Hemolytic Anemias-Thalessemia (Chapter 12)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is one of the most common genetic disorders in the world?
Thalassemia syndrome
What is the cause of thalassemia?
A reduction or absent production of globin chains
What is the first main type of thalassemia?
Alpha (α) thalassemia
What is the second main type of thalassemia?
Beta (β) thalassemia
What is the cause of alpha thalassemias?
Gene deletions
What is the cause of beta thalassemias?
Various genetic mutations
Decreased production of one globin chain leads to:
Reduced amounts of normal hemoglobin
Microcytic, hypochromic anemia (small, pale red cells)
What is the clinical classification of Beta-Thalassemia major?
Homozygous
What is the clinical classification of Beta-Thalassemia intermedia?
Variable (can be homozygous or heterozygous)
What is the clinical classification of Beta-Thalassemia minor?
Trait or heterozygous
Beta thalassemia
Inherited genetic mutations that reduce or eliminate Beta-globin chain production
β⁰ mutations
Cause a complete absence of beta-globin chains
β⁺ mutations
Cause reduced amounts of beta-globin chains
β thalassemia major is also called
Cooley’s Anemia
A patient with β-thalassemia major would have an Hgb typically of:
<7 g/dL
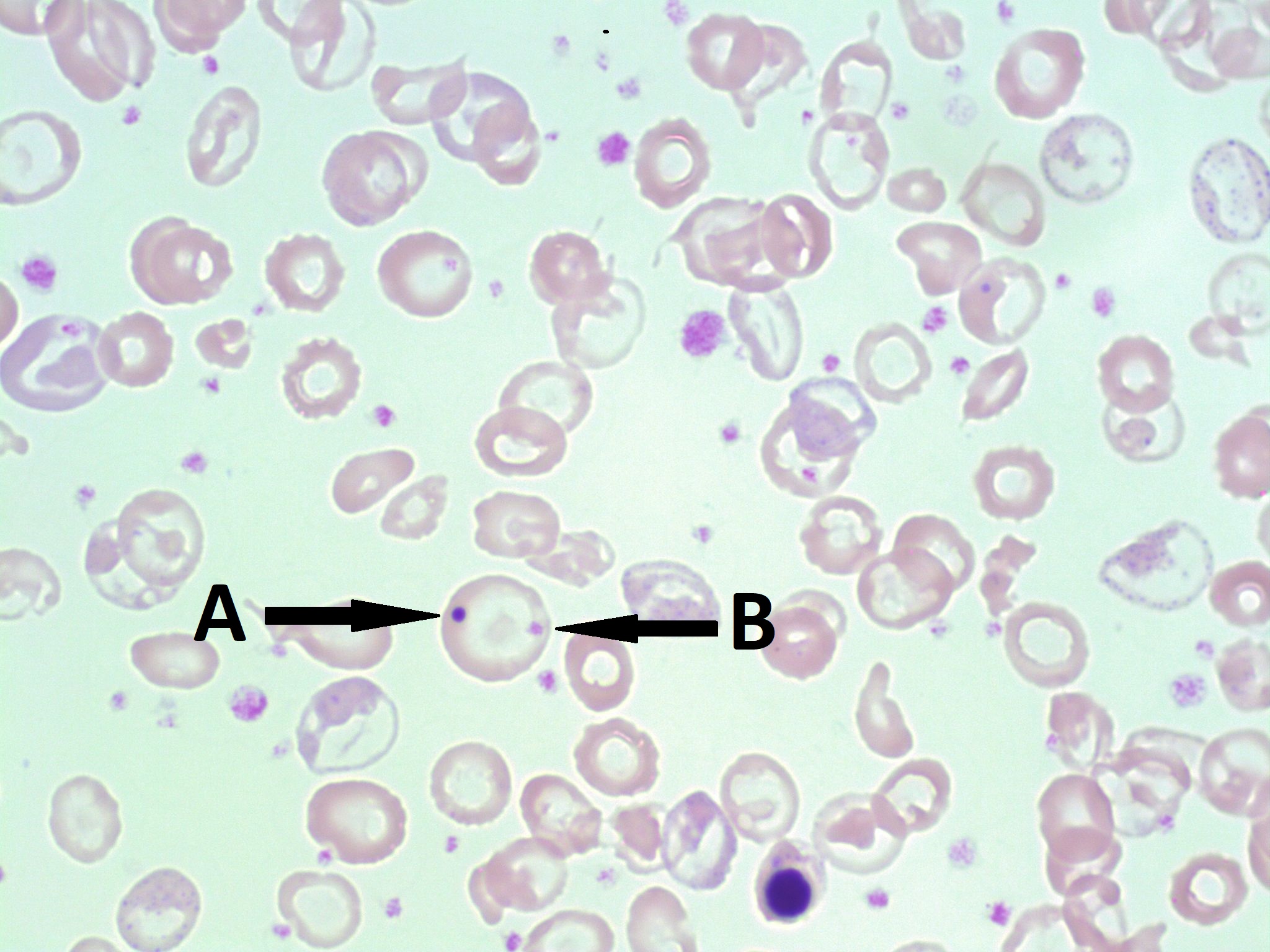
What is the arrow pointing to?
Howell-Jolly body in the hypochromic microcyte
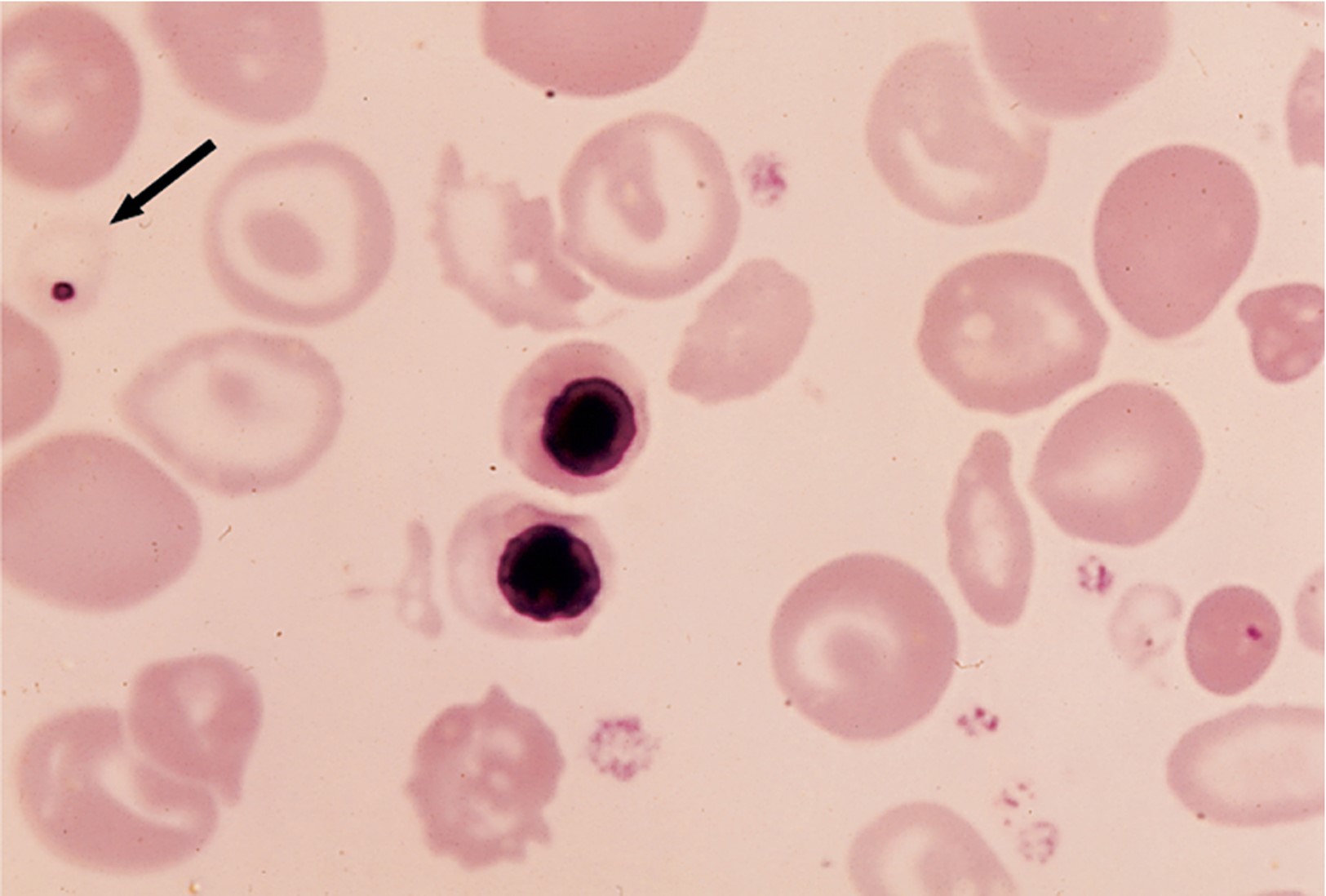
What condition could this smear be showing?
β thalassemia major (Cooley’s anemia)
β thalassemia intermedia
Appears after age 2
Patients maintain a higher Hb level
Variable degrees of symptomatic anemia, jaundice, splenomegaly & some complications of β thalassemia major
Survive into adulthood without a large blood transfusion requirement
β thalassemia minor
Usually discovered incidentally
Mild microcytic, hypochromic anemia
Silent carriers
β thalassemia minor
Why is there such heterogeneity in the clinical presentation of the beta thalassemias?
This is due to a decrease in the production of beta globin chains caused by mutations and several factors
α-thalassemias are based on the:
Number of gene deletions
α-thalassemia major
Occurs when all four alpha-globin genes deleted (no α-chains produced)
In the fetal stage of α-thalassemias what is present?
“Hemoglobin Bart”, which is composed of four gamma globin chains
Hydrops fetalis
