Helminth
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Tapeworms include
Taenia solium, T. saginata, Dipylidium caninum
Roundworms include
Baylisascaris procyonis, Toxocara, Ancylostoma
Taenia saginata is known as
Beef Tapeworm
Taenia solium is known as
pork tapeworm
Definitive host
harbors adult/sexually mature stage of parasite
Intermediate host:
harbors immature stage of parasite
Taeniasis
infection of intestinal lumen with adult Taenia species tapeworms
Cysticercosis:
infection of tissues with larval cysts/cysticerci
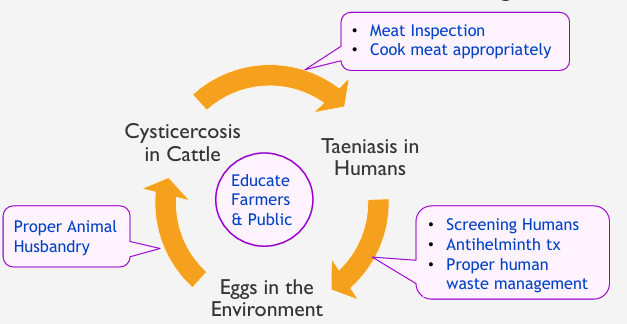
Maintenance & Transmission Of T. saginata
cycle between humans & cattle.
Taeniasis in humans Transmission
Humans infected by eating raw or undercooked beef containing cysticerci.
Cysticerci develop into adult worms in human intestinal lumen.
Tapeworm eggs or proglottids passed in stool.
Cysticercosis in cattle Transmission
Cattle infected by consuming food or water contaminated with human tapeworm eggs
Eggs hatch & develop into cysticerci.
Intervention Points to Prevent T. saginata
EDUCATION
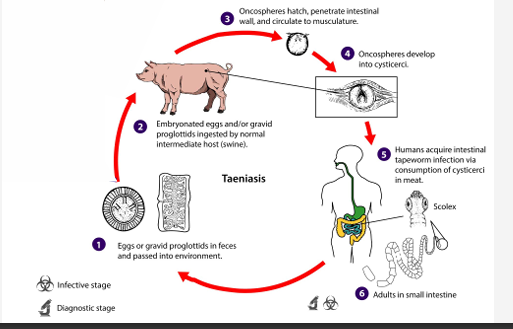
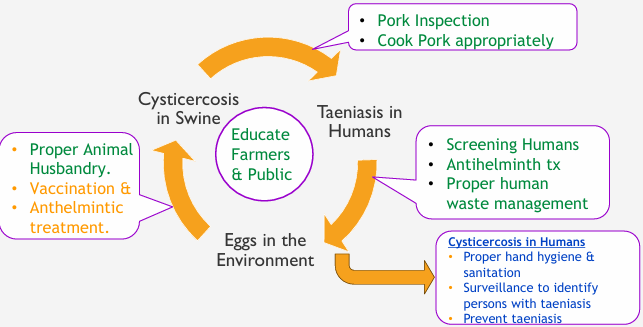
T. Solium Cycle Between Swine & Humans- Transmission
Eggs or gravid proglottids in feces passed into environment
Embryonated eggs/gravid proglottids ingested by normal intermediate host (swine)
Oncospheres hatch, penetrate intestnal wall and circulate to musculature
Oncospheres develop into cysticerci
Humans acquire intestinal tapeworm infection via consumption of cysticerci in meat
Cysticercosis in Humans: infection with larval stage of T. solium
Humans= accidental intermediate host
infected by ingestion of eggs
Swine= natural intermediate host
Humans= definitive host
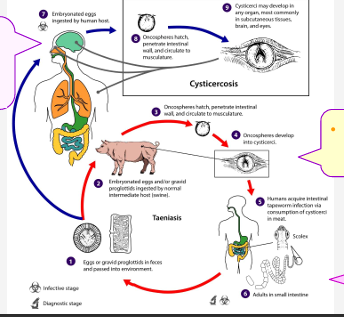
Cysticercosis in Humans: caused by T. solium Source of infection
taeniasis passes eggs/proglottids in feces
Ingesting food/water contaminated with feces containing eggs/proglottids o Person–to–person spread due to poor hand hygiene practices o Autoinfection: person with taeniasis infects self by ingesting eggs
Cysticercosis eggs hatch and cysts develop where in humans?
brain (neuro-cysticercosis), eyes (ocular cysticercosis) & subcutaneous tissues
One Health Intervention Points to Prevent T. solium- humans
Inspect Pork and cook meat to internal temperature of 165F
Screen humans
Proper waste management
Proper hygiene- handwashing, surveillance
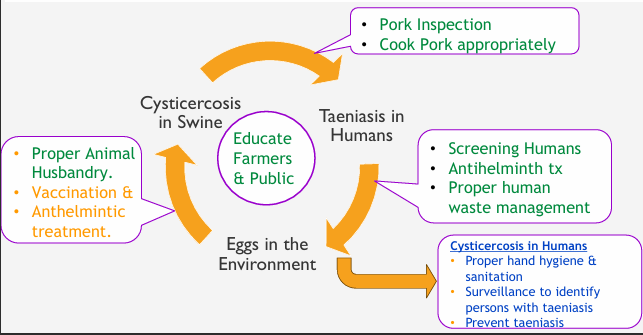
One Health Intervention Points to Prevent T. solium- Swine Cysticercosis
Proper Animal Husbandry- educate farmers, avoid exposure to feed/water
Commercial Vaccine TSOL18 against T/ solium combined with Anthelminitc treatment with Oxfendazole
Taenia solium can cause neuro-cysticercosis in humans. T solium is not endemic in Canada or US but neuro-cysticercosis are reported in those countries. What is most likely source of infection?
