Physio B Lab Midterm 2
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
cardiac axis
the general (mean vector) direction of electric impulses as they travel through the heart
normal axis
upper right to lower left
Leads 1, 2, & 3: positive, 3 is sometimes biphasic
right axis deviation causes
hypertrophy in right ventricle, axis shifts to the right of the heart; NORMAL in children and tall thin adults because the left mass of the heart is heavier, swaying the heart to the right
right axis deviation can tell us..
scoliosis, pulmonary hypertension, enlarged heart
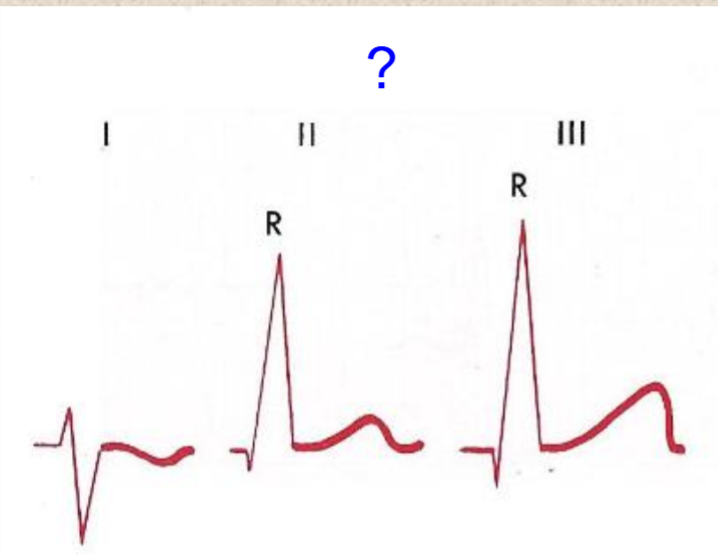
right axis deviation
electric vector towards right side of the body; lead 1: negative; leads 2 & 3: positive
left axis deviation causes
hypertrophy of left ventricle; NORMAL in short and stocky individuals (because diaphragm can push up on the heart, causing it to sway to the left) & asymptomatic athletes
left axis deviation can tell us ..
emphysema, hyperkalemia, tricuspid atresia, systemic hypertension
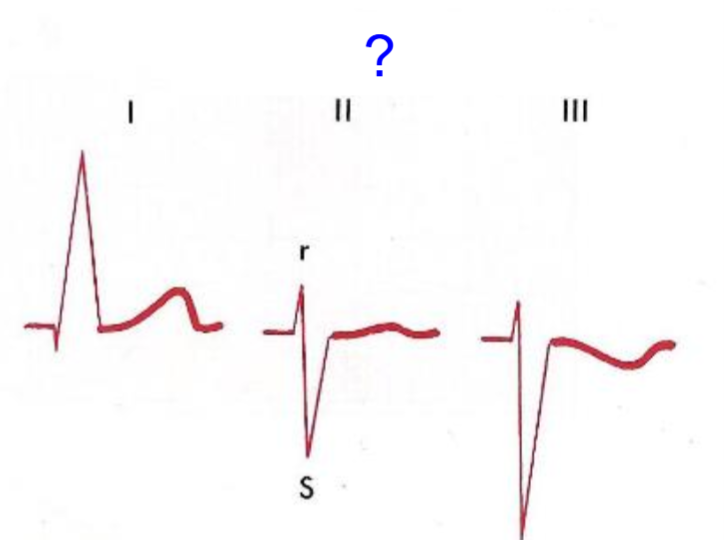
left axis deviation
electric vector toward left side of body;
Lead 1: positive, Leads 2, 3, AVF: negative
right axis deviation
left axis deviation
how fast does EKG paper move?
25 mm/sec
tiny box on EKG paper
1 mm = 0.04 sec
big box on EKG paper
5 mm = 0.2 sec
heart rate
distance between 2 R waves;
HR (bpm) = 1500 / (# of tiny boxes)
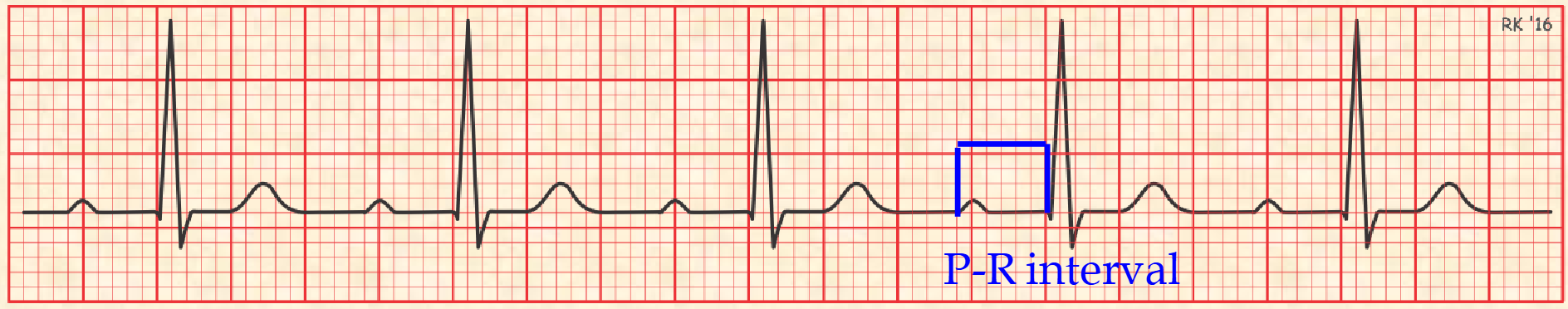
PR Interval definition
