MDA Chapter 25,28,33,34
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
Ergonomics
Adaptation of work environment and tasks to the human body
What is the goal or ergonomics
To help people stay healthy and at the same time perform their work more efficiently
Musculoskeletal Disorders
headaches, neck & shoulder pain, back pain, & carpal tunnel account for many disabling and potentially career-ending musculoskeletal disorders among dental professionals
neutral position
position of the body to maintain for a prolonged period, with a natural curvature of the spine
carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)
condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm associated with continued flexion and extension of the wrist
Maximum horizontal reach
Reach created when the upper arm is fully extended
Maximum vertical reach
Reach created by a vertical sweep of the forearm while the elbow is kept at midtorso level.
Normal horizontal reach
Reach created by a sweep of the forearm with the upper arm held at the side
thenar eminence
the fleshy mass at the base of the thumb
Sprains
Injuries caused by sudden twisting or wrenching of a joint with stretching or tearing of ligaments
Strains
Injuries caused by extreme stretching of muscles or ligaments
ambidextrous gloves
gloves designed to be worn on either hand
Cumulative Trauma Disorder (CTD)
Painful conditions that result from ongoing stresses to muscles, tendons, nerves, and joints.
why patients seek dental care
-As a new patient to begin dental care
-As an emergency patient when in pain or experiencing discomfort
-For consultation with a specialist
-As a returning patient for continued assessment and care
Dental Assistant duties
- Assist the patient with forms
- Take and record vital signs
- Chart and record the dentist's findings during the EOE & IOE
- Expose radiographs
- Take preliminary impressions and fabricate diagnostic models
- Take extraoral and intraoral photographs
- Organize the patient record
- Prepare for the case presentation
visual evaluation
Specific examination areas include:
- Face
- Lymph nodes
- Lips
- Soft tissue within the mouth
- Tongue
- Tooth structure
- Restorations
Missing teeth
Palpation
to examine by touch, feeling for:
- Texture
- Size
- Consistency of hard and soft tissue
Mouth Mirror
used for indirect vision, reflection, tissue protection, & retraction
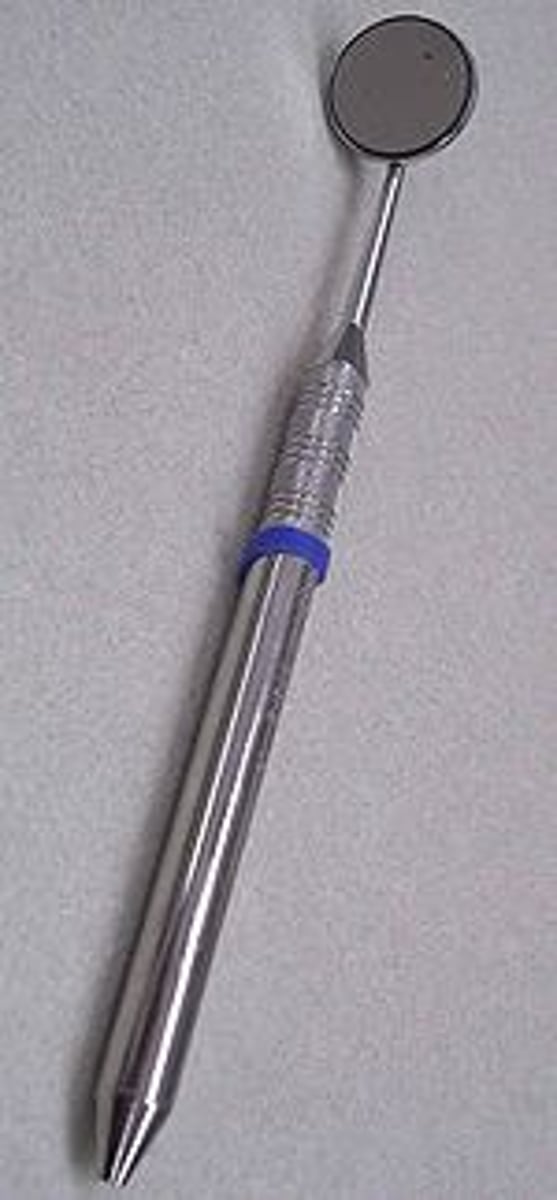

Explorer
Used for tactile feel
- Shepard's hook, pigtail, orban
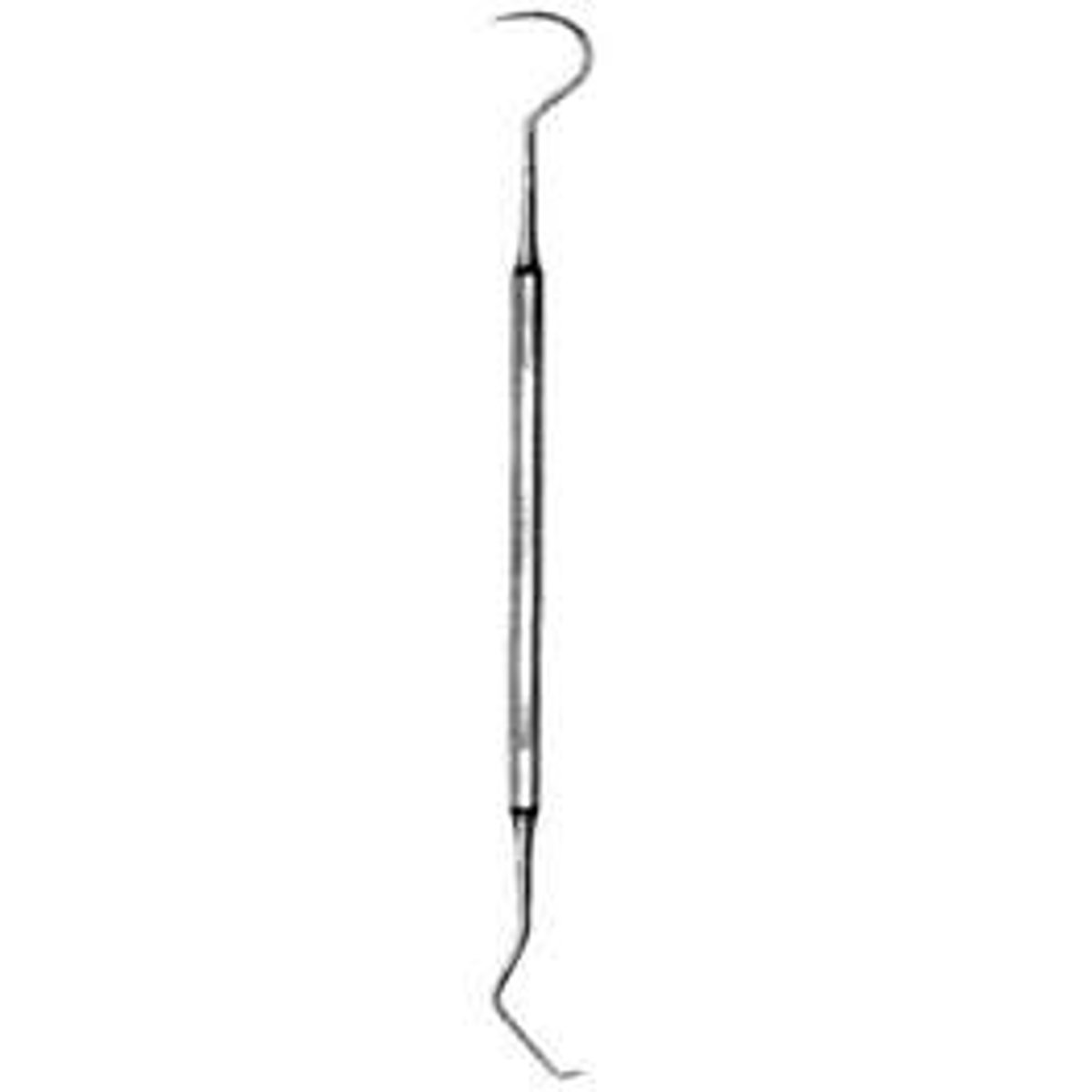

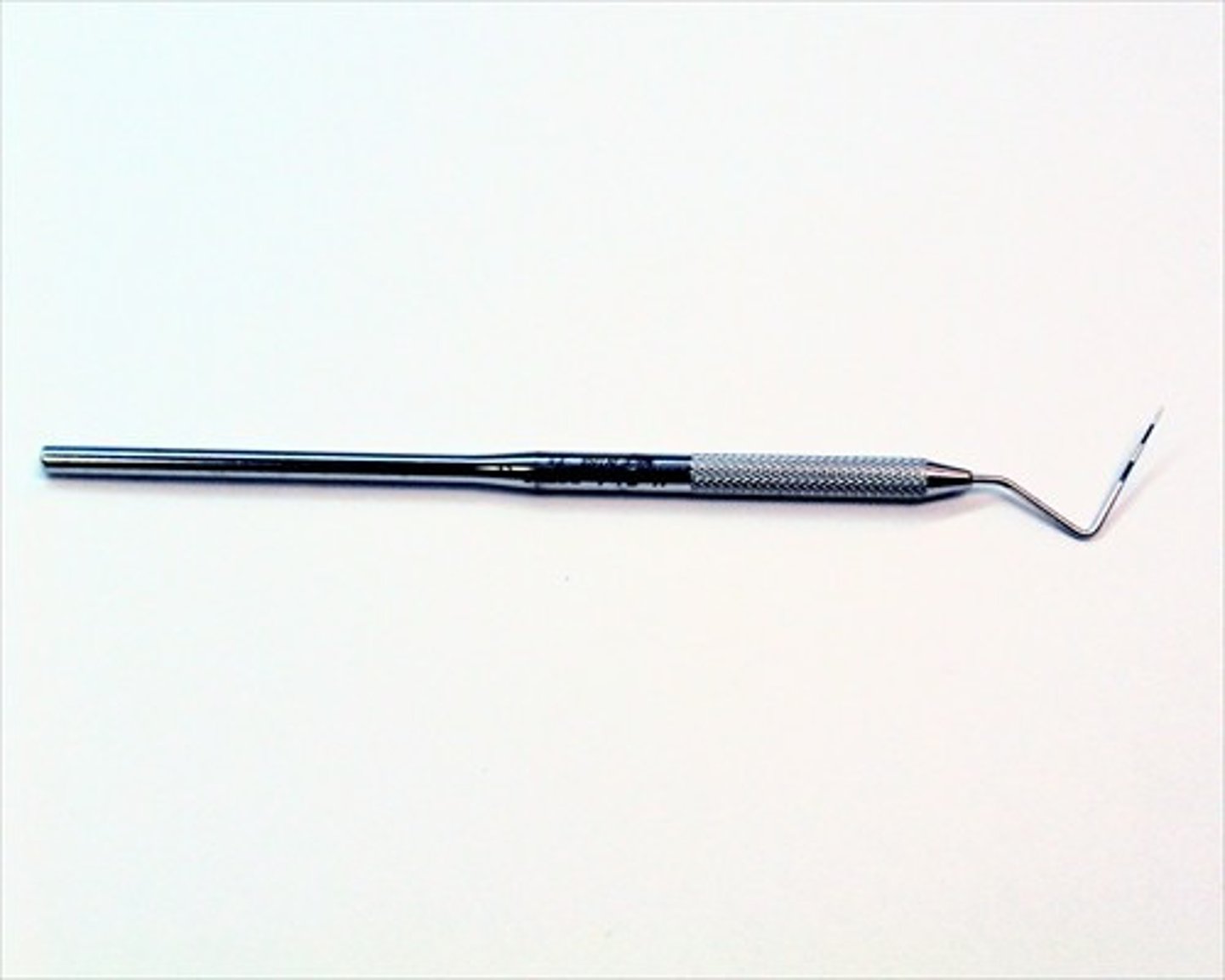
Periodontal probe
An instrument to measure the pocket depths
Radiography
Identifies:
- Decay
- Defective restorations
- Periodontal conditions
- Pathology
- Developmental conditions
- Abnormalities
Intraoral
Inside the mouth
Extraoral
outside the mouth
Intraoral imaging
Allows the use of a video system:
- To magnify an image for better evaluation
For easier access to difficult areas
- For photocopying images for insurance purposes
- For case simulation or presentation
For medical and legal documentation
Photography
A diagnostic tool used for intraoral and extraoral structures
Anatomic Diagram Charting
Illustrations resemble the actual crown and root of the tooth
Geometric Diagram Charting
A circle represents each tooth and is divided to represent each tooth surface.
