IB HL Psychology Master Set
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
What are the differences between sympathy and empathy?
Empathy is the ability to understand and share the feelings of others.
Sympathy is expressing care and concern, but not being able to share the feelings.
What is social imagination (theory of mind)?
The understanding and interpretation of others’ feelings. Ie. recognizing that others have different thoughts, feelings, and emotions.
What are mirror neurons?
A certain type of neurons that activate when observing another’s actions.
Neurons that help people to learn by seeing.
What is maturation?
The unfolding of genetic programming
What is learning?
Reactionary changes from environmental stimuli
What is identity?
How you show who you are
What is the structure and function relationship?
Structure determines function
What are the four stages in structural function?
Neurogenesis: The creation of new neurons
Migration: Neurons move into place
Differentiation: Creating connections
Pruning: Removing connections
Werker and Tees 1984: Can infants differentiate between language structures?
Infants can differentiate between Hindi and English structures better than a child slightly older.
What is the role of the frontal lobe?
It controls movement, expression, and higher level functions
Kolb & Fantie 1989: Why aren’t babies as smart as adults despite having more neural connections?
Because babies have more connections that aren't connected in any meaningful way. As we mature, we prune many of these connections to make room for stronger connections.
Chugani 1999: When do certain brain areas reach maturity?
Used PET scans to look at glucose levels in different areas of the brain. Found that only the very essential areas of the brain were active in infants.
Chugani et al 2001: How does deprivation impact development?
Fast 10 kids for 4 hours. Give PET scans. Limit extraneous stimuli (social interaction/light) to produce a resting awake state. Interview parent's about child's behavior.
Deprivation caused impaired neurological development and development in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus.
Giedd 2004: How does development change as a result of development in children and adolescence?
Used MRI and found that different areas of the brain grow at different rates. This can explain why kids and teens are more likely to take bigger risks.
What structural change does the brain go through as it grows?
Gets bigger
More efficient
Stronger connections
How does a young brain function differently from a more developed brain?
A young brain has more connections, but they’re weaker and less efficient than those in the adult brain.
What methods can be used to study the growing brain?
encephalogram (EEG), MRI, fMRI and, PET scans
What is authoritarian parenting?
A parent with strict rules and strict punishment. Often without clear justification (Rules for the sake of rules).
What is authoritative parenting?
A parent with strict rules, but little to no punishment. More lax, based on trust.
What is permissive parenting?
A parent that functions as a friend to their child. May lead to kids that don’t know how to talk to authority or take criticism.
In extreme cases, parents that go barhopping or doing bad things with their kids.
My mother 2020-2024
This parent will defend themselves by saying “I can’t be judged if they’re doing it too.”
What is an uninvolved parent?
A parent that is neglectful or work based.
My mother now
Simner 1971: Do infants have theory of mind?
Found that infants exposed to other infants crying exhibited stress responses.
Zahn Waxler et al 1992: When does empathy develop?
Found that empathy develops in year two of life.
Premack and Woodruff 1978: Do evolutionarily similar animals feel empathy too?
Used videotapes to determine if Chimpanzees can feel empathy too. Found that they can feel empathetic towards humans.
Call & Tomasello 2008 suggests that the chimps weren’t empathetic, they just found solutions.
Buttelman et al 2007: Do chimps have theory of mind?
Showed chimps a human trying to flick a switch, either with or without an obstructed limb. Found that when the human limb was obstructed, chimps followed the easiest path to flip the switch, but when the limb was free, the chimps mimicked the human. Suggests that chimps might understand intent.
Meltzoff 1995: Will kids replicate an action of an adult vs. a robot?
The kid was able to complete the action if it was completed by a human, but not a robot.
Where are mirror neurons localized?
The inferior frontal cortex.
What is cupboard theory?
Suggests that the bond between a mother and child is based on necessity.
Not backed by enough data on it’s own.
What is attachment?
The mutual development of the relationship between a caregiver and their dependent.
What can a lack of caregiver attachment impact?
Long term memory
Weight gain
Physical traits
What is a type A attachment?
Anxious avoidant: Runs from attachment.
What is a type B attachment?
Securely attached: Empathetic and able to set good boundaries.
What is a type C attachment?
Anxious ambivalent:Anxious with low self esteem and want to be close to others, but are afraid.
What is monotropy?
States that an infant needs to bond with a special caregiver before the age of two (critical period).
What are consequences of not developing a monotropic relationship?