time from the beginning of the P wave (arial depolarization) to beginning of QRS complex (ventricular depolarization) through AV junction
normal PR interval
0.12 sec - 0.2 sec
3 mm - 5 mm
PR interval > 0.2 sec
heart block
PR interval < 0.12 sec
less blood flow to ventricles, lower cardiac output
PR interval calculation
# of tiny boxes from beginning of P wave to beginning of QRS complex * 0.04 sec
causes of heart block
age, scar tissue from previous heart surgery, side effect of medications, electrolyte imbalance
heart blocks that CAN be asymptomatic
1st or 2nd degree
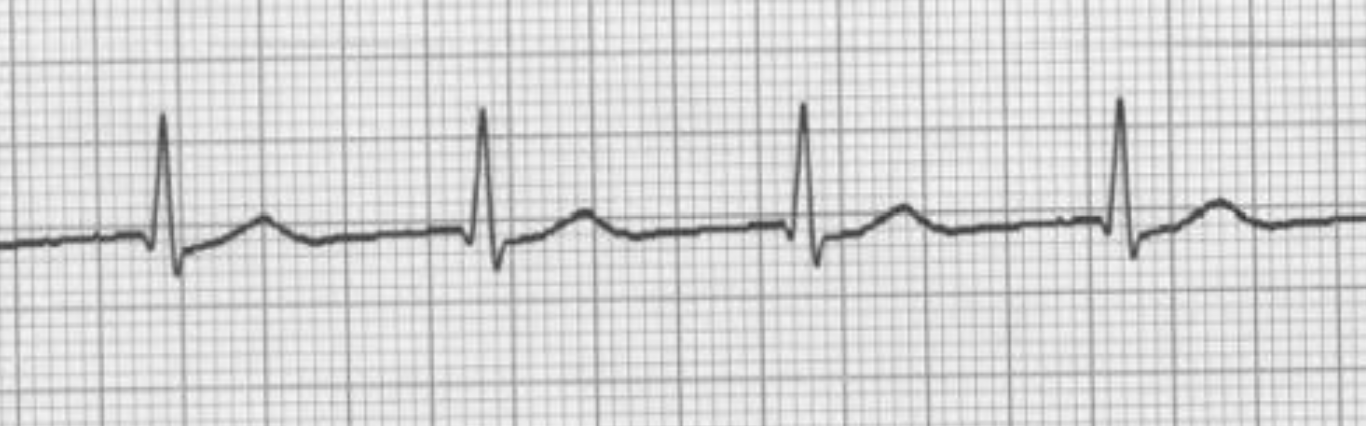
SA block/junctional rhythm
SA node not leading the rhythm, AV node becomes the pacemaker → P and QRS happen at the SAME time (b/c QRS is larger, can’t see P wave); ABSENT P WAVE IN ALL LEADS
First Degree AV Block
delay in transmission of impulse from the atria to the ventricles; prolonged PR interval consistently in all leads (> .20 sec)
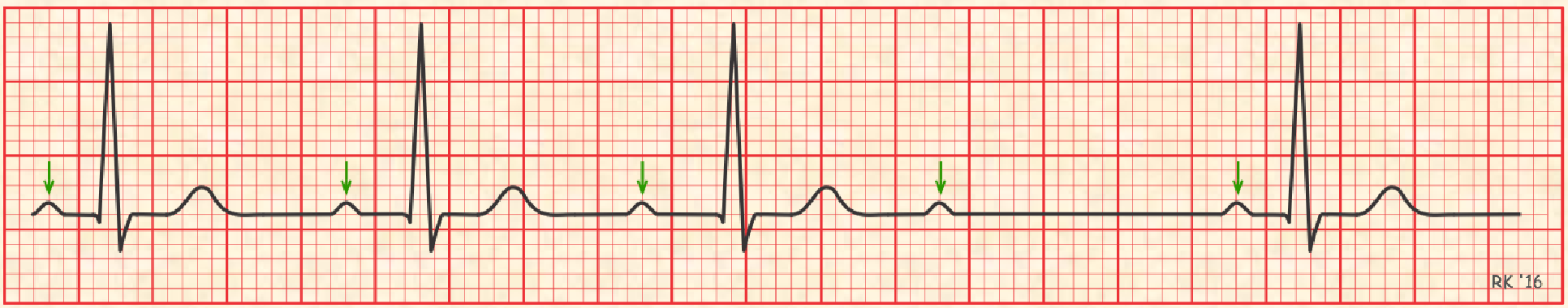
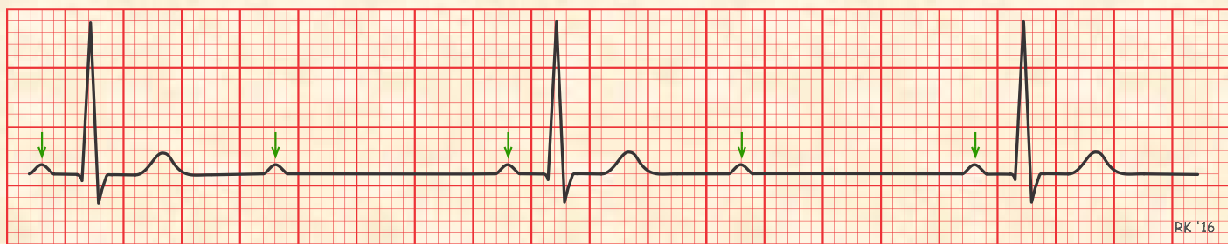
2nd degree AV Block, Type I
increasing PR intervals until a QRS complex is dropped, cycle is resumed with no set pattern; p wave is seen but the impulse does not initiate a ventricular response
2nd degree AV Block, Type II
'“fixed rate” → multiple p waves before the QRS complex; can be a 2:1, 3:1, etc. but will be consistent
Third Degree AV Block/ Complete Heart Block