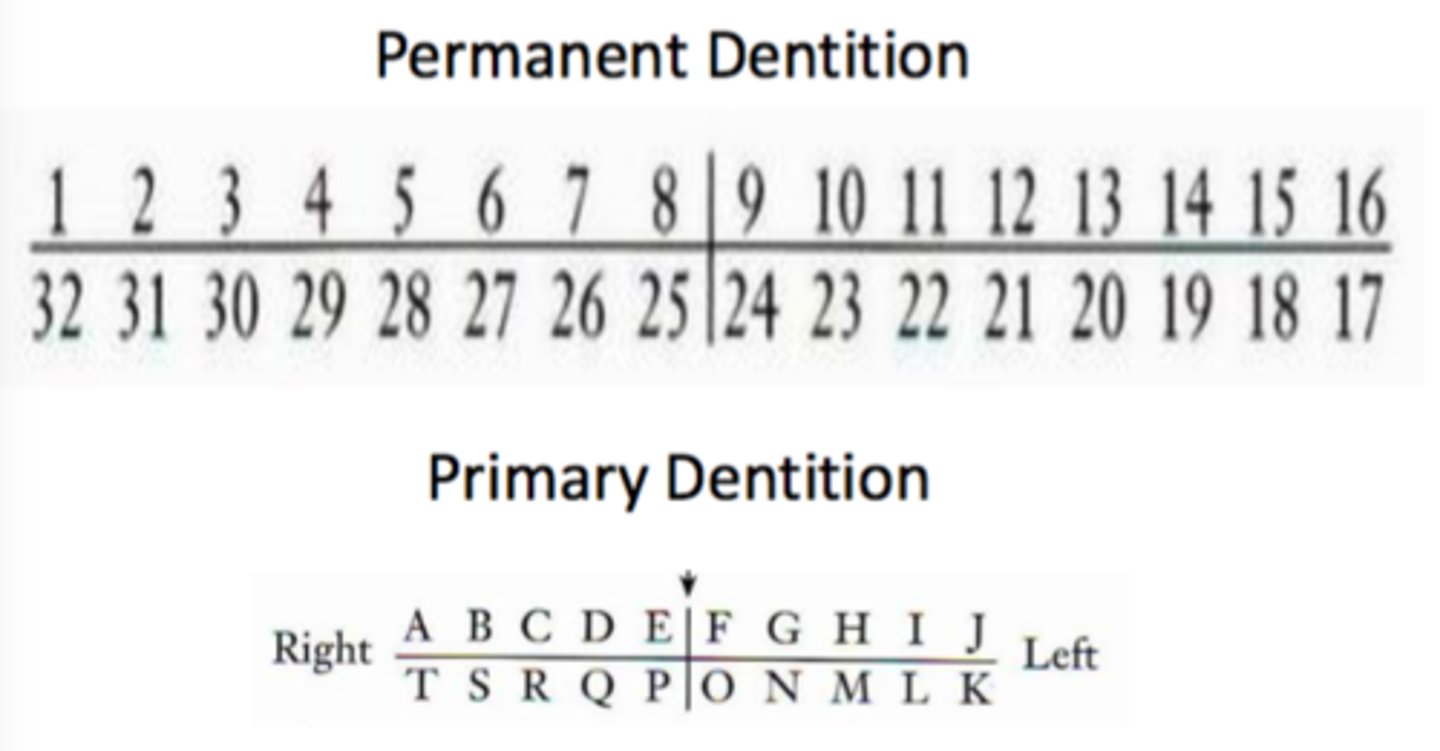
Universal Numbering System
Teeth are numbered from 1-16 on the upper arch, and 17-32 on the lower arch. The primary teeth are lettered A-T.
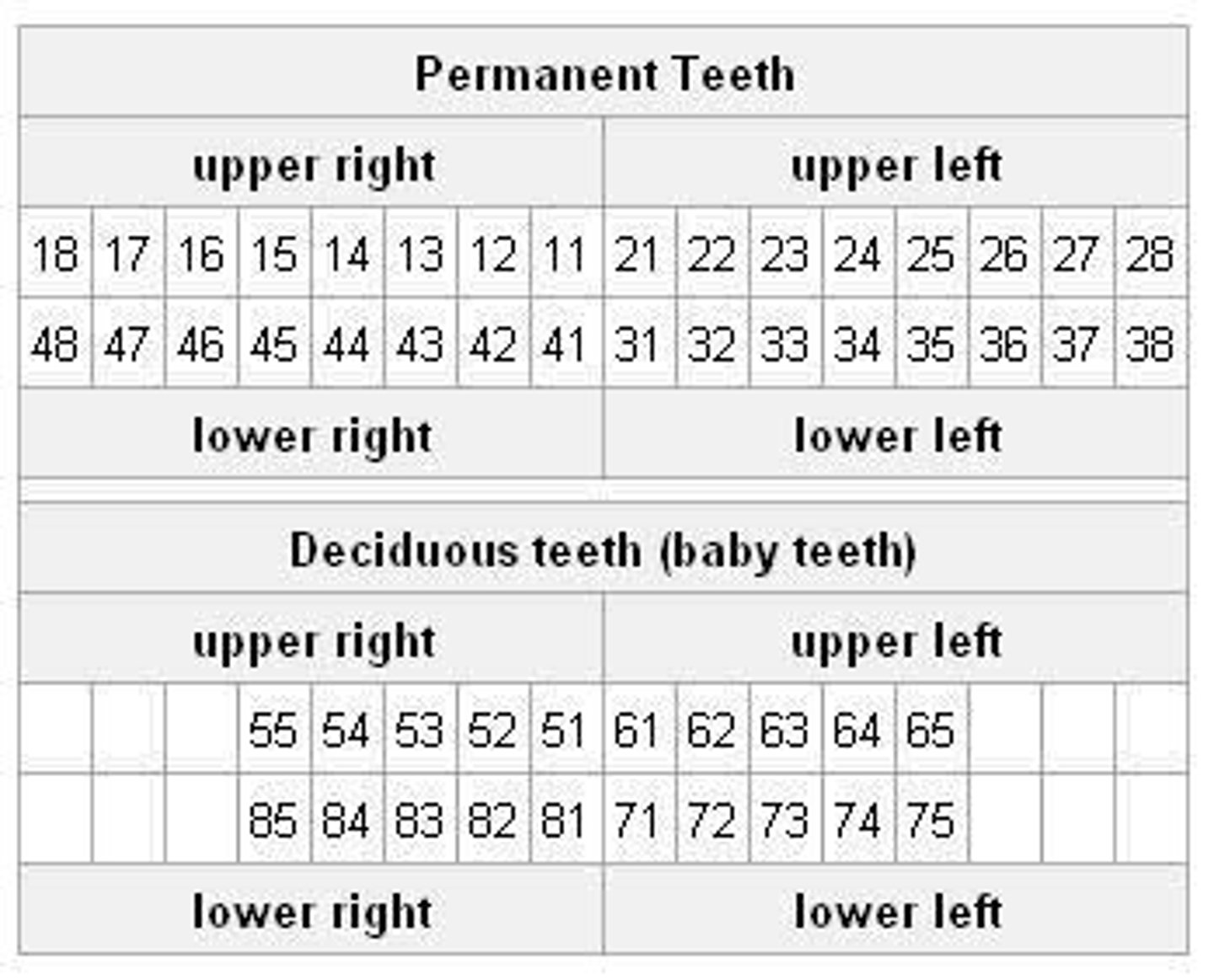
International Standards Organization (ISO)
Assigns a two-digit number to each tooth
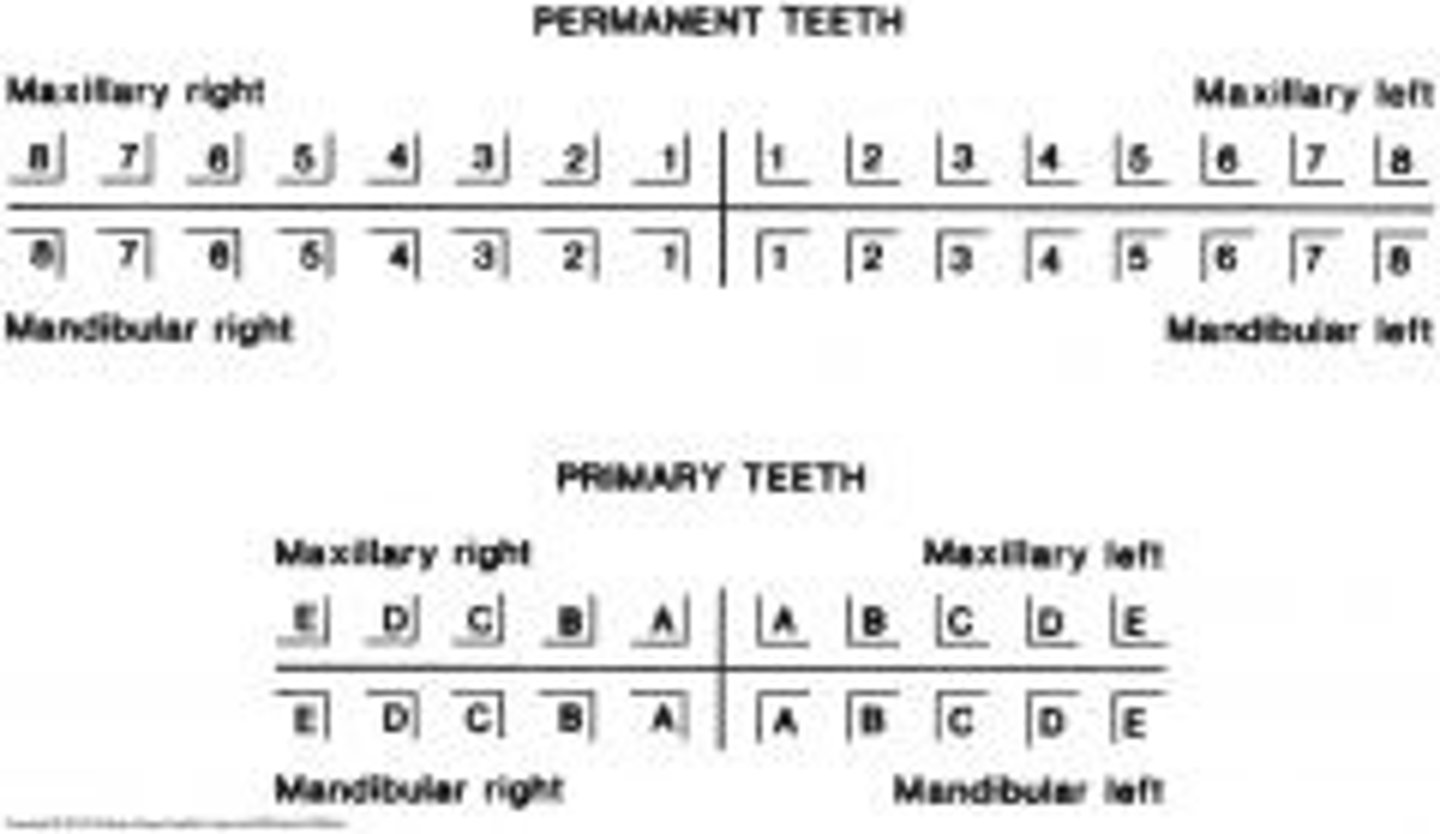
Palmer Notation System
Uses a bracket to designate the four quadrants of the mouth
What does charting in a black/blue pen represent
Dental Work that has been completed
What does charting in a red pen represent
Dental work that needs to be completed
class 1 cavity classification
Decay in the pits and fissures of occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth.
Also in the Lingual pits of maxillary incisors
class 2 cavity classification
Decay in the proximal surfaces of posterior teeth (Mesial and Distal)
class 3 cavity classification
Decay in the proximal surfaces of incisors and canines (mesial and distal)
class 4 cavity classification
Decay in the proximal surfaces of incisors and canines that involve the INCISAL EDGE OR ANGLE of the tooth
class 5 cavity classification
Decay in the Gingival third of the facial or lingual surface of any tooth
Class 6 cavity classification
Decay on the incisal edges of the anterior teeth and the cusps tips of posterior teeth
How many tooth surfaces are there?
There are 7:
Mesial
Distal
Occlusal
Lingual
Buccal
Incisal
Facial
Soft tissue examination
examination of the cheeks, mucosa, lips, lingual and facial alveolar bone, palate, tonsil area, tongue, and floor of the mouth
How many probe readings per tooth?
6:
mesiofacial
facial
distofacial
mesiolingual
lingual
distolingual
How many classes of furcation are there?
There are 4 classes
Furcation
Area between two or more root branches
Dental Mobility
How much the tooth can be moved in the socket (Three Classes)
level 1 treatment plan
emergency care, relieves immediate discomfort
level 2 treatment plan
standard care, restores the patient to normal function
level 3 treatment plan
optimum care, restores the patient to maximum function
What is 4-handed dentistry?
The dental assistant works closely with the dentist on the procedure being performed. This helps to decrease fatigue and increase the success of dental procedures
What position should dental patients be lowered into?
Supine Position (Head below feet)
What is the proper working distance in the dental chair?
approximately 12 to 14 inches
How should dental providers sit?
- As far back on the chair
- Thighs parallel to the floor or knees slightly lower than the hips
- Feet flat on the floor
- operator forearms vent at the elbow and parallel to the floor
How should the dental assistant sit?
- Seated back on the stool
- Feet on the base or foot ring of the stool
- Positioned as close as possible to the dental chair
- Legs parallel to the patient's chair
- Eye level 4 to 6 inches above the eye level of the operator
Class 1 movement
movement of fingers only
Class 2 movement
movement of fingers and wrist
Class 3 movement
fingers, wrist, and elbow
Class 4 movement
use of entire arm and shoulder
Class 5 movement
use of entire upper torso
Where is the operator's zone for a right-handed clinician on a clock?
7 to 12 o'clock
Where is the transfer zone for a right-handed clinician on a clock?
4 to 7 o'clock
Where is the assistant's zone for a right-handed clinician on a clock?
2 to 4 o'clock
Where is the static zone for a right-handed clinician on a clock?
12 to 2 o'clock
Where is the operator's zone for a left-handed clinician on a clock?
12 to 5 o'clock
Where is the transfer zone for a left-handed clinician on a clock?
5 to 8 o'clock
Where is the assistant's zone for a left-handed clinician on a clock?
8 to 10 o'clock
Where is the static zone for a left-handed clinician on a clock?
