Biology 30 Unit 1: Life
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is Biology?
The Study Of Life
“Bios”
Greek word meaning Life
“Logos”
Greek word meaning The Study Of…
What are the 8 characteristics of Life
Contains Genetic Material
Made up of Cells
Maintain a stable internal Environment
Evolve
Reproduce
Grow and Develop
Respond to their Environment
Obtain & use Material & Energy
What is a Virus
A virus is a noncellular particle that is made up of genetic material and protein
How Does a Virus Reproduce
Virus attaches itself to cell wall
Nucleic Acid from the virus enters cell
Nucleic Acid of virus directs cell to make new virus parts
Virus parts are put together, making copies of the virus
Cell bursts open and virus are released
Why aren’t viruses living
Lack cell structure
Do not grow
Do not use energy
Can reproduce when inside living cells
What is spontaneous generation/Abiogenesis
The belief that life arose from Non-Living matter
What is Biogenesis
The belief that living things arise from other living things of the same type
Francisco Redi
First Scientist to prove Biogenesis:
Used Meat, a Jar, and Mesh to show that Maggots couldn’t form even if there was oxygen present
John Needham
Proved Abiogenesis:
Boiled a Gravy, and put a quark stopper to not allow microorganisms to enter, but failed due to quark having little holes.
Lasssaro Spallanzani
Challenged John Needham & proved Biogenesis:
Did the same experiment with Gravy, but melted the glass neck together.
Louis Pasteur
Proved Biogenesis:
Used a Swan Neck Flask to trap the organisms in the elbow of the flask and heated a liquid to kill the organisms. He also proved “Pasteurization”

Label The Light Compound Microscope
What is the most common type of Microscope we use?
Light Compound Microscope
Where should you carry the Microscope by?
Arm
Base
How long is the field of view on low power?
4.4mm
How long is the field of view on medium power
1.66mm
How long is the field of view on high power?
.44mm
How to Calculate the Magnification?
M=size of drawing/size of actual object
Joe viewed an amoeba under a high power (40x)objective lens on his microscope where he estimated that 4.5 would fit across the view of field. He drew the following picture of the amoeba. Calculate its magnification.
What is a Cell?
A cell is the basic unit of life
How did the name “cell” originate?
named after examining cork tissue. The tiny chambers looked like honeycomb or the rooms in a monastery
Van Leuwenhoek
First Biologist to see cells
Robert Hooke?
Coined the term “Cells”
Robert Brown
Discovered the Nucleus
Felix Dujarden
Named the jelly-substance “cytoplasm”/“protoplasm”
Theodore Schwann
A zoologist stated that animal tissue is made up of animal cells
Matthias Schneiden
Stated that plant tissue is made of plant cells
Rudolf Virchow
Stated that all cells come from pre-existing cells(Biogenesis)
What are the two major cell types?
Prokaryotic
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic?
Cells that lack a nucleus ex) only Bacteria
Eukaryotic?
Cells that contain a nucleus ex) all protists, fungi, plants and animals
Characteristics Animal Cells?
Round in shape
Centriole Pair (Cell Division)
Lysosomes
Flagellum
Several Small Vacuoles
Characteristics Plant Cells?
Boxy in shape
Cell Wall (Cellulose)
Chloroplast
On large Central Vacuole
Label Animal Cell?