no association between atria and ventricles; p wave is there but impulse not conducted to ventricles, so a second pacemaker below the block must be active and generate QRS complexes → “escape pacemaker” could be in the Bundle of His or ventricle; P is faster than QRS, could have a double peak T wave
SA block
2nd degree AV Block, type 1
1st degree AV block
2nd degree AV block, type 2 (2:1)
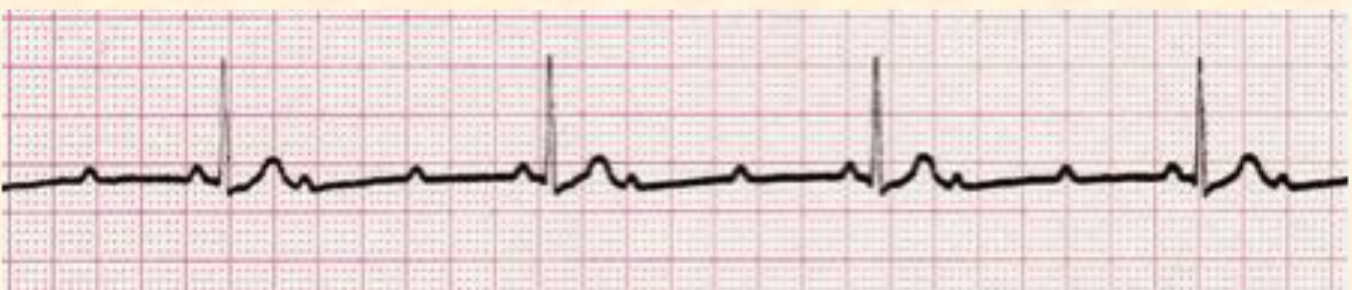
2nd degree AV block, type 2 (3:1)
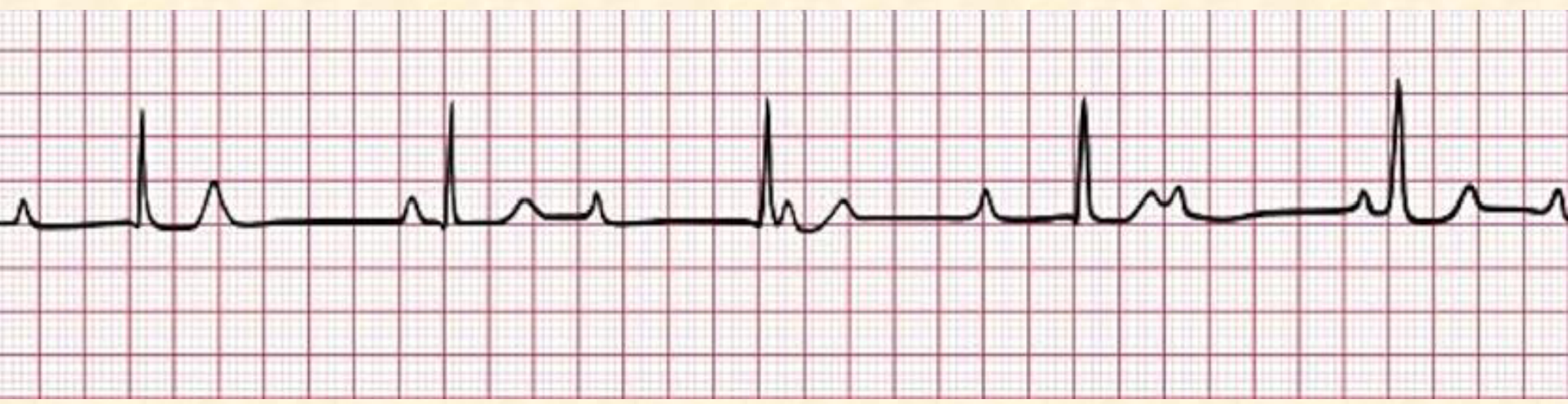
complete heart block
bundle branches
there is a right bundle branch that transmits the stimulus to the right ventricle, and there is a left bundle branch that transmits the stimulus to the left ventricle
if bundle branch is blocked…
stimulus can still reach the ventricular portion that it was supposed to stimulate; pathway to stimulate the ventricular mass that has the blocked bundle branch is through tissue (cell to cell) outside the normal conduction pathway → conduction slower, causing delay in ability to stimulate ventricular side that has blocked bundle branch
causes of bundle branch blocks
cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, hypertension
right bundle branch block (RBBB) can result from…
COPD, pulmonary hypertension
normal deflection of chest leads
V1 & V2: negative; V3 & V4: biphasic; V5 & V6: positive
right bundle branch block (RBBB)
2 upward deflections (R waves) in V1 and/or V2; R’ bigger than R
RBBB why are there 2 R waves?