10 to 12 o'clock
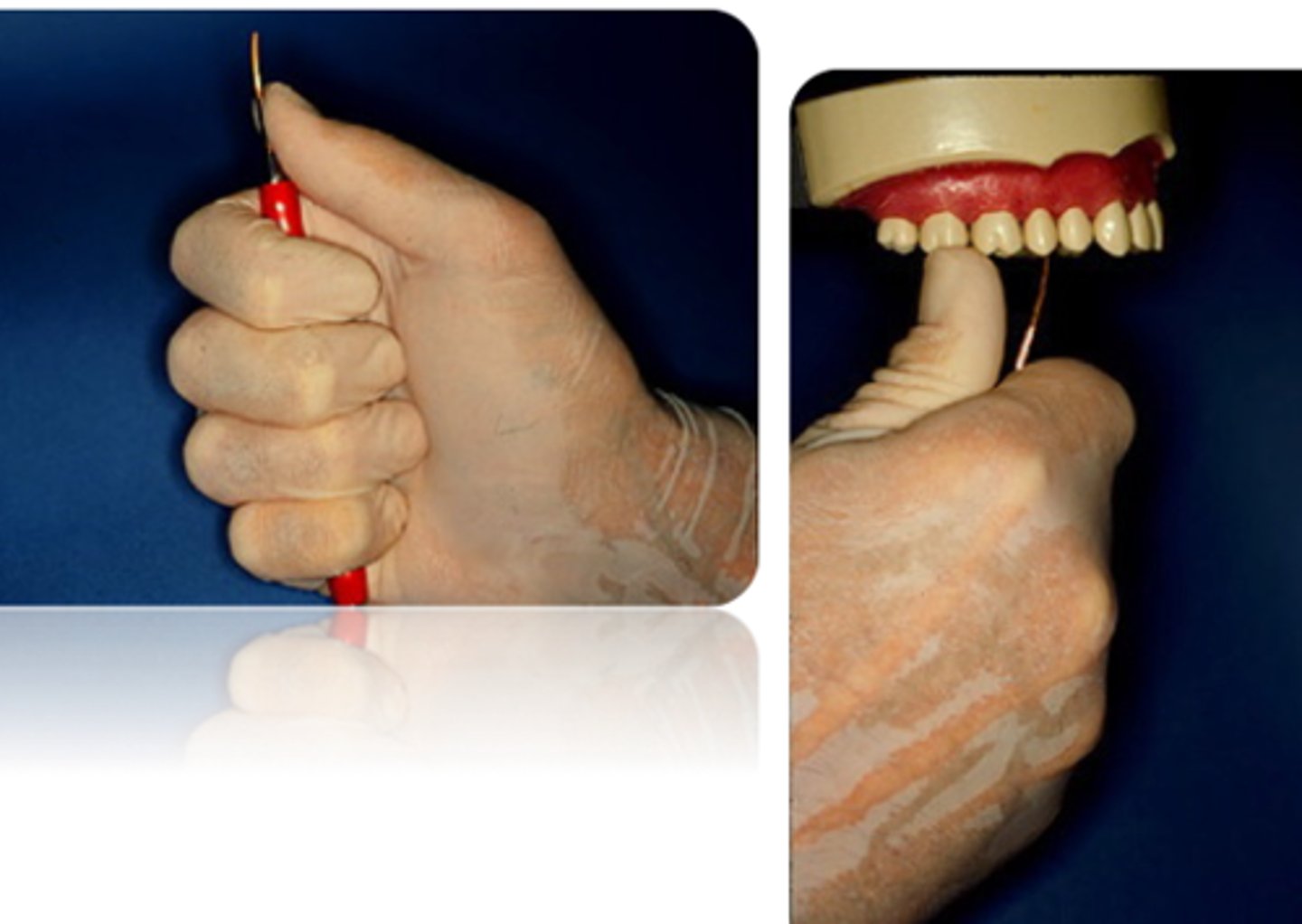
What is the pen grasp?
The instrument is held in the same manner as a pen
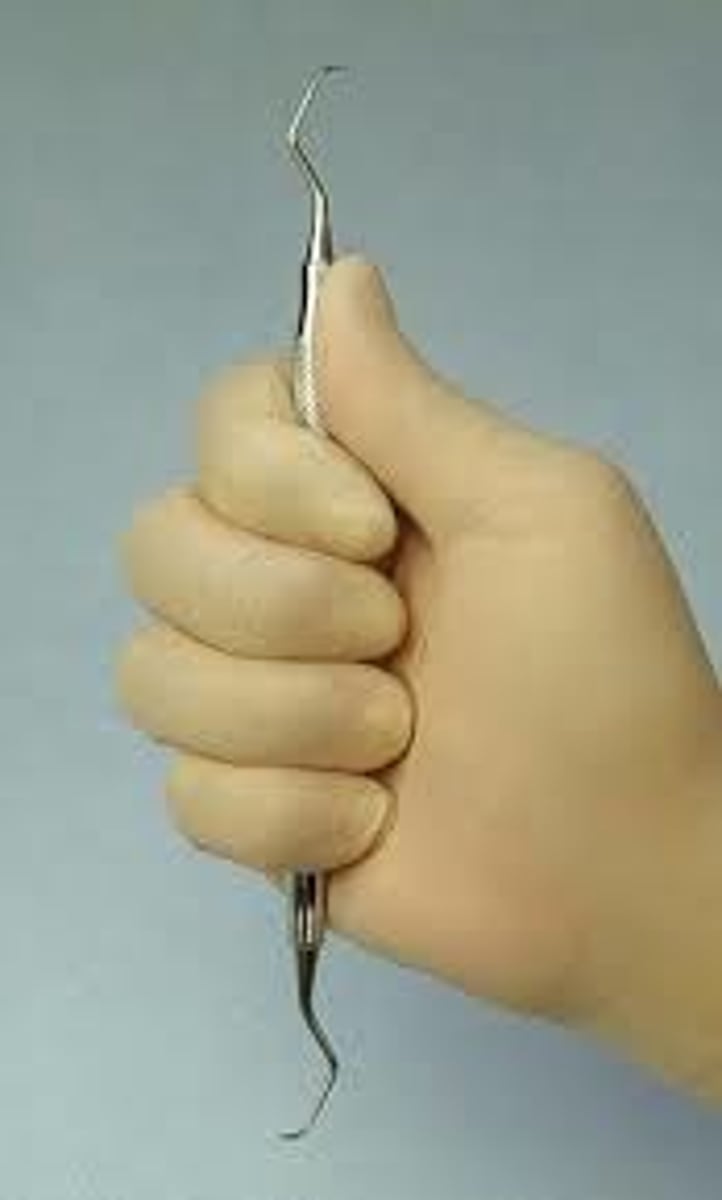
What is the palm grasp?
The instrument is held securely in the palm of the hand
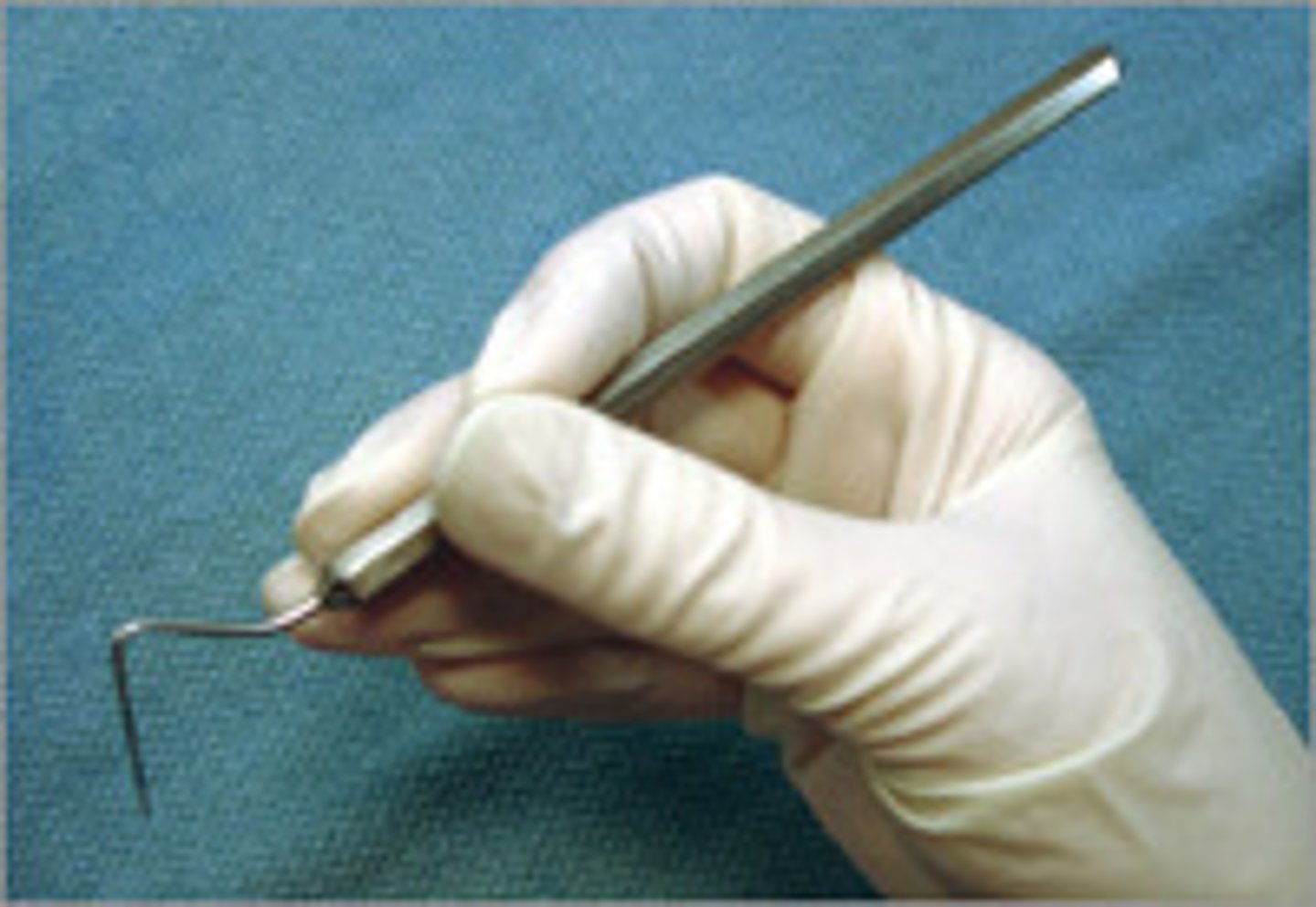
What is palm thumb grasp?
