physics - forces and motion
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Speed
Distance travelled per unit time
Acceleration
Change in velocity per unit time
What is the relationship between final speed, initial speed, acceleration and distance moved?
(Final speed)²= (initial speed)²+(2 x acceleration x distance moved)
Velocity
Speed in a given direction
Distance
Measured in meters (m)
Time
Measured in seconds (s)
Gradient ( v graph )
Velocity in a distance-time graph
Stationary
Horizontal line in a distance-time graph
Curved line
Velocity is changing and accelerating in a distance-time graph
Gradient
Acceleration in a velocity-time graph
Rest
Speed is zero in a velocity-time graph
Friction is a force that
Opposes motion
Area under the line
Distance travelled in a velocity-time graph
Scalars
Quantities with just magnitude
Vectors
Quantities with magnitude and direction e.g force
Identify types of forces
E.g gravitational, weight, friction, drag, tension, up thrust, electrostatic
Describe the forces acting on falling objects
Initially the only force is weight as drag is proportional to velocity. So the object accelerates downwards. As it accelerates the velocity so the drag increases as well. meaning there is a smaller resultant force downwards so a smaller acceleration. Until the object reaches a speed where the drag is equal to the weight meaning there is no acceleration, this velocity is know as terminal velocity.
What is terminal velocity
The maximum speed an object reaches when falling because the forces acting on it become balanced
practical investigate how extension varies with applied force for helical springs, metal wires and rubber bands
Set up your apparatus as shown in the
Measure the length of your spring without
any hanging masses.Hang a mass of 100g on the spring
Measure the new length of the spring
Calculate the extension of the spring
Repeat steps 3-5 for increasing the mass
in increments of 100gTake note of your results in the table.
Force =
Mass x acceleration
Friction
Force between two surfaces that impedes motion
Momentum =
Mass x velocity
Resultant force
Net force acting on an object
Newton's first law
Object has constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force
Newton's second law
Force equals mass times acceleration
Newton's third law
Every action force has an equal and opposite reaction force
Mass
Measure of how much matter is in an object
Describe the effects of forces between bodies such as changes in speed, shape or direction
Forces can act on a body to change the velocity, so the speed, direction or both.
Or forces can change the shape of a body, stretching it squishing it or twisting it.
Deformation
Change in size and shape of a body
Elastic deformation
Object returns to its original shape when load is removed
Hooke's law
Force applied to a spring equals spring constant times extension
Limit of proportionality
Point where linear force-extension graph stops obeying Hooke's law
Non-linear force-extension graph
Deformation not following Hooke's law
Moment of a force
Measure of its turning effect
Equilibrium
Sum of clockwise moments equals sum of anticlockwise moments and no resultant force
Momentum
Product of mass and velocity
Force exerted on an object
Change in momentum over time
Thinking distance
Distance travelled between realizing the need to brake and pressing the brakes e.g drugs, alcohol
Braking distance
Distance travelled between pressing the brakes and coming to a stop e.g road conditions, tire conditions
Stopping distance
Sum of thinking distance and braking distance
What is elastic behaviour
The ability of a material to recover its original shape after the forces causing deformation have been removed
Linear force-extension graph
Elastic deformation following Hooke's law
Moment of a force
Measure of its turning effect
Momentum
Product of mass and velocity
Safety features in cars
Increase time taken to come to rest, reducing force
To reduce the force experienced by the passenger you need to extend the time for a passenger to stop in a collision. As force is the change in momentum divided by time.
Conservation of momentum
Total momentum before collision equals total momentum afterwards
Force =
Change in momentum/time taken
Recoil speed
Speed of gun after firing a bullet
Moment =
Force x perpendicular distance from pivot
Weight of a body acts through
It’s centre of gravity
Use the principle of moments for a simple system of parallel forces acting in one plane
principle of moments states that when the clockwise moments are equal to the anticlockwise moments a body will be in equilibrium.
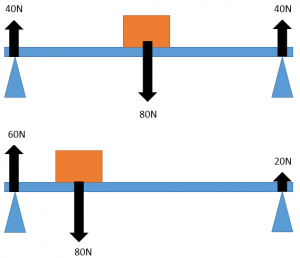
Understand how the upward forces on a light beam vary with the position of a heavy object placed on it
when moments are taken from the right hand side as the block is a greater distance the force from the left hand pivot must be bigger to counteract it. The opposite is true for the left hand side.
Explain why seat belts are used in cars for safety
These are designed to stop a passenger from colliding with the interior of a vehicle by keeping them fixed to their seat in an abrupt stop
They are designed to stretch slightly to increase the time for the passenger’s momentum to reach zero and reduce the force on them in a collision
Explain why airbags are used for car safety
These are deployed at the front on the dashboard and steering wheel when a collision occursThey act as a soft cushion to prevent injury on the passenger when they are thrown forward upon impact
Explain why crumple zones are used in car safety
These are designed into the exterior of vehicles
They are at the front and back and are designed to crush or crumple in a controlled way in a collision
This is why vehicles after a collision look more heavily damaged than expected, even for relatively small collisions
The crumple zones increase the time over which the vehicle comes to rest, lowering the impact force on the passengers
Explain why crash mats are used to reduce risk of injury
They are thick and soft to offer shock absorption of the force created by the person landing on the mat
When a person lands on a crash mat with a large force, for example, after jumping, the soft landing means their body is in contact with the mat for a longer period of time than if it were otherwise not there
This increases the contact time over which their momentum is reduced, creating a smaller impact forceand a lower chance of injury