delay in stimulation of right ventricle, second R wave represents stimulation of the right ventricle; 2 waves: rR’
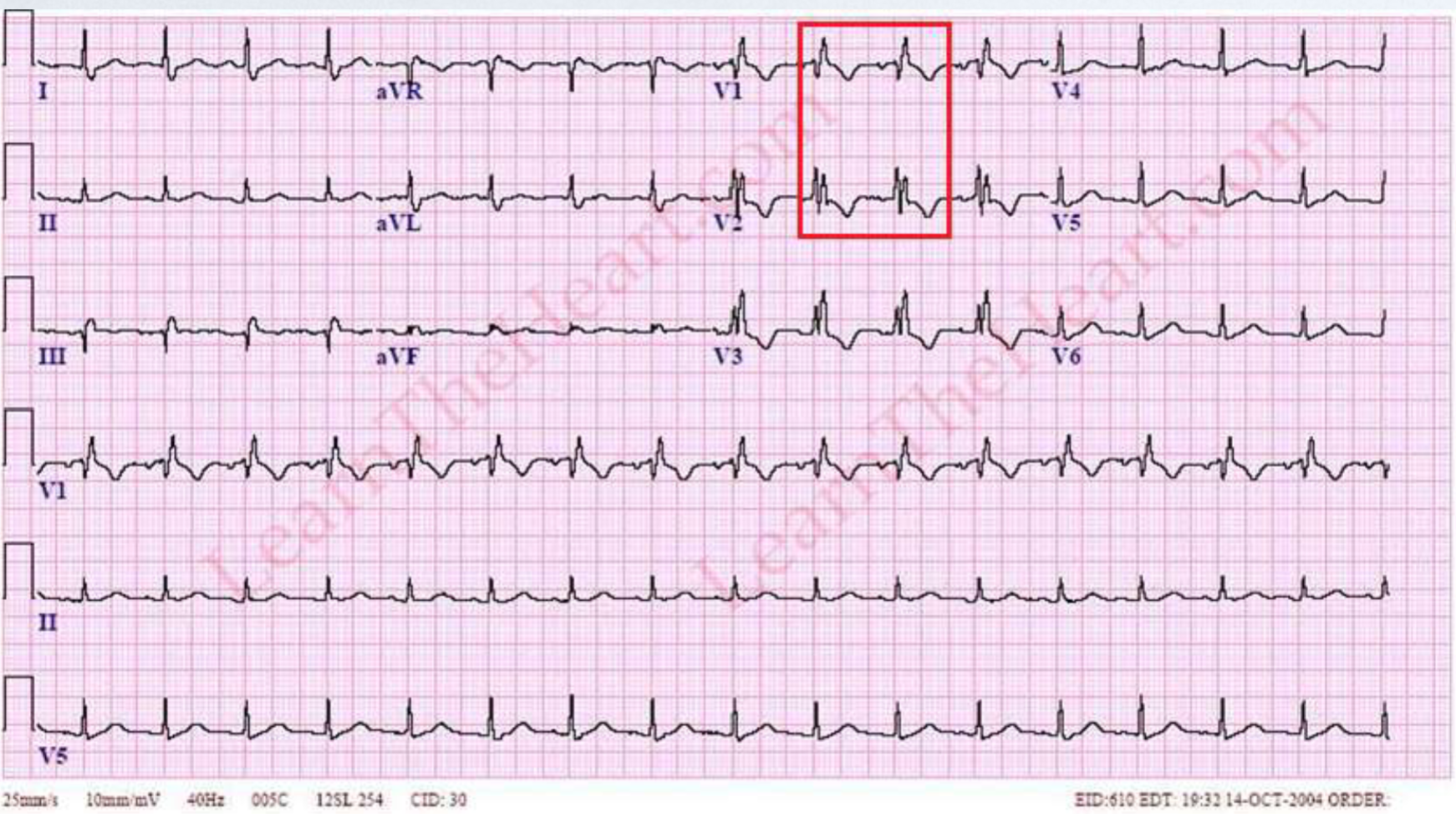
RBBB
left bundle branch block (LBBB)
2 R waves in V5 & V6; R waves similar in height
LBBB why are there 2 R waves?
delay in stimulation of left ventricle, second R wave represents stimulation of the left ventricle; 2 waves: RR’; 2 R waves can ‘slur’ into each other and be seen as a wide QRS complex
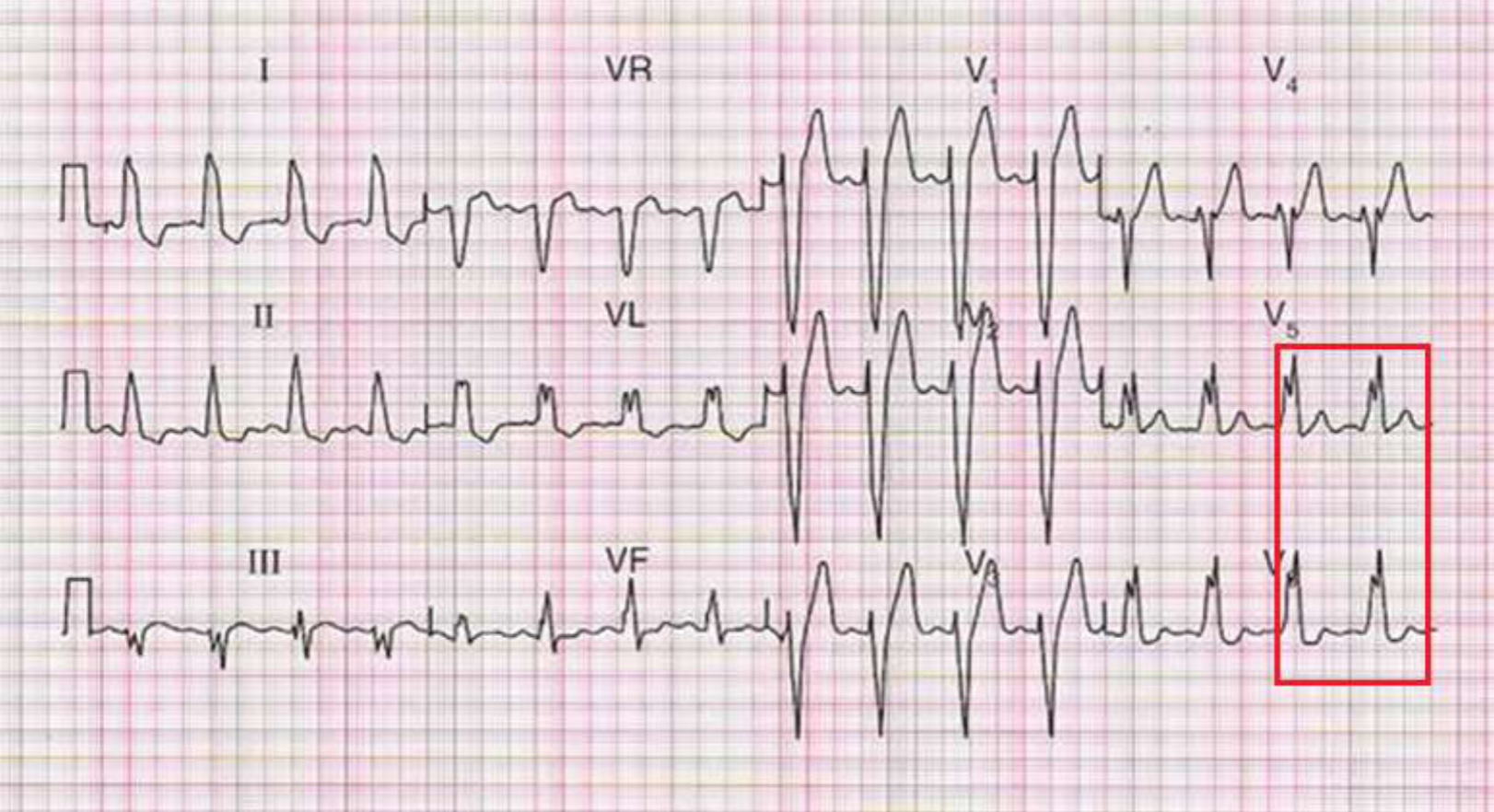
LBBB
right av valve
tricuspid valve
left av valve
bicuspid valve
av valves:
valves between atria and ventricles; also called parachute valves
semilunar valves:
between ventricles and arteries exiting the heart; also called hip-pocket valves (aortic semilunar valve & pulmonary semilunar valve)
hypertrophy
an increase in mass attributable to increases in cell size (not number); term used for elevated mass in ventricles (LVH & RVH)
enlargement
same as hypertrophy but this term is used for elevations in atrial mass (RAE & LAE)
Frank-Starling Law
as larger volume of blood flows into the chambers of the heart, the blood stretches the cardiac muscle fibers, leading to an increase in the force of contraction → hypertrophy or enlargement of that heart chamber
EKG paper vertical axis
magnitude of electrical activity (mV) 1mm = 0.1 mV
normal atrial size
2.5 boxes wide (0.1 sec) and 2.5 boxes high (0.25 mV)
right atrial enlargement (RAE)
tall p wave (>2.5 mm) in 2/3 of the inferior leads (Lead II, Lead III, and aVF)
