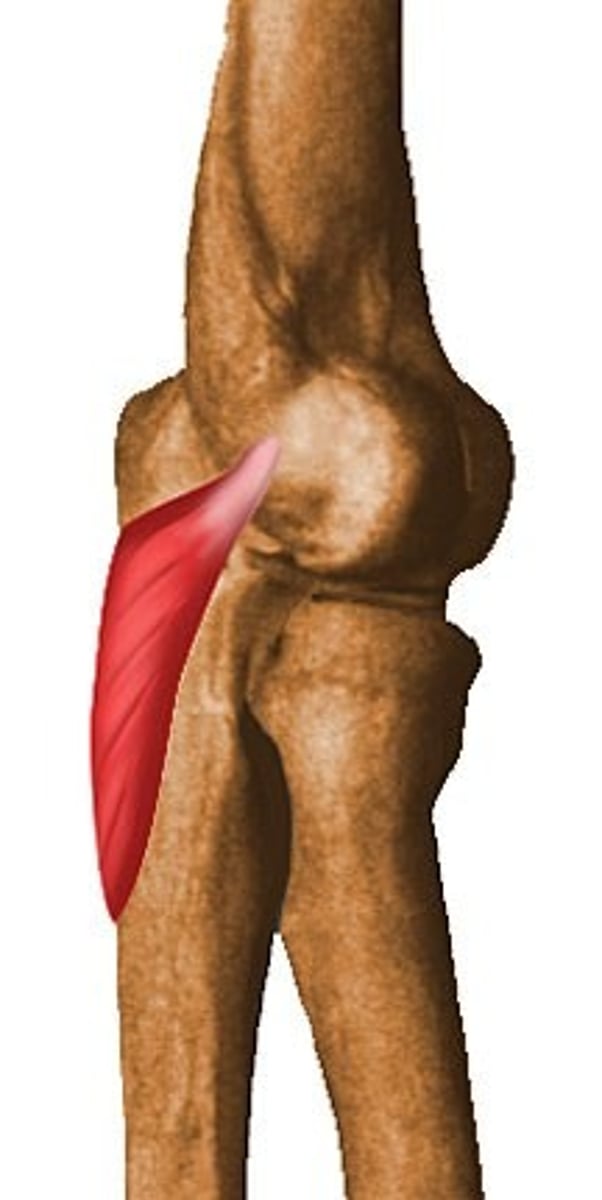
anconeus
-origin: lateral epicondyle of humerus
-insertion: lateral aspect of olecranon process of ulna
-action: elbow extension, fixator of ulna
-innervation: radial nerve C7-T1
muscles that adduct the shoulder
pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, teres major, long head of triceps brachii, coracobrachialis
muscles that abduct the shoulder
deltoid, supraspinatus
muscles that internally rotate the shoulder
subscapularis, pectoralis major, latissimus dorsi, teres major, anterior deltoid
muscles that externally rotate the shoulder
posterior deltoid, infrapsinatus, teres minor
lower subscapular nerve innervates....
subscapularis, teres major
suprascapular nerve innervates....
supraspinatus and infraspinatus
axillary nerve innervates...
deltoid, teres minor
brachioradialis