Person with Taeniasis who acquired infection living/traveling in endemic Countries.. EGGS= infective stage
Dipylidium caninum is known as
Flea Tapeworm
Dipylidium caninum (Flea tapeworm) Hosts
Definitive hosts : dogs & cats
Intermediate host : dog or cat flea (Ctenocephalides spp.)
Dipylidium caninum (Flea tapeworm) Transmission
dogs & cats are infected by ingesting infected fleas.
Dipylidium caninum (Flea tapeworm) Prevention
flea control, deworm based on risk.
Dipylidium caninum (Flea tapeworm) Clinical Manifestation
most pets are asymptomatic, may show pruritis, mild GIT disturbance, pass proglottids.
Infections in humans : accidental ingestion of infected fleas carried by dogs & cats. Human infections are rare seen in children.
What is Larva Migrans
Condition where larval worms migrate through various parts of the body of an animal or human
Forms of Larva Migrans
Cutaneous larva migrans (CLM): larval worms migrate through the skin.
Visceral larva migrans (VLM): larval worms migrate through internal organs.
Ocular larva migrans (OLM): larval worms invade the eyes.
Neural larva migrans: larval worms migrate in the CNS
Larval migrans Causative agents
Baylisascaris procyonis: causes visceral, ocular & neural larva migrans
Toxocara canis & T. cati: mostly cause visceral & ocular larva migrans
Ancylostoma & other zoonotic hookworms mostly cause CLM.
Maintenance of Agents of Larva Migrans
Nonhuman animal vertebrate host and o External environment: essential for development of the agent (embryonation of eggs to become infective).
Baylisascaris procyonis causes and risks
ocular, visceral or neural larva migrans
Playing in dirt is risk factor for infection.
Baylisascariasis Hosts, Maintenance & Transmission
Racoons-reservoir & definitive host.
dogs-definitive host
Embryonation of eggs takes place in external environment.
Humans= accidental hosts by ingesting embryonated eggs with larva, hatch in gut & migrate to viscera, CNS, or eyes
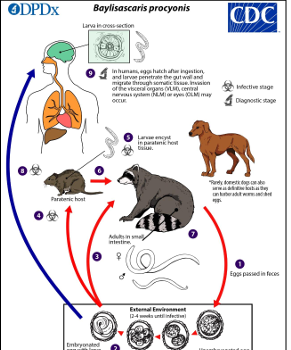
Prevention & Control Of B. procyonis Targeting Source
Reduce environment contamination by identifying, decontaminating & removing racoon latrines near homes.
Discourage racoons by making home environment unsuitable for them
Prevention in other definitive hosts by routine deworming of dogs & exotic species e.g. kinkajous
Preventing Human Exposure
Educate the public about risks of the parasite and practice biosecurity and hygiene
Visceral & Ocular Larval Migrans-main causative agent and main reservoir host
Toxocara canis- Dogs
Toxocara cati-less extent with cats as reservoir
Visceral & Ocular Larval Migrans Toxocara canis cause
ocular larva migran
Whar is Essential for maintenance in nature of Visceral and Ocular Larval migrans
External environment & nonhuman animal vertebrate host
Maintenance & Transmission Of Toxocara canis
Unembryonated eggs take 1 – 3 weeks to become infective in external environment.
Humans=accidental dead-end hosts-infected by ingesting eggs on dirty hands or contaminated food/water- larvae migrate to viscera or eyes.
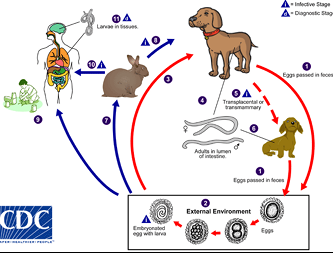
Diagnosis, Prevention/Control of Toxocara in Animals
Detection of eggs in stool using microscopy
Control- deworming: puppies 3 weeks – 3 months; Kittens 2 – 6 months
Young animals shed high load of eggs with high risk of human infection
Remove dog & cat feces (within 1 week)
Restrict cats & dogs from children's playgrounds
Zoonotic Hookworms That Cause CLM are cuased by larval stages include
Ancylostoma braziliense: cats are the main reservoir
Ancylostoma caninum: dogs are the main reservoir
Ancylostoma ceylanicum
Maintenance & Transmission Of Ancylostoma
Cats & dogs shed eggs in feces in environment
Eggs hatch & larvae molt into infective stage.
Infective larvae penetrate exposed human skin=accidental & dead-end hosts
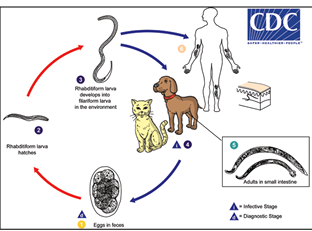
Risk Factors for CLM
US east coast.
Areas with free roaming dogs & cats
Beaches- endemic areas Caribbean, South America
Prevention Of Cutaneous Larva Migrans
deworm cats and dogs & dispose of feces
Avoid skin contact with contaminated soil/sand