Severe edema in unborn/newborn baby
Hemoglobin H Disease
Three alpha-globin genes deleted
Adults have _____% hemoglobin H; have 4 beta chains
5-40%
What is hemoglobin H composed of?
Four β-globin chains
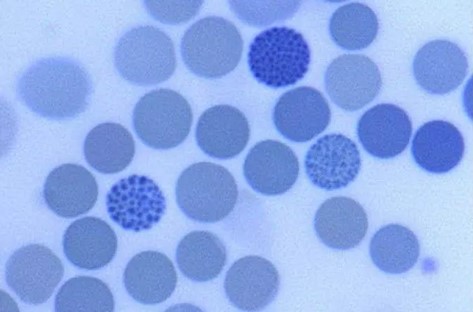
What gives off this “golf ball appearance”?
Hemoglobin H disease
α-thalassemia trait/minor
Occurs when two alpha-globin proteins have been deleted
α-thalassemia silent carrier
Occurs when only one alpha-globin gene is deleted, which can cause children to have hemoglobin H disease
Hemoglobin constant spring (HbCS)
Results of a point mutation in the α2-globin gene
Hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin (HPFH)
A group of conditions with the persistence of fetal hemoglobin synthesis into adult life
How can the automated hematology results, such as the RBC count and RBC indices, be used to aid the diagnosis of thalassemia?
They can be used to check for:
Normal-to-increased RBC
Normal to mildly decreased MCHC
Normal RBC volume distribution width (RDW)
Which types of thalassemias causes elevated (range 1-6 mg/dL), due to hemolysis?
Major
Intermedia
In an individual who is a thalassemia carrier, the serum ferritin level is:
Normal/High