causes of RAE
tricuspid stenosis (narrow) or tricuspid prolapse (leaky)
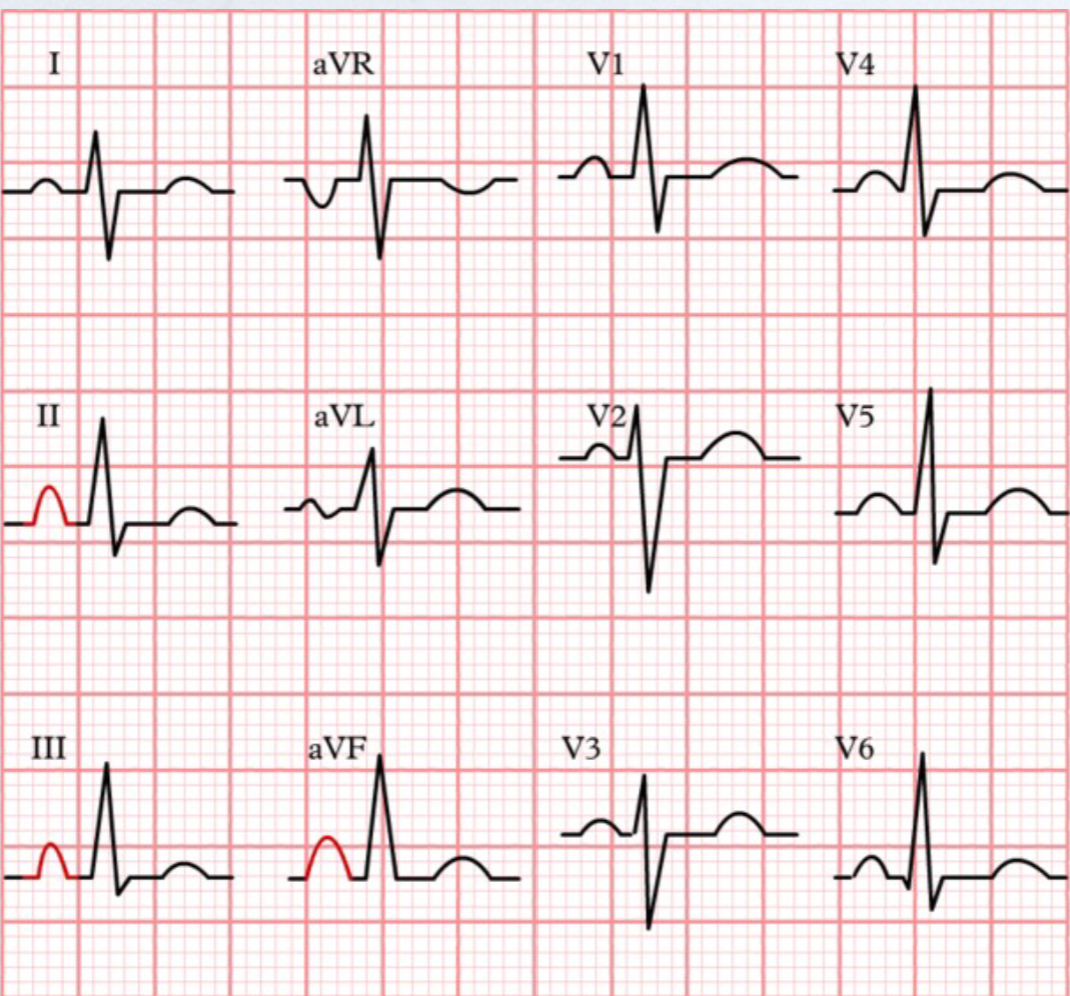
RAE
left atrial enlargement (LAE)
wide P wave (> 0.1 sec in duration) in 2/3 of the inferior leads (Lead II, Lead III, and aVF); b/c takes longer to reach to and depolarize left atria enlarged mass OR wide P wave in Lead 1 AND 2 waves (one up and one down) in V1
causes of LAE
bicuspid stenosis (narrow) or bicuspid prolapse (leaky)
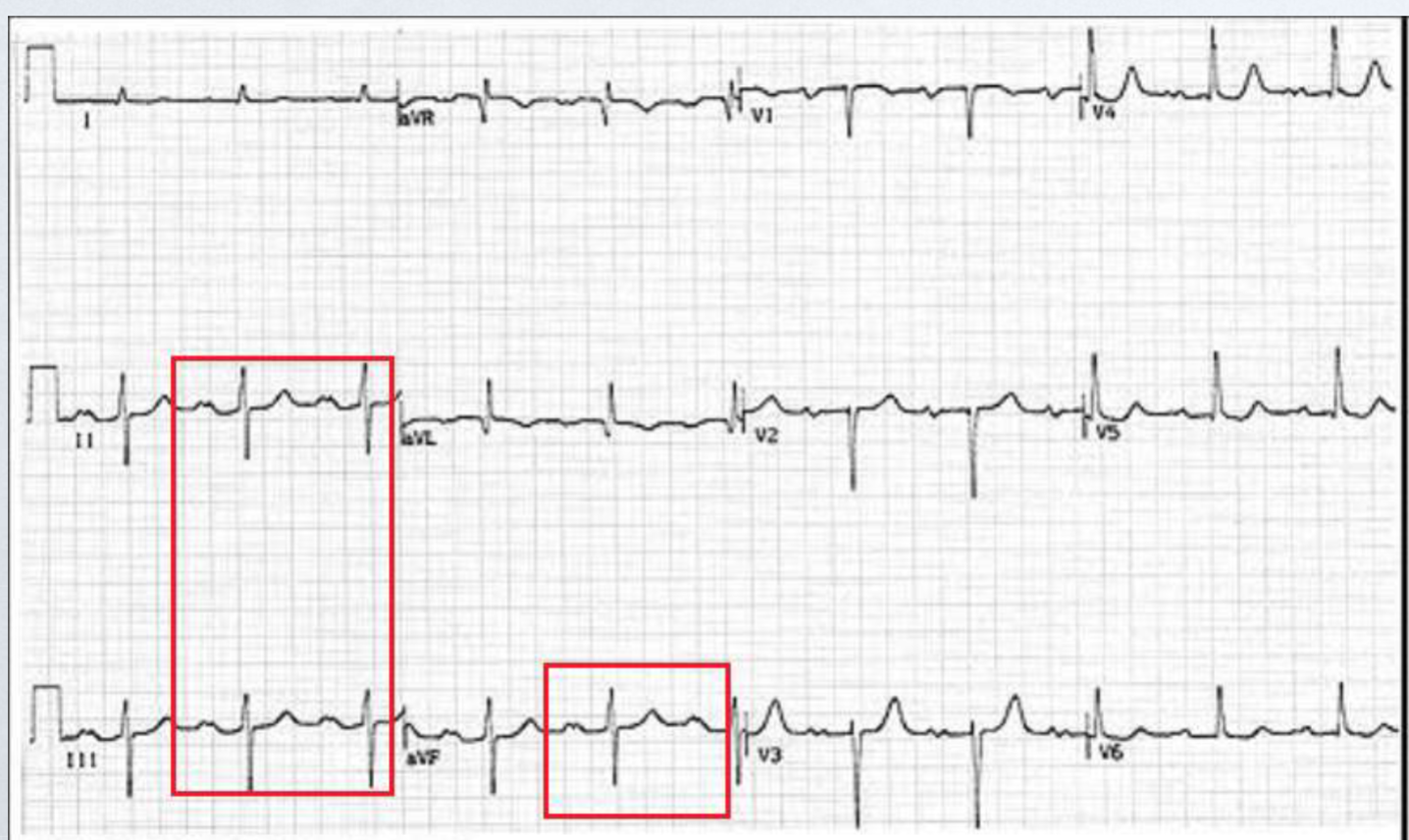
LAE
RVH
electrical vector directed toward right side; positive V1 or V2, biphasic or negative V5 or V5
cause of RVH
pulmonary valve stenosis or prolapse
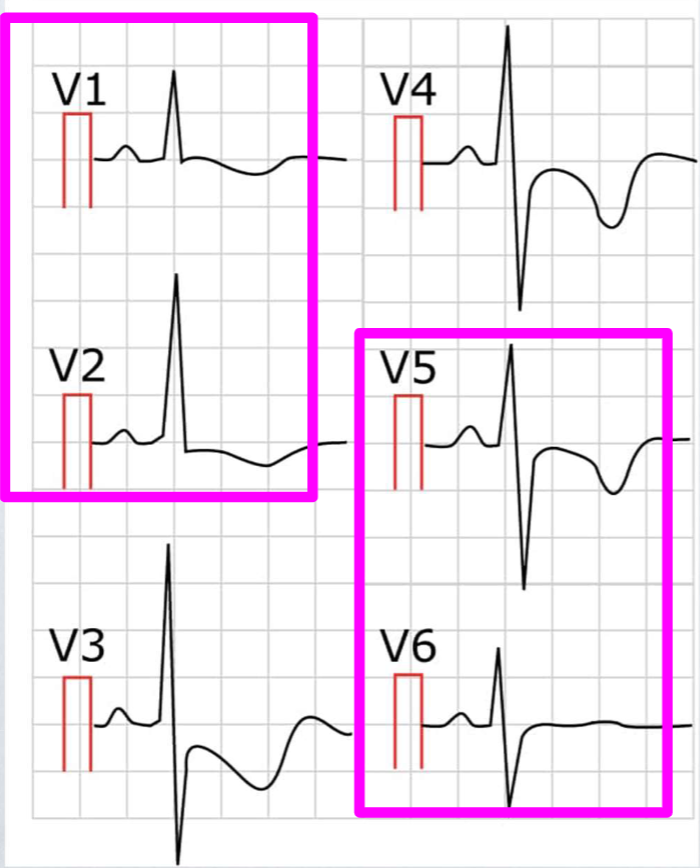
RVH
LVH
deflection pattern normal but because of the larger mass → magnitude of deflection pattern greater than normal; add amplitude of S wave in V1 or V2 + amplitude of R wave in V5 or V6, if greater than or equal to 35 mm
cause of LVH
normal adaptation to exercise, aortic valve stenosis or prolapse
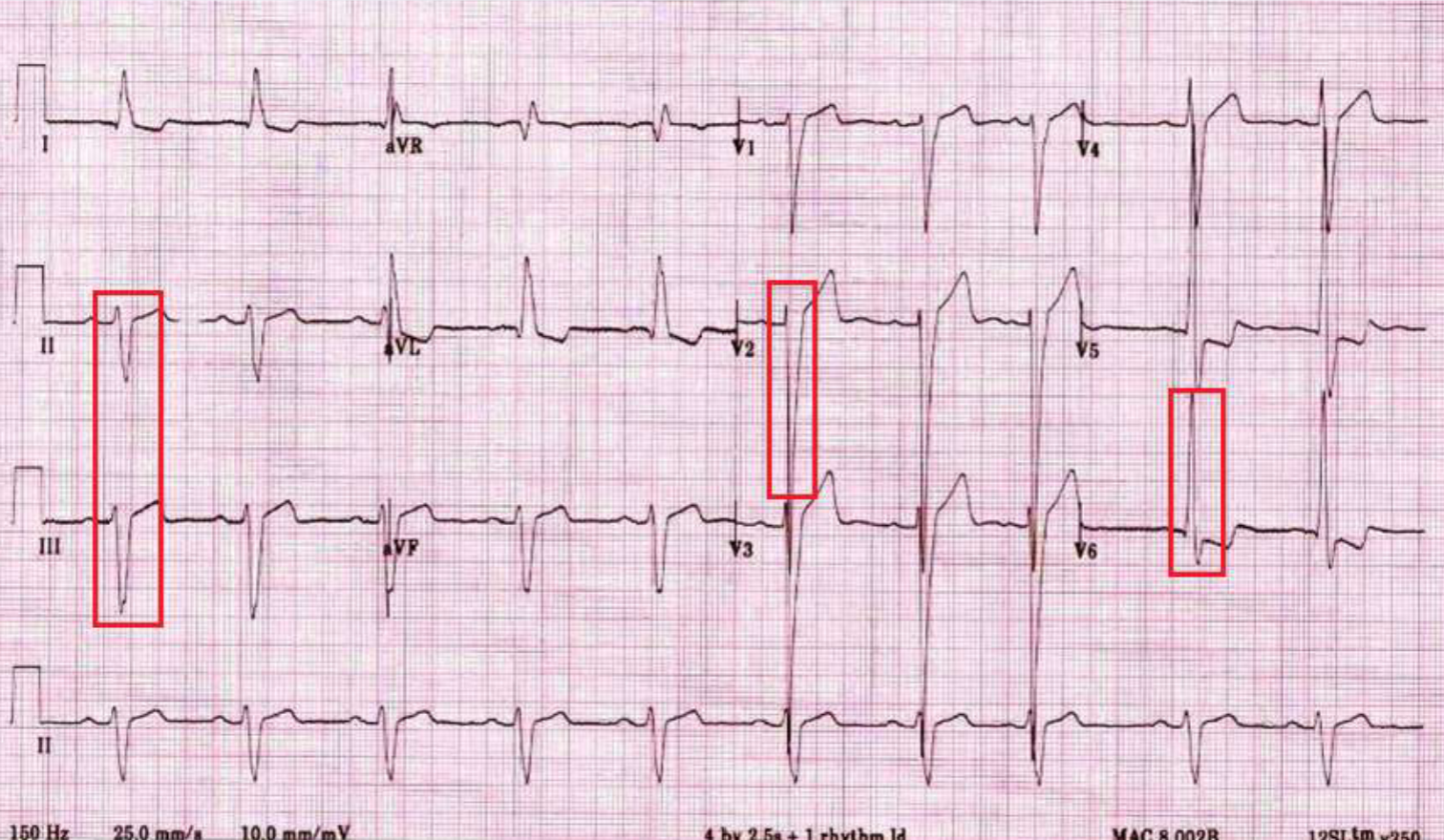
LVH
ectopic focus/pacemaker
an excitable group of cells that causes a premature heartbeat outside the normally functioning SA node of the heart
cause/factors that aggravate ectopic focus:
cause: unknown
factors that aggravate: alcohol, smoking, caffeine
PVC (premature ventricular contraction/complex)
