Geo Unit 1
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
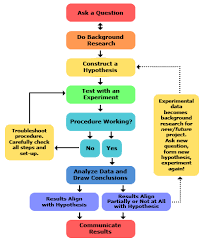
The scientific process
Hypothesis vs theory
a tentative or untested explanation
a well tested and widely accepted view that the scientific community agrees best explains observable facts
Geology vs Physical Geology
scientific study of the Earth
s
tudy of Earth’s materials and seeks to understand the many processes that operate within and upon our planet
Natural process vs geologic hazard
Flooding begins as a natural process but can become a geological hazard
If we allowed to happen, say a dam breaking, its not a natural disaster
Catastrophism
(James Ussher) Belief that Earth was shaped by great catastrophes
Uniformitarianism
(James Hutton) the physical chemical and biological process that operate today have also operated in the same way in the past.
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
Magma
Compacted dust and sediment
Pressure and heat
Three major layers of earf
Crust- Thin and rocky, divided into the oceanic (7 kilometers thick but denser, made of basalt) and contential crust (35-70 kilometer made of granite)
Mantle - high-density rock composed of peridotite
Core - composed of iron nickel alloy ( densest material was pulled to the middle of the earth)
Earths interior by physical properties
Lithosphere - rigid outer layer of the Earth that consists of crust and mantle
Asthenosphere - the soft, weak layer, it is mobile (veeeery slowly)
Transition zone - a zone marked by a big increase in density
Lower mantle - a zone of strong, very hot rocks subjected to gradual flow
Outer core - liquid outer layer of the core
Inner core - solid inner layer of the core
Earths external and internal Heat engines
External - primary driver of atmosphere and hydrospheric circulation - controls the weather of rocks
Internal - primary driver of most geospheric phenoms

ROCK
CYCLE