The instrument is held in the palm of the hand and the thumb is used to stabilize and guide the instrument
What is the assistant transfer technique
Single handed
Direct supervision
The dentist must be in the same treatment area as the EFDA for the assistant to perform the function
Indirect supervision
The dentist must be in the dental office area but not necessarily be present in the same treatment room as the EFDA
Dental instrument handle
Portion of the instrument that the operator grasps
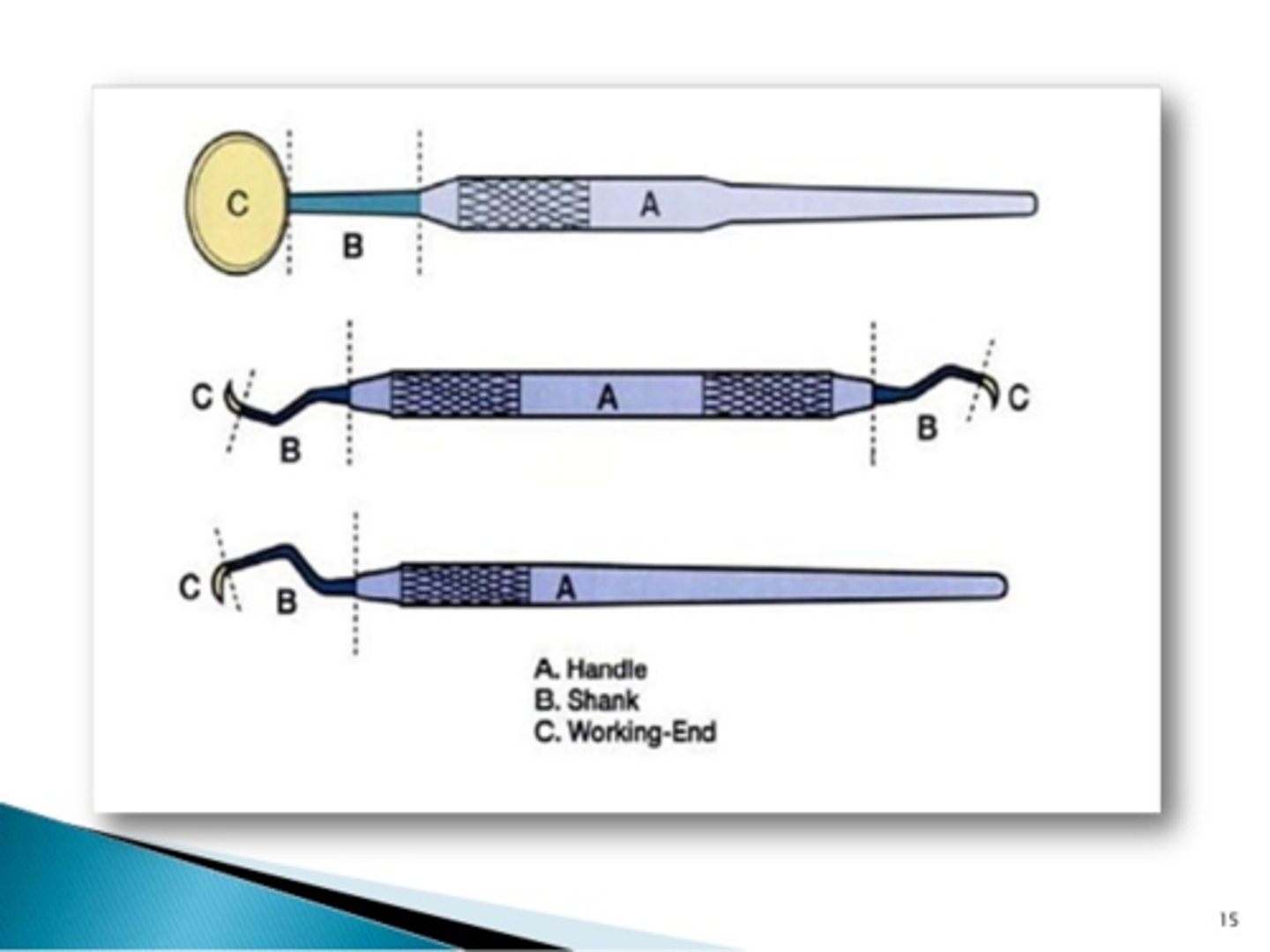
Dental instrument shank
Part of the instrument that connects the working end to the handle
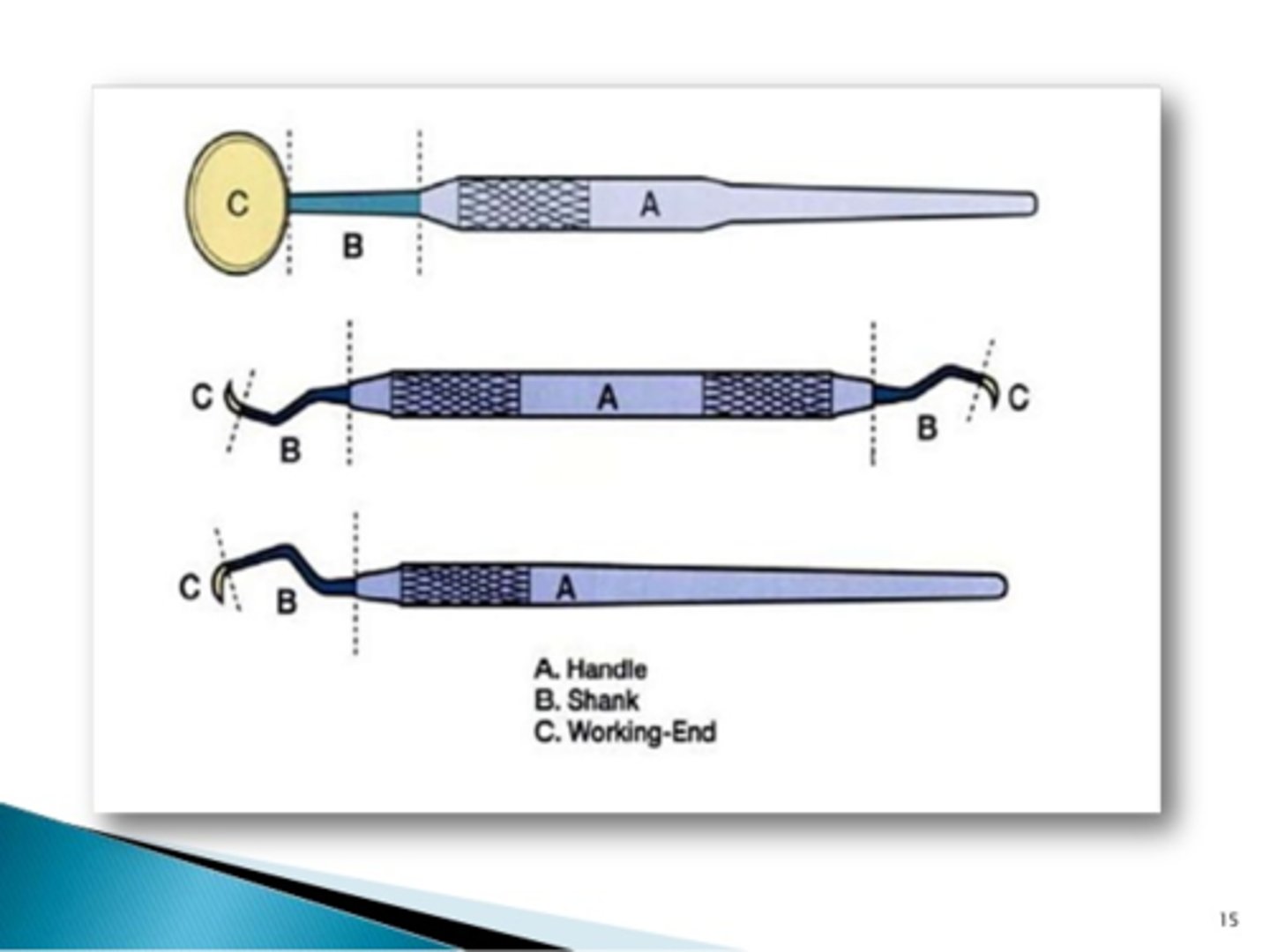
Dental instrument working end
Portion of the instrument designed for a specific function
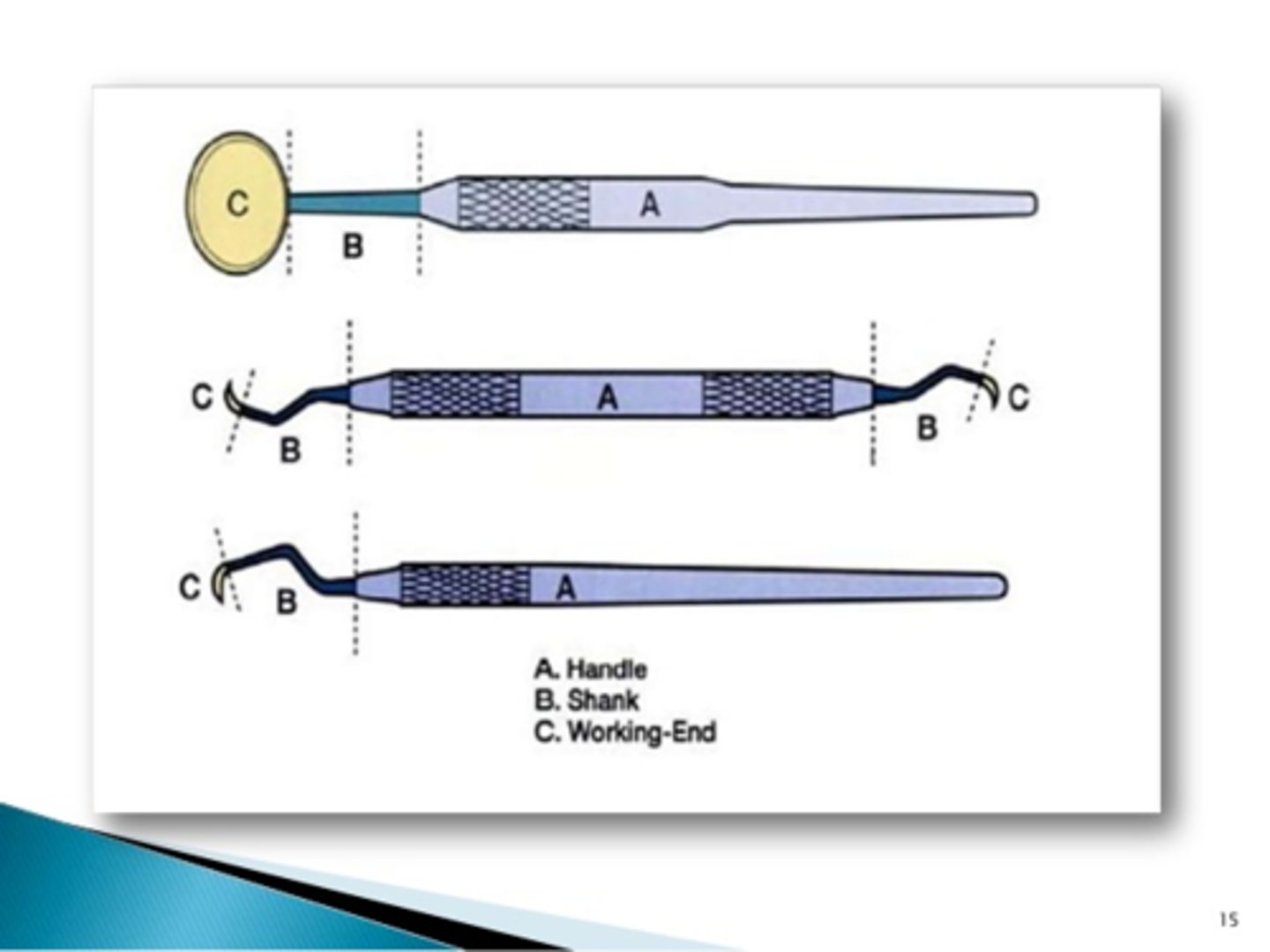
Black's Instrument Formula
A formula describing the angulation and dimensions of the working end of an instrument
What instruments are used in an examination