when stimulation of ventricles (‘ectopic focus’) occur in one or more areas within the ventricle before the normal stimulation from the SA node arrives; longer QRS with weird morphology b/c ectopic firing of a focus disrupts normal sequence of cardiac activation → 2 signals because ectopic foci fires independent of normal firing
criteria to diagnose PVC
no p wave
wide QRS complex (greater than 0.1 sec)
T wave usually points in the direction opposite to the QRS wave
normal QRS interval
0.04-0.1 sec
unifocal PVC
PVC originates in one focal point within the ventricle; looks the same in any lead
multifocal PVC
PVC originates in more than one focal point within the ventricle; looks different in any given lead; can have 2 different morphologies in the same lead
continuous PVCs
PVC with a pattern; if every other beat is a PVC → bigeminy; if every third beat is a PVC → trigeminy; if every fourth beat is a PVC → quadrigeminy
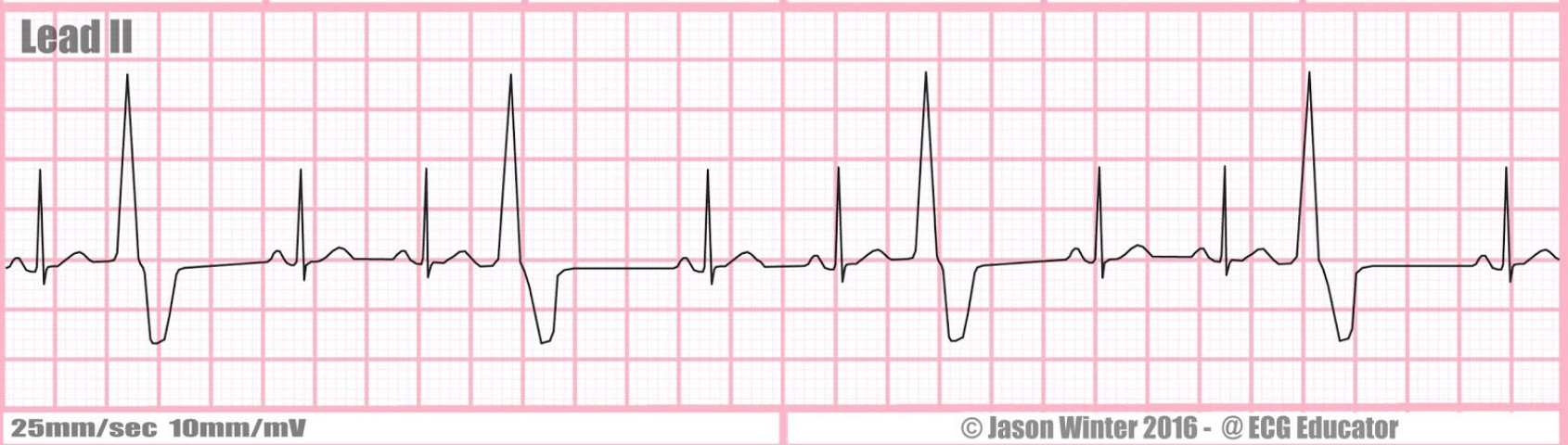
unifocal ventricular trigeminy
V Tach (ventricular tachycardia)
3+ PVCs in a row, looks like the blade of a saw
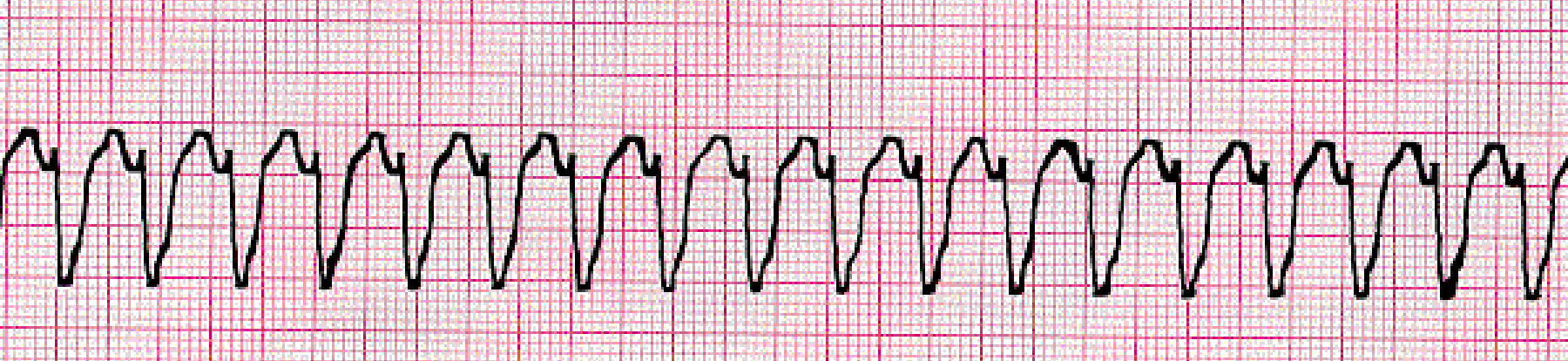
v tach
R on T PVC
R wave of the PVC (or S wave) occurs on the T wave of the preceding beat; when this occurs, individual goes into V fib (ventricular fibrillation) because cells haven’t fully repolarized
V fib (ventricular fibrillation)
rapid, irregular signals causing the heart’s ventricles to quiver uselessly instead of pumping blood
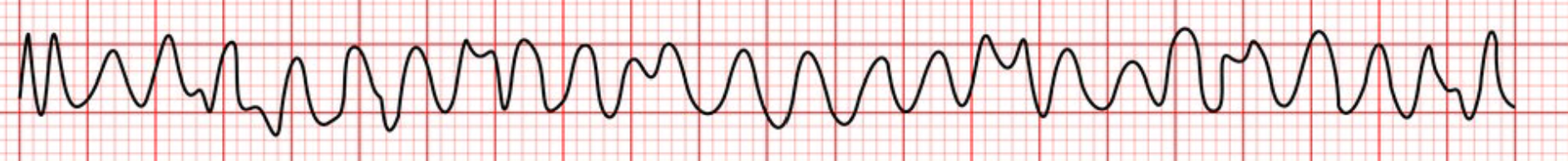
v fib
sudden cardiac arrest (SCA)