In extreme cases, kids lose the ability to feel shame, guilt, or affection. But this may just be correlational
What is the internal working model?
Ones’ view of themself and their interactions with their caregivers
Develops in kids
What does a strong internal working model do for development?
Helps children predict future interactions with just about anybody.
What are secure lovers?
Lovers who prioritize trust, happiness, and friendship.
What are avoidant lovers?
Lovers who are based in jealousy.
What are ambivalent lovers?
Focused primarily on sexual attraction and jealousy.
Where is attachment best seen?
When individuals are seperated.
What is separation distress?
A distress response as a result of being seperated.
Konrad Lorenz 1935: What is imprinting?
Rapid instinctive learning from a parental figure that happens in the critical period.
Harry Harlow 1958: Will monkeys prioritize affection or survival?
Placed monkeys in a cage with a wire mother that gave food and a cloth mother that gave care. Found that monkeys would spend more time with the cloth mother and would explore more around her. They would only spend time with the wire mother when strictly necessary.
Monkeys prioritize affection
What is contact comfort?
Physical care; hugs, massages, cuddling, etc.
What is a secure base?
The idea that infants need comfort and security.
How does attachment play a role in exploration?
When a developing mind is around someone that gives them a secure base, they’re more likely to explore.
Tronick, Moreli, and Winn 1987: Are attachment styles biological?
Looked at the children in the Efe in the DRC. Showed that Efe kids had different attachment styles.
No, attachment styles are sociocultural.
How does attachment develop as a human grows?
Attachment styles slowly change into romantic attachment styles.
Shaver and Hazan 1988: Showed that caregiver attachment and romantic attachment are similar.
Do problems with attachment cause problems in cognitive development?
Yes, it will alter all future relationships.
What happens if a childs’ attachment isn’t reciprocated?
That child will not mature emotionally like other kids.
What are the differences between gender and sex?
Gender is a social construct, sex is what’s in your pants.
What are gender roles?
Societal expectations based on gender.
What is gender identity?
Self assigned ideas of how gender should impact you. Really hard to break once established.
What is an example of a third gender category?
Transgender
Intersex
Non binary
What are examples of sex determining hormones?
Testosterone
Estrogen
When is sex assigned?
In the pre-natal period
Gay and McEwan 1980: What happens when testosterone is removed from male rats?
The rats began to exhibit more feminine traits.
What is congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
A condition where a baby has increased testosterone in the pre-natal period.
What is Turner’s syndrome?
A condition where females have XO chromosomes.
What is Kleinfelter’s syndrome?
A condition where males have XXY chromosomes.
What is one evolutionary explanation for the differences in brain function between the sexes?
Because in the past, men used to be hunters and women used to be gatherers. Therefore, brain function prioritized things that benefited these tasks.
Kohlber 1966: How do children develop gender standards/roles?
Gender roles are instilled, not installed. This happens before the age of five.
What is gender constancy?
After the age of five, gender standards become rigid and are very difficult to break.
Martin & Halverson 1981: When are gender schemas developed?
Gender schema are formed before gender constancy (age 5).
Fagot and Leinbach 1989: How do parents play a role in the development of gender schema?
Found that kids whose parents are gender constant develop these schema much quicker.
Bandura 1977: How do parents play a role in gender socialization?
Children learn gender standards and schema from their parents.
Smith and Lloyd 1978: How big of a role do parents play in the development of gender schema?
Smith and Lloyd 1978: Will kids play with different toys based on their perceived gender?
Found that mothers often chose toys that match the perceived gender of the child.
The mothers were more active with the baby when they thought it was a boy.
David Reimer: How will opposite gender hormones impact ones’ life?
David Reimer was born a boy, but due to complications with his circumcision, he lost his penis. Subsequently, he was given female hormones and given a vagina. He was then raised as a girl. By the age of 13, he already had suicidal thoughts.
Mead 1935: Are gender roles biological?
Looked at three island nations with little global influence. Found that each culture had different views on men and women. Thus, gender roles are sociocultural.
Williams & Best 1982: Are there any biological components in gender?
1) Emotional stability (M):
2) Extraversion (M)
3) Openness (M)
4) Agreeableness (F)
5) Conscientiousness (M)
Found that overall, males were perceived to have significantly higher scores than females on all traits except agreeableness; females however, were perceived to have significantly higher scores than males on this personality dimension.
What is Piagets theory of cognitive development?
The theory that intellectual development was an adaptation.
What is the sensorimotor stage?
0-2 years
The child knows that they’re different from their environment.