Mouth Mirror, Explorer, Periodontal Probe, Cotton Forceps/Pliers
What are some hand cutting instruments?
Excavator, Hoe, Chisel, Hatchets, Gingival Margin Trimmers
What are some restorative instruments?
Amalgam Carrier, Condensers, Burnisher, Carvers, Composite Placement Instruments, Woodson
What are some Accessory instruments?
Spatulas, Scissors, Amalgam Well, Howe Pliers, Articulating Paper Holder
What instruments are in a Basic Setup?
Mouth mirror, explorer, cotton pliers, and sometimes perio probe
Cotton Pliers
used to carry, place, and retrieve small objects, such as cotton pellets, gingival retraction cord, matrix bands, and wedges, to and from the mouth.
- Locking and non locking
Small & large spoon excavator
Excavate decay
Dental Hoe
Blade is perpendicular to handle. Prepares tooth & plane the walls and floors of tooth prep with push and pull action
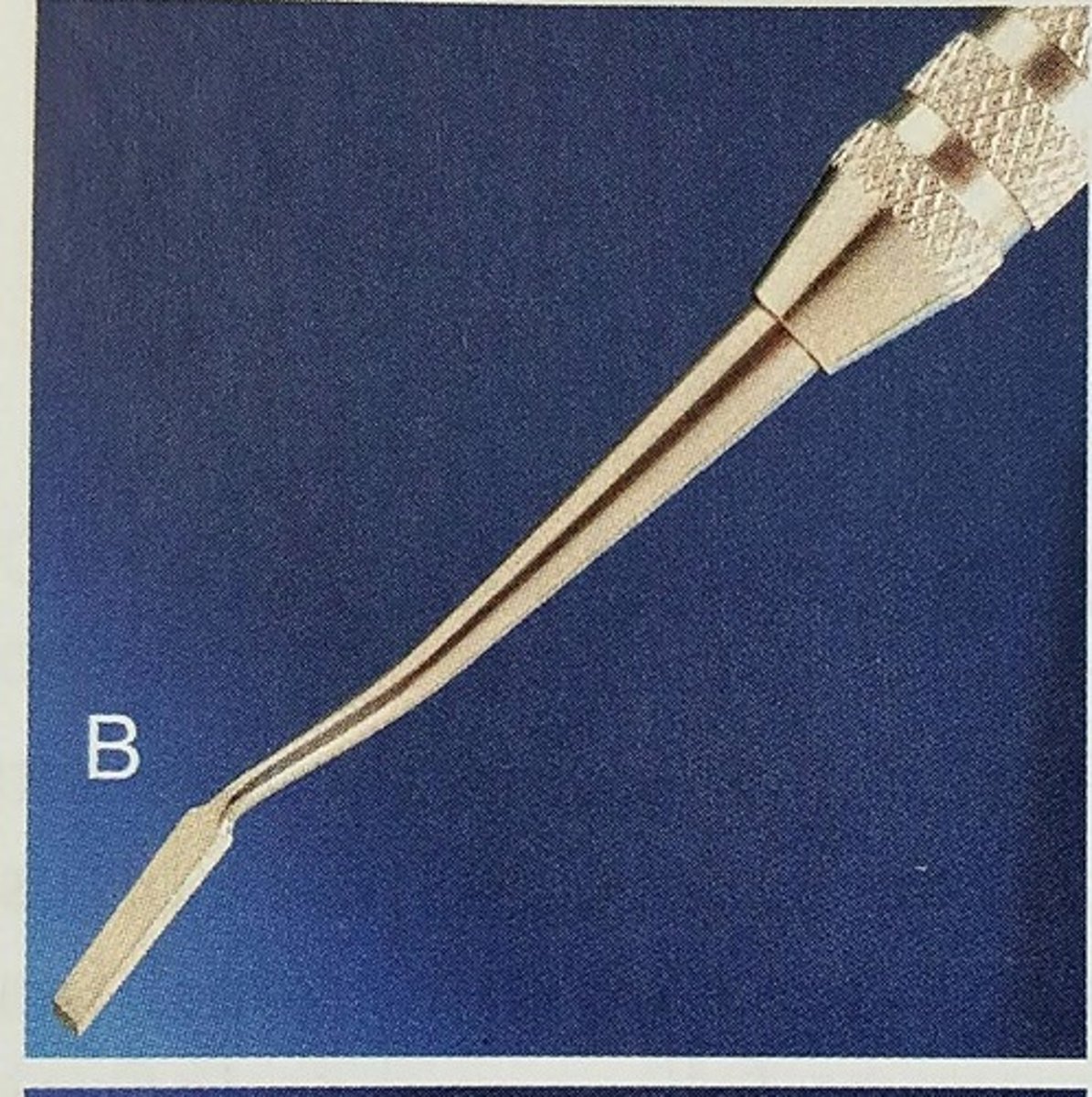
Bin-angle chisel
