Biochem exam 1 (ppts 2-4) (Water, Amino acids and peptides, and 3-D structure of Proteins.)
1/382
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
383 Terms
is water polar or nonpolar
polar
is water a covalent or ionic bond
covalent
what is the 3D structure of water?
tetrahedral
__ is more electronegative than __. It draws electrons towards itself
O2; H+
Water is considered a __pole
di
water dissolves __ and __.
low MW polar (hydrophilic) compounds; ionic solutes
what kind of bonds does water form
Hydrogen bonds
there is __ attraction between d-O and d+H
electrostatic
hydrogen bonds are__, but__
weak; additive
water forms hydrogen bonds with
solutes
In liquid water, at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, each water molecule hydrogen-bonds with an average of __ other water molecules
3.4 (~4)
how many hydrogen bonds are created on each water molecule
4 hydrogen bonds
after 4 hydrogen bonds are created, what kind of crystal is made in water
lattice crystal
lattice crystal makes ice __ dense than water
less
covalent bonding is a major stabilizing factor in
organic compounds
covalent bonding holds
atoms in geometric forms
non-covalent bonding stabilizes and organizes
forces in nature
non-covalent bonding include which kinds of bonds
ionic bonds, hydrophobic forces/interactions, and hydrogen bonds, Van der Waals Interactions (Dispersion forces)
ionic bonding is also called
salt bridge, salt linkage, ion pair
ionic bonds are
electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions
Hydrogen bonds are not unique to water. They are also needed for
cell replication and transcribe DNA
H-bonds are weak and needed to __ DNA strands held together by H-bonds
unwind
Hydrogen bonds are attractive interactions between dipoles when the (+) end of a dipole is an
H atoms bonded to an atom of high electronegativity (most commonly O, N, or C)
Hydrogen bonds are attractive interactions between dipoles when the (-) end of a dipole is an
atom with a lone pair of electron (most commonly O or N)
Hydrophobic forces/interactions
forces that hold non-polar regions of molecules together
Hydrophobic forces/interactions result from
the tendency of water to exclude hydrophobic groups
Hydrophobic forces/interactions are ___ than H-bonds
weaker
amphipathic compounds contain regions that are
polar and nonpolar
when amphipathic compounds is mixed with water, the polar (hydrophilic) region
interacts with solvent and tends to dissolved
when amphipathic compounds is mixed with water, the non-polar (hydrophobic) region
tends to avoid contact with water
micelles (stable structures of amphipathic compounds in water)
nonpolar regions of molecules cluster together to present smallest hydrophobic areas to aqueous solvent- while polar regions are arranged to maximize their interactions with the solvent
van der waals interactions are also called
dispersion forces
van der waals interactions are
attractive forces between 2 atoms when 3-4 amino acids apart
As 2 nuclei draw closer together their
electron clouds being to repel each other- but van der waal interactions balance the repulsive forces
when van der waal interactions balance repulsive forces between two nuclei they are in
van der waal contact

the CH3COOH is the __, and the CH3COO- __
conjugated acid; conjugated base
before any base is added to the acid, the pH of the solution is fairly
low
the best buffering capacities of the solutions are
±1 pH units from the pKa
Buffers are
aqueous solutions that tend to resist changes in pH when small amounts of acid or base are added
Buffer DO NOT
prevent changes in pH
Buffers are the effective __ pH unit from pKa
±1
buffer have __ capacities
limited
maximal buffering capacities when
pH=pKa
the ability to prevent changes in pH is directly proportional to the total
acid and base
a buffer consists of a __ plus its conjugated base
weak acid
a buffer consists of a __ plus its conjugated acid
weak base

What happens to the equilibrium as H+ is added?
H+1 reacts with the base and shifts the equilibrium to the left increasing the [H2PO4-1].

What happens to the pH as H+ is added?
There still a decrease in pH, since the [HPO4-2]/[H2PO4-1] decreases.
The maximum buffer efficiency is when [HPO4-2]/[H2PO4-1] =
1
the only pK relevant at physiological conditions is
6.85
water has a small degree of __ (reversible)
ionization
ionization of water is crucial for
cellular functions
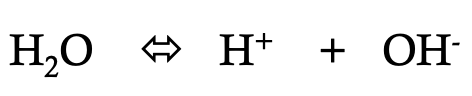
what is depicted on this image
ionization of water
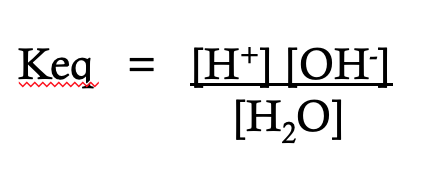
what is depicted on this image
the equilibrium constant of water
the equilibrium constant formula is __ over __
reactants; products
at room temperature (25C), what is the molality of H2O
Keq = 55.5M
what is the Kw (ion-product constant) of water
1 × 10-14
When [H+] = [OH-] = 1 X 10-7 , pH is
7, neutral
the ion production of water is the bases for
the pH scale
the pH formula is
pH= -log [H+]
pOH + pH =
14
pH affects the __ and __ of macromulecules
structure; activity
the more H there is in a solution, the less __ is in a solution
OH
the more OH there is in a solution, the less __ is in a solution
H
HCl and HNO3 are examples of
strong acids
strong acids __ ionize in a solution
completely
weak acids __ ionize in a solution
partially
KOH, NaOH are examples of
strong bases
bronsted acids are proton __
donor
bronsted bases are proton __
acceptors

what is depicted here
a bronsted acid and a brosnted base

HA represents
the conjugated acid

A- represents
a conjugated base
HA and A- are only different by _ proton
1
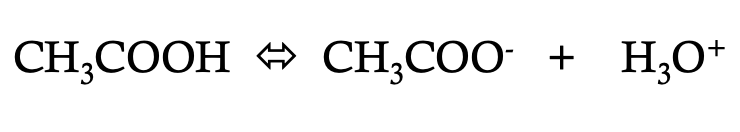
how would you write the Ka of
Ka = [CH3COO-] [H3O+]
[CH3COOH]
Ka is
dissociation (ionization) constant for a given acid when temperature is constant
The greater the Ka, the __ the acid
stronger
The smaller the Ka, the __ the acid
weaker (ka)
pKa formula, pKa=
-log(Ka)
the smaller the pKa, the __ the acid
stronger (pka)
the higher the pKa, the __ the acid
weaker (pKa)
The pH of a solution is solely dependent on the __ of the conjugate acid and base
equilibrium concentrations
The__ of a solution is solely dependent on the equilibrium concentrations of the conjugate acid and base
pH
Henderson-Hasselback equation
pH = pKa + log [conj base]
[conj acid]
In the Henderson-Hasselback equation the pH is equal to the pKa + the log of the __ over the __
conjugated base; conjugated acid
when a base=acid
the pH=pKa
when the pKa=pH
a base=an acid
maximum buffering capacity is when
pH = pKa then a base=an acid
Henderson/Hasselback equation only applies to __ acids and bases
weak
the pKa of an acid is the pH at which and acid is__ ionized
half
since pKa of an acid is at a given temperature constant, the pH changes require changes in
base/acid
when pH less than pKa, the __ predominates
acid
when pH greater than pKa, the __ predominates
base
when the acid predominates
H+ is on
when the base predominates
H+ is off
amino acids are the building
blocks of proteins
Human have enzymes to synthesize __ out the 20 biologically important amino acids
11
the 9 essential amino acids
Arg, His, Ile, Leu, Trp, Lys, Met, Phe,Thr and Val
Arg is essential only in
rats and newborn babies
amino acids are precursors in the ___ of other amino acids
synthesis