Children rely on senses to navigate.
What is the pre-operational stage?
2-7 years
The child is developing an imagination and the ability to think.
Focuses all their attention on one thing.
What is the concrete-operational stage?
7-11 years
Child is able to think through things and problem solve.
What is the formal operational stage?
11-16
The child is able to think abstractly and complexly.
What are examples of higher order functions?
Any voluntary action:
Walking, talking, painting, etc
Can we clearly distinguish stages in development?
No. Each child responds to different stimuli and does so in different ways.
What is the role of education in cognitive development?
It allows for children to be taught higher level ideas rather than needing to figure out everything on their own. This supports maturation as a species since each generation will have access to a wealth of knowledge.
How does a child’s thinking compare to an adult’s?
A child’s way of thinking is much less developed.
Why do infants find peekaboo so fun?
Because they lack object permanence.
As soon as they can’t see you, you’re gone.
Why do infants hide by covering their eyes?
Because they lack object permanence.
They think you can’t see them.
What is trauma?
An emotional scar
What is deprivation?
Not having steady access to necessities.
What are examples of perpetual trauma?
Poverty
Language deprivation
What happens if a function isn’t developed in the critical period?
It will likely never fully develop.
What are symptoms of PSTD?
Disturbing thoughts, feelings, and emotions.
How does someone build resilience?
By having strong support networks.
What makes the difference between whether a child will or will not survive adverse circumstances?
Support networks/resilience
Are the effects of trauma able to be reversed?
They are able to be mitigated, but never erased.
What is localization?
The idea that certain parts of the brain play different roles.
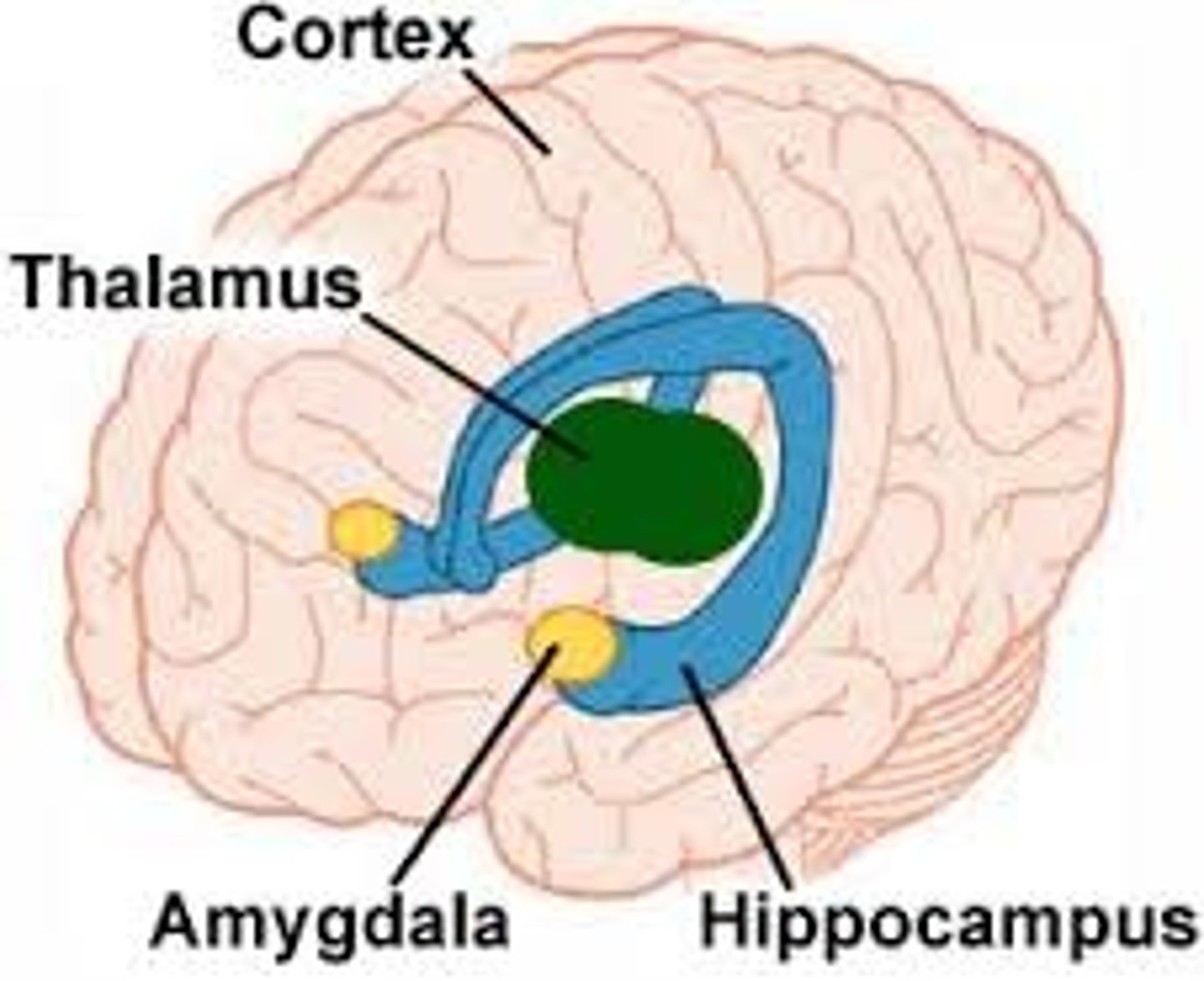
Corkin 1977: Where are memories stored?