Forms the walls of the cavity prep PUSH MOTION
Wedelstaedt Chisel
Forms the wall of the cavity prep. PUSH MOTION
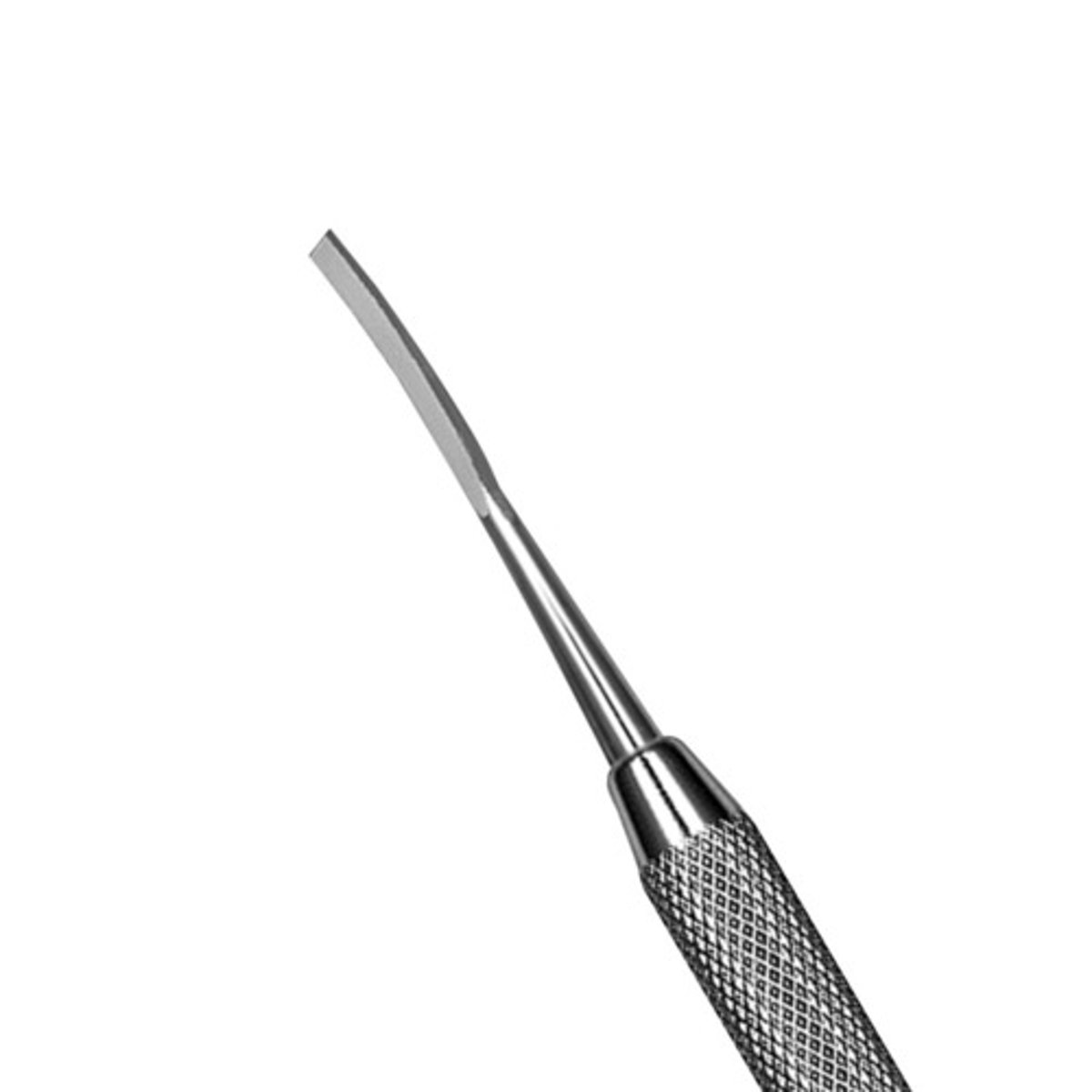

Straight angle hatchet
forms the wall of the cavity prep. PUSH AND PULL MOTION
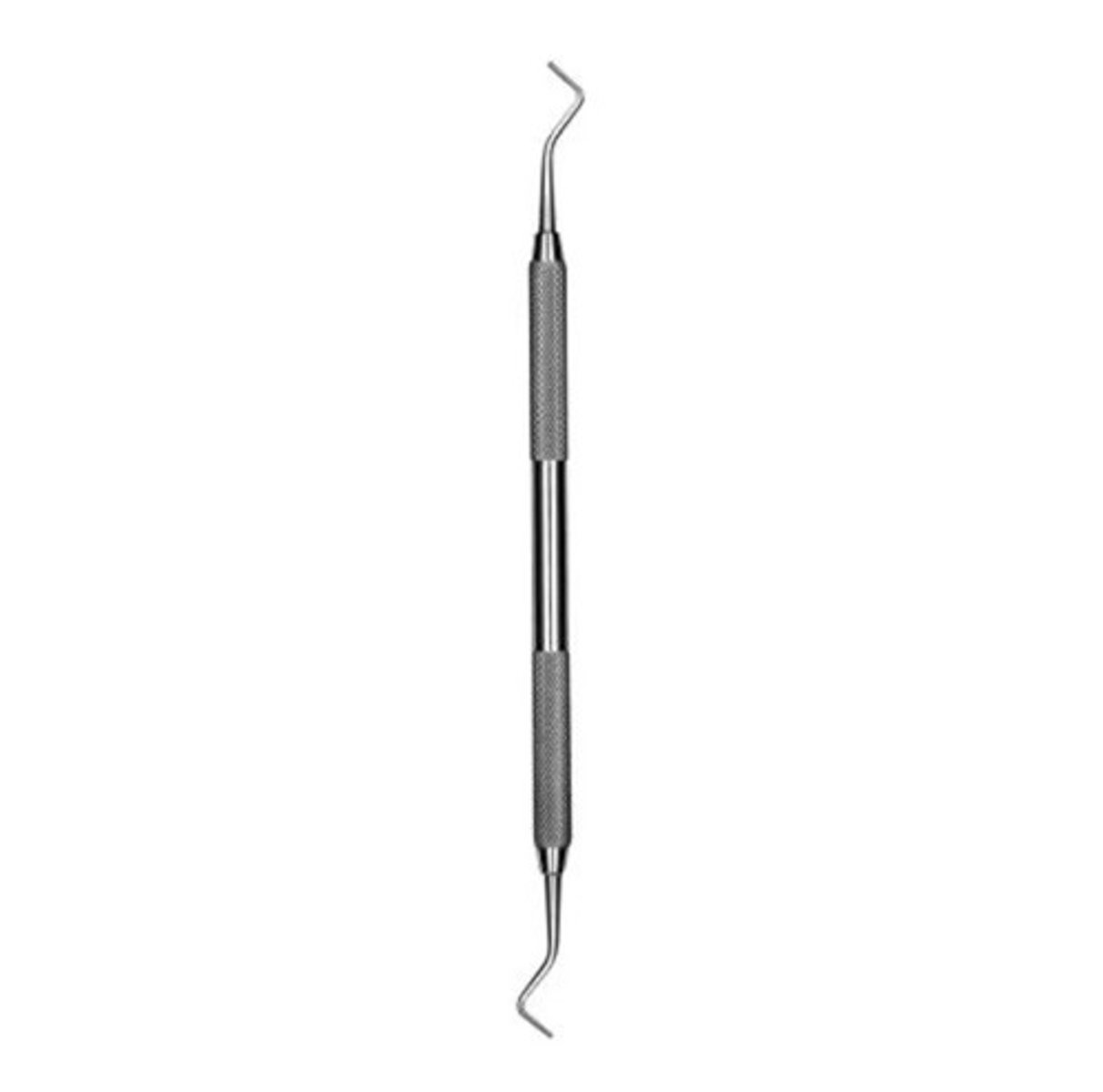

Gingival Margin Trimmer
used to cut enamel and to place bevels along the gingival enamel margins of the preparation
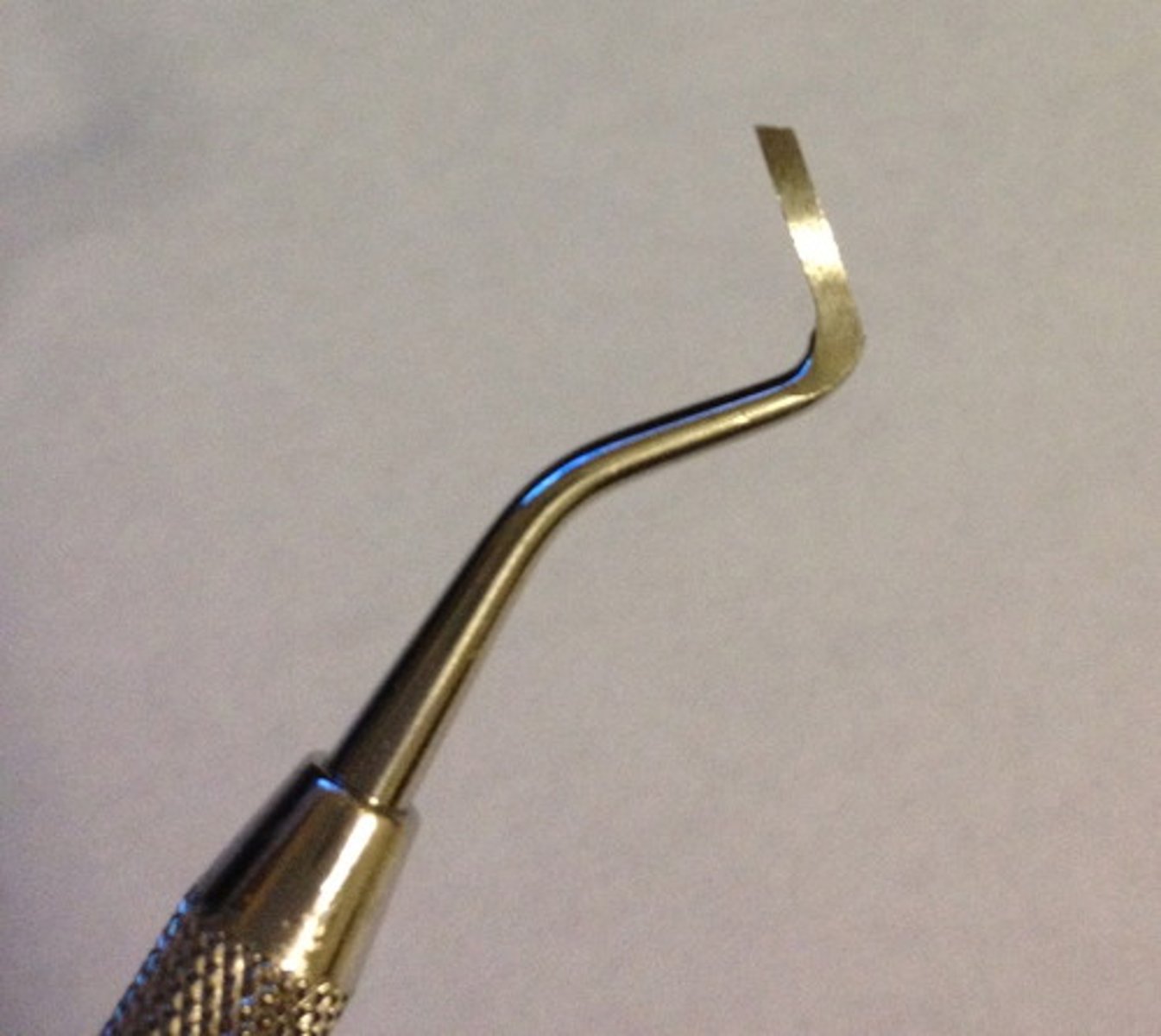
Amalgam Carrier
To carry and dispense amalgam for cavity preparation
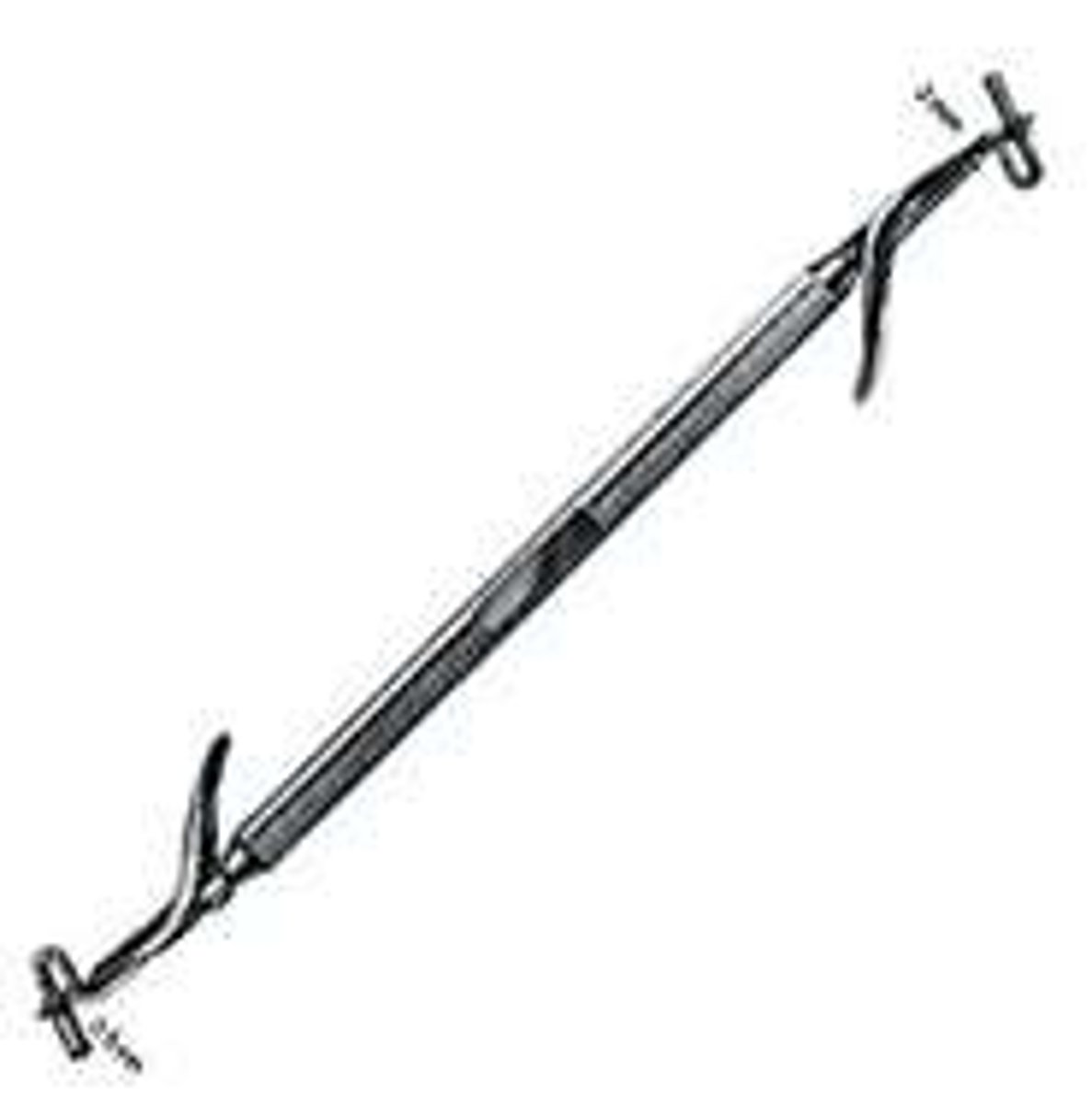

small and large condenser
Condenses. Amalgam or composite into the prepared tooth
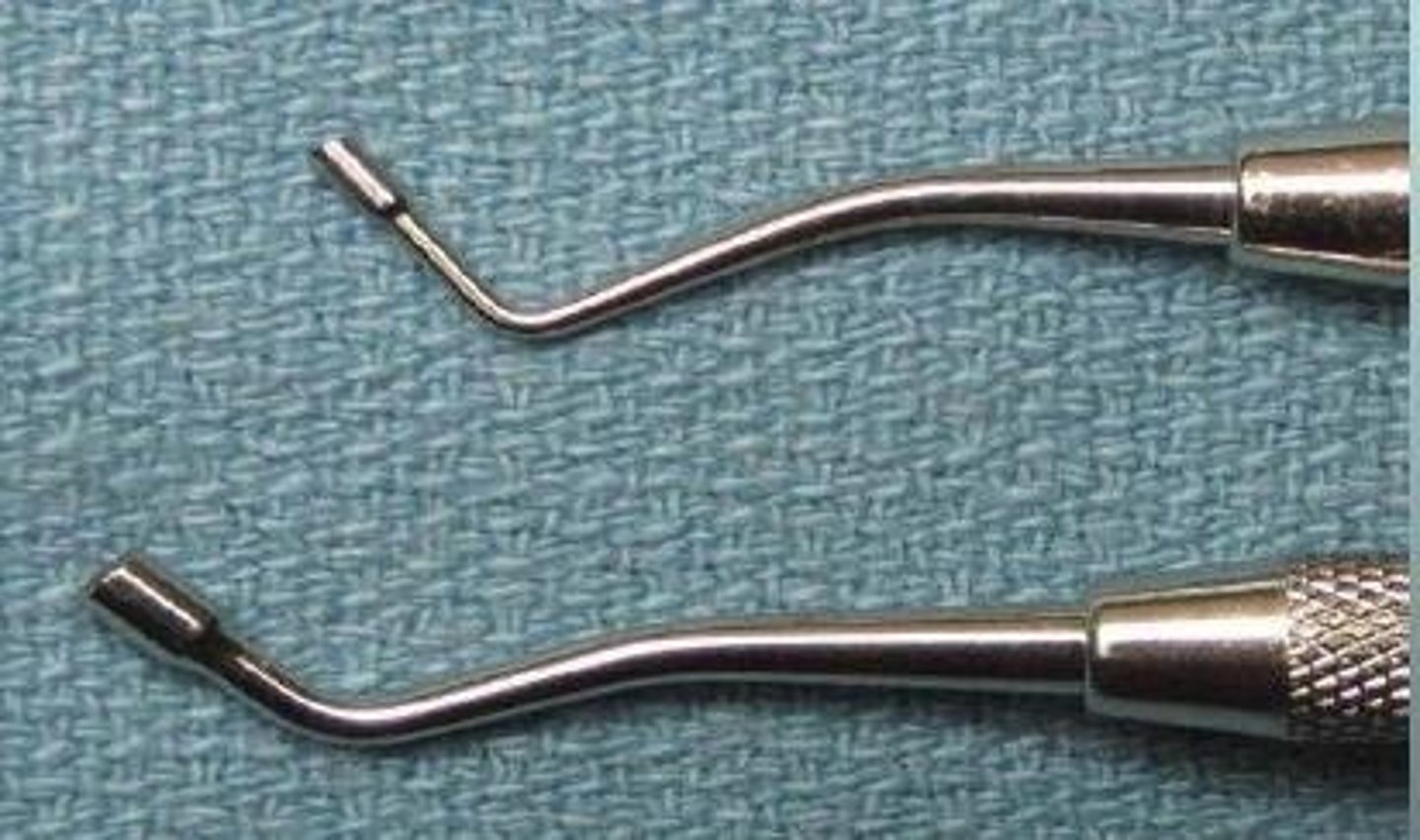
Football Burnisher
polish/finish
polish hardened surfaces of restoration (occlusal)
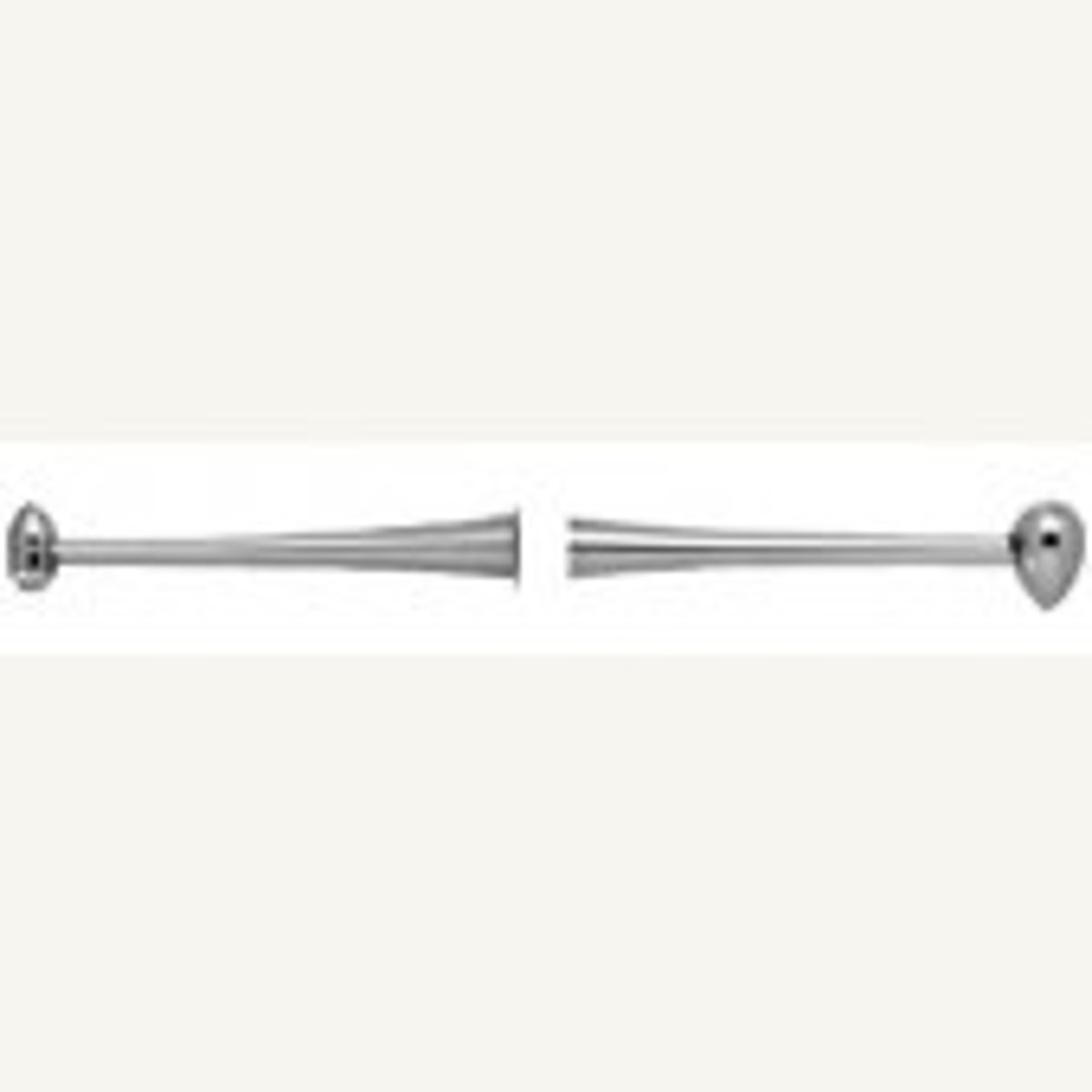

Ball Burnisher
Smoothes occlusal surface of restoration
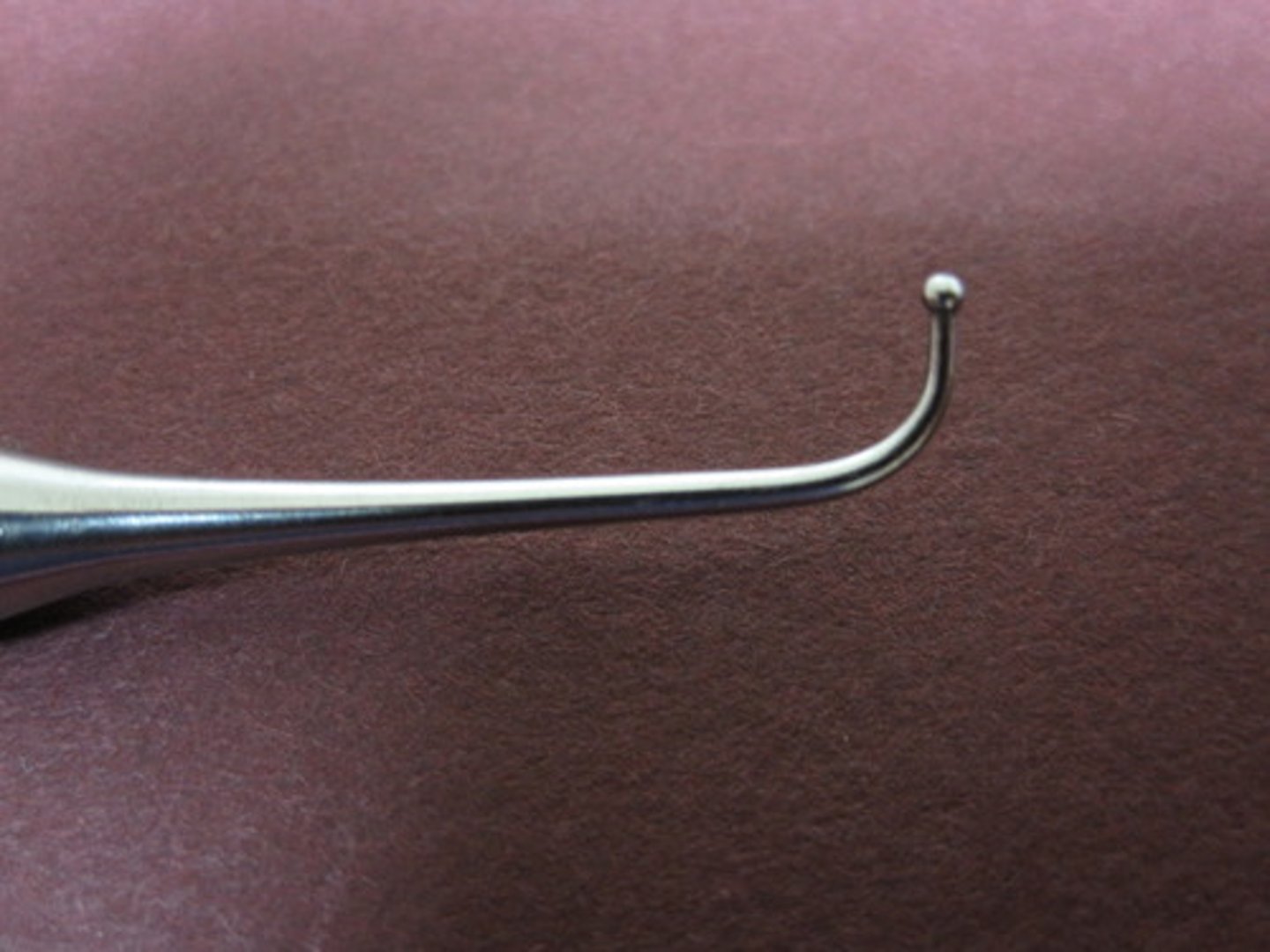

Acorn Burnisher
Carves and burnishes occlusal restorations.