sudden loss of all heart activity due to an irregular heart rhythm; breathing stops, person becomes unconscious; brain cells begin to die within 4-6 minutes; without immediate treatment → death :(
symptoms of SCA
collapse, no pulse, no breathing
causes of SCA
cardiomyopathy (enlarged heart) in young adults and athletes, atrial flutter or atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease
risk factors of SCA
smoking, hypertension, obesity, diabetes
3 phases of cadiac arrest
electrical phase (0-4 minutes after); heart still has supply of oxygen and glucose, conditions favorable for resuscitation; heart can respond to defibrillation
circulatory phase (4-10 minutes after); oxygen stores exhausted, myocardial cells switch to anaerobic metabolism; CPR needed to restore O2 and glucose to enhance possibility of successful defibrillation
metabolic phase (10+ minutes after): heart muscle acidic and ischemic, begins to die; chances of resuscitation are unfavorable
cardiac arrest management
call 911, CPR, AED, act QUICKLY
defibrillation is advised for…
v tach and v fib
defibrillation is NOT advised for…
asystole (absence of electrical activity - flatline; electrical activity organized but there is no cardiac output); use stimulant then do defibrillation
resuscitation
emergency care provided to restore vital body functions; successful defibrillation depends on effective CPR (interruptions in chest compressions minimized)
CPR instructions