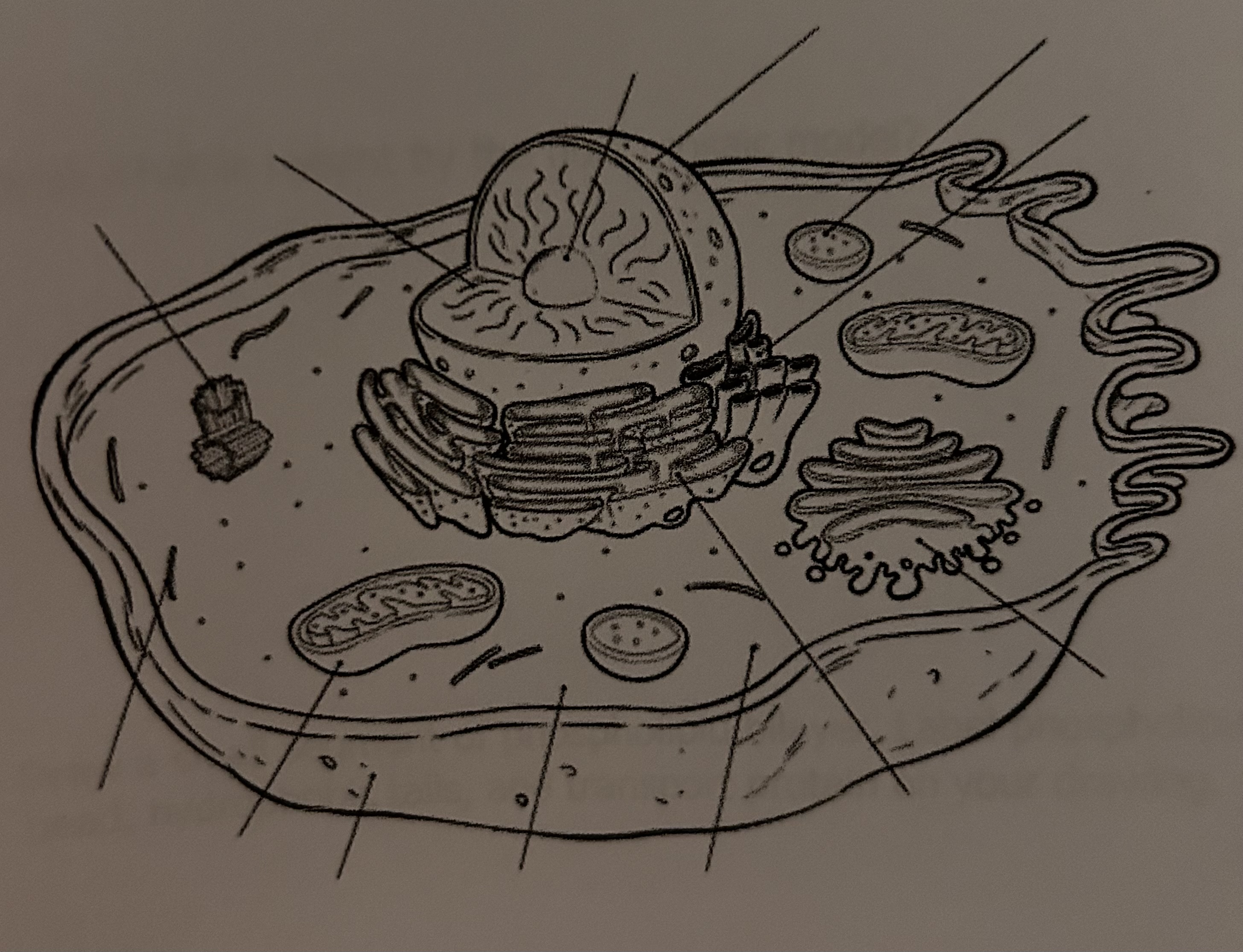
Label Plant Cell?
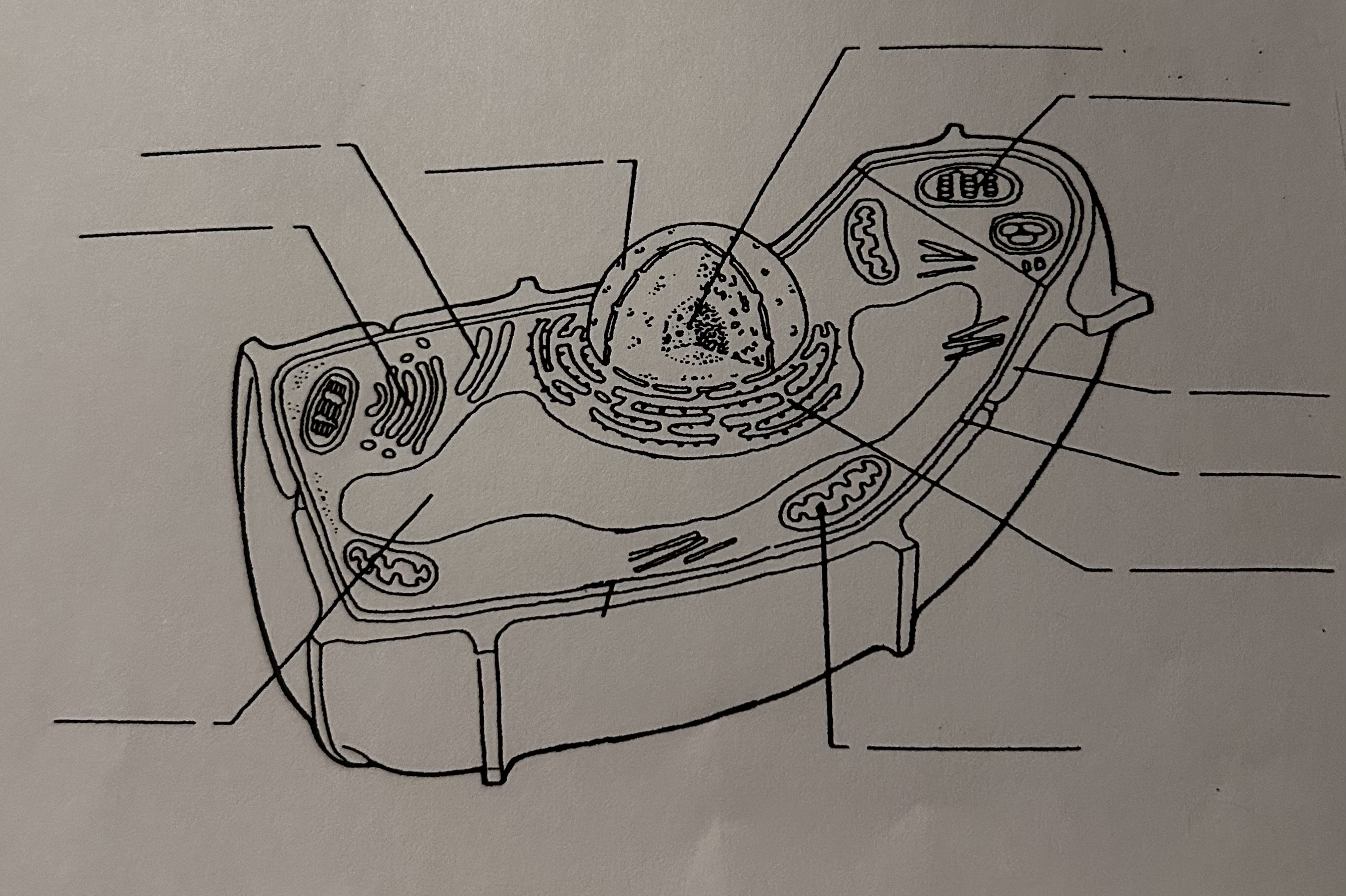
Nucleus(Control Center)
Directs all cells activities
Site of DNA replication and Chromatin (unravelled DNA)
Nucleolus (Ribosome Factory)
Site of ribosome production
Made up of RNA and protein
Nuclear Membrane( Nucleus Gatekeeper)
Surrounds the Nucleus and separates it from cytoplasm
2 layers of lipids called nuclear pores
Nucleoplasm
Cytoplasm of the nucleus
House for nucleolus & Chromatin
Ribosome (Protein Factory)
Smallest organelle within the cell
Site of Protein Synthesis—> Translation (Creates Protein)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum [SER] (Shipper of the Cell)
To ship materials throughout the cell interior
Smooth in Appearance(No Ribosomes)
Network of hollow tubes (subway/Train)
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum [RER] (Shipper of the Cell)
Rough in Appearance ( Has Ribosomes)
Can also synthesize proteins
Same as SER
Golgi Body (Packager)
It packages materials like proteins for Transport
Mitochondria (Power/Energy)
Shaped like a Jelly Bean
Site of Cellular Respiration
Cytoplasm
Jelly like Substance
Provides a residence for all cell organelles
Vacuole (Storage tank of the Cell)
Stores Water
Centriole (Unique to Animal Cell)
Cell division
Lysosome [Stomach of the Cell] (Unique to Animal Cell)
Digestive cells formed from the Golgi Body
Flagellum (Unique to Animal Cell)
A whip like tail made of protein
Permits movement
ex) Sperm Cell
Chloroplast [Photosynthesis] (Unique to Plant Cell)
Green in color containing pigment Chlorophyll
Site of Photosynthesis
Cell Wall (Unique to Plant Cell)
Rigid non-living structure composed of cellulose
Helps maintain shape in Plants and provides protection
Organelles unique to plant cells
Chloroplast
Cell Wall
Organelles unique to animal cells
Centrioles
Lysosome
Flagellum
What is a Fluid Mosaic Model?
Fluid: The many small parts can MOVE
Mosaic: A surface of many small parts
Hydrophilic
Phospholipid Head
Hydrophobic
Phospholipid Tail