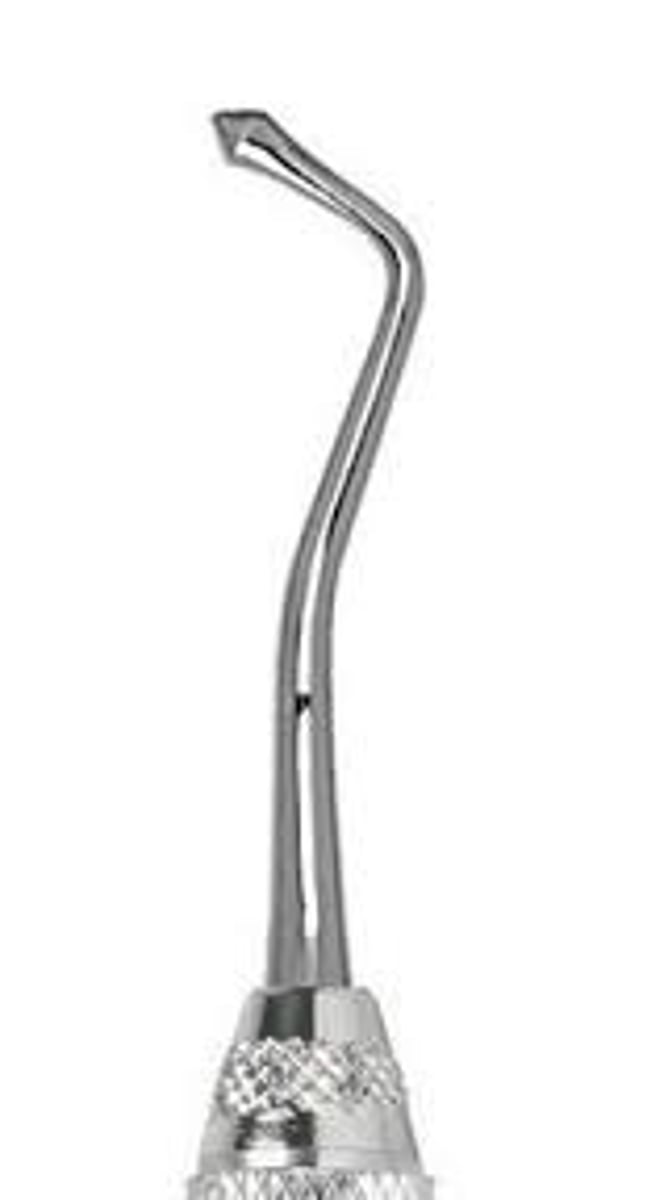

T-ball burnisher
to smooth amalgam after condensing
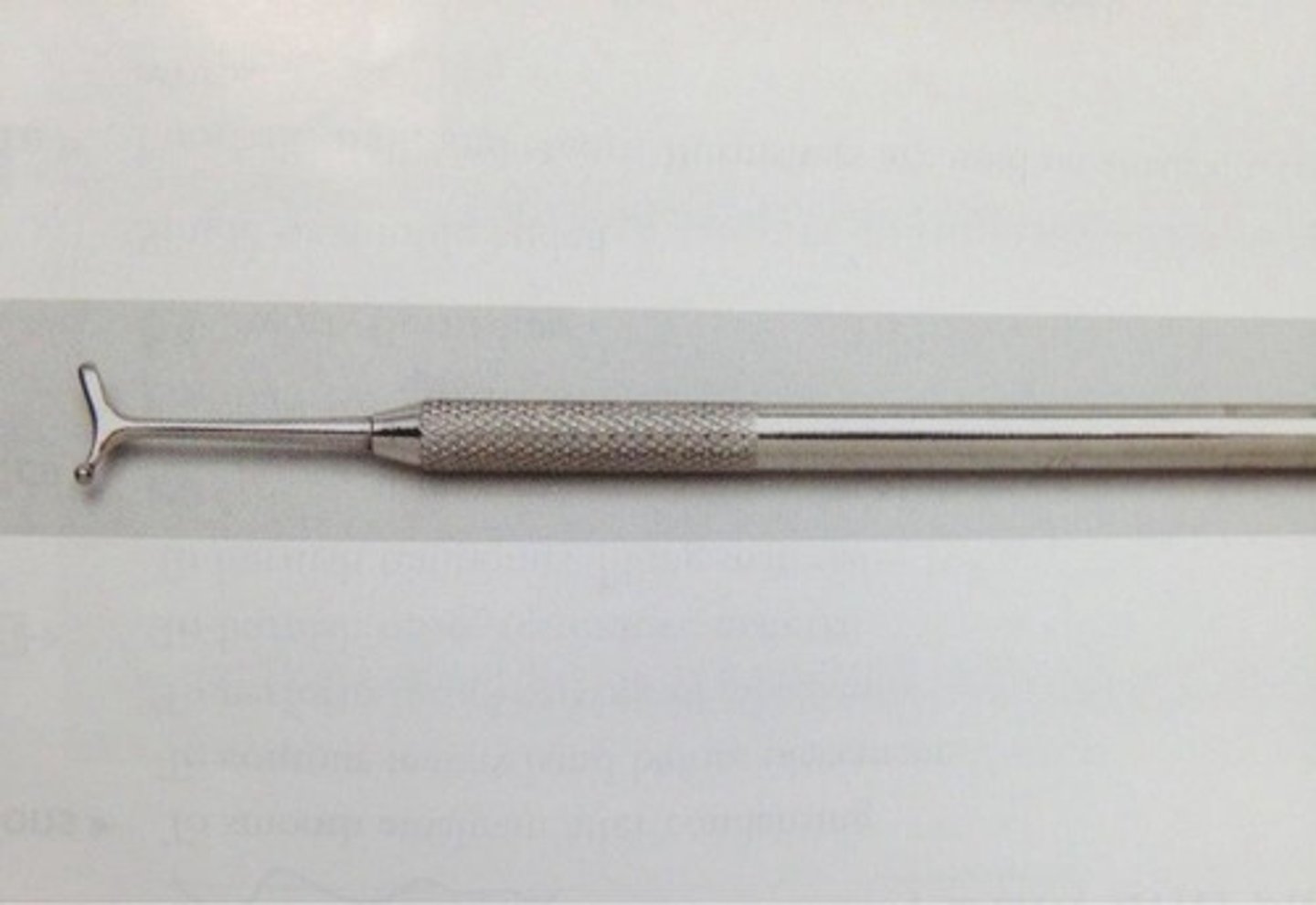

Beaver tail burnisher
Used to smooth the restoration
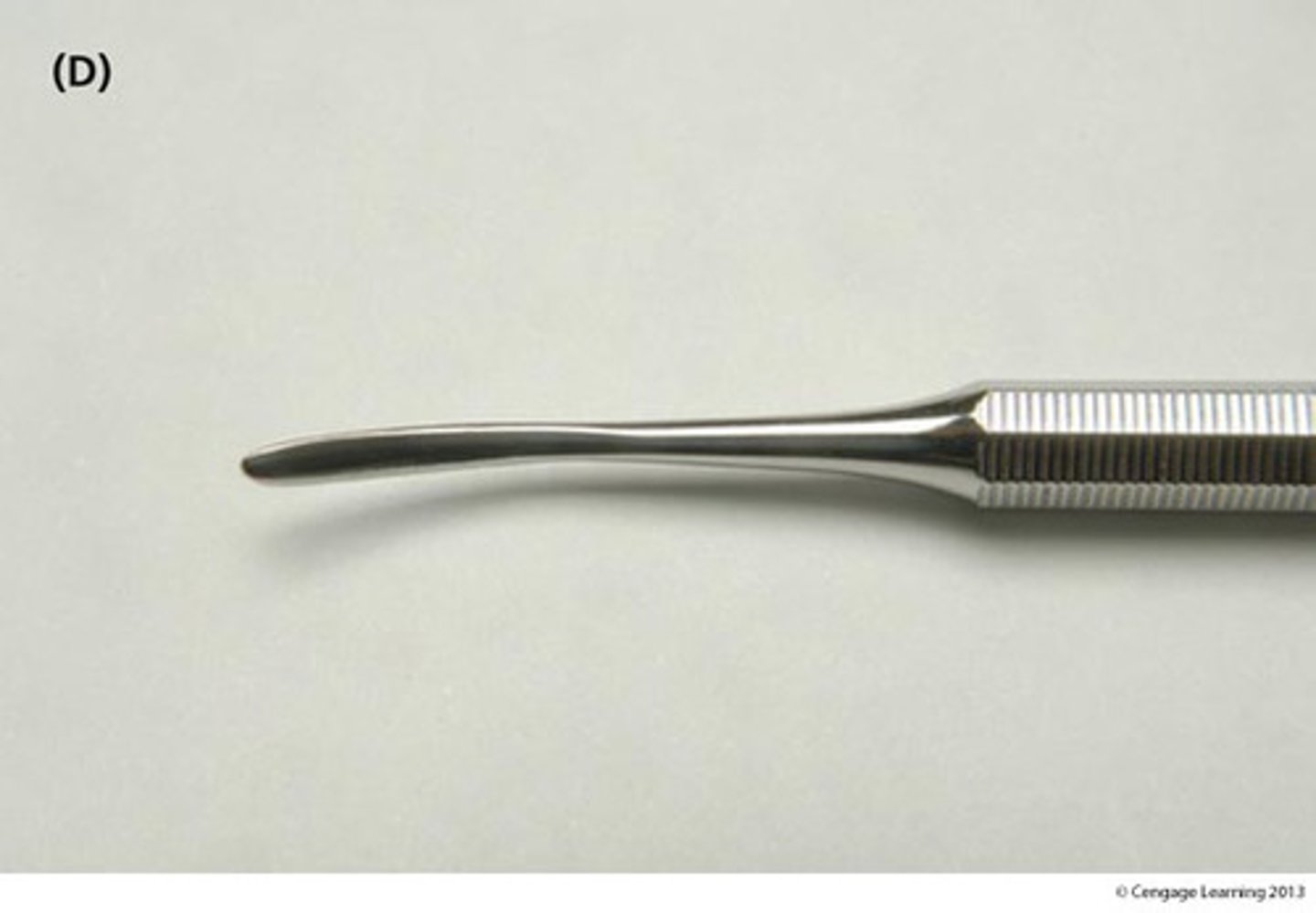
Hollenback carver
Used to contour or remove excess material interproximally
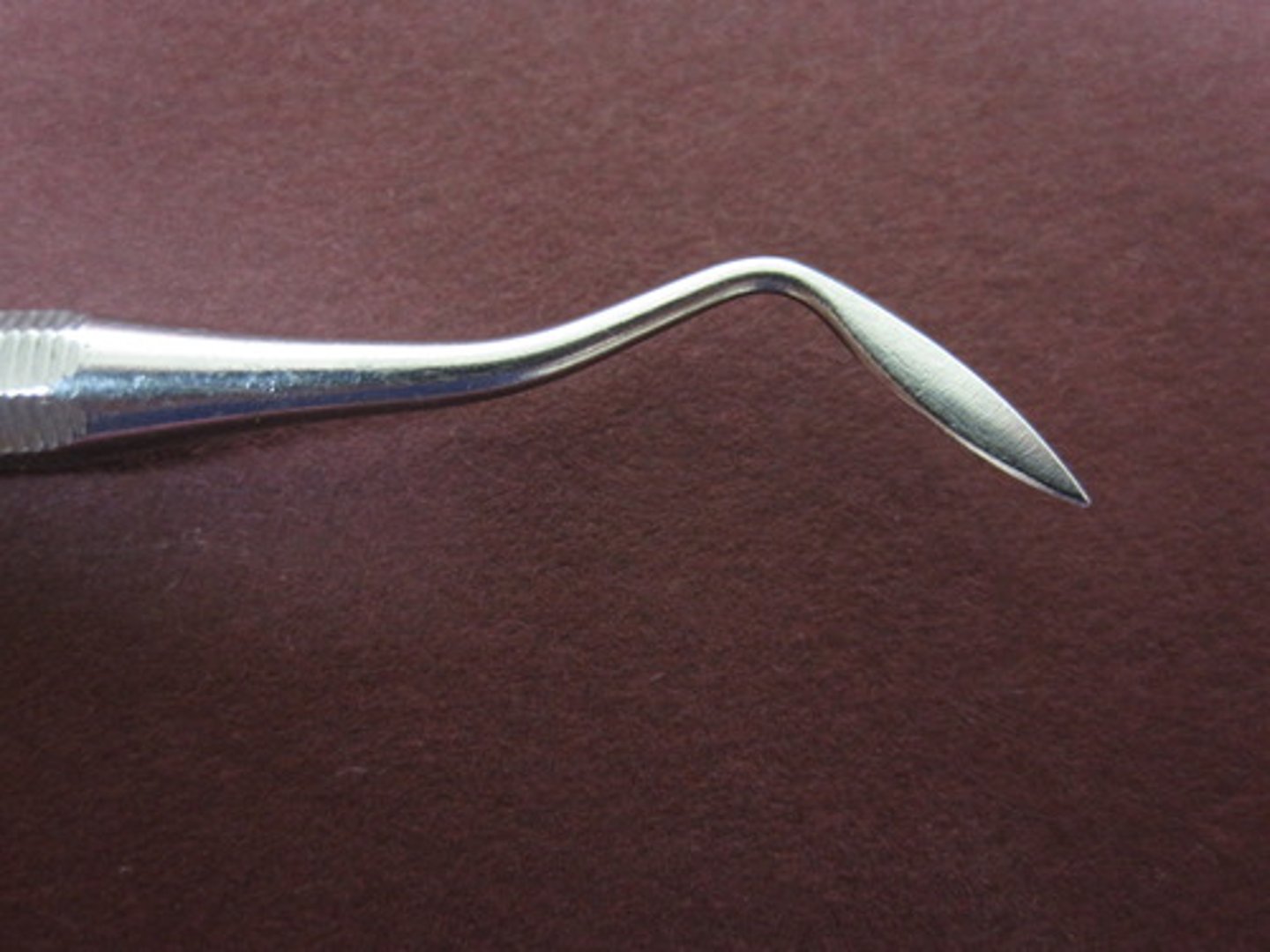
disciod/cleoid carver
Contains sharp working end to remove excess material
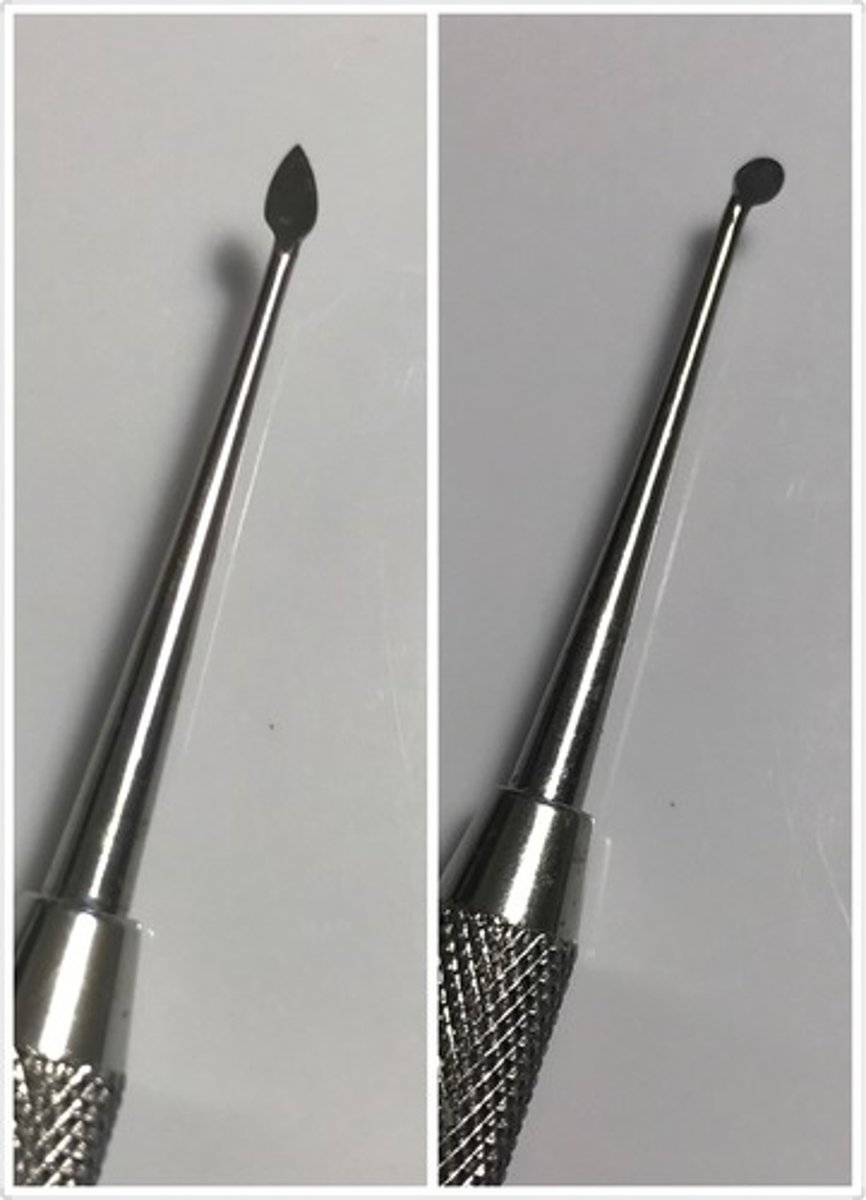

Amalgam Knife
Used for the removal of excess restorative material along the margin where the material and tooth structure meet.
