Exam 1- Radiographs and Films Used in Dentistry, Identification of Radiographs, Mounting and Viewing
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are two types of extraoral radiographs?
Panoramic
Cross-sectional imaging(MRI)
What are the three types of intraoral radiographs?
periapical, bitewing, occlusal
What are the two types of occlusal radiographs?
1. topographic or oblique
2. cross-sectional or true
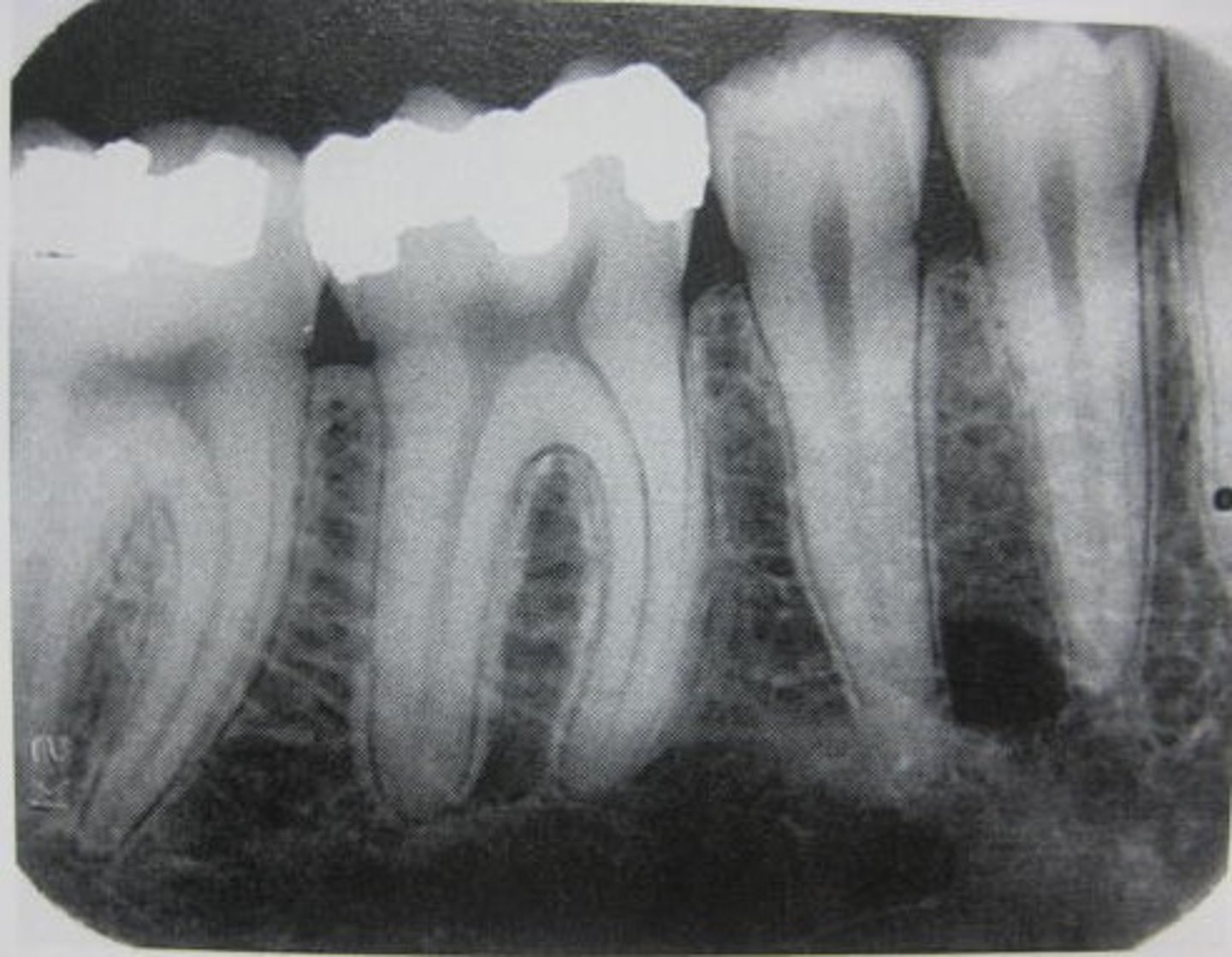
Identify if this is a:
A. Panoramic
B. Cross-sectional image
C. Periapical
D. Bitewing
E. Occlusal
C
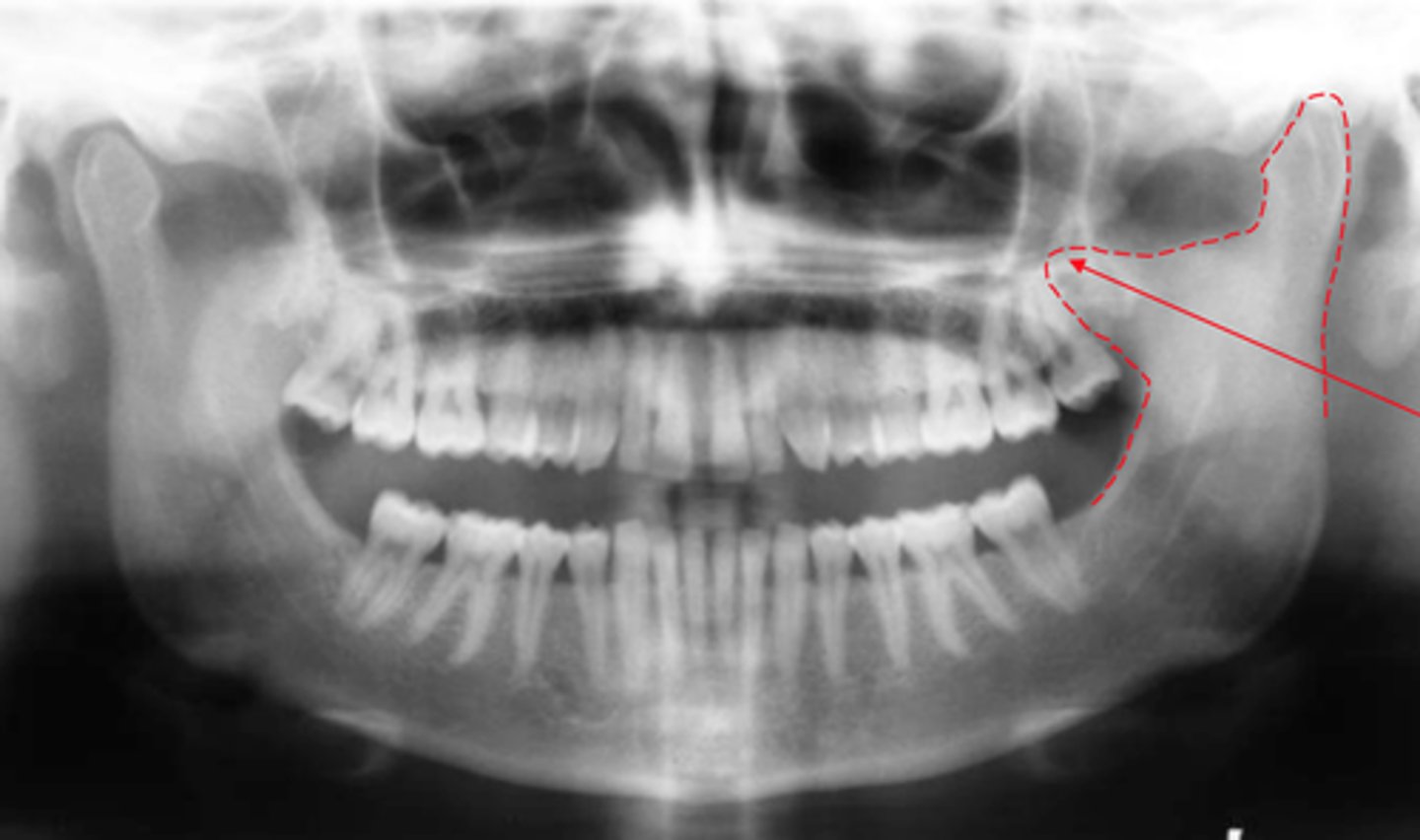
Identify if this is a:
A. Panoramic
B. Cross-sectional image
C. Periapical
D. Bitewing
E. Occlusal
A
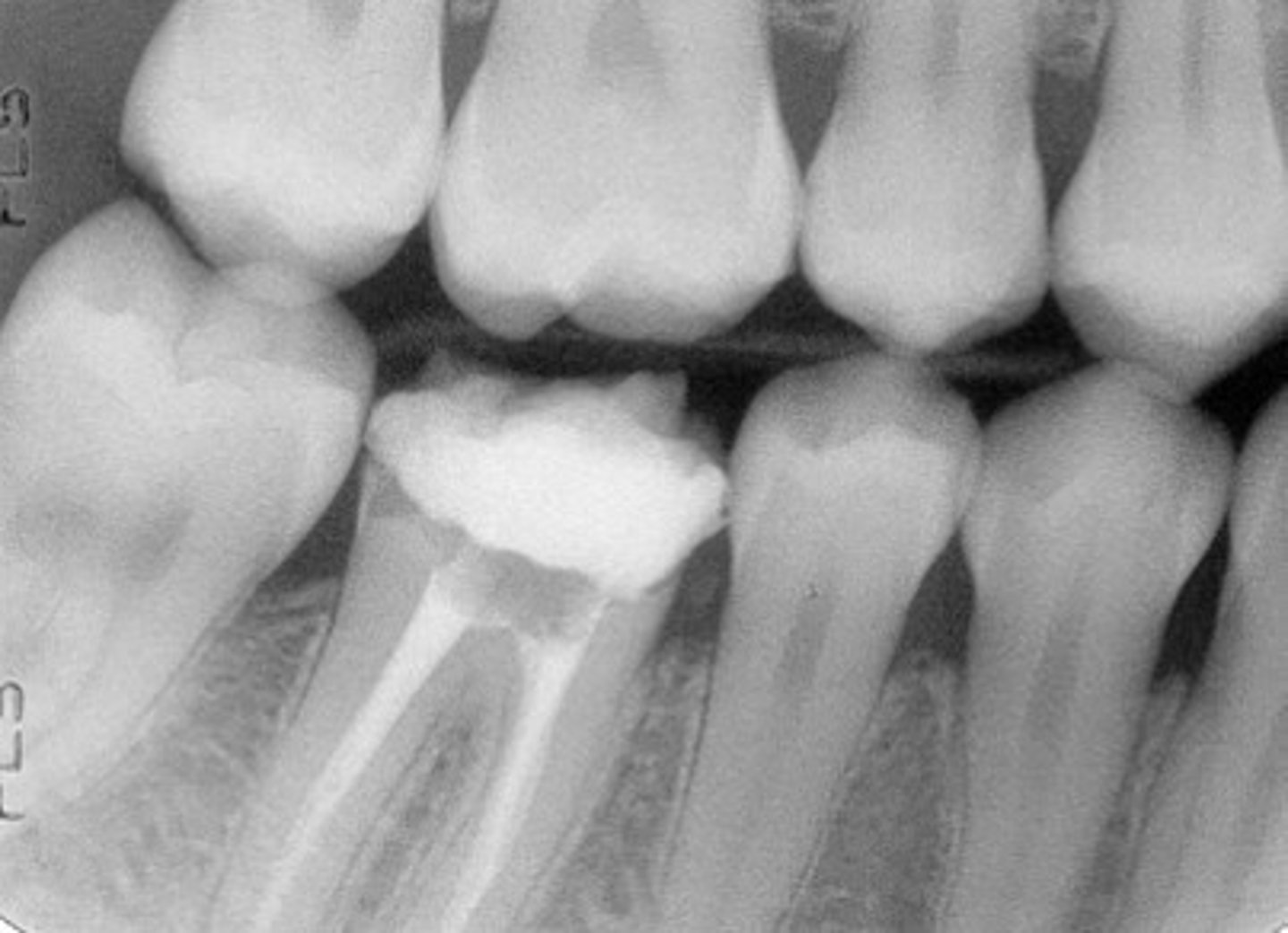
Identify if this is a:
A. Panoramic
B. Cross-sectional image
C. Periapical
D. Bitewing
E. Occlusal
D
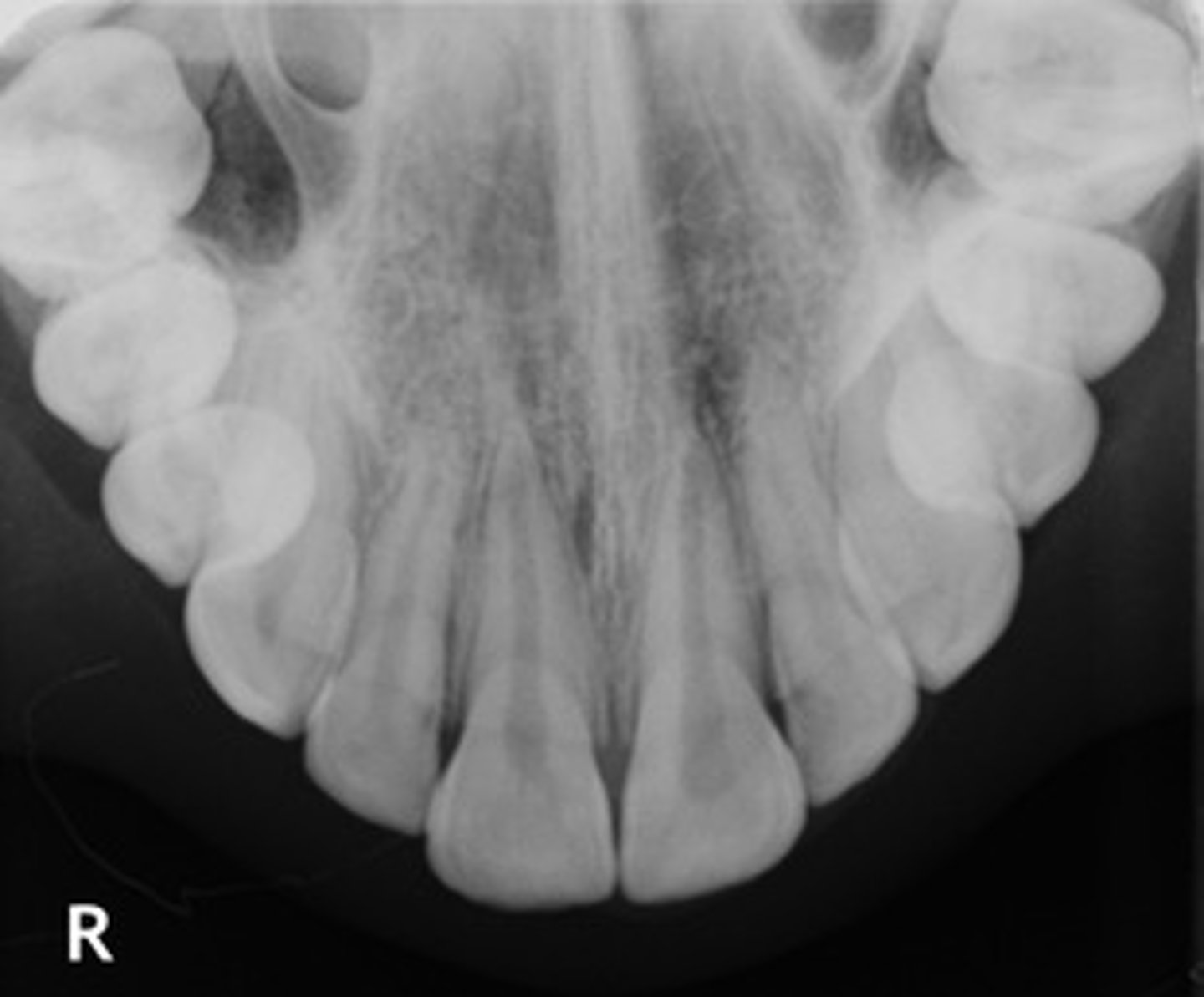
Identify if this is a:
A. Panoramic
B. Cross-sectional image
C. Periapical
D. Bitewing
E. Occlusal
E
describe the general orientation or relationship of an object to an panoramic
Most common extraoral image
Shows entire maxilla and mandible
Single image
describe the general orientation or relationship of an object to an cross-sectional
CBCT, CT, MRI
Shows large areas
Used for:
Pathosis not seen intraorally
Trismus
Gag reflex
Best for locating buccal vs lingual position
describe the general orientation or relationship of an object to an bitewing
Shows crowns of upper and lower teeth
Shows alveolar crest bone level
Best for interproximal caries
Does NOT show root apices
describe the general orientation or relationship of an object to an periapical
Shows crown, root, and apex
Includes 2–3 mm beyond the root tip
Used to detect apical disease
describe the general orientation or relationship of an object to an occlusal
Large film placed on occlusal surfaces
Shows large areas
Used when PA is not possible
describe the general orientation or relationship of a beam of radiation for an extraoral radiographic (pan and cross-sectional)
Object: Teeth and jaws
Beam: Directed from outside the face
Recording surface: Film/sensor outside the mouth
describe the general orientation or relationship of a beam of radiation to a intraoral radiographic
Object (tooth): Inside the mouth
Beam: Directed through the tooth
Recording surface: Sensor/film inside the mouth
Define Radiopaque
Light on image
High density
Examples: enamel, cortical bone, amalgam
Define radiolucent
Dark on image
Low density
Examples: pulp, sinus, air spaces