Determined that memories are stored in the hippocampus.
What is the prefrontal cortex?
The outermost layer of the frontal lobe and is responsible for many of the executive functions in the brain
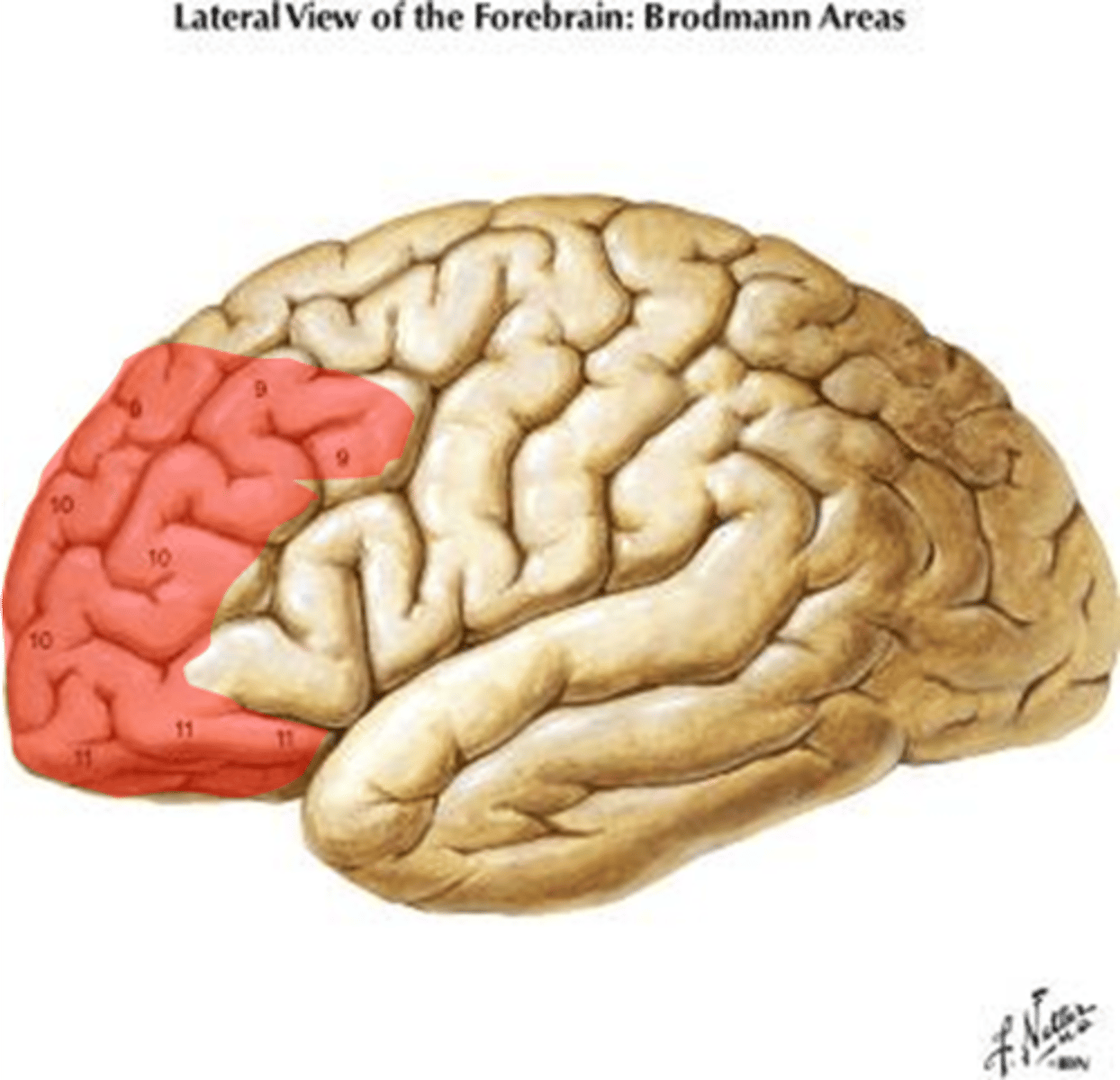
What is Broca's area?