no breathing → do CPR; push hard and fast at 100-120 compressions/minute; check airway, deliver rescue breaths after every 30 compressions IF YOU HAVE BEEN TRAINED; if not: continue chest compressions, allow chest to rise completely between chest compressions; AED (automated external defibrillators)
a fib (atrial fibrillation)
crash cart
self-contained, mobile unit that contains lifesaving supplies; defibrillator and heart monitor usually on top of the cart
first drawer of the crash cart
medications, alcohol swabs, NaCl, dopamine, etc.
2nd drawer of the crash cart
intubation materials, endotracheal tubes, laryngoscope
3rd drawer of the crash cart
airway suction materials, intubation materials, suction catheter kit, endotracheal tubes
4th drawer of crash cart
IV starting equipment, disinfectant, tape, etc.
5th drawer of crash cart
IV solutions, NaCl solution, dextrose solution, etc.
6th drawer of crash cart
prepackaged kits for various urgent and emergent procedures, sterile gloves, lumbar puncture kit
layers of the heart wall
epicardium (largest) → myocardium → endocardium; blood supply comes from outside of the heart and goes in
blood supply to the heart wall
left anterior descending artery (aka ‘widow maker’) → if blocked, heart attack is fatal; patients can have multiple heart attacks depending on the location
coronary arteries
vessels that deliver oxygen rich blood to the myocardium
coronary circulation
circulation of blood in the blood vessels of the heart muscle; epicardium to endocardium