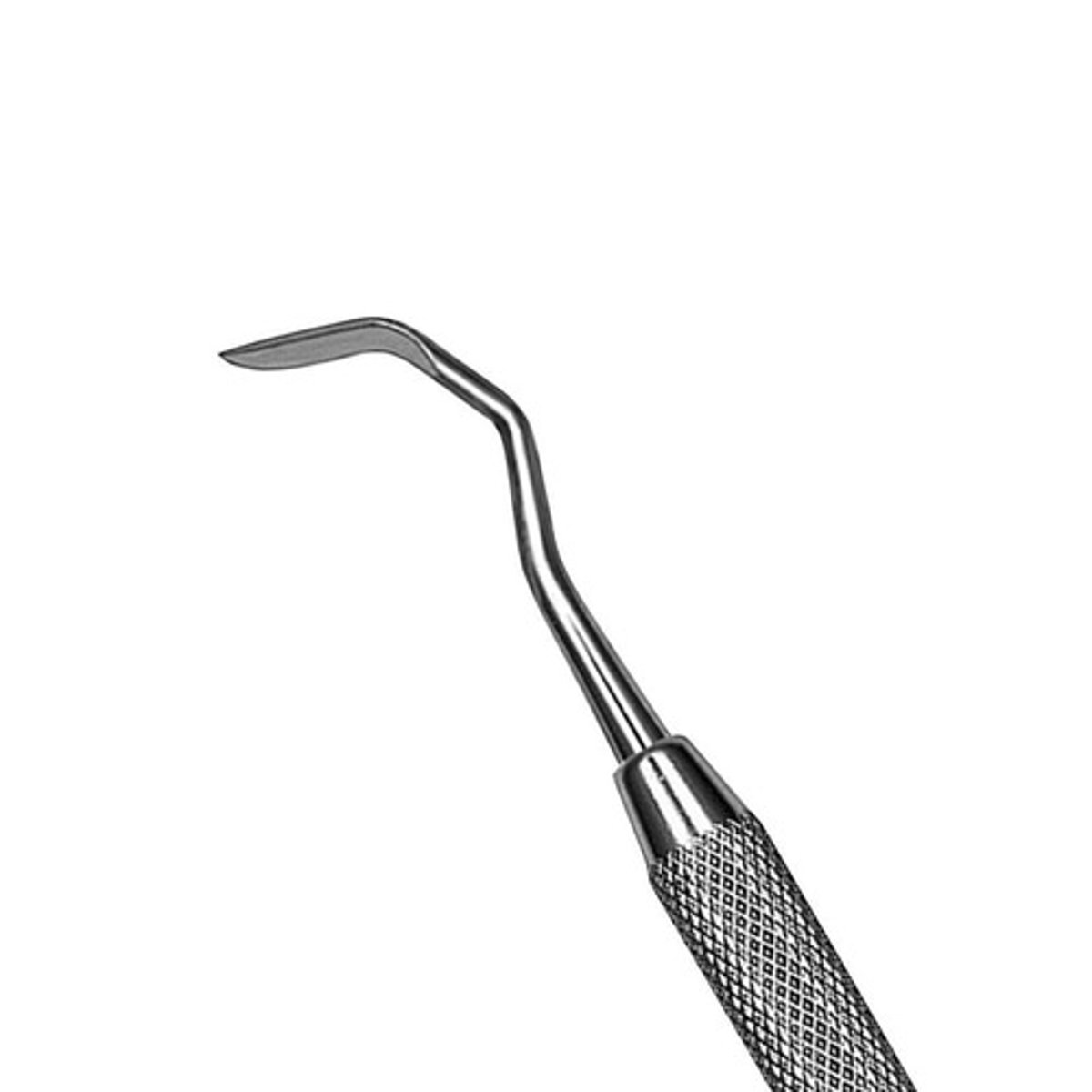
Plastic Instrument
Used to place and shape composite material. Can be either plastic or metal. (hockey stick looklike)
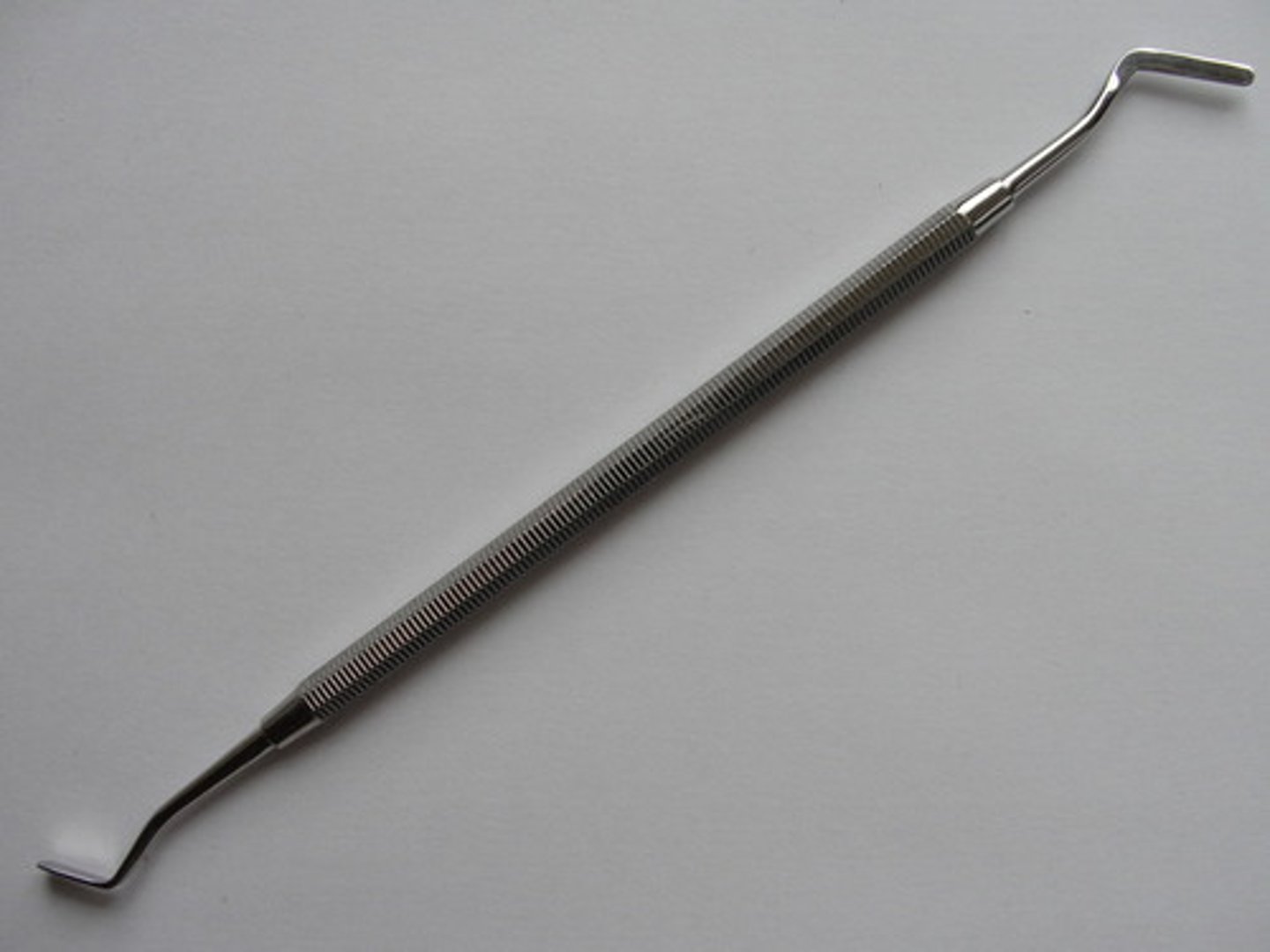

Articulating Paper Holder
Holds articulating paper
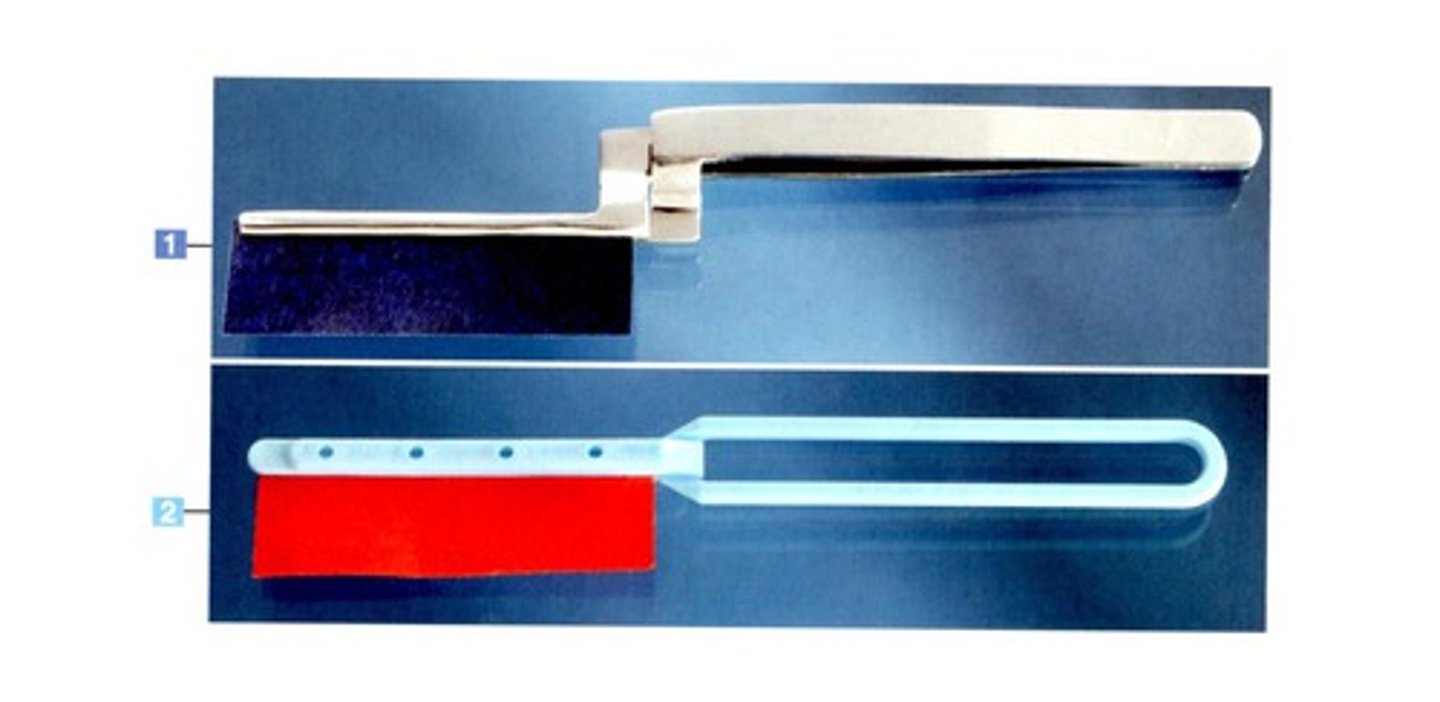
Amalgam Well
holds amalgam