Found in the left frontal cortex. Responsible for speech.
What is the amygdala?
The emotional center of the brain and is part of the limbic system. It activates our stress response and our ability to experience emotions such as fear.
What is neuroplasticity?
refers to the brain's ability to adapt by forming new connections as a result of experience, learning, or following an injury.
What is dendritic branching?
the process by which the part of one neuron establishes a connection with other neurons
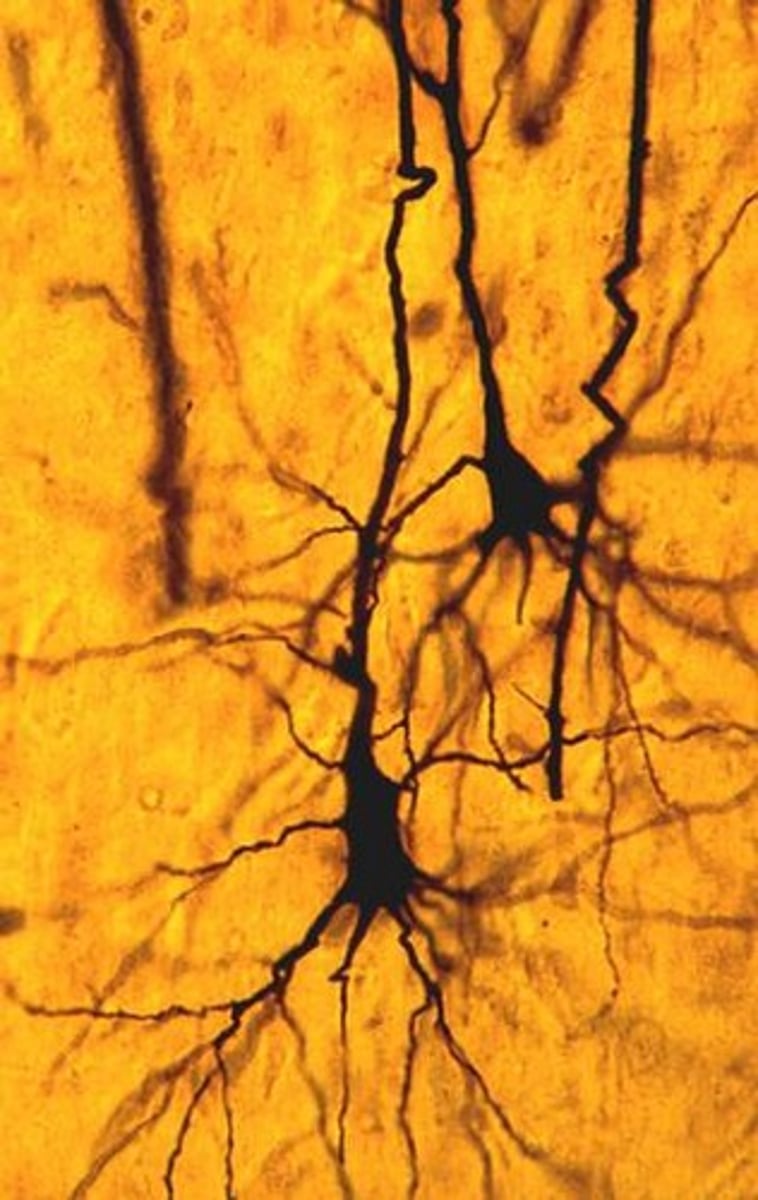
What is synaptic plasticity?
the ability of one neuron to form new connections and break up the old ones.
What is corticial remapping?
when brain area X assumes the functions of brain area Y due to injury
Rosenzweig and Bennet 1972: How does environment impact neuroplasticity?
The study suggests that being in a more stimulating environment causes new connections to form in the brain, altering brain structure