cardiac control in mammals 9.8
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
what region of the brain controls the heart
medulla oblongata
The centre that is linked to increasing heart rate is linked t which branch of the autonomic nervous system
sympathetic
The centre that is linked to decreasing heart rate is linked t which branch of the autonomic nervous system
parasympathetic
how does the body know which centre to activate
using chemoreceptors and baroreceptors
these detect the changes in the chemical composition and the pressure of the blood. eg pressure increases and CO2 increases
what do baroreceptors do
These are a more of stretch receptors the more the arteries stretch the higher the blood pressure.
( all we needed to know is that they detect changes in pressure)
what do chemoreceptors
these measure chemical changes in the blood especially change in ph due to increased carbon dioxide levels.
what does myogenic mean
something myogenic means starts in the muscle itself, not from nerves or hormones. in this case contracts start without an impulse from a nerve
what is the equation for cardiac output
cardiac output= heart rate x stroke volume
what is the role of the CNS as it doesn’t initiate heartbeat how not autonomic
it controls both the heart rate and the stroke volume
describe how the heart rate is increased
event ( stressful one) eg running from a lion
stimulus = change in O2 concentration in the blood as well as increase in CO2 levels so change in Ph ( more acidic). This increases blood pressure.
Receptors= This change in pressure and change in chemicals is detected by baroreceptors and chemoreceptors in the aorta and in the carotid arteries.
Coordinator= sensory neurones transmit these signals to the cardiac centre in the medulla in this case the centre that increases heart rate. e
Effector =the signals are transmitted down the sympathetic nervous system to the SAN
response =change in heart rate /increase
describe how the heart rate is decreased
event (calming down again )
stimulus = change in O2 concentration in the blood as well as decrease in CO2 levels so change in Ph (less acidic ). Also a decrease in blood pressure.
Receptors= This change in pressure and change in chemicals is detected by baroreceptors and chemoreceptors in the aorta and in the carotid arteries.
Coordinator= sensory neurones transmit these signals to the cardiac centre in the medulla in this case the centre that decreases heart rate.
Effector =the signals are transmitted down the parasympathetic nervous system to the SAN
response =change in heart rate / decraese
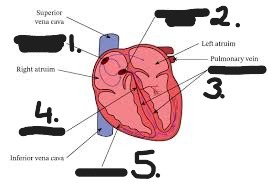
sinoatrial node ( pacemaker\0
atrioventricular node
bundle branches
bundle of His
Purkinje fibres