Topic #14: Design Requirements of Specific Places in Towns & Cities Planning Educational Campuses
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Refers to a land on which a college or university and related institutional buildings are situated. Usually a college campus includes libraries, lecture halls, residence halls, student centers or dining halls, and park-like setting.
Planning Educational Campuses
Is a dynamic process of planning the distribution, size and spacing of schools and physical facilities requirements for optimum utilization and benefit.
It is a process of identifying current inadequacies in distribution and of providing appropriate types and pattern of school campus.
It is a continuous process involving the uninterrupted recording of basic information required for analysis of the school map at any given point in time.
School Mapping
Specific Areas for Expansion
Basic Data Needed for the conduct of School Mapping
School –Community Relations
Ergonomics
Anthropometry
5 School Mapping Process:
Construction Activity Pollution Prevention
Environmental Site Assessment
Site Selection
Development Density & Community Connectivity
Brownfield Redevelopment
Alternative Transportation
6 Sustainable Sites
Reduce pollution from construction by controlling soil erosion, waterway sedimentation and airborne dust generation.
Construction Activity Pollution Prevention
Ensure that the site is assessed for environmental contamination and if contaminated, that the environmental contamination has been remediated to protect children’s health.
Environmental Site Assessment
Avoid development of inappropriate sites and reduce the environmental impact from the location of a building on a site.
Site Selection
Channel development to urban areas with existing infrastructure, project green fields and preserve habitat and natural resources.
Development Density & Community Connectivity
Rehabilitate damaged sites where development is complicated by environmental contamination, reducing pressure on undeveloped land.
Brownfield Redevelopment
reduce pollution and or land development impacts from individual
automobile use
public transportation access,
bicycle use,
low emitting fuel efficient vehicles and
parking capacity.
Alternative Transportation
Conserve existing natural areas and restore damaged areas to provide habitat and promote biodiversity.
Site Development
Limit disruption of natural hydrology by reducing impervious cover, increasing on-site infiltration, and managing storm water runoff.
Quality control
Quantity control.
Storm water Design
Reduce heat islands (thermal gradient differences between developed and undeveloped areas) to minimize impact on microclimate and human and wildlife habitat.
Heat Island Effect
Minimize light trespass from the building and site, reduce sky-glow to increase night access, improve nighttime visibility through glare reduction and reduce development impact on natural environment.
Light Pollution Reduction
Ensure the environmental site issues included in the initial development of the site and project are continued throughout future development due to changes in programs or demography.
Site Master Plan
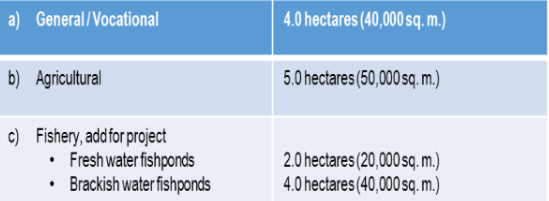
Minimum Standard Requirements for School Sites
Secondary School
A. For Rural Areas
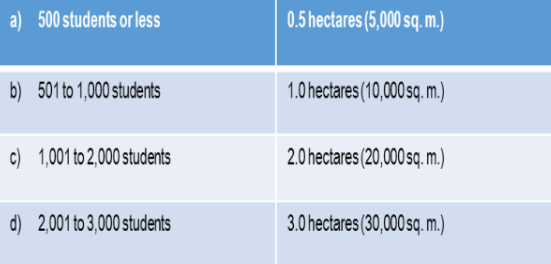
Minimum Standard Requirements for School Sites
Secondary School
B. For Urban Areas